Anna University Coimbatore 2010 B.E Computer Science and Engineering Two ks with Answers for Numerical Methods(unit-1) - Question Paper
TWO MARKS QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
UNIT-1
1.
State the iterative formula for Regula
falsi method to solve![]() .
.
Solution: The iteration formula to find a root of the equation ![]() which lies between
which lies between ![]() is
is ![]() .
.
2. Give an example of a) algebraic b) transcendental equation.
Solution:
a)
Algebraic equation: The equation ![]() is called Algebraic if
is called Algebraic if ![]() is a polynomial.
is a polynomial.
Example: (1) ![]()
(2) ![]()
b)
Transcendental equation: The
equation ![]() is called Transcendental if
is called Transcendental if ![]() contains logarithmic,
exponential and trigonometric functions.
contains logarithmic,
exponential and trigonometric functions.
Example: (1) ![]()
(2) ![]()
3. Mention the methods to solve the equation which is either, algebraic or transcendental.
Solution:
a) Bisection method
a) Regula Falsi method
b) Iteration method
c) Newton Raphson method.
4. What are the two types of errors involving in the numerical computation?
Solution:
(1) Round off Error
(2) Truncation Error
5. Define Round off Error.
Solution: While dealing with decimal numbers, it is very inconvenient to work with all
decimal places. So we take approximates to facilitate calculation work. These
approximations lead to error in the final result, known as Round off error.
6. Define Truncation Error.
Solution: The error caused by using approximate formula in computations is known as
Truncation Error.
Example: ![]() . If we are
writing
. If we are
writing ![]() (approximately).
(approximately).
We get Truncation Error.
7. What is the criterion for the convergence in Newton Raphson method?
Solution: The sequence ![]() converges
to the exact value if
converges
to the exact value if ![]() .
.
i.e., if ![]() .
.
8. Write the iterative formula of Newton Raphson method.
Solution: The iterative formula of Newton Raphson method is 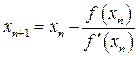 .
.
9.
Show that the iterative formula
for finding the reciprocal of N is ![]() .
.
Solution: Let ![]() i.e.,
i.e., ![]() .
.
Let ![]()
W.K.T., 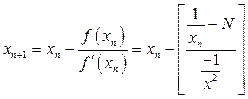
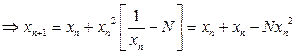
![]() .
.
10.
Derive Newtons algorithm for
finding the ![]() root of a number N.
root of a number N.
Solution: If ![]() then
then ![]() is the equation to be solved.
is the equation to be solved.
Let ![]() .
.
By Newton Raphson method, if ![]() iterate
then
iterate
then
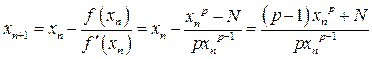
11.
What is the condition for applying
the fixed point iteration method(successive approximation method) to find the
real root of the equation![]() ?
?
(OR) If ![]() is continuous in
is continuous in ![]() , then under what condition
the iterative method
, then under what condition
the iterative method ![]() has
has
a unique solution
in ![]() ?
?
Solution: Let ![]() be a root of
be a root of ![]() . Let I be an interval
combining the point
. Let I be an interval
combining the point ![]() . If
. If
![]() for
all x in I, the sequence of approximation
for
all x in I, the sequence of approximation ![]() will
converge
will
converge
to the root r , provided that the initial approximation ![]() is chosen in I.
is chosen in I.
12. What is the order of convergence for fixed point iteration?
Solution: The convergence is Linear and the convergence is of order one.
13. In what form is the coefficient matrix transformed into when AX=B is solved by Gauss-Elimination method.
Solution: Upper Triangular Matrix.
14. In what form is the coefficient matrix transformed into when AX=B is solved by Gauss-Jordan method.
Solution: Diagonal Matrix.
15. State the principle used in Gauss-Jordan method.
Solution: Coefficient matrix is transformed into Diagonal matrix.
16. When Gauss Elimination method fails?
Solution: This method fails if the element in the top of the first column is zero. We can
rectify this by interchanging the rows of the matrix.
17. Write a sufficient condition for Gauss-Seidel method to converge.
Solution: The process of iteration by Gauss-Seidel method will converge if in each
equation of the system, the absolute value of the largest coefficient is greater than
the sum of the absolute values of the remaining elements in that row.
[ i.e., The Coefficient of matrix should be Diagonally dominant].
18. Give two indirect methods to solve a system of linear equations.
Solution: (1) Gauss-Jacobi method
(2) Gauss-Seidal method.
19. Give two direct methods to solve a system of linear equations.
Solution: (1) Gauss-Elimination method
(2) Gauss-Jordan method.
20. Why Gauss-Seidal method is a better method than Jacobis iterative method?
Solution: Since the current value of the unknowns at each stage of iteration are used in
proceeding to the next stage of iteration, the convergence in Gauss-Seidal method
will be more rapid than in Gauss-Jacobi method.
21.
Solve by Gauss-Seidal method ![]() correct to four decimal
places.
correct to four decimal
places.
Answer: ![]()
22. What do you mean by Diagonally dominant?
Solution: A matrix is diagonally dominant if the absolute value of the leading diagonal
element in each row is greater than or equal to the sum of the absolute values of
the remaining elements in that row.
23.
Find the inverse of the
coefficient matrix by Gauss-Jordan elimination method ![]()
Answer: ![]()
24. What type of eigen value can be obtained using power method?
Solution: The dominant eigen value can be obtained by power method.
25.
Find the dominant eigen value of ![]() by power method.
by power method.
Answer: The dominant eigen value ![]() and
the corresponding eigen vector
and
the corresponding eigen vector ![]()
26.
Determine the largest eigen value
and the corresponding eigen vector of the matrix ![]() correct
to two decimal places using power method.
correct
to two decimal places using power method.
Answer: The largest eigen value = 2 and the corresponding eigen vector ![]()
27. How to reduce the number of iterations while finding the root of an equation by Regula falsi method?
Solution: The number of iterations to get a good approximation to the real root can be
reduced, if we start with a smaller interval for the root.
28. What are the merits of Newtons method of iteration?
Solution: Newtons method is successfully used to improve the result obtained by other
methods. It is applicable to the solution of equations involving algebraical
functions as well as transcendental functions.
29. Define order of convergence.
Solution: Let ![]() be the successive
approximations of the root
be the successive
approximations of the root ![]() of
of ![]() .
.
Let ![]() be the error in the root
be the error in the root ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
If ![]() is the exact root,
is the exact root, ![]() .
.
If ![]() can be found out such that
can be found out such that ![]() where k is a
positive constant for
where k is a
positive constant for
every i, then p is called the order of convergence.
Note: If P = 1, the convergence is linear.
If P = 2, the convergence is quadratic.
30. Is the iteration method, a self correcting method always?
Solution: In general, iteration is a self correcting method, since the round off error is
smaller.
31. Explain power method of finding the eigenvalues of a matrix.
Solution: The power method is an iterative technique. The method may not converge very
fast. We can accelerate the convergence as well as get eigenvalues of magnitude
intermediate between the largest and smallest by shifting. The power method with
its variations is fine for small matrices. However, if a matrix has two eigenvalues
of equal magnitude, the method fails in the successive normalization factors
alternate between two numbers. The duplicated eigenvalues in this case is the
square root of the product of the alternating normalization factors. If we want all
the eigenvalues for a larger matrix, there is a better way.
32. Write the types of Pivoting.
Solution: There are two types of Pivoting
(1) Partial Pivoting,
(2) Complete Pivoting.
*******************************************************
| Earning: Approval pending. |
