University of Hyderabad (UoH) 2009 Ph.D Statistics Entrance - Question Paper
Find the correct answer and mark it on the answer sheet on the top page.
PART A
A right answer gets 1 mark and a wrong answer gets mark.
3
1. Class of all generalized inverses of a m x n real matrix A
(a) is a non-empty vector space.
(b) is a non-empty convex set.
(c) can be empty.
(d) is a non-empty finite set.
2. Consider a real valued function f such that for some x0 in R, f (x0) = e2/c, suppose c E (1, 2), the value of f (x0) can be
|
\ n 1 (1 + 1 )n) is nn 2 |
-1 1/2 1/2 -1
4. Let Ai and A2 be the characteristic roots (eigen values) of the matrix A
then
(a) both A1 and A2 are positive.
(b) both A1 and A2 are negative.
(c) one of Ai and A2 is positive and the other is negative.
(d) one of A1 and A2 is zero and the other is positive.
5. Let Ri be the rank of ith observation in a random sample of size N, i
1, 2,..., N, then E(Ri) is
(a)
(b)
2
N
N +1
(c) N.
(d) N+1.
6. In a randomized block design (RBD) with 3 treatments, it is given that the ratio of degrees of freedom for treatments to that of total source of variation is 0.25. Hence the number of blocks is
(a) 6.
(d) 3.
7. Suppose X is N(0,1) random variable and Y = \X|. Then the correlation coefficient between X and Y is
(a) -1.
(b) 0.5.
(c) 0.
(d) 1.
8. Suppose X and Y are two random variables with E(Y \X) = X. Then
(a) Var(Y) = Var(X).
(b) Var(Y\X) = Var(X).
(c) Cov(X, Y) = Var(X).
(d) Cov(X, Y) = Var(Y).
9. Let Xi, X2 and X3 be independent U(0,1) random variable, P(Xi < X2 < X3) is
(a) 2.
(b) 3.
(c) 4.
(d) 6.
10. Let X1,..., Xn be i.i.d from U(9,9 + 1). Define X(1) = min{X1,..., Xn} and X(n) = max{X1,..., Xn} , then
(a) X(1) is sufficient for 9.
(b) (X(1),X(n)) is sufficient for 9.
(c) X(n) is sufficient for 9.
(d) X(2n) is sufficient for 9.
11. Let Xi,X2, , Xn be a random sample with common location and scale pa
rameters and a2 respectively, then the statistic Wn-i (X - X)2 is
i=I
(a) location invariant.
(b) scale invariant.
(c) both location invariant and scale invariant.
(d) none of the above.
12. Let XI,X2 be i.i.d N(9,1). Let (XI) = Eg(X|XI), then (XI) is
(a) 2Xi + 19.
(b) Xi + 9.
(c) 1 Xi + 9.
(d) Xi + 29.
13. The proportion of households in a town with 0,1,2, 3 and more than 3 children is 1 10p, 2p, 4p, 3p and p respectively, 0 < p < i0. In a random sample of 10 households one household had no child, 3 had one child, 5 had 2 children and one had 3 children. The maximum likelihood estimate for the proportion of households with 2 children is
(a) 25.
(b) 25.
(c) 25.
(d) 2.
14. Let Xi,...,Xn be a random sample from the exponential distribution with mean A. To test the hypothesis H0 : A = A0 versus Hi : A > A0, the p value based on the test statistic using sample mean is p0. Xn was wrongly observed to be 100 when the correct value was 120. Let pi be the p-value of the same procedure after making the required correction on Xn, then
(a) pi > po.
(b) pi = po.
(c) pi < po.
(d) pi will have no specific relation with p0.
15. For a random variable X with parameter 9, if L(.) and U(.) satisfy
Pq (L(X) < 9) = 1 a1 and Pq (U(X) > 9) =1 a2 and L(x) < U(x) for all x, then Pq (L(X) < 9 < U(X)) is
(a) 1 ai a2.
(b) ai + a2 1.
(c) 1+2
2
aia2 2 '
(d)
16. Let P be a probability measure on the class of events on = [0, to). Suppose P (a,b]j = e-xdx, 0 < a < b < to, further for any E C Q and
z eR,E + z = {x + z;x G E}. Then P(2, 4] + 3 is
(a) less than P(2, 4]j.
(b) greater than P(2, 4]
(c) equal to P(2,4]j.
(d) cannot be determined.
17. The characteristic function <(t) of a random variable X is -+2, then E(X)
(a) is 1.
(b) is 0.
(c) does not exist.
(d) cannot be uniquely determined.
18. Suppose Xi, i = 1, 2,...,n are Bernoulli random variables on { 1,1} with
n
mean 1. Then the characteristic function of the random variable Y = Xi2
i= 1
is
(a)
(c) enit.
(d) e3it.
19. Let {Xn} be a sequence of independent random variables with probability distributions as follows: P (X1 = 0) = P (X1 = 2) = 1; P (Xn = 1 i/n) = P (Xn = 1 + /n) = n, P (Xn = 1) = 1 n, n =2, 3, . If Sn = X1 + ... + Xn, then lim P (Sn > n)
(a) is 0.
(b) is 1.
(c) is 2.
(d) does not exist.
20. A population of 60 units is split into 3 strata of equal sizes. The within stratum variances of the variable of interest Y are a2, 4a2, 9a2 for stratum 1, 2 and 3 respectively. A stratified sample of 18 units is to be drawn, the optimal allocation of the sample from strata 1, 2, 3 is respectively
(a) 2, 8, 10.
(b) 3, 6, 9.
(c) 3, 7, 8.
(d) 2, 5, 11.
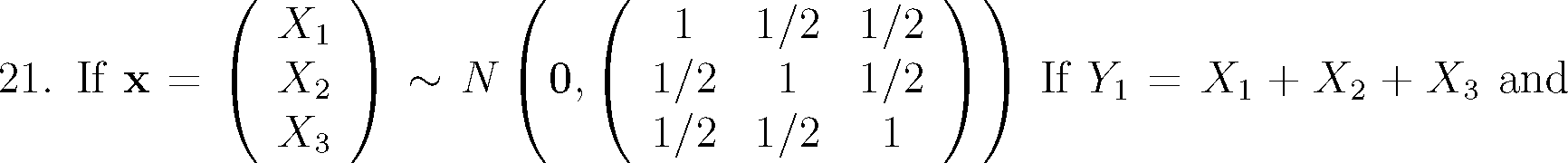 |
|
Y2 X1 + X2 2X3, then |
(a) Y1 and Y2 are not independent.
(b) Y1 and Y2 are uncorrelated but not independent.
(c) Y1 and Y2 are correlated with correlation coefficient equal to 1/2.
(d) Y1 and Y2 are independent.
22. The transition probability matrix of a Markov chain with state space S =
{1, 2, 3} is
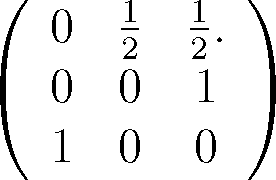
This Markov chain is
(a) irreducible and hence recurrent.
(b) not irreducible.
(c) does not process a stationary distribution.
(d) irreducible but not recurrent.
23. Suppose E(Y\X) = 15X, where X ~ Beta(2,1), then E(Y) is
(a) f.
(b) 5.
(c) .
(d) 10.
24. Let X be a standard normal random variable and Y = max(0, X), then E(Y) is
(a) 0.
(b) vfc.
(c) v4n.
(d) .
25. Consider the following Linear Programming Problem
max 3xi + 2x2
such that 2x1 + x2 + x3 = 100
x1 + x2 + x4 = 80
x1 + x5 = 40
x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 > 0
The basic variables at the point (20,60) are
|
(a) |
X1 |
, X3 |
, X5 |
|
(b) |
X1 |
, X2 |
, X5 |
|
(c) |
2X to |
3 ,X3 |
, X4 |
|
(d) |
X1 |
, X4 |
, X5 |
There are 17 questions in this part. Answer as many as you can.
The maximum you can score is 50. Marks are indicated against each question.
The answers should be written in the separate answer script provided to you.
1. The probability density function of a random variable is
ax2 exp{-kx}, 0 < x < to, a,k > 0
f (x) 1 0, otherwise.
Given the constant k > 0, (i) find a. (ii) find the modal value of X.
[6 marks]
2. Suppose X and Y are the times of receipt of two signals with uniform distribution on [0,T]. Further suppose that the channel gets jammed if the time difference in the receipt of the two signals is less than t, which is known. What is the probability that the channel will be jammed?
[6 marks]
3. Xi, X2,... are independent and identically distributed random variables given by
, 1 with probability p Xi
0 with probability 1 p where p itself a random variable taking two values a and b, and 0 < a < b < 1.
n
Let P (p = a) = 9, 0 < 9 < 1 and let Sn = Xi.
i=1
(a) Compute 0n(r) = P (p = a|Sn = r) for r = 0,1, 2, 3, , n.
i
(b) Show that n(r) > ()"(i=g)+1.
(c) Find E (p|Sn = r). [6 marks]
4. Let the random variable Y have exponential distribution with pdf:
f (V 0) = i (1/0) exp(-y/0) y - 0 0 > 0
f (V; ) | 0, otherwise.
Let X = [Y], the integer part of Y.
(a) Determine how X is distributed.
(b) Show that X and Y X, the fractional part of Y, are statistically independent.
[6 marks]
5. Consider the sampling design with N = 7 and n = 3
|
n |
P(s) | ||
|
U1 |
U2 |
U4 |
1/7 |
|
U2 |
U3 |
U5 |
1/7 |
|
U3 |
U4 |
U6 |
1/7 |
|
U4 |
U5 |
U7 |
1/7 |
|
U5 |
U6 |
U1 |
1/7 |
|
U6 |
U7 |
U2 |
1/7 |
|
U7 |
U1 |
U3 |
1/7 |
Compute the inclusion probabilities n and , i, j = 1, , 7, i = j. How does this design compare with an SRSWOR design (N = 7, n = 3)?
[8 marks]
( ( 211
6. If X - N I 0, ( 1 2 1
112
/ Xi X2 \
(a) Find the distribution of Z = I X2 X3 I
V X3 Xi )
(b) Let Y1 = X1 + X2 + X3,Y2 = X1 + X2 X3. Find the conditional expectation and variance of Yi given Y2 = 2. [6 marks]
7. Let X1,X2,...,Xn be i.i.d Binomial (k,0). Find the uniformly minimum variance unbiased estimator for the probability of exactly one success.
[6 marks]
8. Let X be a Binomial (N, 1/2) random variable where N, the number of trials is unknown, N G {1, 2,...}. To estimate N based on a single observation the following two confidence sets were considered:
(i) {X,X + 1,X + 2,...}
(ii) {X, X + 1,X + 2,..., 2X}.
Which of the two confidence sets will you prefer? Justify your choice.
[8 marks]
9. X is a discrete random variable on A = {0,1,..., 5} with probability mass function Pg(X = x), x E A, 9 E {9o,91} given below
|
x |
0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
Pg0 (X = x) |
1/6 |
1/6 |
1/6 |
1/6 |
1/6 |
1/6 |
|
Pg! (X = x) |
1/12 |
1/12 |
1/4 |
1/4 |
4/15 |
1/15 |
Based on a single observation on X, the hypothesis to be tested are
H0 : 9 = 90 against H1 : 9 = 91.
(a) Derive a likelihood ratio test of size 0.2.
(b) Find the value of the power function of the proposed test under the alternative.
(c) If X=2 is observed, find the p-value of the proposed procedure and state your conclusion.
(d) What is the critical region of the likelihood ratio test at a = 0.5 level of significance? [10 marks]
10. Ei, i = 1, 2, 3 are three independent events such that the probability that only Ei occurs is pi. Show that the probability q that none of E1,E2, E3 occur is a root of the equation (q + p1)(q + p2)(q + p3) = q2.
[6 marks]
11. A square matrix B is said to be idempotent if B2 = B. Let I be the identity matrix of the same order as B.
(a) Show that I + B is nonsingular.
(b) Show that I B is nonsingular if and only if B = 0.
[6 marks]
12. The value of Y is estimated for X = x0 from the linear regression of Y on X. Let this estimated value of Y be y0. The value of X for Y = y0 is estimated from the linear regression of X on Y. Let this estimated value of X when
Y = y0 be xQ. Compare x0 and x0. Interpret the answer. [6 marks]
13. To compare the effects of three treatments A, B and C, the experimental field was split into three homogeneous blocks B1, B2 and B3. Treatment A was given to all three blocks, treatment B was given to block B1 and treatment C was given to blocks B2 and B3.
(a) Verify whether the resulting block design is (i) complete (ii) balanced (iii) connected (iv) orthogonal.
(b) Can the two treatments B and C be compared? Justify.
14. Let {Xn} be a Markov chain on {1, 2,..., M}. The conditional distribution of Xn+1 given Xn = j, j = 1, 2,..., (M 1) is discrete uniform on {j + 1,..., M} and when Xn = M, Xn+1 is equal to 1 with probability one. Obtain the mean time to return for each state j = 1, 2, . . . , M.
[8 marks]
15. Let X = {x : Ax = b, x > 0}, where A is m x n matrix of rank m. Let x be a feasible solution, x = (x1,..., xq, xq+1,..., xn)' whose first q components, x1,..., xq are positive and next nq components xq+1,..., xn are zero. Assume that a1,..., aq, the columns of A corresponding to x1,..., xq, are dependent. Explain how you would construct feasible points x and such that x is a convex combination of x and x".
[6 marks]
16. A company manufactures three products A, B and C. The unit profit from making A is 3, B is 1 and C is 5. The amount of labour (in hours) required to make one unit of product A is 6 hours, one unit of product B is 3 hours, one unit of product C is 5 hours. The amount of material required to make one unit of product of A is 3 units, that of product B is 4 units and that of product C is 5 units. Total amount of labour hours available is 45 hours and total amount of material available is 30 units. The company wants to maximize its profit.
(a) Formulate the problem as a linear programming problem.
(b) Suppose the unit profit from B is increased from 1 to 4. What happens to the optimal solution?
(c) A new product D with unit profit 5, labour requirement 3 hours and material requirement 4 units is planned to be introduced. Is it profitable for the company to produce D? [10 marks]
17. Consider the following initial problem
P = min cx such that Ax = b, x > 0.
Suppose P has a finite optimal solution. Show by Duality that the problem
P' = min cx
such that Ax = b', x > 0. can not be unbounded, no matter what value b' might take. [8 marks]
10
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
