The Institute of Cost and Works Accountants of India 2008 Certification CWA/ICWA Management Accounting-Enterprise Performance Management - Test 2 - Question Paper
PAPER - 15
MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING-ENTERPRISE PERFORMANCE
MANAGEMENT
TEST PAPER - IV/15/EPM/2008/T-2
Section A Multiple Choice Questions (All questions carry equal marks. Total Marks for this Section - 50)
Answer ALL the 20 questions in this Section
1. Balanced Scorecard is a methodology dealing with Choice :
A) Strategy management and performance measures
B) Strategy deployment and performance measures
C) Strategy deployment and performance management
D) Strategy management and performance management
2. Given:
Cost of risk free debt = 8.5%
Market premium = 6%
Beta = 0.8
what is the cost of equity?
Choice
A) 12.8%
B) 15.3%
C) 11.6%
D) 13.3%
3. Which one of the following is not included as a criterion for determining a reportable segment given by the 10% threshold limit?
Choice
A) Net worth
B) Sales
C) Assets
D) Net income
4. Which one of the following is not a basic element in a control system? Choice
A) A comparator/assessor
B) An effector or action taking subsystem
C) The causative factor of deviation
D) A control object or variable to be controlled
5. The following table captures some of the distinctions between strategic planning and management control. The only catch is the pairs are not matched properly.
|
(a) Strategic planning |
(b) Management control | |
|
1 |
On one aspect at a time |
Lead to desired results |
|
2 |
Unstructured and irregular: each problem different |
Integrated; more internal and historical; more accurate |
|
3 |
Tailor-made for the problem; more external and predictive; less accurate |
Rhythmic: prescribed procedures |
|
4 |
Show expected results |
Emphasis on both planning and control |
|
5 |
Planning dominant, but some control |
On whole organization |
When rearranged how would this table look like?
Choice
A) 1a 5b, 2a 1b, 3a 2b, 4a 3b, 5a 4b
B) 1a 5b, 2a 3b, 3a 2b, 4a 1b, 5a 4b
C) 1a 4b, 2a 3b, 3a 2b, 4a 1b, 5a 5b
D) 1a 2b, 2a 3b, 3a 5b, 4a 4b, 5a 1b
6. Which of the following is NOT a basic problem in design of organization structure
Choice
A) Ensuring coordination
B) Recognizing behavioral issues
C) Ensuring functional excellence
D) Ensuring synergy between operational units
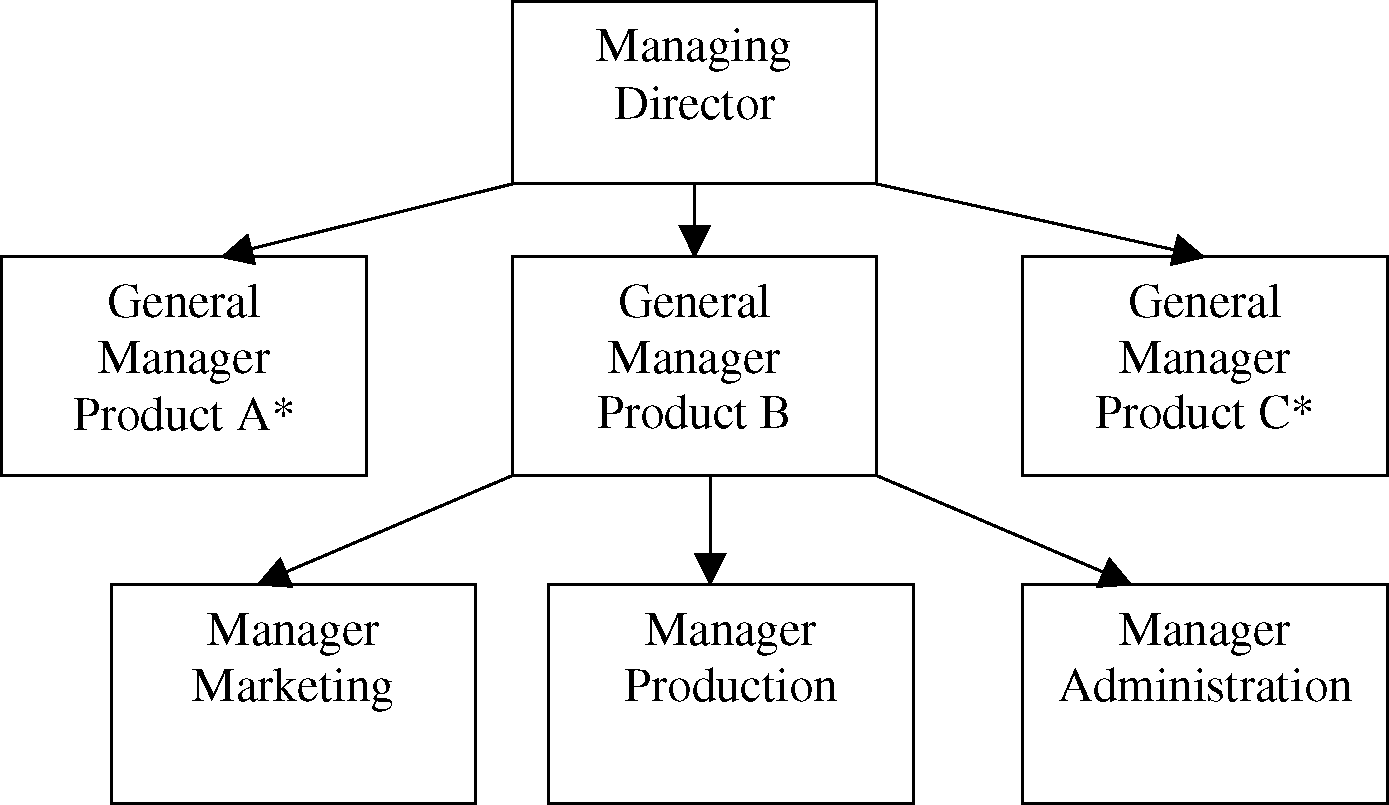
* Similar set up for A and C
Choice
A) Matrix
B) Functional
C) Divisional
D) Hybrid
8. Which two of the following do not belong to the Lean Accounting tool set?
a. Value stream mapping
b. Six sigma
c. SOFP
d. Cost driver analysis
e. Visual performance boards
f. Transaction elimination matrix
Choice
A) b, d
B) b, c
C) c, d
D) a, f
9. Here is a list of attributes a company seeks to attain. Classify them into Order Winners and Order Qualifiers by marking them as W or Q respectively.
a) On time Delivery
b) Lower cost of operation
c) Zero defects
d) Process innovation
e) Complete product range
If your classification is correct, which of the following would it match with?
Choice
A) WWWQQ
B) WWWQW
C) WQQWW
D) WQWQW
10. Which among the following does not fit in the design of major parent categories that represent virtually all the content on a corporate intranet
a) News
b) About Us
c) Products & Services
d) Forms & Tools
e) Resources
f) HR
Choice
A) e
B) d
C) b
D) a
11. Which of the following statements is not true?
Choice
A) Technology and transferability of the process to other products is intertwined with long-term capacity planning
B) Capacity planning is relevant in both the long term and the short term since the same issues are at stake for both.
C) Alternatives for making short-term changes in capacity can include the decision to not meet demand at all
D) Capacity requirements planning is only applicable in firms using MRP or MRP II.
12. An application of functional process benchmarking that compares a particular business function at two or more organisations, selected without regard to their industry.
The above definition applies to which of the following Choice
A) Strategic benchmarking
B) Functional benchmarking
C) Generic benchmarking
D) Process benchmarking
13. Which among the below is not one of the four basic phases that constitute the QFD methodology
Choice
A) Process Planning
B) Part Deployment
C) Product Development
D) Product Planning
14. Which one of the following does not belong to the five general types of risks companies face?
Choice
A) Technological risks
B) Market risks
C) Operational risks
D) Legal risks
15. Given:
Sales Rs 100000 V. Cost 40000 F Cost 25000
Which of the following changes will affect the profit most
A 10% change in
Choice
A) Fixed Cost
B) Selling Price
C) Unit Variable Cost
D) Sales volume
16. The probability of an expected profit of Rs 2000 is 0.34, The probability of an expected profit of Rs 1850 is 0.15 The probability of an expected profit of Rs 1000 is 0.30 The probability of on expected loss of Rs 3000 is 0.21
What is the probability of a profit of Rs 1000 or less?
Choice
A) 0.30
B) O.49
C) 0.51
D) 0.21
17. For a project the following data is given:
|
Best revenue estimate |
Rs |
3000 crores |
|
Likely revenue estimate |
Rs |
1800 crores |
|
Worst revenue estimate |
Rs |
1500 crores |
|
Expected Revenue |
Rs |
2500 crores |
|
Standard Deviation |
Rs |
600 |
What is the coefficient of variation?
Choice
A) 600 / 3000
B) 600 / 3100
C) 600 / 2150
D) 600 / 2500
18. Which of the following statements is not an attribute of Decision Trees?
Choice
A) Clearly lay out the problem in a graphic visual manner ,so that all options can be challenged
B) The decision tree can become more complicated by the inclusion of more and more alternatives.
C) The decision tree can become less complicated by the inclusion of alternatives that are interdependent
D) Provide a framework to quantify the values of outcomes and the probabilities of achieving them
19. Which one of the following does not belong to the quality trilogy of Joseph Juran? Choice
A) Quality Function Deployment
B) Quality Improvement
C) Quality Control
D) Quality Planning
20. Which of the following statements is not one of the Four Absolutes of Quality Management as per Phil Crosby
Choice
A) Quality prevention is preferable to quality inspection
B) Zero defects is the quality performance standard
C) Quality is measured in monetary terms - the price of non-conformance
D) Quality is exceeding customer expectations
Section B Short Answer Questions (Each question in this section carries 6 marks. Total Marks for this Section - 30) Answer ALL the 5 questions in this Section
1. Briefly outline the behavioral issues encountered while introducing the budget process as a part deploying management control system in an organisation.
2. Describe briefly the Learning and Growth Perspective and recommend suitable performance measures
3. A company has six industry segments with operating profits and loses as follows: Industry Segment Operating profit (Loss) (Rs in lakhs)
4. (3)
5. (2)
6. (20)
Which are the reportable segments for the company?
4. What are the three key performance measurements to evaluate in Goldratts Theory of Constraints? Briefly explain how they are to be used.
5. A software company has just won a contract worth Rs.80,000 if it delivers a successful product on time, but only Rs.40,000 if it is late. It faces the problem now of whether to produce the work in-house or to sub-contract it. To subcontract the work would cost Rs.50,000, but the local sub-contractor is so fast and reliable as to make it certain that successful software is produced on time.
If the work is produced in-house the cost would be only Rs.20,000 but, based on past experience, would have only a 90% chance of being successful. In the event of the software not being successful, there would be insufficient time to rewrite the whole package internally, but there would still be the options of either a late rejection of the contract (at a further cost of Rs.10,000) or of late subcontracting the work on the same terms as before. With this late start the local sub-contractor is estimated to have only a 50/50 chance of producing the work on time or of producing it late. In this case the sub-contractor still has to be paid Rs.50,000, regardless of whether he meets the deadline or not.
Draw a decision tree for the software company, using squares for decision points and circles for outcome (chance) points, including all relevant data on the diagram
Section C Long Answer Questions (Total Marks for this Section - 20) Answer ONE question from this Section
1. A company manufactures three products - X,Y and Z, whose direct costs are given below:
|
X |
Y |
Z | |
|
C |
Rs. |
Rs. |
Rs. |
|
Direct material |
67.92 |
63.27 |
56.79 |
|
Direct labour @ Rs. 3/hour): |
30.00 |
40.00 |
50.00 |
13.08 14.73 17.01
24.00 27.00 31.20
Machining
Assembly
105.00 105.00 105.00
The data below was used in calculating the direct labour costs above, and will be used to determine the production overhead charged to each product under the traditional costing method.
X
Y
Z
Total
|
Machine time(hours) Direct labour (hours): Machining Assembly Production(units) Total Machine hours Total Labour hours Machining Assembly |
11.00 4.36 8.00 50,000 500.000 218.000 200,000 |
9.00 8.00 5.67 10.40 16,250 130.000 92,137 169.000 4.91 9.00 30,000 270.000 900.000 457,437 839.000 147,300 270.000 |
Information on the companys overheads is as follows
Production overhead Rs.
Rs.
000
000
Indirect labour
Machinery 900
Assembly 600
Purchasing/order processing 600
Factory management 100
2200
500
Power
Machining 400
Assembly 100
Indirect materials
Machining 200
Assembly 200
Purchasing 100
Factory management 100
Depreciation
Machining 600
Assembly 300
Purchasing 200
Building 400
Security 1500
Grounds maintenance 100
Total production overhead 100
5000
At present the company uses the traditional method to compute the product cost.
The machining department uses a machine hour absorption rate and the assembly department a labor hour rate.
Now the company wants to switch over to Activity Based Costing method.
The information and data in the following tables may be used to determine cost drivers and calculate overheads.
|
Product X High Volume Large batches Few purchase orders placed Few customer orders placed Few customer orders placed |
Product Y Medium volume Medium batches Medium purchase orders placed Medium components Medium customer orders placed |
Product Z Low volume Small batches Many purchase orders placed Many components Many customers orders placed |
|
Product X Product Y Product Z Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Prepare an ABC analysis and calculate product costs. |
2. Jiraram has developed a new pocket calculator to compete in the rapidly expanding home market. As a management accountant, you are consulted as to the viability of marketing this calculator.
Jiraram makes the following estimates after a great deal of research :
Sales level (units)
3.60.000
4.50.000
5.40.000
Profit (Rs.) (9,00,000) 45,00,000 99,00,0000
The selling price will be Rs. 150.
a) Calculate the expected profit if the probabilities of sales for the above sales levels are :
Sales level (units) Probability
3.60.000 0.2
4.50.000 0.5
5.40.000 0.3 :
b) Calculate the margin of safety based on (a) above.
c) Jiraram's pocket calculators are of two sizes, each of which varies from the other in respect of price and variable cost. The above estimates of Jiraram are the averages of the two sizes. After a discussion with you, Jiraram wants to know more of margin of safety and how to improve the margin of safety for his calculators.
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
