University of Mumbai 2008-5th Sem M.E Mechanical Engineering Finite Elent Analysis -e - Question Paper
(2) Attempt any four questions out of the remaining six questions.
(3) Assume any suitable data, wherever required.
(4) Figures to the right indicate marks.
Jslng RaytaighFuJz nwfoa, over general element, solve the following differential equation to get Element 20 )
Using Matrix Equation.
Temperature different = T8-T,.
where
e
T,
T.
K
A
P
> Temperature at a distance 'x* from Left Hand End, *C Surrounding Temperature, *C
i Thermal conducting, w/m, C Cross-sectionat Area, m2 Convective Heat Transfer Co-efficient. w/m2 *C Perimoter. M Write all the steps carefully.
Boundary conditions * (i) 0(0) * 0O
(if) No heat transfer at Right Hand end.
Taking Lagrange's linear or quadratic interpolation function derive the appropriate element matrix equation.
Take 3 linear or 2 quadratic elements to get global matrix equation.
Find Temperature Distribution and Heat Input Rate.
Use the data given below:
K * 100, h b 50, D * 2 cm, Length L 6 cms, 0o - 600, Compare your answers with exact.
(a) Say 'True or 'Fatso' and Justify your answer in brief. Rectify the statement if False.
10
(i) FEW is a method to solve a differential equation.
(ii) Shape function and Interpolation (unction are synommous words,
(iii) Natural Boundary conditions are the values of primary variable.
(iv) in Galerkln method the weight function has a value 'o' at a point Essential Boundary condition is defined.
(v) Essential Boundary conditions are also called as Geometric Boundary conditions.
(b) Solve by Finite difference method, the following differential equation :
10
d2u
-~T - 25 u 10 = 0 dx*
B.C. S. u(0) a 0, u(2)*4 Take 4 sub intervals.
Compare your answer at x * 0-5,1,1-5 with exact.
4
3
13
Compare fcr advantages, the weak form methods over are non weak form methods.
<)
(b)
(c)
Explain ; Degree of freedom, Dirichlet Boundary conditions.
Solve the differential equation by using any two methods
16u 10x2 o
dx2
(iv) Subdomain method.
(iy) Ritz method mapped over entire domain.
20
I.
dx
(i) Collocation method
(ii) Subdomain method.
(iii) Galerklng method.
Compare your answers with exact at x * 0-3, 0 7.1
Analyse completely any two :
(a) One clmensionaf fluid flow In porous medium.
B.C.S. u(0) 0,
 |
d. |
K - permeability, om/s
- 1*25 cm/S.
Fluid hold at the top is 25 cm and that at Ihe bottom is 2-5 cm. Area of cross-section Is 5 cm*. Determine : (i) Fluid head distribution.
(ii) Velocity at the upper part.
Hilt Volumetric Hnw rale in upper part. T1IRW DVFR
K a permeability, m/s
dtscharge. m3/8
|
Data: plO P* - 1 K b 1 for all elements (smooth pipe) Find: (a) Potential at the junctions, (c) Volumetric flow rate.  |
pressure head, m K x
| ||||||||||||||||
5. (a) Derive the oriented (w.r.t. GCS) stiffness matrix for an element of a plare truss,
(b) For the element shown befow, global displacements have been detormired to be-J,10 mm,
V, a 0 0 v2s 15 mm
J4 * 5 mm
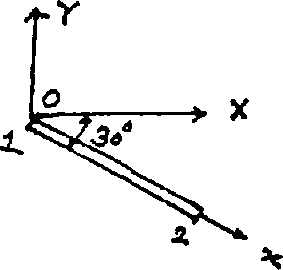
E * 130 GPa, A * 200 mm2, L 100 cm
Detemine; Elemental (local) displacements at each end
Data: E a 120 QPa for all elements L 3m

10
A s 6 cm2 lor all elements P, - 4 KN P- 6kN
(a) Explain in Brief: (I) Effect d node numbering in FEA, (Ii) h and p methods.
(b) Compare Newton cotes Method with Guass Quadrature Method.
(c) Find, using both the methods, M23 and K13.
dx
dT Sx
he )
Attempt any two
(a) Beam Analysis.
(b) Error Analysis.
(c) isoparametric Analysis.
7.
20
|
kz dx |
(d) Software package used for FEA.
(e) Plane stress problems using CST element.
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
