Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada 2009 B.Tech Computer Science and Engineering Probability and statistics - Question Paper
Code No: V0121
SET -1
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations -Dec, 2009
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS
(Common to CE, ME, CHEM, AME)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Code No: V0121
SET -1
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
|
7. a) Two independent sample of sizes 7 and 6 had the following values | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
|
Examine whether the sample have been drawn from normal populations having the same variance. |
|
b) 4 methods are under development for making discs of a super conducting material. Fifty discs made by each method and they are checked for super conductivity when cooled with liquid_ | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Test the significant difference between the proportions of super conductors at 0.05 level. |
8. a) Explain pure birth and pure death processes?
b) A self service canteen employs one cashier at its counter. Eight customers arrive for every ten minutes on an average. The cashier can serve an average one per minute. Assuming that the arrivals are poisson and the service time distribution is exponential; determine (i) the average number of customers in the system, (ii) the average queue length and (iii) the average time a customer spends in the system.
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations -Dec, 2009
(Common to CE, ME, CHEM, AME)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Code No: V0121
SET -1
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
6. a) A manufacturer claims that only 4% of his products are defective. A random sample of 500 were taken among which 100 were defective. Test the hypothesis at 0.05 level.
b)) In a random sample of 60 worker ,the average time taken by them to get to work is 33.8 minutes with a standard deviation of 6.1 minutes. Can we reject the null hypothesis = 32.6 minutes in favour of alternative null hypothesis > 32.6 at k = 0.025 level of significance?
7. a) A random sample of six steel beams has a mean compressive strength of 58,392 p.s.i (pounds per square inch ) with a standard deviation of 648 p.s.i. Use this information and the level significance k = 0.05 to test whether the true average compressive strength of the steel from which this sample came is 58,000 p.s.i Assume normality.
b) From the following data, find whether there is any significant liking in the habit of taking soft drinks among the categories of employees
|
Soft drinks |
Clerks |
Teachers |
Officers |
|
Pepsi |
10 |
25 |
65 |
|
Thums up |
15 |
30 |
65 |
|
Fanta |
50 |
60 |
30 |
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations -Dec, 2009
(Common to CE, ME, CHEM, AME)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Code No: V0121
SET -1
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
7. a) The heights of 10 males of a given locality are found to be 175, 168,155,170,152,170,175,160,160, and 165cms.Based on this, find the 95% confidence limits for the height of males that locality.
|
b) Twelve dice were thrown 4096 times and a throw of 6 was considered a success. The observed frequencies were as given below._ | ||||||||||||||||||
|
and over test whether the dice were unbiased.
8 a) A TV repair man finds that the time spent on his jobs has an exponential distribution with mean 30 minutes. He pairs sets in the order in which they arrive. The arrival of the sets is approximately poisson with an average of 10 per an eight hour day. Find the repairmans idle time each day. How many jobs are ahead of the average set just brought in?
b) Explain pure birth and pure death process?
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations -Dec, 2009
PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS
(Common to CE, ME, CHEM, AME)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
6. a) A random sample of size 100 is taken from a population with a = 5.1. Given that the sample mean is x = 21.6, construct a 95% confidence interval for the population mean . b) A random sample size 100 has a standard deviation of 5. What can you say about the maximum error with 95% confidence?
|
7. a) The nicotine contents in milligrams in 2 samples of tobacco were found to be as follows | ||||||||||||||
|
Can it be said that 2 sample came from same normal population.
b) A random sample from a companys very extensive files show that the orders for a certain kind of machinery were filled, respectively in 10, 12, 19, 14, 15, 18, 11, and 13, days. Use the level of significance K = 0.01 to test the claim that on the average such orders are filled in 10.5 days. Assume normality.
Arrival rate of telephone calls at a telephone booth are according to poisson distribution with an average time of 12 minutes between 2 consecutive call arrivals. The length of telephone calls is assumed to be exponentially distributed with mean 4 minutes.
8.
(i) Find the probability that a caller arriving at the booth will have to wait.
(ii) Find the average queue length that forms from time to time
(iii) Find the fraction of a day that the phone will be in use.
(iv) What is the probability that an arrival will have to wait for more than 15 min before the phone is free.
(v) The telephone company will install a second booth.
POWER SYSTEM-I (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) What are the factors to be considered for selection of the site for a thermal power station?
b) A steam power station has an overall efficiency of 20% and 0.6Kg of coal is burnt per kWh of electrical energy generated. Calculate the calorific value of fuel.
2. Draw the schematic diagram of a nuclear power station and discuss its operation.
3. a) Derive an expression for the voltage drop for a uniformly loaded distributor fed at one end.
b) How does A.C distribution differs from D.C distribution.
4. a) Describe briefly how will you solve a.c distribution problems.
b) A single phase distributor one km long has resistance and reactance per conductor of
0.1 ohm and 0.15 ohm respectively. At the far end, the voltage VB=200V and the current is 100 A at a p.f of 0.8lagging. At the mid-point M of the distributor, a current of 100 A is tapped at a p.f. of 0.6 lagging with reference to the voltage VM at the mid-point. Calculate
(i) Voltage at mid-point
(ii) Sending end voltage, VA
5. a) What is sub-station? Name the factors that should be taken care of while designing and erecting a substation.
b) State the advantages of out-door sub-stations over in-door sub-stations.
6. a) Discuss the disadvantages of a low power factor?
b) What are the various methods of voltage control in a power system?
7. a) What do you understand by the load curve? What informations are conveyed by a load curve?
b) A generating station has a connected load of 43MW and a maximum demand of 20MW. The unit generated being 615x106 per annum. Calculate (i) demand factor
(ii) load factor.
8. Write short notes on
a) Simple tariff
b) Flate rate tariff
c) Three part tariff
POWER SYSTEM-I (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. Briefly describe the main parts and the working of a steam power station with a neat sketch.
2. a) What are the methods of producing nuclear reaction? What is chain reaction? b) Explain the working of a gas turbine plant with a schematic diagram.
3. a) How are distribution systems classified?
b) Discuss the relative merits and demerits of underground and overhead systems.
4. a) What is the importance of load power factors in a.c. distribution systems.
b) A 500 m long single-phase A.C. distributor has a total impedance of (0.02+j0.04)ohm and is fed from one end at 240V. It is loaded as follows:
50A at unity power factor, 200m from feeding point ;
100A at 0.8 p.f. lagging , 300m from feeding point ;
50A at 0.06 p.f. lagging at the far end.
Calculate: (i) Total voltage drop and (ii) voltage at the far end.
5. a) Discuss the different types of gas insulated sub-stations.
b) What are the considerations for the selection of site for an out-door sub-station.
6. a) Explain the causes of low power factor of the supply system?
b) Discuss the importance of voltage control in the modern power system.
7. Define and explain importance of the following
a) Connected load
b) Maximum load
c) Demand factor
8. a) Describe the desirable characteristics of a tariff?
b) What is mean by power factor tariff? What are its types?
1 of 1
POWER SYSTEM-I (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) What are the functions of economizer and super heater in a thermal power plant? b) A thermal power stations ha the following data:
Max. demand =20,000KW, Load factor =40%
Boiler efficiency= 85%, Turbine efficiency=90%
Coal consumption= 0.9Kg/KWh , Cost of 1 ton of coal=Rs.300 Determine (i) thermal efficiency and (ii) coal bill per annum.
2. a) Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of Nuclear power station.
b) What are factors to be considered for the selection of site of a nuclear power station?
3. a) State the main types of distribution systems used and compare their applications. b) What are the requirements of a distribution system?
4. a) Draw the phasor diagram of a.c. distributor power factor with respect to receiving end. b) A single phase a.c. distributor AB 300 meters long is fed from end A and is loaded as under:
(i) 100A at 0.707 p.f. lagging 200 m from point A
(ii) 200A at 0.8 p.f. lagging 300 m from point A
The load resistance and reactance of the distributor is 0.2 ohm and 0.1 ohm per kilometer. Calculate the total voltage drop in the distributor. The load power factors refer to the voltage at the far end.
5. What are the different types of bus-bar arrangements used in sub-stations? Illustrate your answer with suitable diagram.
6. (a) Derive an expression for the most economized of power factor which may be attained by a consumer.
(b) Explain the purpose of Booster transformer? What are its limitations?
7. Explain briefly (i) Load duration curve
(ii) Load curve
(iii) Plant use factor.
8. Describe some of the important types of tariffs commonly used?
1 of 1
POWER SYSTEM-I (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) What are the advantages and disadvantages of a thermal power station?
b) How the coal is utilized in power generation? Describe how it is handled starting from delivery of coal to final combustion stage.
2. What are the basic components of nuclear reactor? Explain the function of each component.
3. a) Give the comparison between over head system and underground system. b) Write short notes on Ring main distributer.
4. a) What is the method of calculations in A.C. distribution?
b) A single phase distributor 2 kilometers long supplies a load of 120 A at 0.8 p.f. lagging at its far end and a load of 80 A at 0.9 p.f. lagging at its mid-point. Both power factors are referred to the voltage at the far end. The resistance and reactance per Km (go and return) are 0.05ohm and 0.1 ohm respectively. If the voltage at the far end is maintained at 230V, calculate the voltage at sending end.
5. a) Give the comparison of out-door sub-stations and in-door sub-stations. b) What ate advantages of Gas insulated sub-stations
6. a) Discuss the various methods for power factor improvement? b) Explain with a neat sketch on-load tap changing transformer.
7. Define the following
(i) Diversity factor
(ii) Utilization factor
(iii) Load factor.
8. a) What do you understand by tariff? Discuss the objectives of tariff.
b) What is mean by two-part tariff? What are the advantages and disadvantages of two-part tariff?
1 of 1
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
(Common to ECE, BME, E.CON.E, ECC, ICE)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) A symmetrical square - wave of peak-to-peak amplitude V and frequency f is applied to a high-pass RC circuit. Show that the percentage tilt is given by
~2 fRC
1 - e
x 200%
P
1 + e fRC
If the lilt is small, show that this reduces to the following form P
T
x 100%
2RC
b) A square wave whose peak-to-peak amplitude is 2V extends 1V with respect to ground. The duration of the positive section is 0.1 sec and that of the negative section 0.2sec. If this waveform is impressed upon an RC integrating circuit whose time constant is 0.2 sec. What are the steady-state maximum and minimum values of the output waveform. (8+8M)
2. a) Explain the working of a two-level diode clipper with the help of circuit diagram, waveforms and transfer characteristics.
b) Assume that the diodes are ideal. Make a plot of v0(t)against vi(t) for the range of vi(t) from 0 to 150V. Indicate all slopes and voltage levels. Indicate, for each region, which diodes are conducting. (8+8M)
3. a) Discuss the switching times of a transistor
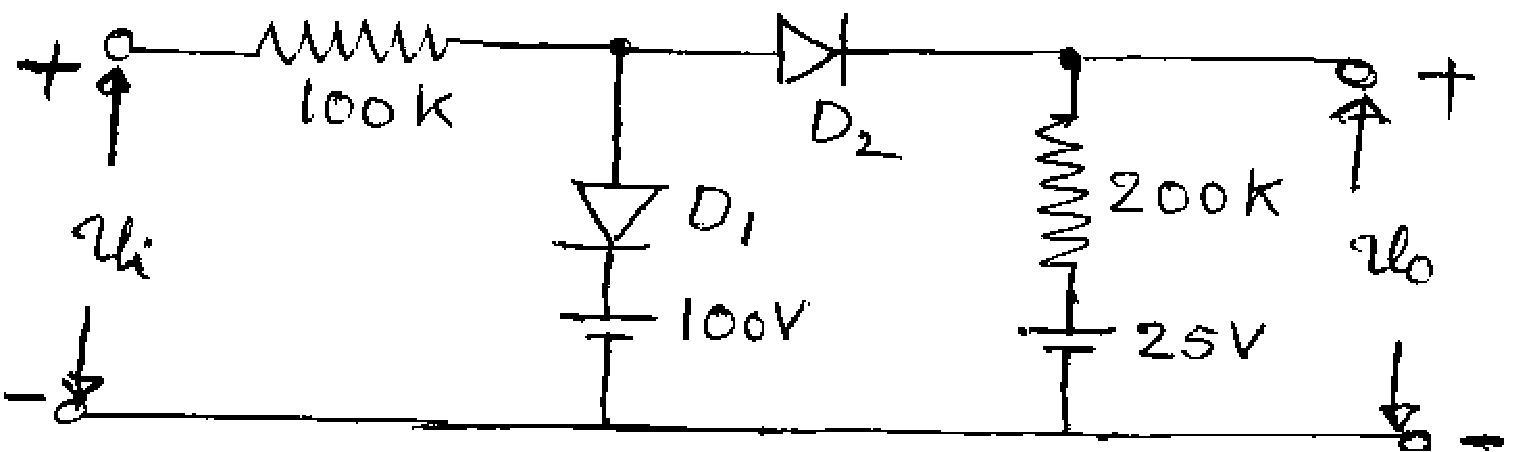
b) If silicon transistor in figure has a minimum value of hFE of 40, find the output levels for input levels of 0 and 15 V. Prove that it works as Inverter. (8+8M)
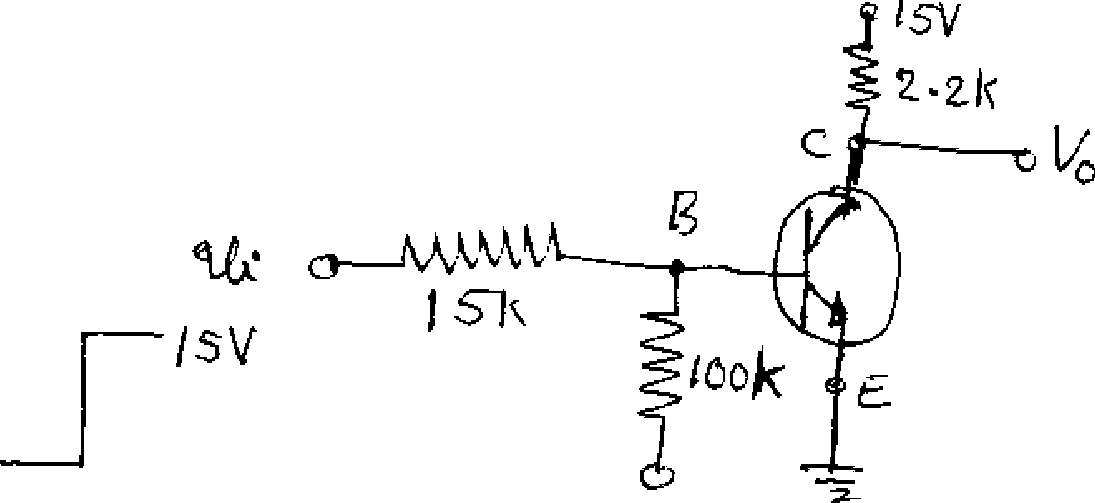
/S'V Figure: Inverter circuit
4. a) Draw the circuit diagram of collector-coupled monostable multivibrator and explain the operation with the help of base and collector waveforms.
b) The fixed-bias binary uses n-p-n silicon transistors with (hFE)mn =25. The circuit parameters are Vcc =10V, Vbb= 2V, Rc =1K , R1= 5K and R2 =10K ,VCE(sat)=
0.3V and VBE(sat)=0.7V. Verify that one transistor is in cut-off and the other in saturation and find the stable state currents and voltages. (8+8M)
5. a) What are the methods of generating a time base waveform? Explain each method.
b) Derive the expressions for sweep speed error, displacement error and transmission error of exponential sweep circuit. (8+8M)
6. a) With the help of a neat circuit diagram and waveforms, explain synchronization with frequency division of sweep circuit with pulse signals.
b) What is relaxation oscillator? Explain pulse synchronization of relaxation oscillator with necessary diagrams. (8+8M)
7. a) What is pedestal? Illustrate the effect of control voltage on gate output.
b) Draw the circuit diagram of the unidirectional diode gate with more two inputs and explain its operation. (8+8M)
8. a) Compare different logic families.
(8+8M)
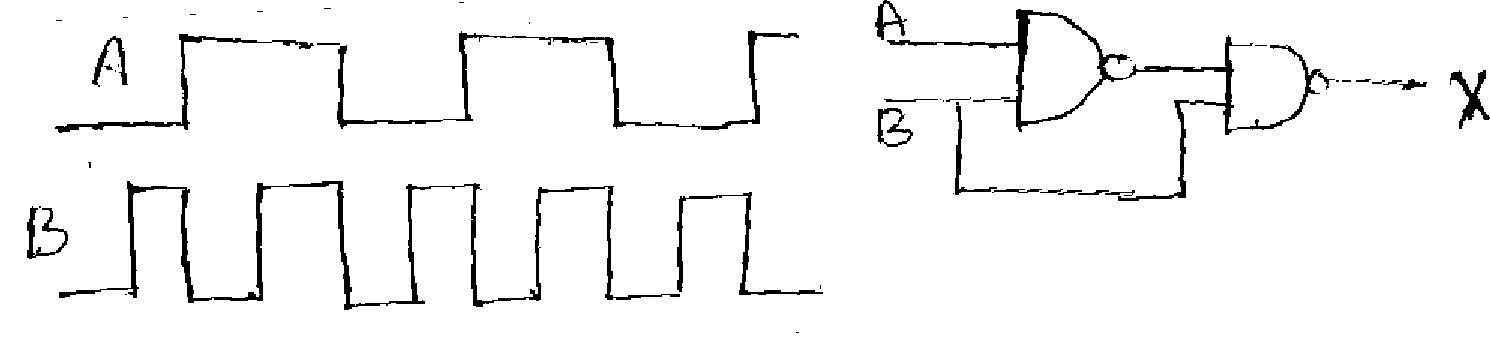
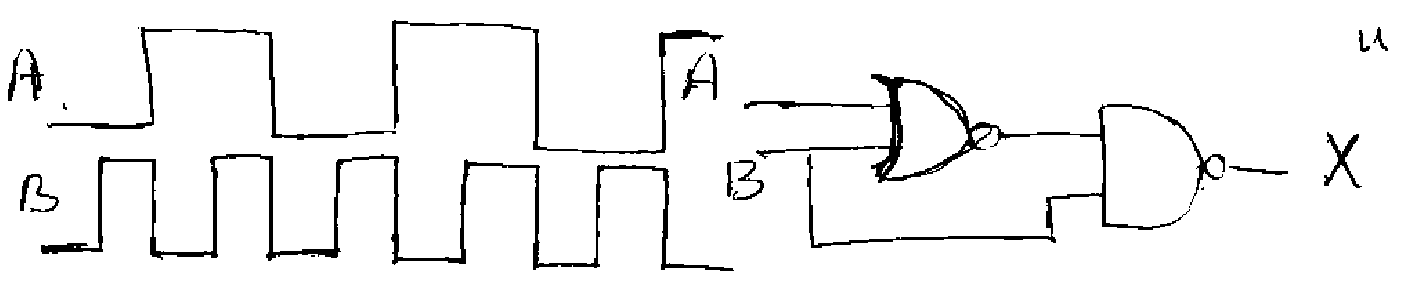
b) Draw the output of X for the given inputs
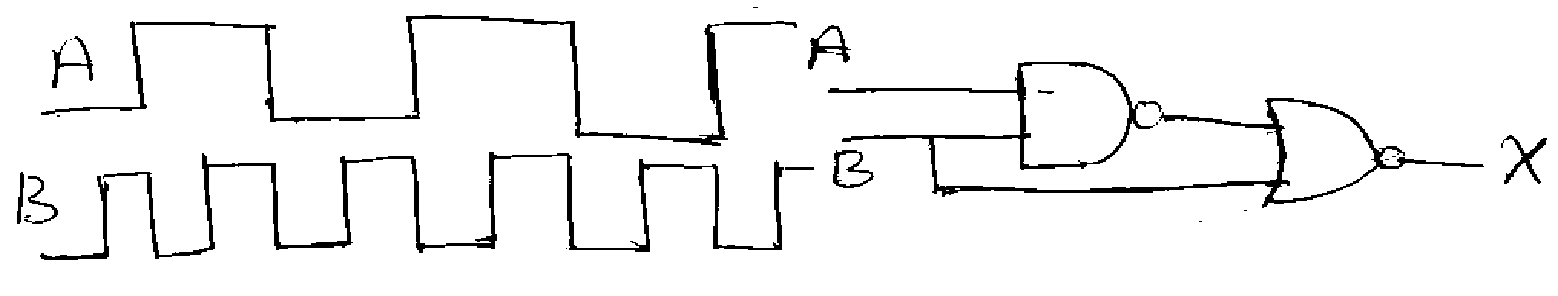
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
(Common to ECE, BME, E.CON.E, ECC, ICE)
Max Marks: 80
Time: 3 Hours
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Derive an expression for the output of a high-pass RC circuit excited by an exponential input.
b) A square wave whose peak-to-peak amplitude is 4V extends 2V with respect to ground. The duration of the positive section is 0.3sec and that of the negative section is 0.1sec. If this waveform is impressed on an RC differentiating circuit whose time constant is 0.3sec, find the steady-state maximum and minimum values of the output waveform. (8+8M)
2. a) Explain the working of a transistor clipper with the help of necessary diagrams.
b) For the diode clipping circuit of figure shown below assume that VR= 10V, Vi(t) = 20 sin wt, and that the diode forward resistance is Rf = 100 Q while Rr =10K Q and Vr = 0. Neglect all capacitances. Draw to scale the input and output waveforms and label the maximum and minimum values if (i) R=100 Q, (ii) R= 1K Q, and (iii) R=10K2. (8+8M)
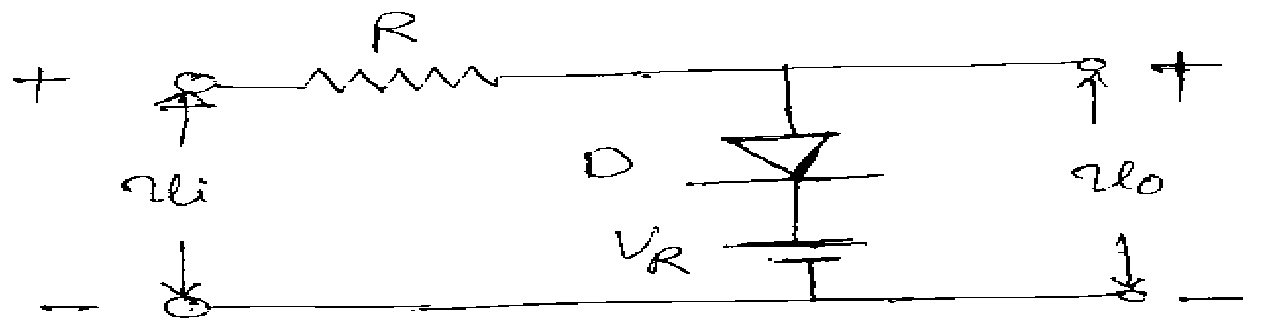
3. a) Discuss the switching times of a junction diode.
b) Design a transistor switch with the following data: VCC = 10V; VBB=6V; (hFE)min= 40, Icsat = 5mA ; the input is varying between 0 and 10 V. The transistor is silicon NPN type. Consider junction voltages. (8+8M)
4. a) Draw the circuit diagram of collector-coupled Astable multivibrator and explain its operation with the help of base and collector waveforms.
b) Design a collector-coupled bistable multivibrator with the following specifications. Vcc= 10V; Vbb= 6V, Icsat =5mA; neglect Icbo, the transistor is silicon NPN type. Assume junction voltages. Find R1, R2 and RC. (8+8M)
5. a) What is a linear time base generator?
b) Write the applications of time base generator
1 of 2
c) Define sweep speed error, displacement error and transmission error of voltage time base waveform. (5+5+6M)
6. a) What is synchronization? What is synchronization on a one-to-one basis? What is synchronization with frequency division? Give an example of synchronization with frequency division.
b) A free-running relaxation oscillator has a peak-to-peak signal amplitude of 100V and a period of 1200 sec synchronizing pulses are applied of such amplitude that the switch break down voltage is lowered by 50V at each pulse. The sync pulse frequency is 4kHz.What are the amplitude and frequency of the synchronized oscillator waveform? (8+8M)
7. a) What is a sampling gate?
b) Illustrate the principle of sampling gates with series and parallel switches and compare them.
c) Draw the sampling gate with four diodes and explain its operation. (4+4+8M)
8. a) What are different logic systems? Explain them.
b) Draw the output waveform X for the inputs A and B (8+8M)
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
(Common to ECE, BME, E.CON.E, ECC, ICE)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Derive an expression for the output of a high-pass circuit excited by a ramp input b) The limited ramp is applied to an RC high-pass circuit. Draw to scale the output waveform for the cases (i) T=RC, (ii) T=0.2RC and (iii) T = 5RC. (8+8M)
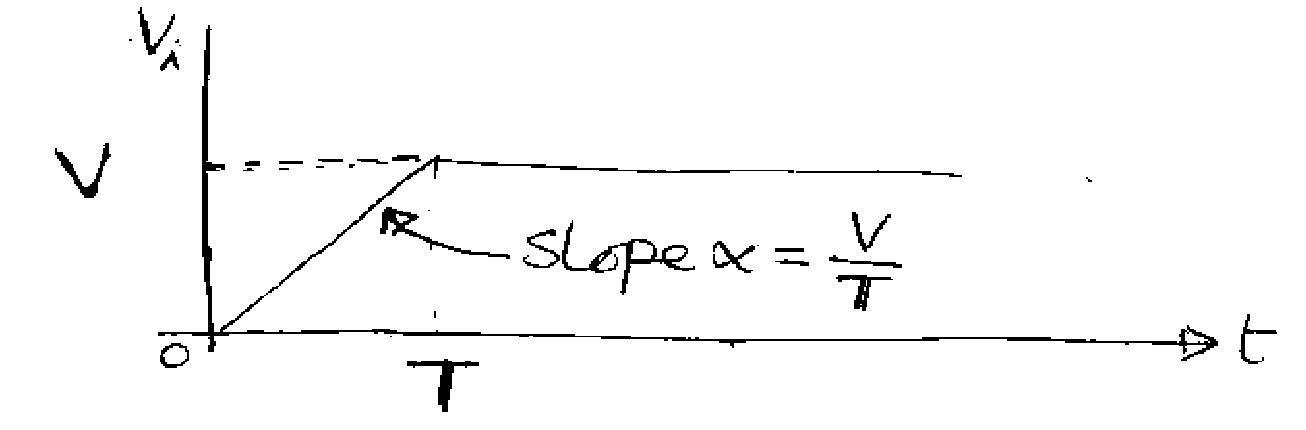
2. a) Describe the operation of a simple clamper with the help of necessary diagrams. b) In the d.c. restorer circuit, Rs= 5K , R= 15K , Rf = 100 , Rr=< ,Vr= 0 and C = 0.5|iF The input vs(t) = 0 for t < 0 and for t > 0 is a square-wave of frequency 5KHz and makes excursions between 0 and 10V. The capacitor is initially uncharged. Draw the output waveform for the first three cycles, labelling all voltage levels and time constants. (8+8M)
3. a) Discuss the switching characteristics of junction diode.
b) Design a transistor switch with the following data:
Vcc = 12V; Vbb=8V, (hFE)min=30, Icsat = 5mA . The input is varying between 0 and 12V. The transistor is silicon NPN type. Consider junction voltages. (8+8M)
4. a) Derive expressions for V1 (upper trigger potential) and V2 (lower trigger potential) of Schmitt trigger.
b) Design a collector-coupled monostable multivibrator using n-p-n silicon transistors. Neglect IcBO. Assume junction voltages.(hFE)min = 30, VBE = -1V for the transistor in cut-off .Vcc =Vbb= 10 V, Icsat = 8mA. The gate width T=2msec.Find Rc , R1 , R2 and R. (8+8M)
1 of 2
5. a) Draw the circuit diagram of UJT sweep circuit and explain its working with waveforms.
b) Explain the basic principle of miller and Bootsteap time base generators and derive the equations for sweep speed-error. (8+8M)
6. a) What is phase delay and phase filter?
b) Explain with the help of block diagram and waveforms for achieving division of relaxation devices without phase filter.
c) Write the factors which influence the stability of a relaxation divider. (4+6+6M)
7. a) Write the advantages and disadvantages of unidirectional diode gate.
b) How do you overcome the loading effect of signal sources on control voltages?
c) Draw the circuit diagram of a sampling gate with more than one control voltage and explain its working. (6+5+5M)
8. a) Draw the circuit diagram of diode-resistor logic AND gate and explain its operations
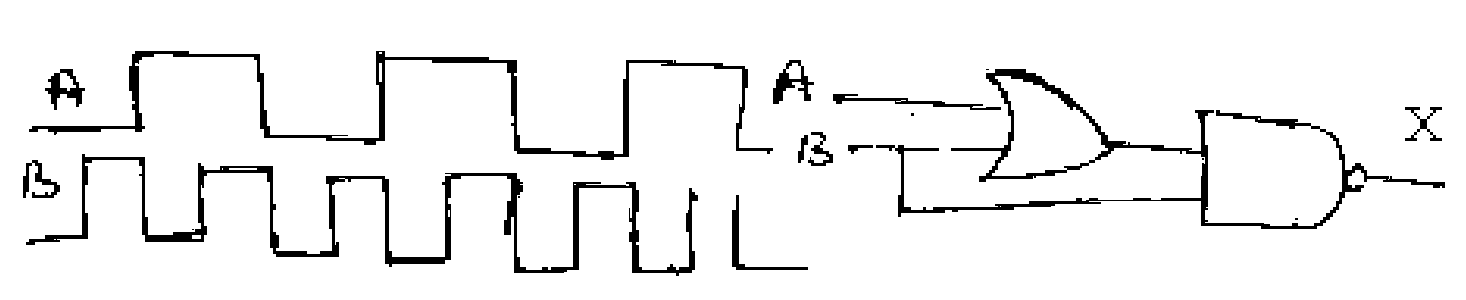
b) Draw the output waveform X for the given inputs (8+8M)
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
(Common to ECE, BME, E.CON.E, ECC, ICE)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
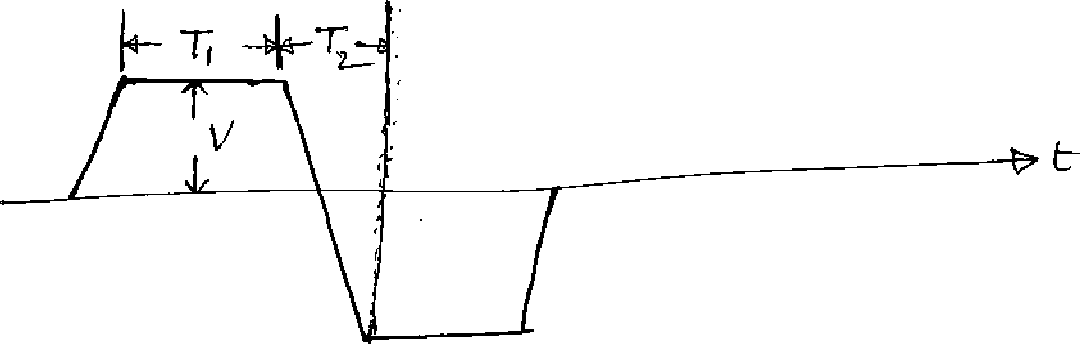
1. a) Derive an expression for the percentage tilt of the output of a high-pass circuit with large time constant excited by a symmetrical square wave with zero average value. b) The input to a high-pass RC circuit is periodic and trapezoidal as indicated. Assume that the time constant RC is large compared with either T1or T2. Find and sketch the steady the state output if RC =10 T1 = 10 T2. (8+8M)
2. a) State and prove clamping circuit theorem.
b) In the clamping circuit, Rs= 100 Q , Rf =50 Q , R=100K Q and C = 2F. A symmetrical square wave signal of amplitude 20V and frequency 5KHz is applied at t=0. Draw the first three cycles of the output waveform. (8+8M)
3. a) Discuss the switching characteristics of a transistor.
b) In a transistor Inverter circuit, the transistor is silicon NPN type. RC = 2.2k Q ,
R1 = 15k Q, R2 = 100kQ ,Vcc = Vbb=10V, (hFEmin) = 50. Consider junction voltages.
The input is varying between 0 and 10 V. Show that it works as Inverter. (8+8M)
4. a) Draw the circuit diagram of a non-saturated binary and explain its operation.
b) Compute the voltage levels for the base and collector waveforms of collector-coupled monostable multivibrator whose components and supply voltages are as follows:
Vcc = 12 V; Vbb= 3 V; VBEsat = 0.7 V and VCEsat= 0.3 V , Rc = 2K Q, R= 20K Q,
Ri= 20K Q, R2 = 20K Q, rbb! = 100 Q, Neglect IcBO. Silicon transistors are used with hFE min= 50. (6+10M)
5. a) Draw a simple current sweep circuit and explain its working with the help of diagrams. b) With the help of neat diagrams explain the working of transistor Bootsteap time base generator. (6+10M)
1 of 2
6. a) Explain with neat diagrams, the synchronization of a sweep circuit with symmetrical signals.
b) A UJT sweep operates with a valley voltage VV =12V, and a peak voltage Vp = 15 V. A sinusoidal synchronization voltage of 2V peak is applied between bases. The standoff ratio is n = 0.6. If the natural frequency of the sweep is 1000Hz, over what range of sync-signal frequency will the sweep remain in 1:1 synchronism with the sync signal?
(8+8M)
7. a) With the help of neat diagrams explain the working of bidirectional diode gate and derive the expression to control voltages and gain.
b) Draw the bidirectional gate using transistor and explain its working. (8+8M)
8. a) Draw the circuit diagram of diode-transistor logic NAND gate explain its operation.
b) Draw the output X for the given inputs (8+8M)
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (Common to CSE, IT)
Max Marks: 80
Time: 3 Hours
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Explain about different software myths? b) Write short notes on evolution of software.
2. Explain about linear sequential model with neat diagram.
3. a) What is meant by Requirements analysis? Explain? b) Explain about context model with examples.
4. Explain about different design concepts with examples.
5. a) Differentiate between white-box-testing & Black-box-testing. b) Explain about system Testing.
6. a) Explain about function - oriented Metrics. b) Write a short notes on software Risks.
7. Explain about object oriented design process.
8. Explain about the following
a) SQA activities.
b) Software reliability
c) SQA plan.
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations,Dec-2009
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (Common to CSE,IT)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Explain how Software Engineering practices are adopted to the industry? b) Explain about the Applications of Software.
2. Explain about the incremental process model with a neat diagram.
3. a) Explain about the Requirements Validation.
b) Explain about Behavioral model with examples.
4. Explain about different design concepts with examples.
5. Explain about Black-box-testing.
6. a) Give the outline for RMMM plan.
b) Explain about Risk identification.
7. Explain about User interface analysis & design.
8. Explain about the following
a) Cost of Quality.
b) ISO 9000 Quality Standards.
c) SQA plan.
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (Common to CSE,IT)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Explain about different Software Engineering myths. b) Explain about changing nature of Software.
2. a) Differentiate between functional & non-functional requirements of Software. b) Explain about Software requirement document.
3. a) What is meant by Requirements elicitation? Explain? b) Explain about different structured methods.
4. a) Do you design software when you write a program? What makes software design different from coding?
b) Explain about Architectural design process.
5. a) Who should perform the Validation test - the software developer or the Software User? Justify your answer?
b) What are the general characteristics for software testing?
c) Explain about Validation Testing.
6. a) Explain about Extended function point Metrics.
7. Explain about User interface analysis & design.
8. Explain about the following
a) Statistical Quality Assurance.
b) SQA plan.
c) Formal Technical Reviews.
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (Common to CSE, IT)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Explain about the evolving role of Software?
b) Explain how Software Engineering Practices are adopted to the industry?
2. Explain about the Incremental Process model with a neat diagram.
3. a) Explain about Feasibility study of requirements engineering process. b) Explain about Object models with examples.
4. a) Provide examples of three data abstractions & the procedural abstractions that can be used to manipulate them.
b) Explain about the set of principles for data specification.
5. a) Differentiate between Verification & Validation? Do both make use of test case design methods and testing strategies. b) Explain about White - box- testing.
6. a) Explain about size-oriented Metrics. b) Explain about Risk Projection.
7. Explain about Object oriented design process.
8. Explain about the following
a) Quality Concepts.
b) ISO 9000 Quality Standards.
c) Formal Technical Review.
1 of 1
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 CALIBRATION AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS (Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks k k k k k
1. Six determinations of a quantity as entered on the data sheet and presented for analysis are 12.35, 12.71, 12.48, 10.24, 12.63 and 12.58. Calculate
(a
(b
(c
(d
(e
(f
2. (a (b
the arithmetic mean the deviation from the mean the average deviations Standard deviation Variance
Probable error. [16]
Describe the international standard of mass, length and volume?
State the SI units, unit symbols and define each unit for the following
i. Electric current
ii. Charge
iii. Voltage
iv. Resistance. [8+8]
3. (a) Write short notes on the concept of traceability?
|
(b) _ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
For the 30 and 70 readings in the calibration chart shown above determine the instrument accuracy as a percentage of the reading and as a percentage of full scale? [8+8]
4. (a) Explain the successive approximation type DVM?
(b) Distinguish between series and shunt type ohmmeter from the dial calibration? How can you estimate the internal resistance of an ohmmeter from its dial?
[8+8]
5. (a) Explain how a Kelvins double bridge can accurately measure low resistances.
Also derive the condition for balance.
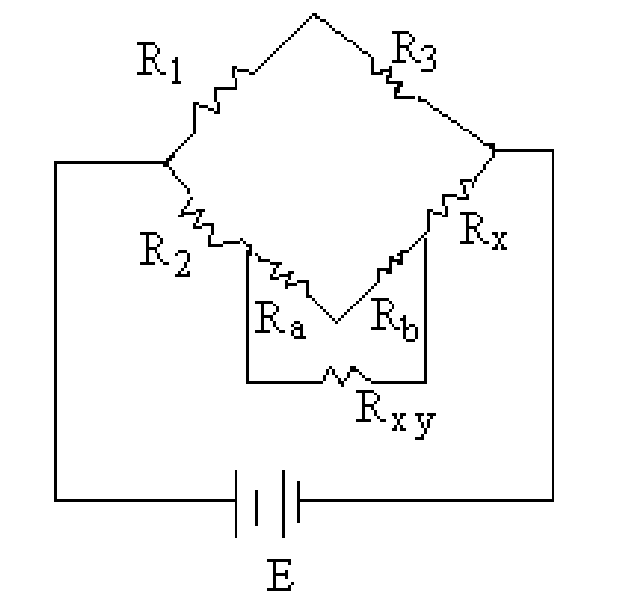
(b) In the Kelvins Bridge shown in figure 1 the ratio of Ra to Rb is 2000Q,R1 is 10Q and R1=0.2 R2. Calculate the value of Rx . [10+6]
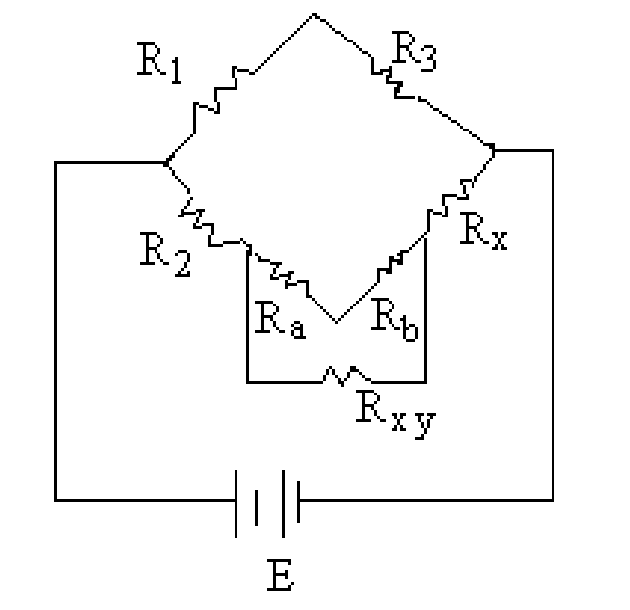 |
|
Figure 1: |
6. (a) With a suitable block diagram and waveforms explain the operation of a fre
quency counter.
(b) How many displays (total decades) should a frequency counter have if its accuracy and resolution are to be 0.001 percent? [3+3+4+6]
7. (a) Draw the simplified block diagram of the sampling oscilloscope and explain
with the waveforms .
(b) Write short notes on the synchronization of the sweep.
[3+5+2+6]
8. (a) With a schematic diagram explain the operation of pulse duration modula-tion(PDM) recording system.
(b) Draw the block diagram of a logic analyzer and explain its operation. [8+2+6]
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 CALIBRATION AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS (Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. Write short notes on any of the FOUR:
(a) Arithmetic mean
(b) Deviation from the mean
(c) Average deviation
(d) Standard deviation
(e) Variance. [16]
2. (a) What are the differences between International and absolute standards?
(b) Describe the international standard of length and volume?
(c) Define the seven base units of SI system [4+4+8]
3. (a) Explain the following terms:
i. Accuracy
ii. Bias
iii. Calibration
iv. Calibration interval.
|
(b) _ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
For the 20 and 60 readings in the calibration chart shown above determine the instrument accuracy as a percentage of the reading and as a percentage of full scale? [8+8]
5. (a) Explain how a simple AC bridge circuit operates and derive an expression for the unknown parameters.
(b) The ac bridge of figure 1 is in balance with the following constants arm AB, R=200Q; arm BC R=100Q in series with L=20 mH ; arm CD, unknown ; arm DA, R=50Q in series with C=0.1F. The oscillator frequency is 10 KHz.Find the constants of arm CD. [8+8]
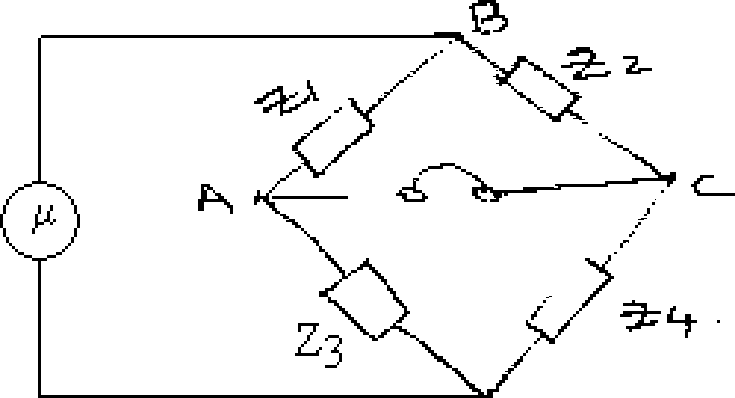 |
|
D Figure 1: |
6. (a) When is period measurement preferred over frequency measurement and obtain the condition ?
(b) With a suitable block diagram explain the operation of a pre scaled frequency
[4+4+8]
counter.
7. (a) Describe the electrostatic focusing system of a CRT.
(b) What is the minimum distance L, that will allow full deflection of 4 cm at the oscilloscope screen with a deflection factor of 100 V/cm and with an acceler-
[8+8]
ating potential of 2000 V ?
8. (a) Explain the operating principle of LCD display.
(b) Draw the block diagram of a logic analyzer and explain its operation.[4+4+3+5]
k k k k k
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 CALIBRATION AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS (Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) What are the different types of systematic errors present? Explain each of
them with an example?
(b) A voltmeter having a sensitivity of 1KQ/V is connected across an unknown resistance in series with a milli ammeter reading 80V on 150V scale. When the milli ammeter reads 10mA, calculate the
i. Apparent resistance of the unknown resistance
ii. Actual resistance of the unknown resistance
iii. Error due to the loading effect of the voltmeter. [8+8]
2. (a) Distinguish between secondary standards and working standards
(b) What are the international standards of mass and volume?
(c) Write short notes on the seven base units of SI system. [4+4+8]
3. (a) Explain the following terms
i. Measurement and test equipment
ii. Traceability
iii. Reliability
iv. Tolerance limits
(b) Explain the procedure that should be followed before attempting to calibrate deflecting instruments? [8+8]
4. (a) Describe the working principle of integrating type DVM?
(b) Write short notes on shunt type ohmmeter? [8+8]
5. (a) Explain how a Kelvins double bridge can accurately measure low resistances.
Also derive the condition for balance.
(b) In the Kelvins Bridge shown in figure 1 the ratio of Ra to Rb is 2000Q,R1 is 10Q and R1=0.2 R2. Calculate the value of Rx . [10+6]
6. (a) Distinguish between time and phase measurements?
(b) Explain any two methods generally used to extend the frequency range of a frequency counter? [6+5+5]
7. (a) Draw the block diagram of vertical amplifier and explain its working.
(b) Briefly summarize the characteristics of commonly used Phosphors in Cathode ray oscilloscopes. [8+8]
 |
|
Figure 1: |
8. (a) With a neat sketch explain the operation of Magnetic recorder (b) Explain the operating principles of LCD display.
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 CALIBRATION AND ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS (Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Define the following terms:
i. Absolute error
ii. %Error
iii. Precision
iv. % of accuracy.
(b) What are the four sources of possible errors in instruments and explain each
of them briefly? [8+8]
2. (a) Explain the concept of capacitance standards?
(b) Define the seven base units of SI system? [8+8]
3. Write short notes on different types of calibrations used? [16]
4. (a) A dual slope integrating type A/D converter has an integrating capacitor of
0.01f and a resistance of 10 KQ. If the reference voltage is 2V and output of an integrating is not to exceed 10V what is the max time the reference voltage can be integrated?
(b) Explain the performance characteristics of DVMs? [8+8]
5. (a) Explain how a Kelvins double bridge can accurately measure low resistances.
Also derive the condition for balance.
(b) In the Kelvins Bridge shown in figure 1 the ratio of Ra to Rb is 2000Q,R1 is 10Q and R1=0.2 R2. Calculate the value of Rx . [10+6]
Rl
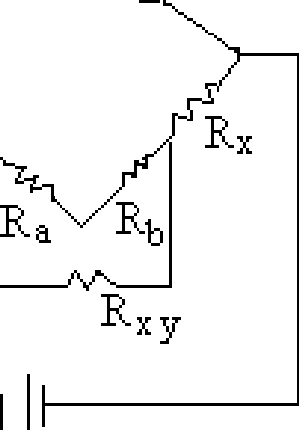 |
|
E Figure 1: |
6. (a) What is an electronic counter? How can it be used for the measurement of
the following.
i. Average time period mode
ii. Totalizing.
(b) What is trigger level errors and suggest the means to obtain the maximum accuracy. [2+6+2+2+2+2]
7. Describe the following:
(a) Sources of synchronization
(b) Blanking circuit
(c) Focus control [6+4+6]
8. (a) Explain the operation of logic timing analyzer and logic state analyzer.
(b) What are the merits and demerits of Magnetic recording? [5+5+6]
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 MATHEMATICS FOR AEROSPACE ENGINEERS (Aeronautical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Prove that y21fx+f2 = Po(x) + Pi(x) t + p2(x) t2+ ....
(b) Write J5/2(x) in finite form. [8+8]
2. (a) Derive Cauchy Riemann equations in polar coordinates.
(b) Prove that the function f(z) = z is not analytic at any point.
(c) Find the general and the principal values of (i) log e (1+\/3i) (ii) log e(-1).
[5+5+6]
3. (a) Expand as a Taylor series in f(z) = 2r+1 about z=1.
(b) Express f(z) = (z_ 1):z_3) in a series of positive and negative powers of (z-1).
[8+8]
4. (a) Find the poles and the residues at each pole of f (z) = where z=0 is a
pole of order 4
(b) Evaluate f z2+2-+5) dz where c is the circle using residue theorem.
c
i. I z | = 1
ii. | z+1-i | = 2. [6+10]
5. (a) Show that the image of the hyperbola x2-y2=1 under the transformation
w=1/z is r2= cos 20.
(b) Show that the transformation u = z+T changes the circle x2 + y2 -4x = 0 into the straight line 4u+3=0. [8+8]
6. (a) A covariant tensor has components 2xz, x2y, yz in cartesian coordinate system.
Find its components in cylindrical coordinates.
(b) Show that the any inner product of the tensors Ap and Eqs is a tensor of rank three. [8+8]
7. (a) Two cards are selected at random from 10 cards numbered 1 to 10. Find the
probability that the sum is even if
i. the two cards are drawn together
ii. the two cards are drawn one after the other with replacement.
(b) State and prove Bayes theorem.
(c) The probabilities of A,B,C to become M.DS of a factory are 10, 10, _2_ The probabilities that bonus scheme will be introduced if they become M.Ds are .02, .03 and .04. Find the probabilities A,B,C to be become M.Ds if bonus scheme introduced. [5+5+6]
6x + k if 0 < x < 3
8. (a) If X is a continuous random variable with distribution.
f (x) = 6
0 elsewhere
determine
i. the value of k
ii. the mean
iii. P(1 < x < 2).
(b) Derive the formula to find the mean and variance of Binomial distribution.
[8+8]
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 MATHEMATICS FOR AEROSPACE ENGINEERS (Aeronautical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks k k k k k
1. Evaluate using 0 T functions.
i
(a) / x2 (log X)3dx.
0
7t/2
(b) f sin7/2 Ocos3/2 OdO.
0
1
(c) Show that f (1 + x)m 1(1 x)n 1dx = 2m+n+10(m,m). [5+5+6]
-i
2. (a) State necessary condition for f ( z ) to be analytic and derive C-R equations in Cartesian coordinates.
(b) If u and v are functions of x and y satisfying Laplace's equations show that
dU andt = du + |y.
(s+it) is analytic where s = |U dtXandt = dt + . [8+8]
dy dx dx dy
3. (a) Evaluate f (z (-.SnfZi dz) with C: | z | =2 using Cauchys integral formula.
c 2
(i,i)
(b) Evaluate J (3x2 + 4xy + ix2) dz along y=x2.
(c) Evaluate/ ez(zwhere C: | z | = 2 Using Cauchys integral theorem. [5+5+6]
C
2n
4. (a) Evaluate by residue theorem/ t+osu
o ( cos
TO
(b) Use the method of contour integration to evaluate / (XX+dX)3. [8+8]
(x2 + a2)3 *
-TO
5. (a) Under the transformation w=1/z, find the image of the circle |z-2i|=2.
(b) Under the transformation w = fZ, find the image of the circle |z |=1 in the w-plane. [8+8]
6. If (ds)2 = (dr)2 + r2(dO)2 + r2sin2O(d$)2, find the values of
|
(a) [ 22, 1 ] and [ 13, 3 ] | ||||||
|
[8+8]
(b)
7. (a) If A and B are two events and P(A) = 3/5, P(B)=1/2 prove that
5
10 * V n 2 '
i. P(AUB) > 5
ii. 10 < P (A n B) < i.
(b) An integer is chosen at random from the first 200 positive integers. What is the probability that the integer chosen is divisible by 6 or 8.
(c) There are 3 boxes. Box-I contains 7 Red, 3 Black, and 4 White balls, box -II contains 9 Red, 2 Black, 4 White, box-III 10 Red, 5 Black, 5 white balls. One box is chosen and one ball is drawn from it. What is the probability that the ball is
i. Red
ii. Black
iii. White. [5+5+6]
8. (a) If a Poisson distribution is such that P(x=1). | = P(x=3).
Find
i. p(x >1)
ii. p(x < 3)
iii. p(2< x < 5).
(b) A sales tax officer has reported that the average sales of the 500 business that he has to deal with during a year is Rs.36,000 with a standard deviation of 10,000. Assuming that the sales in these business are normally distributed, find
i. the number of business as the sales of while are Rs.40,000
ii. the number of business the sales of while are likely to range between Rs. 30,000/- and Rs.40,000/-. [8+8]
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 MATHEMATICS FOR AEROSPACE ENGINEERS (Aeronautical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. Evaluate the following using 0 T functions.
a
b
[5+5+6]
c
Show that w = zn (n , a positive integer) is analytic and find its derivative.
If w = f(z) is an analytic function, then prove that the family of curves defined by u(x,y) = constant cuts orthogonally the family of curves v(x,y) = constant.
If a + i0 = tanh (x + i n/4) prove that a2 + /32 =1. [6+5+5]
Show that J (z +1) dz = 0 where C is the boundary of the square whose
C
vertices at the points z = 0, z = 1, z = 1+i, z = i.
If F(a)= f 3z +J-+)1)dz using Cauchys integral formula where C is |z| = 2 find
C
[8+8]
2.
3.
b
F(1) F(3) F"(1-i).
3
Find the poles and the corresponding residues of the function (z_1)(zz_2)(z_3).
Evaluate J (?ZZZ+-1)d where C is |z| = 1 by residue theorem. [8+8]
c )
Discuss the transformation w=cos z.
Find the bilinear transformation which maps the points (l, i, -l) into the points (o,1,ro). [8+8]
Prove that ApqBpcq is an invariant if Bp and Cq are contra variant tensors and Apq is covariant tensor.
If (ds)2 = (dr)2 + r2(dO)2 + (r2 sin2 O)(d$)2 then prove that
4.
5.
6.
a
b
= [22,1] = r
1
22
i. both have blue eyes
ii. at least one has blue eyes.
(b) Define conditional probability. Give an example. State the general multiplicative rule and special multiplication rule ( when the events are independent).
[8+8]
8. (a) For the continuous probability function f(x) = kx2e-x when x > 0, find i. k
ii. mean
iii. variance.
(b) Calculate mean and standard deviation of the following frequency distribution.
[8+8]
|
4.5 - 12.5 |
4 |
|
12.5 - 20.5 |
24 |
|
20.5 - 28.5 |
21 |
|
28.5 - 36.5 |
18 |
|
36.5 - 44.5 |
5 |
|
44.5 - 52.5 |
3 |
|
52.5 - 60.5 |
5 |
|
60.5 - 68.5 |
8 |
|
68.5 - 76.5 |
2 |
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2009 MATHEMATICS FOR AEROSPACE ENGINEERS (Aeronautical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
2
1. (a (b
2. (a (b
3. (a (b
4. (a (b
5. (a (b
6. (a (b
7. (a (b
Prove that r(2n)
Prove that 0(m,n) = /
[8+8]
dx.
Evaluate / (x2 + 2xy + i(y2 x)) dz along y=x2.
sin2 9 d9
Evaluate
a+ b cos 9
x2 dx
[8+8]
Evaluate
(x2 +1) (x2+4)
Prove that the transformation w=sinz maps the families of lines x=constant and y=constant in to two families of confocal conics.
Find the bilinear transformation which maps the points (i, -i, 1) of the z-plane into (0,1, to) of the w-plane. [8+8]
Define a tensor of first order. If aki...............are two tensors of the same
order then, prove that Cijkl.......=ajke.......+ bijkl is a tensor of same order.
Show that aj Akj=A$ik where A is a determinant of three and Aj are cofactors of aij. [8+8]
Define a random experiment, sample space, event and mutually exclusive events. Give examples of each.
Box A contains 5 red and 3 white marbles and box B contains 2 red and 6 white marbles.
Define analyticity of a complex function at a point P and in a domain D. Prove that the real and imaginary parts of an analytic function satisfy Cauchy Riemann Equations.
Show that the function defined by f (z) = x (1+J2)-y2(1-i) at z = 0 and f(0) = 0 is continuous and satisfies C-R equations at the origin but f'(0) does not exist.
[8+8]
Evaluate/ (sinnZ J+CZ8)) dz where C is the circle |z| = 3 using Cauchys integral
using residue theorem.
using residue theorem.
xm-1+xn-1
(1+x)m+n
formula.
[8+8]
Z=1 + i
OO
C
0
0
z=0 2n
i. If a marble is drawn from each box, what is the probability that they are
both of the same colour?
[8+8]
8. (a) A Poisson distribution has a double mode at x = 2 and x = 3, find the maximum probability and also find p(x>2).
(b) The weekly wages of 1000 workers are normally distributed around a mean of Rs.70 and S.D of Rs.5/- Estimate the number of workers whose weekly wages will be
i. between Rs.70 and Rs.72
[8+8]
ii. between 69 and 72.
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
MASS TRANSFER AND SEPARATION (Biotechnology)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) A student attempts to measure the diffusivity of A in air by using the Stefan tube. The boiling point of A is only several degrees higher than the experimental temperature. Do you think that the pseudo-steady state approximation is valid in this case? Give a qualitative explanation. (6M)
b) Calculate the rate of diffusion of hydrogen (A) through non-diffusing methane (B) at 250C and 101 kN/m2 pressure ( DAB = 6.6x10-5m2/s ). The diffusion path is 5 mm long and concentration of hydrogen at two ends of the path in terms of partial pressure is 12 kN/m2 and 8.4 kN/m2 respectively (10M)
2 . a) Discuss the important and applications of mass transfer analogies. (8M)
b) A plate, 0.5 m square, coated with a layer of benzoic acid, is placed in a stream of water flowing at a velocity of 0.25m/sec at a temperature of 21c. Calculate the average rate of dissolution of the acid per unit area of the plate and also the mass transfer.
The following data are available: solubility of benzoic acid in water at 25C =3.01 kg
3 -9 2
/m ; diffusivity of benzoic acid in water =10 m /s and velocity of water at 25C=8.9x10-4 kg/m.s. (8M)
3
3. a) The solubility of A in water is 0.5 kmol/m at a partial pressure of 60 mm Hg. If the total pressure is 1.2 atm and the Henrys law is applicable, calculate the Henrys law constant (6M)
b) What are parameters which will effect the equilibrium diagram (6M)
c) What is Marnogine effect? (4M)
4. Ammonia is to be removed from air-NH3 mixture containing 20% of volume ammonia in a counter current absorber using water at 1 std atm and 200c. The absorber is to be designed to remove 99.5% by volume of ammonia in the entering gas. Calculate the minimum water rate and the number of theoretical plates necessary for absorption, if 1.2 time the minimum water rate us used for a gas rate of 1 kg/s. Equilibrium data:
Partial pressure of 12 18 32 50 70 166
Ammonia, mm hg
Gm.NH3/100gm water 2 3 5 7.5 10 20 (16M)
5. An equimoloar mixture of A and B is to be prepared in a try tower. A top product having 95 mo1% A is acceptable. However, a very pure bottom product having not more then
0.1 mo1% A is required. The feed is liquid at its bubble point. A reflux ratio of 2.0 is suggested. The relative volatility of A with respect to B is aAB=2.2. Determine the number of ideal stages. (16M)
6. a) What are the important characteristics of a good solvent in liquid-liquid extraction? b) What is the difference between a type I and type II ternary system? Can a system transition from one type to the other by changing the temperature? Why? (8+8M)
7. a) Draw and explain apparent adsorption equilibrium diagram when adsorption occurs from concentrated solution.
b) Name five of the most important commercial adsorbents? What is the distinguishing feature of the molecular-sieve zeolites? (8+8M)
8. a) Explain the phenomena of gas separations in porous membranes. (8M) b) Differentiate between osmosis and reverse osmosis with neat sketch. (8M)
MASS TRANSFER AND SEPARATION (Biotechnology)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Explain why and how molecular diffusivity in gases changes with pressure and temperature. (6M) b) Calculate the rate of diffusion of NaCl at 180C through a stagnant film of water 1 mm thick when the concentrations are 20% and 10% respectively on the either side of the film.
Data: Density of 20% NaCl at 180C = 1.15x103 kg/m3 Density of 10% NaCl at 180C = 1.07x103 kg/m3 Diffusivity of NaCl in solution at 180C = 1.36x10-9 m2 /sec.
(10M)
2. a) Write short note on Convective Mass Transfer Coefficients. (6M)
b) A large volume of pure gas B at 1 atm .pressure is flowing over a surface from which pure A is vaporizing. The liquid A completely wets the surface which is a blotting paper. Hence the partial pressure of A at the surface is the vapor pressure of A at 298 K
15 2
which is 0.2 atm. The ky has been estimated to be 6.78x10- kg mol/s.m .mol fraction. Calculate NA ,the vaporization rate and also the value of ky and kG. (10M)
3. a) The solubility of a gaseous substance (mol. Wt. = 26) in water is given by Henrys law: pA = 105xA, where pA in mm Hg and xA liquid phase mole fraction. Convert the equilibrium relation to the following forms: (i) yA= mxA if the total pressure is 10 bar; (ii) pA =m!CA, CA in gmol/litre. Also write down the equilibrium relation using the mole ratio unit. Assume that the solution is dilute and has a density equal to that of water (1000 kg/m3). (10M)
b) Differentiate between local overall mass transfer coefficient and overall mass transfer coefficient (6M)
4. Carbon disulphide is to be remove from CS2-N2 mixture by absorption. It is carried out at
I std pressure and 240 and the partial pressure of CS2 in the gas entering is 50mm of Hg. The gas is blown into the tower at a rate of 2000m /hr and gas coming out will contain
0.5% CS2 by volume. Average mole wt of oil is 180. The oil enters the tower essentially stripped off all CS2 and solution of oil and CS2 are ideal. The vapor pressure of CS2 at 240C is 345mm of Hg. Determine (i) The minimum L/G ratio. (ii) The number of theoretical plates for L/G of 1.5 times the minimum. (16M)
5. A mixture of di- and tri-ethylamines containing 55 mole% of the former fed to a distillation column at a rate of 40 kmol/h. The feed is at its bubble point. The column is to operate at Atmospheric pressure and the top product should not have more than 2.5 mol% of the less volatile. Also, not more than 2% of the dim ethylamine in the feed should be allowed to leave at the bottom. The reflux to the column is a saturated liquid. Determine
(a) the minimum reflux ratio. (b) the number of theoretical plates if the actual reflux ratio is 1.4 times the minimum.
X 0.020 0.039 0.052 0.065 0.090 0.140 0.215 0.430 0.601 0.782 0.853 0.932 0.985 Y 0.042 0.085 0.124 0.153 0.225 0.316 0.449 0.678 0.802 0.910 0.948 0.970 0.993 (16M)
6. a)Does a concurrent cascade have any merit for liquid-liquid extraction? If not, Why not? Explain
b) Can a crosscurrent cascade accomplish complete extraction with an infinite number of stages?
c) When liquid-liquid extraction is used, are other separation operation needed? Why?
(6+4+6M)
7. a)What is an adsorption isotherm? How can the heat of adsorption be determined from a series of isotherms?
b) What is ideal fixed-bed adsorption? What assumptions are necessary for it to apply? What is meant by breakthrough? (8+8M)
8. a) Explain briefly the classification of membrane processes and provide suitable example for each clas sification. (10M) b) Write short notes on effect of operating parameters in gas separation. (6M)
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
MASS TRANSFER AND SEPARATION (Biotechnology)
Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) How does the binary gas-phase diffusivity depend upon the total pressure and temperature? Can you give qualitative explanations? (6M) b) In a laboratory is 3x10-4 m3 of toluene was accidentally spilled over and has been quickly spread over an area of 0.85 m . If the diffusion is tacking place through a stagnant air of 1 mm thick, calculate the time required for the toluene to be evaporate
5 2
completely at 298 K and 1.013x10 N/m . For toluene, at prevailing conditions, density = 866 kg/m3, diffusivity in air = 8.4x10-6 m2 /sec and vapor pressure = 3.99966x103 N/m2. (10M)
2. (a) Do velocity, temperature, and concentration boundary layers on a flat plate all build up at the same rate? If not, why not? (8M)
(b) A stream of air flowing at 30 m/sec over a 2.25 m thin square plate of solid
naphthalene. Determine the rate of sublimation rate from the plate. The air is at 250C and
the plate at 250C. The diffusivity of naphthalene in air at 00C and 1 atm is 5.14x10-6 20 m /sec. The vapor pressure of naphthalene at 25 C is 25 Pa. The viscosity of air is
1.85x10-8 kg/m sec. (8M)
3. a) In a wetted-wall tower, H2S is being absorbed from air into water at 1.6 bar total pressure and 250c. The gas-phase mass transfer coefficient is predicted to be kc=3.42
23
mol/(h) (m )(AC,kmol/m ).. At a given point in the column , the mole fraction of H2S in the liquid at the gas-liquid interface is 1.8*10-5 and that in the bulk gas is 0.15. The solubility of H2S in water at the given temperature is 0.00337 mass fraction per atmosphere pressure of the gas. Calculate the local flux. (10M)
b) Explain the concept of Overall Co-efficient (6M)
4. A coal gas is freed of its light oil content (benzene) by absorption into an a absorbent oil. The inlet gas contains 2% benzene by volume and 95% removal is required. Inlet gas flow rate=0.25cu.m/s; Pressure =1.07x105N/sq.m; Temperature = 260C; Oil inlet flow
_3
rate (Ls) =1.787x10 k mol/s; Solute content of inlet oil=0.005 mole fraction benzene; Average molecular weight of oil = 260. Equilibrium data Y=0.125x (mole fraction units). Determine the number of trays required graphically. (16M)
5. A distillation column which separates pinene and limonene consists of a reboiler, 15 theoretical plates and a total condenser. The feed is at its bubble point and has 72% pinene in it. The overhead product contains 95 mol% pinene and the bottom product has 95% limonene. Determine (a) The reflux ratio to be maintained, (b) The location of the feed plate, (c) Number of ideal stages required for the above separation for total reflux.
Given: a = 1.71. (16M)
6. Write about the system of three liquids -two pairs partially soluble with the help of an equilibrium diagram. Give example. Also discuss the effect of temperature on the above system. (16M)
7. a) Write short notes on Chemsorption (6M)
b) Define relative adsorpvity and write typical values for few systems (5M)
c) Write short notes on applications of adsorption (5M)
8. a) Write short notes on application of dialysis process for kidney failure cases. (8M) b) What are pressure driven membrane process and explain briefly. (8M)
II B.Tech II Semester (R07) Supply Examinations, Dec- 2009
MASS TRANSFER AND SEPARATION (Biotechnology)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. a) Methane diffuses at steady state through a tube containing helium. At point 1, the partial pressure of methane is pA1 = 55 Kpa and point 2, 0.03 m apart pA2 =15 K pa and temperature is 298 K. At this pressure and temperature, the value of diffusivity is 6.75x10-5 m2/s
i) Calculate the flux of CH4 at steady state for equimolar counter diffusion.
ii) Calculate the partial pressure at 0.02 m apart from point 1. (10M) b) Write short notes on permeability (6M)
2 . a) Give the physical significances of the dimensionless groups in mass transfer (8M)
b) In order to measure the gas-phase mass transfer coefficient in a stirred cell at a given stirrer speed, absorption of ammonia diluted with dry air in aqueous sulphuric acid is carried out for a given period of time. The gas in the cell is well-stirred and the cross-sectional area is 31.5 cm . If the volume of acid taken is 100 ml at 1(N) concentration and at the end of 20 minutes the liquid is found to contain 0.82 g mole ammonia per litre, calculate the gas-phase mass transfer coefficient. (8M)
3.a ) Give the physical significances of the dimensionless groups in mass transfer (8M)
b) At certain level in the wetted wall column the ammonia concentration in gas and liquid phases 0.6 and 0.35 by mole fractions. Equilibrium relation is y=0.58x, ky=2 and 65% controlled by gas phase resistance. Find the interfacial concentrations.(10M)
4. An acetone-air mixture containing 0.025 mole fraction acetone has to its acetone
reduced to 1% of this value by counter current absorption in a packed tower. Gas flow
22 rate of pure air is 1kg/m sec and water is1.6 kg/m . For this system the equilibrium
diagram is given by Y=1.75X/(1-0.75X) where Y is kg moles of acetone /kg mole
of air in gas phase and X is kg moles of acetone per kg mole of water in liquid phase.
What is the tower required if height of overall transfer unit is HtoG =50 cm. (16M)
5. Distillation column is to be designed to separate A and B continuously. The feed is 35% A and 65% B at its dew point. The distillate and the residue compositions are 0.95 and 0.025 respectively.
i) Find the quantities of distillate and bottoms per hour.
ii) Find the number of equilibrium stages required in the column if the reflux ratio is 2.5.Assume the relative volatility as 2.25.
6.a) Write about the use of equilateral coordinates to describe the concentrations in ternary
systems. (8M)
b) What are the various parameters to be considered in making a choice of solvent.(8M)
7.a) In adsorption, why are adsorbents having a microporous structure desirable? (5M)
b) What is absorption hysterisis? (5M)
c) What is an adsorption isotherm? Does it have anything to do with phase equilibrium? (6M)
8. a) How do you separate the mixture of gases using membranes? Explain its operating principle. (8M)
b) Explain briefly dialysis process. (8M)
2 of 2
[13, 3 ] = rsin2O.
7. (a) Out of 10 girls in a class , 3 have blue eyes. If 2 of the girls are chosen at random, what is the probability that
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
