Indian Institute of Science 2010 Ph.D Chemistry Entrance for ( ) - Question Paper

INSTRUCTIONS
1. This question paper consists of only multiple-choice questions. All questions carry one mark each.
2. Answers are to be marked in the OMR sheet provided.
3. For each question, darken the appropriate bubble to indicate your answer.
4. Use only HB pencils for darkening the bubble.
5. Mark only one bubble per question. If you mark more than one bubble, the answer will be evaluated as incorrect.
6. If you wish to change your answer, please erase the existing mark completely before marking the other bubble.
7. There will be NEGATIVE marking. NEGATIVE marking for each wrong answer will be 1/3.
8. A periodic table is given at the end.
9. Some useful physical constants:
R = 8.31451 J mol'1 K'1
0.08206 L atm mol'1 K'1
h = 6.626 x IO04 J.s
g = 9.8 m s"2
c = 2.998 x 108 m s"1
N = 6.023x 1023 mol1
k = 1.380 x 10'23 JK'1
e = 1.602 xlO'l9C
me 9.109 x 10J1 Kg
o = 8.854 x 10'12 F m*1
F = 9.65 x 104Cmor
= 4.184 J
= 760 Torr
= 1.6022 x 1019 J
(A) Universal gas constant
(B) Plancks constant,
(C) Acceleration due lo gravity
(D) Speed of light in vacuum
(E) Avogadros number
(F) Boltzmann constant ((Electron charge
(H) Electron mass
(I) Permittivity of the vacuum (J) Faraday constant (K) 1 Calorie (L) 1 atm (M) I eV
1 Temperature dependence of the rate constant for a reaction obeys the Arrhenius
. According to this equation, as T approaches infinity, k
equation: k = AxeK will approach:
(B) infinity
(C)l
(D)0
2. Among the following molecules, the one that is NOT infrared active is:
(A) C2H2, acetylene
(B) CH4, methane
(C) N2, nitrogen molecule
(D) CO2, carbon dioxide
3. The molar entropy of a molecule that can have three distinct orientations at absolute zero is approximately:
(A) 9.13 J K.'1
(B) 5.76 J K'1
(C)24.9J K'1
(D)3.96 J K"1
4. For the reaction of oxygen in equilibrium with ozone: 302 (g) 20j (g), the number of intensive variables to be specified to describe the state of the system, is:
(A)l
(B)2
(C) 3
5. The atomic term symbol for the helium atom in its ground state is
(A)3S|
(B)3p2
(C)JS0
(D)lS0
6. The operation of a Carnot engine between a high temperature TH and a low temperature Tl is shown next in terms of temperature T and entropy S of some working fluid.
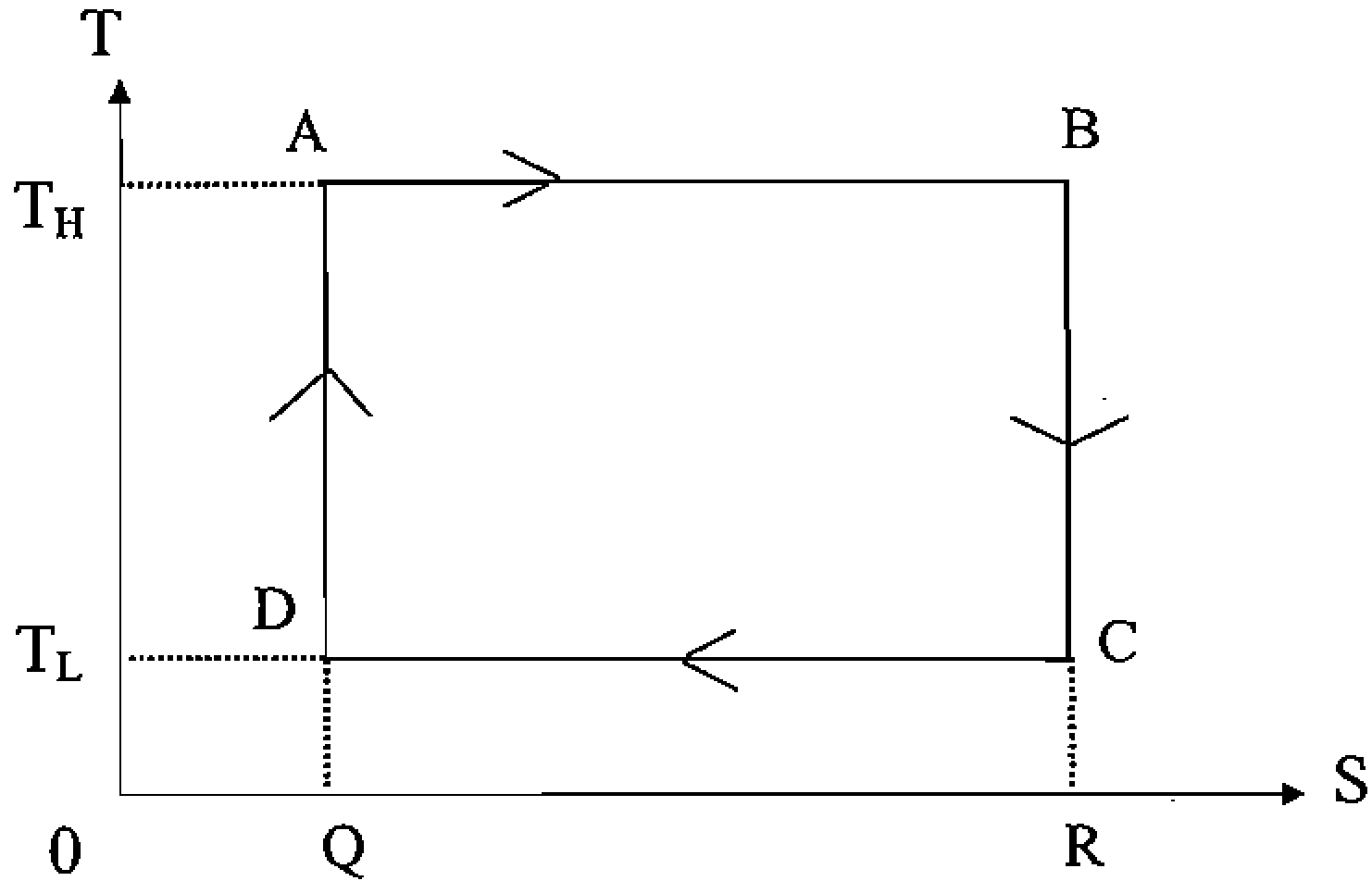
Among the following statements about this figure, the one that is NOT TRUE is:
(A)The network done by the system is the area ABRQ - DCRQ.
(B)The step C D corresponds to an isothermal expansion of the working fluid.
(C) The heat deposited by the system in the thermal reservoir at Tl is the area DCRQ.
(D)Both the steps D -> A and B C describe adiabatic processes.
7. Among the following forms of carbon, the thermodynamically most stable one is:
(A) Carbon nanotube
(B) Fullerene
(C) Diamond
(D) Graphite
8. One mole of an ideal gas expands from 5 aim against a constant pressure of 1 atm at 298 K. The magnitude of work done by the gas is:
(A)1981J
(B)3988J
(C)991J
(D)7282 J
9. The total degeneracy for a d1 ion in spherical symmetry ic:
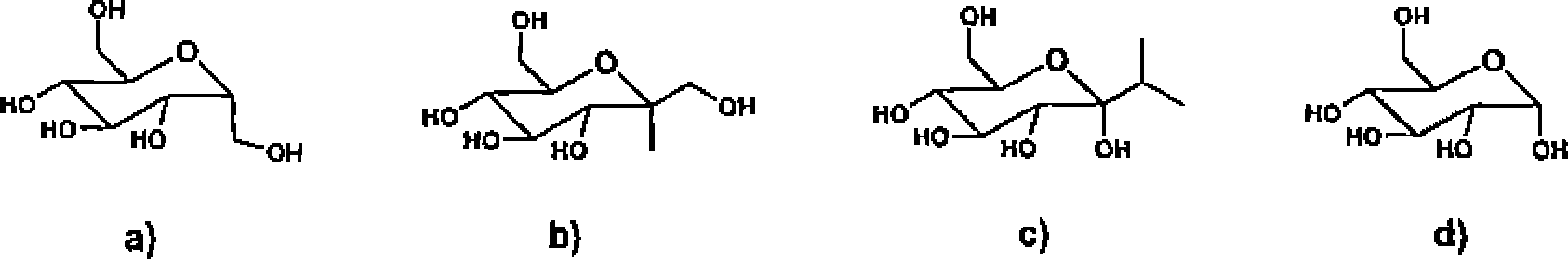
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 5
(D) 10
10. A molecule has two Q axes perpendicular to each other. Hence,
(A) the molecule would have a non-zero dipole moment which may point either along one of the two axes.
(B) the molecule would have a non-zero dipole mcment, which would point in the direction midway between the two axes, i.e. making an angle of 45 to each axis.
(Cjlhe molecule has a non-zero dipole that would point in a direction perpendicular to the two axes.
(D) the molecule would have zero dipole mcment.
11. Twenty four grams af zinc metal is dissolved in 1M HC1 solution. The charge produced by the oxidation process is:
(A) 96500 Coulombs
(B) 70836 Coulombs
(C) 48250 Coulombs
(D) 35418 Coulombs
12. The pH of 80 % ionised 0.0IN acid solution is:
(A) 2.0969
(B) 0.2096
(C) 20.09
(D) 0.0269
13. Given the standard cell potentials as below:
AgCl + e = Ag + CP, E = 0.2223 V
The solubility product for the reaction; AgCl = Ag+ + C1 is:
(A) 2.80 x 10lt}
(B) 0.80x 10'10
(C) 28.0 x 10'10
(D) 1.80 x 10'10
14. Concentration of the reagent A, [A], varies with time according to the graph shown next:
1.2 1
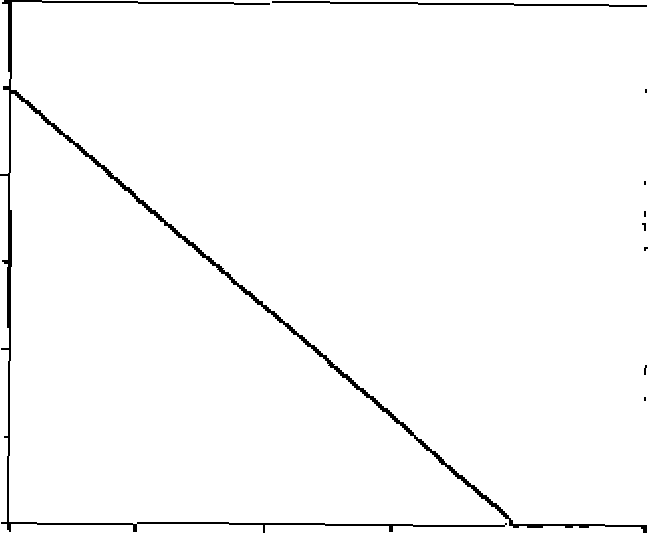 |
|
O 0.0S 0.1 0.1S 0.2 0.25 Ume In ms |
0J>
7 0.6
0.4
0.2 0
The order of the reaction is:
(A) not defined
(B) I
(D)0
15. The point group symmetry for the molecule NH3 is:
(A) The concenaation of the catalyst does not enter in to the expression for equilibrium.
(B) The enthalpy of reaction does not change in the presence of a catalyst.
(D) Without the catalyst, the reaction can still proceed.
17. For the reaction: 2 NHj(g) 3 H2 (g) + N2 (g), AH0 = 92.22 kJ mol'1 and AS0 = 198.75 J K*1 mol'1. With all reactants and products in their standard stare, this reaction will bc spontaneous at:
(A) temperatures below 464 K
(B) temperatures above 464 K
(C) no temperature.
(D) all temperatures.
18. Among the following groups of metals, the one having the lowest melting points
is:
(A)alkaline earth
(B) transition
(C) alkali
(D)lanthanide
19. The composition of a sample of iron oxide is Feo.930. The percentage of Fe in the +3 oxidation state in this sample is approximately:
(A) 0.07%
(B)7.0%
(C)30.0%
(D) 15.1 %
20. For the reaction 2P + 3Bt2 2PBr3, the heat evolved is -243 kJ (AH). Hence, the enthalpy change when 2.63 g ofP reacts with an excess of Br2 will be:
(A) 10.3 kJ
(B)24.3 kJ (Cj1.03kJ
(D)20.6kJ
21. The product of the reaction of anisole with sodamide is:
(A) m-anisidine
(B) p-anisidine
(C) 1,2-diaminobenzene
(D) 1,3-diaminobenzene
22. The major product in the following reaction is:
S
?
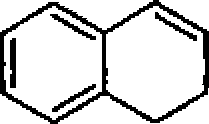
A
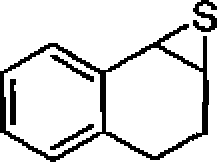
(A)
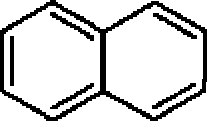
(B)
|
S |
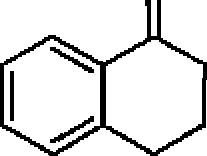 |
<C>
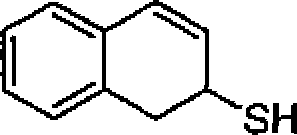
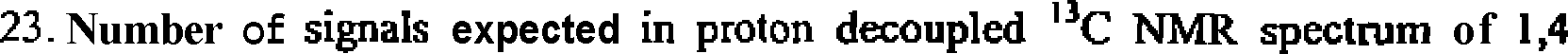 |
|
dihydroxynaphthalene and 1,8-dihydroxynaphthalene are: |
(A) 5 and 5
(B) 5 and 6
(C) 5 and 10
(d) 10 and 6
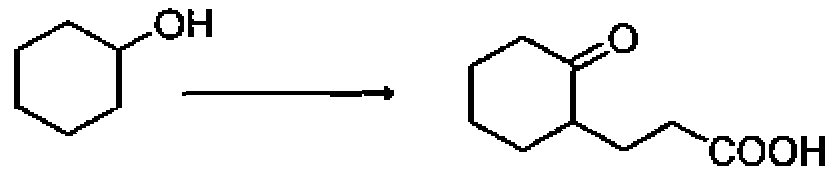
(A) (i) Cr03, (ii) methyl acrylate, (iii) H20/H+
(B) () 02> () methyl acrylate
(C) (i) Cr03 (ir) pyrrolidine (iii) methyl acrylate, (iv) H20/H+
(D) (i)H202, (ii) methyl acrylate,
25. In the multi-step synthesis given below, the overall yield for the formation of S from P is:
(A) 72%
(B) 40 %
(C)36 %
(D)50 %
i
J
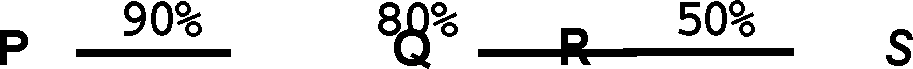
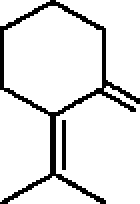
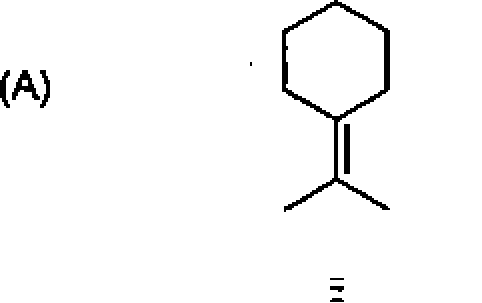
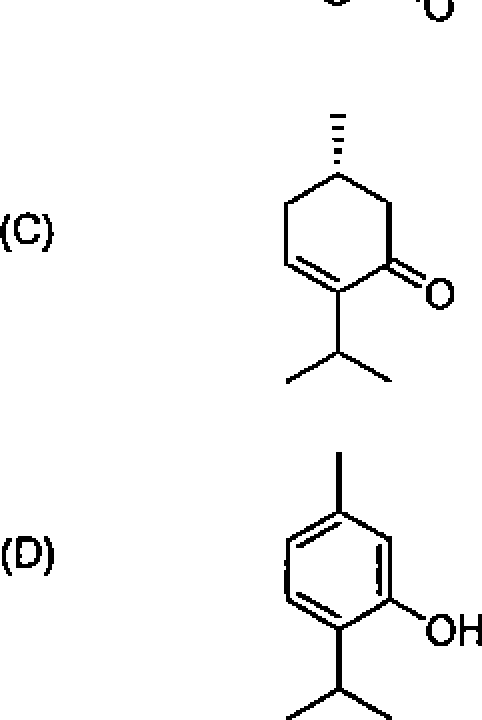
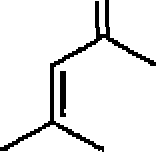
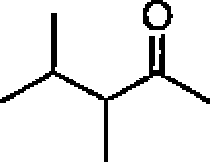
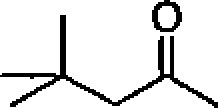
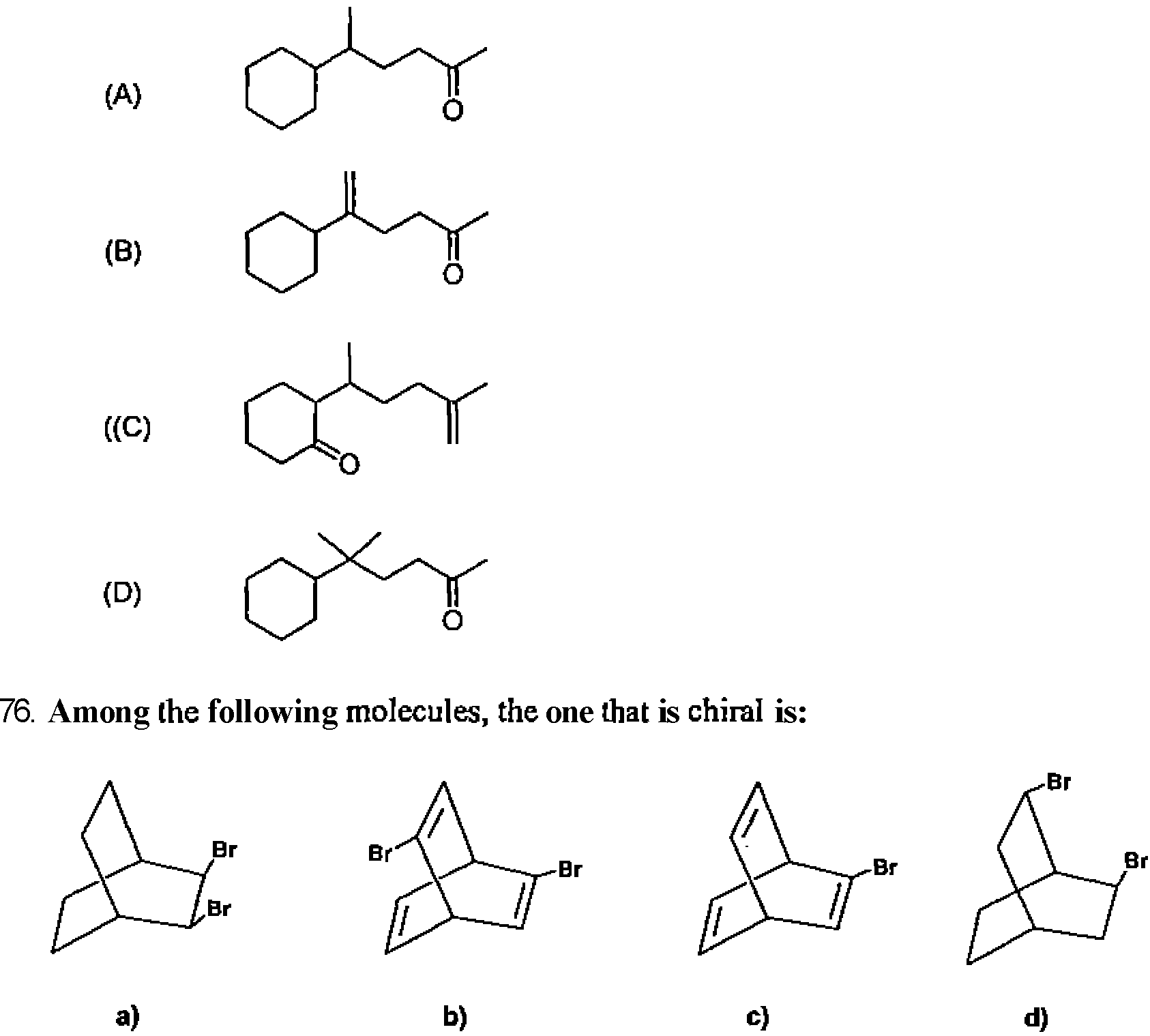
26. Among the following molecules, the one that yields 2,3,6-trimethylcyclohex-2-enone on treatment with dil. KOH is:
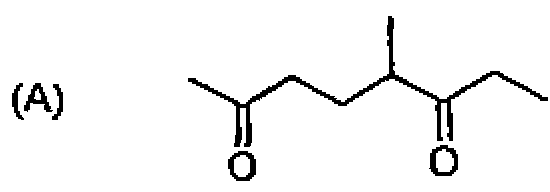
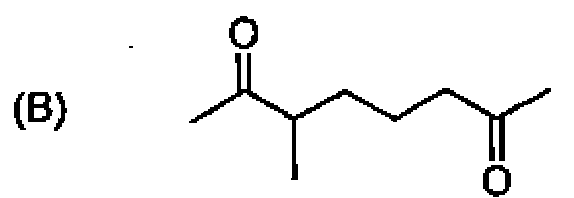
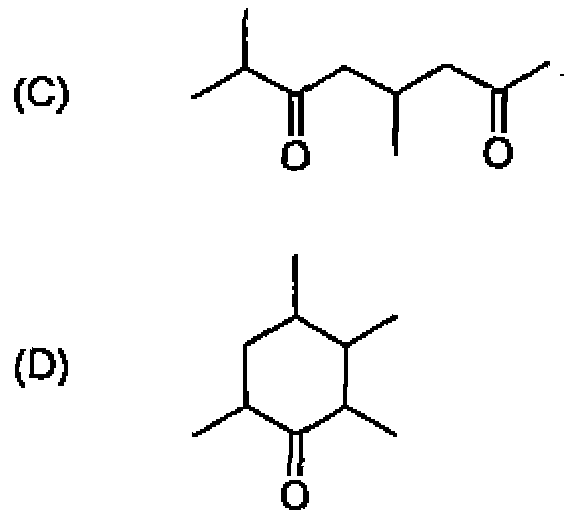
27. CfcL heating, 1,3-butadiene reacts with elemental sulfur to yield:
(A)thiophene
(B) 2,5-dihydrolhiophene fC72,3-dihydrothiophene
(D) tetrahydrothiophene
|
0 |
 |
29. The reagent of choice for the selective reduction of ketones in presence of an ester is:
(A) lithium aluminium hydride
(B) sodium hydride
(C) hydrogen and palladium on carbon
(D) sodium borohydride
I
I
I
 |
1M aq. NaOH O |
31. The biogenetic precursor for cholesterol is:
(A) mevalonic acid
(B) cyclopentaphenanthrene
(C) acetyl CoA
(D) fatty acid
(A)
(B)
|
OAc |
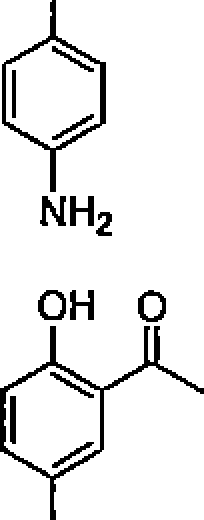 |
|
NH2 |
|
OH |
 |
|
NH2 0 |
(C)
CD)
|
OH |
 |
|
NHAc |
33. An organic compound of molecular formula C4H8 exhibits only a singlet at 5 1.9 ppm with reference to tetramethylsilane in 'H NMR spectrum. The compound is:
(A) 1-butene
(B) cis-2-butene
(C) cyclobutane
(D) trans-2-butene

Ph
(A)
(B)
Ph
0o oh
(C)
Ph'xO<r ''OH
OH
(D)
OH
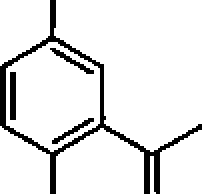
35. The IUPAC name for the following molecule is:
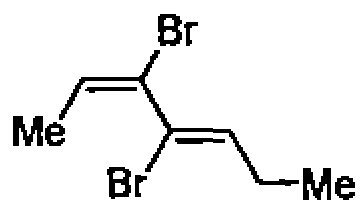
(A) (2E,4Z)-3,4-dibromo hepta-2,4-diene
(B) (2Z,4E)-3,4-dibromo hepta-2,4-diene
(C) (2Z,4Z)-3,4-dibromo hepta-2,4-diene
(D) (2E,4E)-3,4-dibromo hepta-2,4-diene
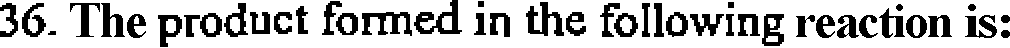
Me2CuLi
o
I OH
I OH
(C)
37. Among the following aldehydes, the one that does NOT undergo Cannizzaro reaction is:
|
(A) formaldehyde (B) acetaldehyde (C) benzaldehyde |
 |
38. R'-2-octyl tosylate is solvolyzed in 80% aqueous acetone under ideal SnI conditions. The product(s) will be:
(A)R-2-octanol and S-2-octanol in a 1:1 ratio
(B) R-2-octanol and S-2-octanol in a 2:1 ratio
(C)i?-2-octanol only
(D)S-2-octanol only
(A)a
(B)b
(C)c
40. Major product obtained in the reduction of 4-/er/-butyl cyclohexanone with NaBH4 is:
|
OH |
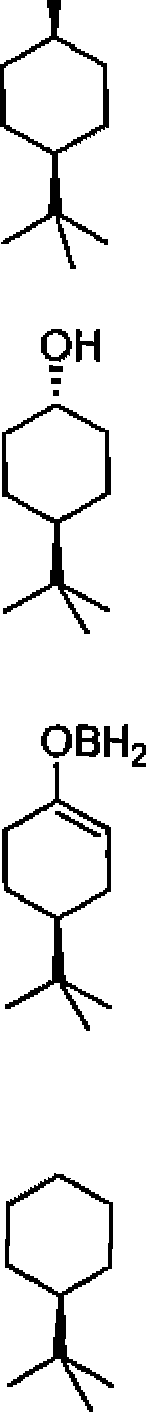 |
(A)
(C)
(D)
1
\
j
42. For the preparation of 1 litre each of 1 M NaOH and 1 M ICOH solutions, the quantities of NaOH and KOH required are, respectively:
(A)40 gand 47.6 g
(B) 40 g and 56 g
(C) 20 g and 56 g
(D)40 g and 28 g
43. Zinc selenidc crystallizes in zincblende structure. The numbers of atoms of Zn and Se present in its unit cell are:
(A) 8
(C) 4
(D)12
44. The role of Br2 in the reaction H;0 + Br2 HOBr + HBr is:
(A)reducing agent
(B) oxidizing agent
(Cjneifher oxidizing nor reducing agent
(D)both oxidizing and reducing agents
45. Among the following complexes, the one ihat undergoes Zm distortion is:
(A)[Ni(CO)4]
(B) [CuCl4]2"
(C) [Cr(H20)6]2+
(D)[Cu(NH3)6]2
46. The ground state for the V3+ ion in a tetrahedral environment is:
(A)3T,
(B)3t2
(C)3a3
(D)3e
47. Treatment of MofCOJe with Na+CjH5~ results in:
(A)Na[Mo(V-C5H5)(CO>i] +2C0
(B) Na[MoCTi5-C5H5)(CO)33 + 3C0
(C)Na[Mo(ri3-C5H5)(CO)2] + 4C0
(D)Na[Mo(ns-C5H5)(CO)] + 5C0
48. The reaction:
[Ir(H)2Cl(CO)(PPh3)2] [IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2] + H2 is an example for:
(A)oxidative addition
(B) substitution
(C) insertion
(D) reductive elimination
49. The smallest cation amongNa+, Mg2+, Al3+, Si4+ is:
50. The two main isotopes of poiassium are 39K and ''K. The atomic mass of potassium may be used as 39.1. The abundances of the isotopes are:
(A) 95% 39K and 5% 41K
(B) 90% 39K and 10%4,K
(C) 5% 39K and 95% 4IK
(D) 10% 39K and 90% 4lK
51. The metal ions that have the highest mobility in biological media are:
(A)Zn(II) and Ni(II)
(3)Fe(II) and Cu(II)
(C) Na(I) and K(I)
(D)Mg(II) and Ca(II)
52. Hcmerythrin belongs to the group of:
(A) non-herne iron protein
(B) binuclear copper protein
(C)herne-iron protein
(D) non-heme non-iron protein
53. Among the following bonds, the least stable one is:
(A) S-S
(C) P-P
54. The number of isomers possible for octahedral [CrCh(H20)4]+ and octahedral [CoCl2(en)z]+ are, respectively,:
(A) two and two
(B) three and three
(C)two and three
(D) three and two
55. The cis-platin is:
(A) diamagnetic.
(B) paramagnetic.
(C) ferromagnetic.
(D) anti-ferromagnetic.
56. Among the following organometallic compounds, the one that follows the 18-electron rule is:
(A)[Ni(75-C5H5)2]
(D)[Cd(-C3Hs)J
I
I
57. Among the following oxides, the one having a normal spinel structure is:
(A)CuO
(B) C03O4
(C)Fe304 (DJTiO*
58. Among the following complexes, the one having a metal-metal quadruple bond is:
(A)[Re2Cl8f
(B)[Cu2(OAc)4]
(C)[Mo2(OR)6]
(D)[Ru2C1(OAc)4]
59. Among the following complexes, the one that is expected to show three d-d bands in the electronic spectrum is:
(A)[Mn(H20)6]2*
(B) [FeCI4]"
CC)[Ti(H20)6]3+
(D)[Ni(H20)6]2+
60. One hundred gram of CaCOj contains (N is the Avogadro's number):
(A)50N protons
(B)N protons
(C) 5N protons
(D) 25N protons
61. Among the following pairs of ions/molecules, the one having similar shapes is:
(A)COz and H20
(B) BF3 and HjC+
(C) CCU and PtCl4
(D) NH3 and BF3
62. The number of orbitals present in the n = 4 atomic shell is:
(A) 64
(B) 32
(C)16
63. There are two containers having two moles of Ar each at a temperature of 298 K. and a pressure of 1 bar. Both are heated such that they gain 1 KJ of energy each. First container was heated at constant V and the second container was heated at constant P. The final temperatures in the two containers will respechvely be:
(A) 298 K and 350 K
(B) 350 K and 400 K
and 322 K  and 350 K
and 350 K
64. The molecular weight of an ideal gas having a density of 1.5 g L'1 at 100 C and
600Torr is:
(A)45.9g/mol
(B) 4.59 g/mol
(C)5.82 g/mol
(D)58.2 g/mol
65. According to ideal gas law,:
(A) molecules have neither attraction between them nor have any finite size, being treated as a point mass.
(B) molecules do have attraction between them but do not have any finite size, being treated as a point mass.
(CJmolecules have no attraction between them but do have a finite size.
(D)molecules have both attraction between them and have a finite size.
66. For the gas phase reaction: CO + NO2 - CO2 + NO, the activation energy is found to be 116 kJ mol'1. The enthalpy of formation for CO, N02, CO2 and NO are -110, 33, -394 and 90 kl mol'1, respectively. The activation energy (in kJ mol*1) for the reverse reaction is:
(A) 343
(B) -227
(C) 227
(D) 116
67. Factors affeciing the average kinetic energy of gas molecules are:
(A) pressure only
(B) temperature only
(C) both temperature and pressure
(D) neither temperature nor pressure
68. The figure below shows the dependence at some fixed temperature T of the total vapour pressure P of a mixture of two volatile liquids A and B on the mole fraction Xa of component A, with Pa the vapour pressure of pure A and Pb the vapour pressure of pure B.
|
J k |
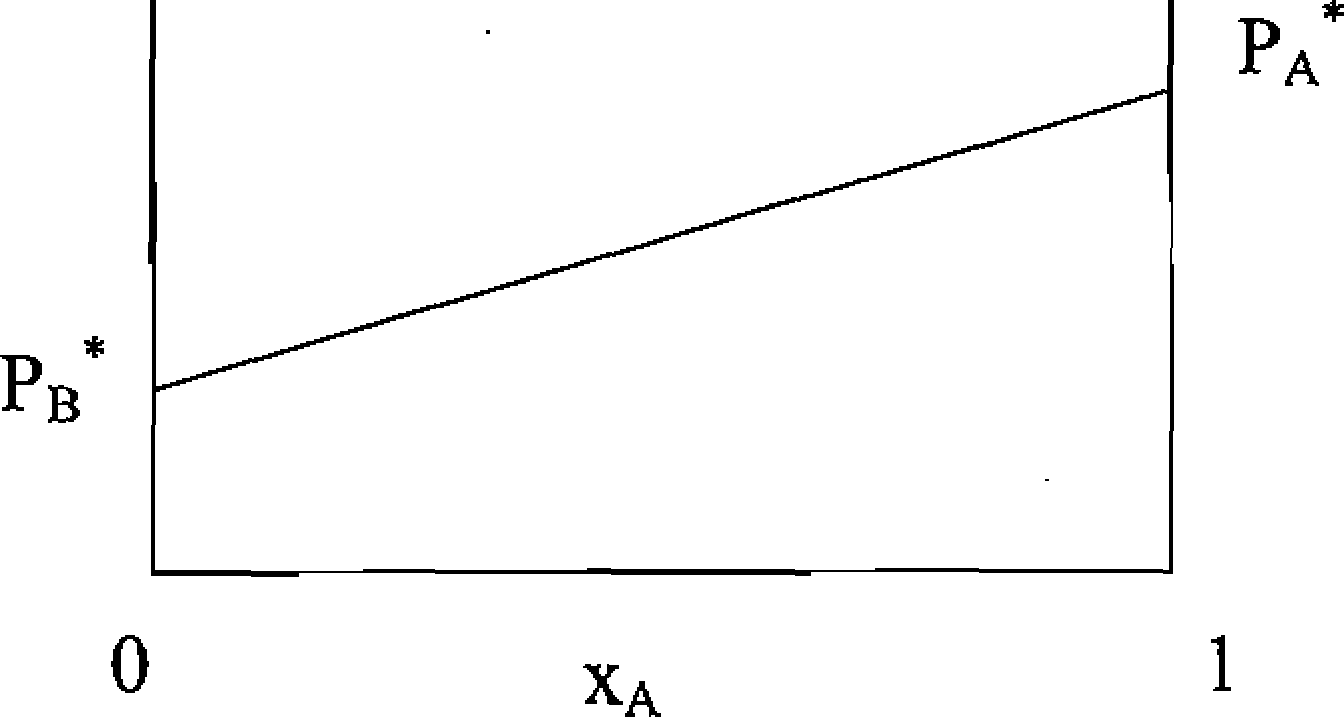 |
P
Among the following statement about this figure, the one that is NOT TRUE is:
(A) The mixture is ideal.
(B) In the region above the line Pb*Pa*, the liquid phase of the mixture is the stable phase.
(C) Along the line Pb*Pa\ the liquid and vapour phases of the mixture are in equilibrium.
(D)The vapour pressure of component B, Pb, is given by the relation Pb = Pa'O-Xa).
69. The enthalpy of fusion of HzO at 0 C is 1.436 kcal mol"1. The AS for the process HOfl) <> H20(s) at 0 C is:
(A) 52.6 cal mol'1 K'1
(B) -5.26 cal mol'1 K'1
(C) 5.26 cal mol'1 K1
(D)-52.6 cal mol1 K'1
70. Among the following graphs, the one that does not correspond to ideal gas behaviour is: (P = pressure, V = volume, T = temperature in K):
(A) At constant T
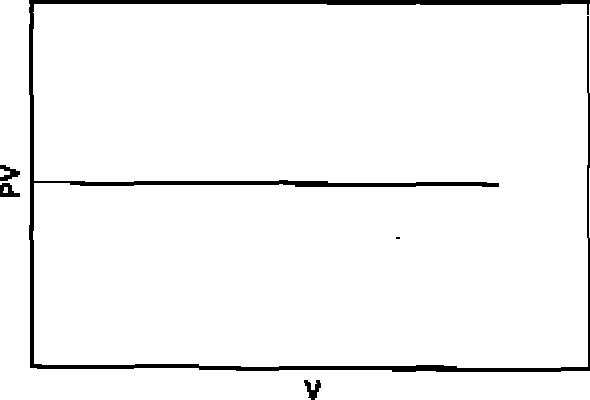
(B) At constant T
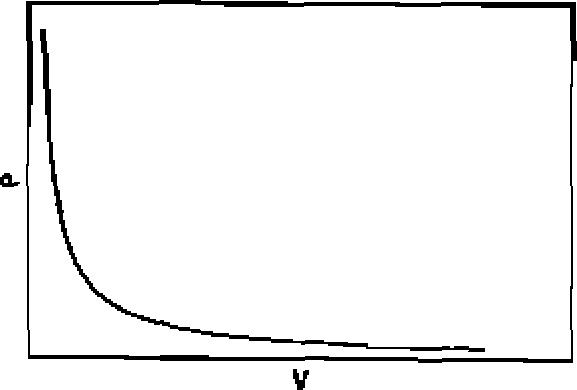
(C) At constant P
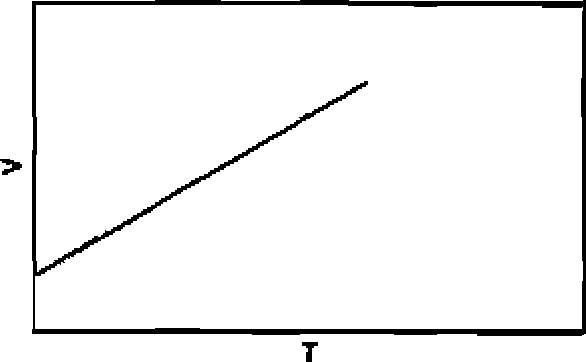
|
(D) At constant V |
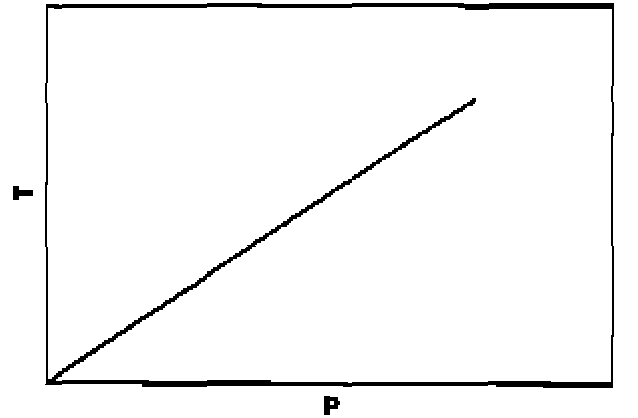 |
23
71. A particle is confined to a one dimensional box of length 2a extending from x=~a to x = a along the x-axis. The average value of position and momentum, for the particle, if it is sitting in the lowest possible state is:
(A) {*) = 0 and {p.t) = 0
(B) (x) = al2 and (pT) = 0
(C) (x) = 0 and (p,) =
(D) (x) = 0 and (pf) = r]
72. In the following N denotes a suitable constant that one may choose as desired. Of the following the functions, the only function that is NOT an acceptable wave function for an electron in the Hydrogen atom is:
(B) N exp(r)
(C) M-exp(-r)exp(i)
(D) Nr exp(-r2) exp(i)
73. In the electromagnetic spectrum, the wavenumber decreases in the order:
(A) X-ray > microwave > infra-red > ultra-violet
(B) X-ray > microwave> ultra-violet > infra-red . (C) X-ray > ultra-violet > infra-red > microwave
(D) microwave > infra-red > ultra-violet > X-ray
74. The number of electrons (per second) that pass ihrough a cross section of copper wire carrying a current of 10"9 A is:
(A)62.5 x 10l0e/s
(B) 120 e/s
(C) 12000 e/s
(D)0.625xl0e/s
(A) a
Pb(OAc)4
(B) b
(C)c
(D)d
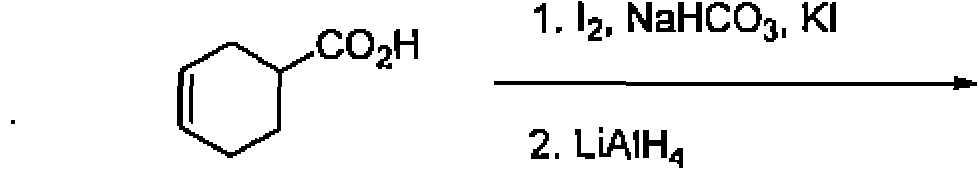
ch2oh
(A)
ch2oh
T7
(B)
(C)
78. Arrange the following in the increasing order of acidity:
(i) Benzoic acid (ii) /J-Methoxy benzoic acid (iii) p-Methyl benzoic acid
(A) (i) < (ii) < (iii)
(B) (iii) < (ii) < (i)
(C)(n)< ( iii) < (i)
(D)(ii)<(i) < (iii)
|
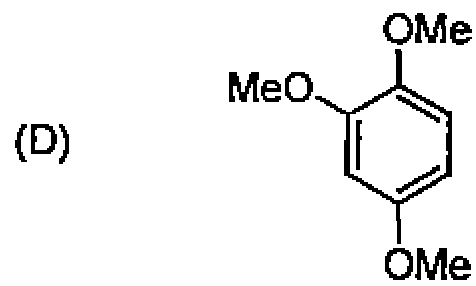
OMe |
 |
(C)
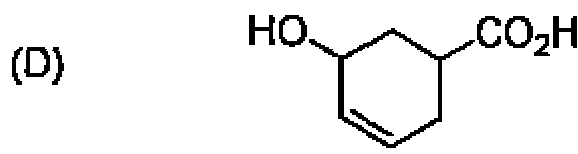
80. The number of diastereomers possible for the following compound is:
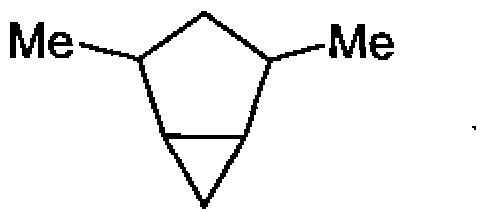
(A) 4
(B)3
(C)2
(D)l
(A)
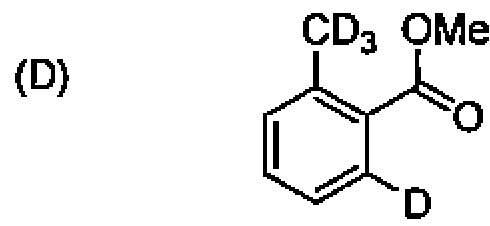
82. Among the following molecules, the one that will NOT undergo a Diels-Alder reaction is:
(A) ethylene
(B) 2-butene
(C) maleic anhydride
(D) succinic anhydride
83. The generic names for the following molecules are, respectively:
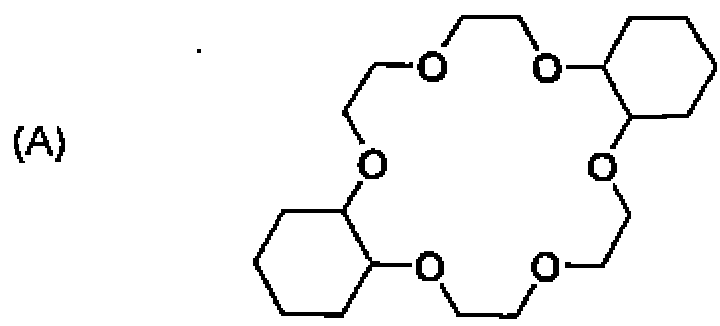
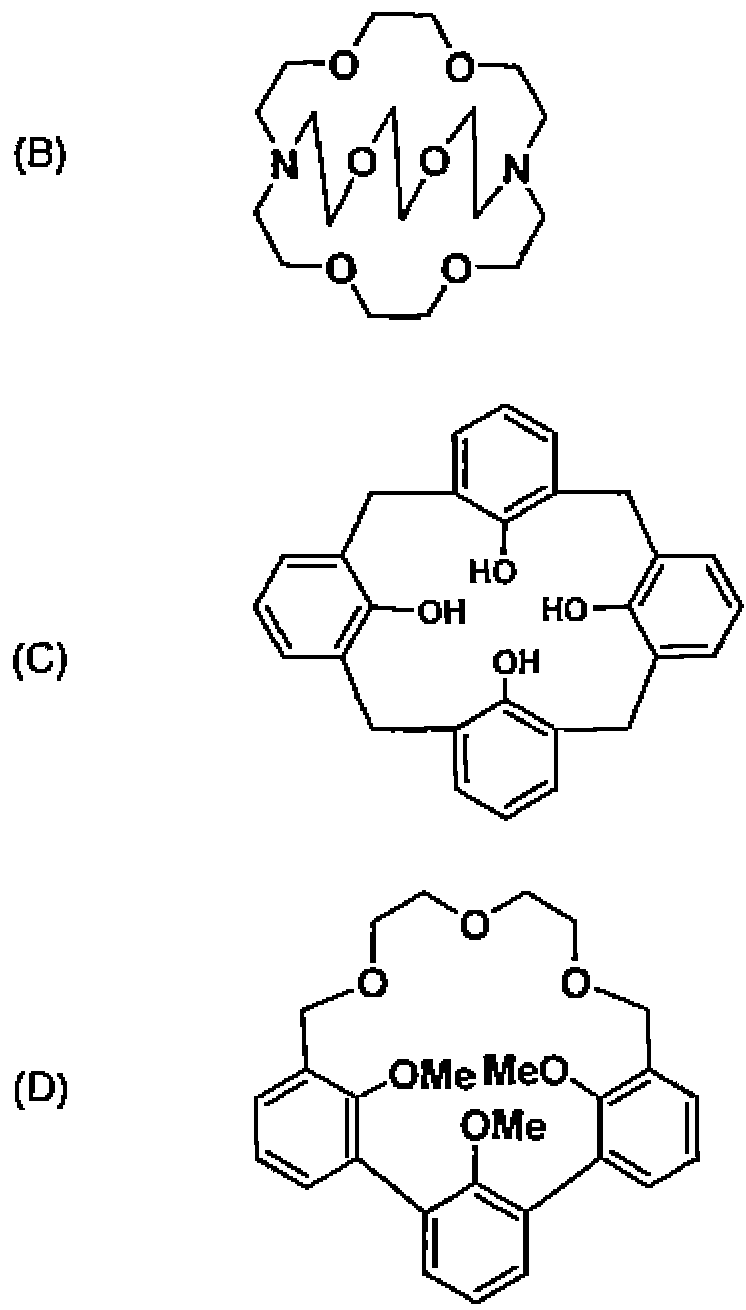
(A) crown ether, cryptand, calixarene, and hemispherand.
(B) cryptand, calixarene, crown ether and hemispherand.
(C) crown ether, hemispherand, cryptand, and calixarene.
(D) crown ether, calixarene, cryptand, and hemispherand.

84. The major product in the reaction of rnethyl acrylate and benzylamine under ambient condi tions is:
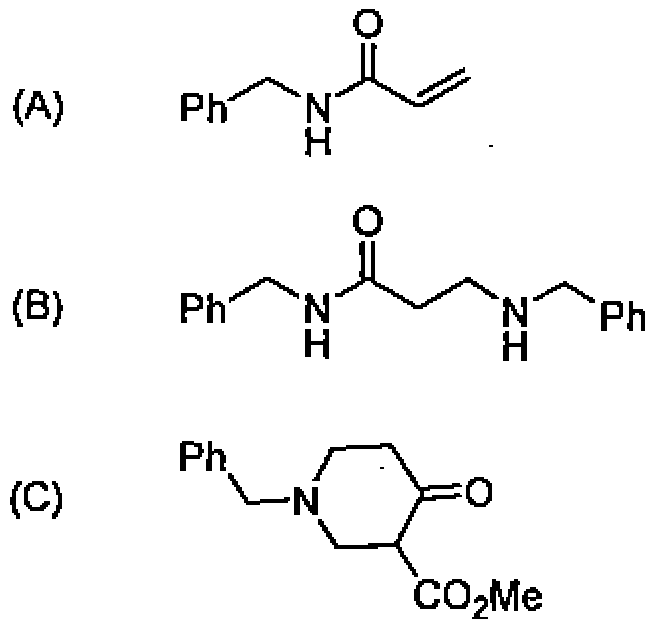
(D) Poly-(N-benzylacrylamide)
85. The major product of the reaction of 2-chlorocyclohexanonewith NaOMe is:
X)
(A)
(8)
(C)
COOMe
(A)
(B)
(C)
COOH
O
'COOH
(D)
87. In the mass spectrum of CH2CI2, the ratio of peaks at mass values 84, 86 and 88 will respectively be:
(A) 3:1:1
(B) 3:2:1
(C) 4:2:1
(D) 9:6:1
88.The enthalpy change, AH, for the following process are given in kj/mol: sublimation of K(s) = +89, ionization of K(g) = +425; dissociation of 02(g) = +244, electron gain by Cl(g) = -355, formation of KCl(s) = 438. Using a Bom-Haber cycle, the lattice enthalpy of KCl(s) is calculated to be:
(A) 719
(B) 0
(CJ-719
(D)1438
89. The absorption maximum of a given sample of cadmium sulfide is 470 nm.The approximate band gap is:
(A) 200 kJ mol'1
(B)250kJ mol"1
(C) 100 kJ mol"1
(D)150 kJ mol'1
31

90. For a 6p sub-shell, the most positive value that mi can have is:
(A)+l (B )+6
(C)+3
(D)+7
91. PhMgBr reacts with methanol to give:
(A) a mixture of anisole and Mg(OH)Br
(B) a mixture of toluene and Mg(OH)Br
(C) a mixture of phenol and MeMgBr
(D)a mixture of benzene and Mg(OMe)Br
92. C2Bn.2H is an isoelectronie analogue of:
(A)BnHn
(B)BnHn-
(C)BnHn3-
(D)BnHn2-
93. The point group symmetry of cis-tCofNtCli]* is:
(B)Oh
94. The electron transfer reaction between [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ and [Cr(H20)6]2+ in acidic medium leads to the formation of a chranium species of formulation:
(A)[Cr(NH3)s(H20)]2+
(B)[Cr{NH3)5C]]2+
(C) [Cr(H20)5Cl]2+
(D)[Cr(NH3)6]3+
95. Among the following molecules, the one that is polar is:
(AJCR,
(B)BFj
(C)SF6
(D)NH3
96. The VSEPR model is based on the:
(A) number of bonded pairs of electrons around the central atom.
(B) number of bonded and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom.
(C) number of lone pairs of electrons around the central atom.
(D) number of protons around the central atom.
97. According to Irving-WilHam series, Cu(II) is more stable than Ni(II) because of:
(A) Jahn-Teller distortion
(B) higher trans effect
(C) complexation with labile ligands
(D) induction effect
98. Among the hydrogen halides, the one having the highest bond energy is:
(A) HI
(B) HF
(C) HBr
(D) HC1
99. Among the following ligands, the strongest ir acceptor is:
(A)CN~
(B)CO
(C)N2
(D)NO+
100. Among teflon, water, benzoic acid and protein, hydrogen bonding is not important only in:
(A) teflon
(B) water
(C) benzoic acid
(D) protein
|
1 H |
liAit He | |||||||||||||||||
|
a Li |
4 Be |
hw 5 B v-*n |
C c lJrtl |
<troi 7 N Uisr |
na 1 0 |
kuW F lP'K* |
nw 10 Ne *T iftl | |||||||||||
|
11 Na |
raMwtln 12 |
tnnihin 13 Al Xl5*J |
bjt 34 Si |
Ktatmu 1$ P Jri-Vi |
lillr 16 S vr-tt |
(Mthr 17 Cl 19(43 |
ia Ar Ylf-4* | |||||||||||
|
frCUIIB Tft K |
ntwn io Ca |
VUMW 31 Sc jir* |
22 Ti 4/tU |
23 V MW |
24 Cr MW |
nipwn 25 Mn MW |
Kn 26 Fe |
27 Co 'AOTl |
Him 2a Ni |
nnw 2B Cu |
m 10 Zn a >j |
fan 31 Ga |
frfTTMn 32 Ge ft i |
wnt 33 As f*.M. |
KMfl 34 Se w* |
imw'* 35 Br |
rrrtn 36 Kr rjh} | |
|
nu&n 37 Rb |
aa Sr 44 |
vTfUl 39 Y |
jnnifcn Zr a* 7H |
vtul 41 Nb |
r>pfWT 4* Mo ti* |
43 Tc n* |
AfnVi U Ru <r*l w |
MB,!) 45 Rh |
ritnim* 46 Pd lOSO |
*iiTf 47 9 |
OPlhJU 41 Cd JiJ.ii |
mn 49 In 1UM |
- in M Sn urn |
51 Sb Wl/fl. |
hMtn M Te \tra> |
WjUKT 53 1 13* f. |
54 Xe 1114 | |
|
Citiun 55 Cs _1W till Fr -T?J* |
56 Ba |
57-70 * |
Uflfl 71 Lu 1 UJ |
linn 72 Hf |
73 Ta |
tr*n 74 W 'HIM |
75 Re it?y |
nnUi 16 0 s * |
iuiai 77 Ir 19? |
KAu* TB Pt 1M** |
n n Au |
B0 t!0 |
l(kn 61 TI |
ku J ez Pb 2 |
I1W 03 Bi /!* |
U Po |
05 At mu |
B6 Rn &7JI |
|
BB Ra iri |
BM02 * * |
LMHron 103 Lr nfti |
riwtaii* 104 Rf ctm |
105 Db PNI |
1M 9 |
KOIfl 107 Bh |Jwi |
town 1DB Hs |
U4WID 109 Mt im |
110 Uun B/'l |
111 Uuu P'fl .. |
imwn 112 Uub rm |
114" m | ||||||
34
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
