University of Delhi 2010-2nd Year M.Tech Information Technology 1st nd semmathematical & numerical methods in nuclear engneering UNIVERSITY - Question Paper
[This question paper contains 7 printed pages ]
Your Roll No
7017 J
M.Tech/II Sem
NUCLEAR SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY Paper NST - 608 Mathematical & Numerical Methods m Nuclear Engineering
Time 3 Hours Maximum Marks 70
(Write your Roll No on the top immediately on receipt of this question paper )
Attempt all questions
1 Attempt any five of the following Each part carries two marks
(a) How many real zeroes does the function
fix) = 2** + 2x + Sx-S- k has 7 (k is anv real number )
(b) Ten iterations of the bisection method are applied to the function
fix) = 2r + x- - 2x - 6 to find its zero lying between 1 and 2 To how many decimal places the result is expected to be correct7
(c) Given that f(x) = 0 479, 0 565, 0 644 at x = 0 5, 0 6 and 0 7 respectively, use the three-point difference formulas to find f\x) at x - 0 5, 0 6 and 0 7
(d) The integral f dx is obtained by composite Jo
Sirapson rule If the error is to be less than 10 H, find the minimum number of subintervals required (ei For the linear system
*1 + *2 + *3 = 4 xl + 2axi + xs =6,
oq-j + x2 + (2 - a)jc3 = 4.
find a foi which the system has (l) no solution,
(n) infinite number of solutions
(f) For what values of k is the mstrix
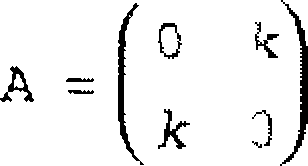
convergent 9
(g) Find the spectral radius, the /2 norm and the norm of the matrix
(h) Show that the initial value problem
y{$=ty ' + ec, 0 < t< l,y(0) = 1,
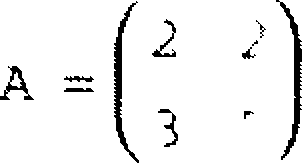
( 3 ) 7017
has a unique solution by applying the relevant theorem 2x5=10
Attempt any five of the followings Each part carries four marks
(a) Show that the function
x4 - 3 + 3
f(x) = ------
x + 2
has a fixed pomt m x e {0, 2] Ls the fixed point unique 9
(b) Find ct) c{ and xp so that the quadrature formula
f()
has the highest degree of precision
(c) Show that the inverse of a non-singular lower tnangular matrix is a lower tnangulai matrix
(d) Show that the matrix AB is non-smgular, if and only ii, both A and B are non-smgular
(e) Show that for any vector i e TR",
, 1< tS2,y(L) = l
y=--
t
7017 ( 4 )
(ft The mtial value problem
t
has the solution Yt$ z:- Find the error
i+ ii ca
bound m the value of y(2) obtained by Euler's method with h - 0 1
(g) Show that for the initial value problem
y' (x) = p{x) y (x) + q(x) y(x),
a< x< b, y(a) - 0,y (a) = 1,
if q(x) and p(x) are continuous an (a, 6] and <3r(x) > 0 on [a, 6], then y(6) cannot be zero
(h) The partial differential equation
d2u dii
- +-= f(xt y)f u (x,y) = gix,y)
on the boundary of 0 < x < 1, 0 < y < 1, is to be solved by finite difference method
2u txl,yJ)+ u 0c]_llyJ)
+ h2 /}? [uixy)- 2u CxJ,y1)+ 4 (xy)]
- h2 f (xl,yJ) { 5 ) 7017
by dividing both the intervals (0, 1) into three equal parts, write down the equations obtained m a convenient form 4x5=20
Attempt any five of the following. Each part carries 8 marks
(a) Obtain the formula for finding the zeroes of a function by Newton's method Interpret it geometrically How is this method modified to obviate the need for evaluation of the denvative
(b) Show that for the Simpson rule
| f(x} dx:=[f(a}+4 f()+ f(b)],
b- a b+ a --f =-f error term is
jfl
90
(c) Show that for any polynomial P(x) of degree less than 2n,
ri 12 J_i P ix)dx=
where xt are the zeroes of Legendre polynomials P(x) and et are given by
x. - X
T=1 1* -
X~ X
dx
(d) Show that for any vector xe?n, the sequence {x'} defined by
xyk) = Tk1,+CVJc>1(
converges to the unique solution of x - Tx + C (where T is an n x n matrix, and C a vector ) if and only if p(T), the spectral radius ot T is less than 1 Reduce the Jacobi and Gauss-Seidel techniques for solving the linear system Ax = b to the above form and thereby state the corresponding result for these techniques
(e) Describe the Q*R algorithm for finding the eigenvalues of a tridiagonal symmetric matrix
(f) What is the main drawback of the Taylor's methods for solving an initial value problem Describe the basic idea of the Runge-Kutta class of methods for such problems Obtain the formula for the mid-pomt method, a Runge-Kutta method of order 2
(g) Describe the finite difference method for the solution of the boundary value problem
y"{x)= p(x) y (x) + q(x) y(x)+ r(x),
a < x< h, y(a) ~ a , y(b) - (3
What are the conditions that need to be satisfied ior the method to work 7
(h) Describe the finite difference method for the solution of parabolic type of partial differential equation
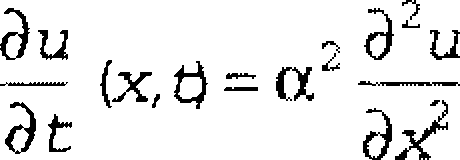
< x< X t> 0,
= u(X 0, t> 0, u(x,0)= f(x),0<x<l
What is the drawback of the forward difference method and how is it corrected m the backward
8x5=40
100
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
