Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University Kakinada 2009 B.Tech Computer Science and Engineering Mathematical Methods - Question Paper
Code No: Z0224/R07 Set No. 1
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 MATHEMATICAL METHODS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering, Computer Science & Engineering, Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Information Technology, Electronics & Control Engineering, Mechatronics, Computer Science & Systems Engineering, Electronics & Telematics, Electronics & Computer Engineering, Production Engineering, Instrumentation & Control Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks k k k k k
1. (a) Express the following system in matrix form and solve by Gauss elimination
method.
2xi + x2 + 2x3 + x4 = 6; 6xi - 6x2 + 6x3 + 12x4 = 36,
4xi + 3x2 + 3x3 - 3x4 =- 1; 2x1 + 2x2 - x3 + x4 = 10.
(b) Show that the system of equations 3x + 3y + 2z = 1; x + 2y = 4;
10y + 3z = - 2; 2x - 3y - z = 5 is consistent and hence solve it. [8+8]
2. Determine the eigen values and the corresponding eigen vectors of the matrix A, 1 0 2
0 0 0 [16] 2 0 4
where A =
3. Reduce the quadratic form 3x2+5y2+3z2-2yz+2zx-2xy to the canonical form and specify the matrix of transformation. [16]
4. (a) Find a positive root of the equation by bisection method: x3 - 4x - 9 = 0 (b) Find the positive root of x3 = 2x + 5 by False Position method. [8+8]
5. (a) It is known that x, y are related by y = X + bx and the experimental values
are given below: x: 1 2 4 6 8 y: 5.43 6.28 10.32 14.86 19.5 Obtain the best values of a and b.
(b) Find the first two derivatives of the function tabulated below at x=0.6
x: 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 [8 8]
y: 1.5836 1.7974 2.0442 2.3275 2.6511 [ ]
6. Find y(0.1), y(0.2), z(0.1), z(0.2) given dX = x + z, jX = x y2 and y(0) = 2, z(0) = 1 by using Taylors series method. [16]
7. (a) Find the Fourier sine transform of e-ax cosx.
(b) Find the Fourier cosine transform of x.e -ax. [8+8]
8. (a) Solve (x+y)p+(y+z)q=(z+x).
(b) Solve the difference equation, using Z-transform y(k+2)-2cosa.y(k+1)+y(k)=0, given y(0)=1, y(1)= 1. [8+8]
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 MATHEMATICAL METHODS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering, Computer Science & Engineering, Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Information Technology, Electronics & Control Engineering, Mechatronics, Computer Science & Systems Engineering, Electronics & Telematics, Electronics & Computer Engineering, Production Engineering, Instrumentation & Control Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Express the following system in matrix form and solve by Gauss elimination method.
2xi + x2 + 2x3 + x4 = 6; 6xi - 6x2 + 6x3 + 12x4 = 36,
4xi + 3x2 + 3x3 - 3x4 =- 1; 2x1 + 2x2 - x3 + x4 = 10.
(b) Show that the system of equations 3x + 3y + 2z = 1; x + 2y = 4;
10y + 3z = - 2; 2x - 3y - z = 5 is consistent and hence solve it.
determine matrix P such that P 1 AP is a
410
141
014
2. For the matrix A =
diagonal matrix.
[16]
3. (a) Show that every square matrix can be expressed as a sum of Hermitian and a skew Hermitian matrix.
(b) If A
[8+8]
then find a skew Hermitian matrix.
2 + 3i 1 - i 2 + i -2i 4 2i 4i 4i i
4. (a) Find a positive root of x4 - x3 - 2x2 - 6x - 4 =0 by bisection method.
(b) Find an approximate root of x log10x - 1.2 = 0 by Regula False method.
[8+8]
5. (a) Fit a second degree parabola to the following data:
x: 0 1 2 3 4 f(x): 1 1.8 1.3 2.5 6.3
(b) The velocity v of a particle moving in a straight line covers a distance x in time t. They are related as follows: Find f' (15). x: 0 10 20 30 40 v: 45 60 65 54 42
6. Find y(0.1) and y(0.2) from = xy + V2, y(0) = 1 by using Runge-Kutta method and hence obtain y(0.4) using Adams method. [16]
7. Find the Fourier Transforms of f (x) = < a , x ; |x! < 1
J w \ 0; |x| > 1
Deduce that
OO OO
J sint-3cos t dt = 41 Using Parsevals identity prove that / (sint-3 cos t)2dt = 15. [16]
o' 0
8. (a) Form the partial differential equations by eliminating the arbitrary constants
i. x2 + y2 + (z c)2 = a2
ii. z=(x2+a)(y2+b)
(b) Find the Z-transform of the sequences {x(n)} where x(n) is
i- (I)
ii. (3)n cos. [8+8]
k k k k k
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 MATHEMATICAL METHODS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering, Computer Science & Engineering, Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Information Technology, Electronics & Control Engineering, Mechatronics, Computer Science & Systems Engineering, Electronics & Telematics, Electronics & Computer Engineering, Production Engineering, Instrumentation & Control Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
(2 -4 3 -1 0 \
1 -2 -1 -4 2
1. (a) Find the rank of
0 1 -13 1
\ 4 -7 4 -4 5 /
(b) Solve the system of equations 3x+y+2z =3, 2x-3y-z= -3, x+2y+z=4. [8+8]
54
12
2. (a) Determine the eigen values and eigen vectors of the matrix A=
20
01
100
[8+8]
, find A
(b) IfA
3. Reduce the quadratic form 3x2 - 2y2 - z2 + 12yz + 8zx - 4xy to canonical form by an orthogonal reduction and state the nature of the quadratic form. [16]
4. (a) Find a positive root of the following equation by bisection method
x3 - x2 -1 = 0
(b) Find the interpolating polynomial f(x) from the table
[8+8]
|
x |
0 |
1 |
4 |
5 |
|
f(x) |
4 |
3 |
24 |
39 |
5. (a) Fit a curve of the form i(d) = adn for the data: d: 1720 2300 3200 4100 i(d): 655 789 1000 1164
3
(b) Evaluate J 1+3 using Simpsons one-third rule, by dividing the range by
[8+8]
choosing h=0.5.
6. Evaluate the values of y(1.1) and y(1.2) from y'' + y2y' = x3; y(1)=1, y' (1)=1 by using Taylor series method. [16]
OO
7. Find the Fourier Transforms of f(x) = e x| and deduce that f c+f dt = f e-|x 1.
0
Hence show that F(xe-|x 1 )=i +2)2. [16]
8. (a) Form the partial differential equations by eliminating the arbitrary constants
i. x2 + y2 + (z c)2 = a2
ii. z=(x2+a)(y2+b)
(b) Find the Z-transform of the sequences {x(n)} where x(n) is
n
ii. (3)n cosr-f. [8+8]
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 MATHEMATICAL METHODS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Mechanical Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering, Computer Science & Engineering, Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Bio-Medical Engineering, Information Technology, Electronics & Control Engineering, Mechatronics, Computer Science & Systems Engineering, Electronics & Telematics, Electronics & Computer Engineering, Production Engineering, Instrumentation & Control Engineering and Automobile Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Express the following system in matrix form and solve by Gauss elimination method.
2xi + x2 + 2x3 + x4 = 6; 6xi - 6x2 + 6x3 + 12x4 = 36,
4xi + 3x2 + 3x3 - 3x4 =- 1; 2x1 + 2x2 - x3 + x4 = 10.
(b) Show that the system of equations 3x + 3y + 2z = 1; x + 2y = 4;
10y + 3z = - 2; 2x - 3y - z = 5 is consistent and hence solve it. [8+8]
314
026
005
10
03
(b) If A =
[8+8]
, find A256.
3. Reduce the quadratic form 3x1 - 2y2 - z2 + 12yz + 8zx - 4xy to canonical form by an orthogonal reduction and state the nature of the quadratic form. [16]
4. (a) Using Lagranges formula, fit a polynomial to the data
| ||||||||||
|
Also find y at x =2. |
(b) If the interval of differencing is unity, prove that Atan-1 (= tan 1 .
[8+8]
5. (a) Fit a curve of the form i(d) = adn for the data:
d: 1720 2300 3200 4100 i(d): 655 789 1000 1164
3
(b) Evaluate f j+X. using Simpsons one-third rule, by dividing the range by
0
choosing h=0.5. [8+8]
6. (a) Using Eulers method, find y(0.2), y(0.1) given y'= x2 + y2, y(0)= 1
(b) Evaluate y(0.8) using R - K method given y'= (x+y)1, y = 0.41 at x=0.4.
[8+8]
7. (a) Find the Fourier sine transform of e-ax cosx.
(b) Find the Fourier cosine transform of x.e -ax. [8+8]
8. (a) Solve xp - yq=z
(b) Solve the difference equation, using Z-transform x(k+1)-2x(k+1)=1, given x(0)=0. [8+8]
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (Chemical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1
[6+4+6]
c
What is the role of chemical engineer in food processing industry. Explain briefly ideal solution.
Write short notes on flotation.
Define heat capacity and explain how to calculate mean heat capacity for gases.
2
a
b
c
Differentiate between Cp and Cv and also write the relation between these two for ideal gases.
Write short notes on equivalent mass. [6+6+4]
Describe the boundary layer formation on a flat plate for a fluid stream. State and explain the equation of continuity. [12+4]
3
4.
Explain the mechanism of heat transfer by conduction, convection and radiation.
a
b
c
Write the equation for the rate of heat flow by conduction. Explain the terms in it?
Write brief note on conductivities of solids, liquids and gases. [6+4+6]
Explain mass transfer coefficient in terms of film coefficient.
5
6
Discuss about the flux equation for diffusion in gases and diffusion in liquids.
[16]
Explain with the help of suitable equations how to estimate the vapour and liquid composition for flash distillation.
a
b
How many ways the azeotropes are classified and how to separate them.[8+8]
Write short notes on the fields of applications of liquid-liquid extraction.
7.
In a ternary extraction system, what are the solute, solvent, and carrier? What you understand about solute and raffinate?
Define and explain distribution coefficient. [4+4+4+4]
Explain briefly adsorption equipment.
Write expressions for Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms. [16]
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING
(Chemical Engineering)
Max Marks: 80
Time: 3 hours
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Differentiate between frothers and Depressors.
(b) What are the mixers used for mixing of dry powders.
(c) Differentiate between Dodge crushers and Blake crusher.
[6+4+6]
[4+4+8]
2. (a) Explain a combined detailed flow diagram of process.
(b) State the different forms of energy associated with mass.
(c) What are the steps to follow in energy balance calculations?
3. Explain the physical significance of Reynolds number and describe Reynolds ex-
[16]
periment.
4. (a) Explain: convection, forced convection, Natural convection and heat transfer
coefficient
(b) Write the relation between overall heat transfer coefficient and individual heat transfer coefficients. Also mention the meaning of various terms in it. [9+7]
5. (a) Name the two mass transfer operations for the following phases in conact:
i. liquid-liquid
ii. solid-vapour.
(b) Mention the similarities between various mass transfer operations.
(c) Mass diffusion exists between various mass transfer operations. Explain with examples. [4+6+6]
6. Describe the criteria of selection of equipment for gas-liquid operation. [16]
7. Write the advantages or uses of:
(a) Mixer settlers
(b) Pulse column
(c) Spray column
(d) Rotating disc contactors. [4x4]
8. (a) Explain rotary drier with neat sketch.
(b) Explain process of humidification and dehumidification with suitable example.
i i i i i
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (Chemical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks k k k k k
1. Discuss briefly:
(a) Flotation
(b) Screening. [2x8=16]
2. Give details about humidity and saturation. [16]
3. (a) Differentiate between pseudo-plastic and Dilatant fluids with suitable example.
(b) What are the time dependent fluids and explain with suitable examples.
(c) Write salient points of one dimensional flow. [6+6+4]
4. Write about types of evaporators in details. [16]
5. (a) What are three main problems that exists when a gas and liquid flow through
a packed bed? Discuss indetail about their effect on mass transfer and suggest ways of reading them.
(b) Write overall mole balance at steady state for designing a packed absorption column, and explain the terms involved. [9+7]
6. Explain briefly:
(a) Venturi scrubber
(b) Spray column. [8+8]
7. (a) Write short notes on selection of liquid-liquid contactors.
(b) Write short notes on selection of disperse phase. [8+8]
8. (a) Define molecularity, order and rate of a reaction.
(b) Distinguish between elementary and non elementary reactions with suitable
[9+7]
examples.
kkkkk
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING (Chemical Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks k k k k k
1. (a) Explain the electro mechanical operation.
(b) Differentiate between Geometric and Kinematic Similarities. [8+8]
2. (a) How do you classify energy associated with mass.
(b) Derive Kirchoffs equation for effect of temperature on heat of reaction.[6+10]
3. (a) With the help of a neat figure discuss about the development of a boundary
layer on a flat plate.
(b) Write the expression for thickness of boundary layer if the boundary layer is laminar and turbulent, respectively. [12+4]
4. (a) Define capacity and economy.
(b) Explain forward feed triple effect evaporator with suitable sketch. [6+10]
5. (a) Mass transfer may occurs in different ways, name any five.
(b) What are phenomena that must exists in a mass transfer opeartion.
(c) There are many similarities and differences between various mass transfer operations mention them. [5+3+8]
6. (a) What is differential distillation? Derive Rayleigh equation.
(b) Explain briefly classification of gas-liquid contact equipment. [8+8]
7. Explain in detail about classification of industrial liquid-liquid contactors. [16]
8. (a) How many ways the crystallization takes place.
(b) What are the steps involved for crystallization to takes place?
(c) Write short notes on classification of crystallization equipment. [4+4+8]
kkkkk
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 ENGINEERING MECHANICS ( Common to Metallurgy & Material Technology and Aeronautical
Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
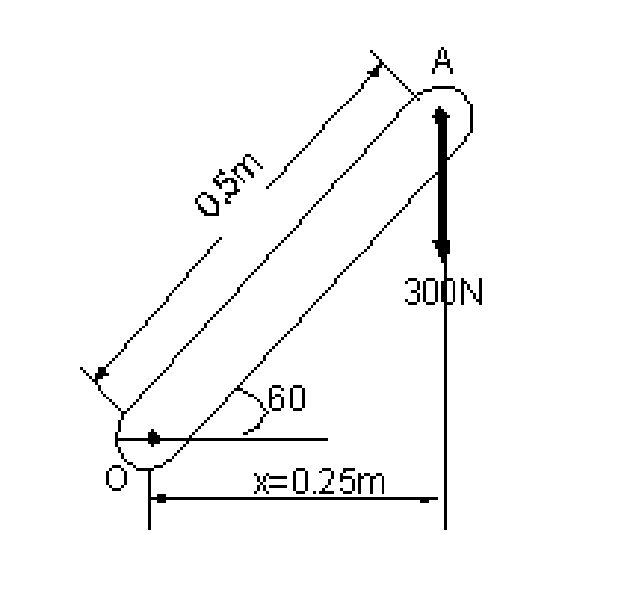
|
1. A 300 N vertical force is applied at the end of a lever which is attached to shaft at O as shown in figure 1. Determine |
 |
|
Figure 1 |
(a) The moment of the 300 N force about O.
(b) The magnitude of the horizontal force applied at A which creates the same moment about O.
(c) The smallest force applied at A which creates the same moment about O. [16]
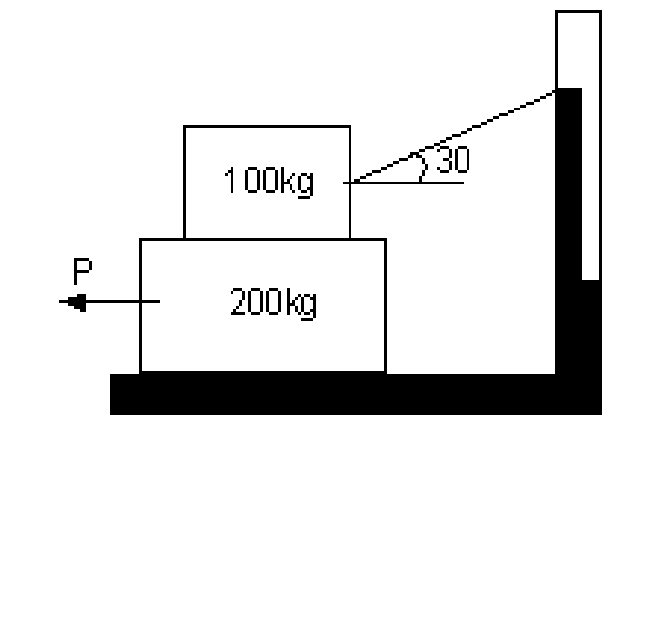
2. A block of mass 200 kg resting on a horizontal surface supports another block of 100 kg as shown in figure 2. The smaller block is attached to string from the wall. Find the horizontal force P just to move the 200 kg block to the left. = 0.35 for all rubbing surfaces. [16]
3. Determine the width of a 9.75 mm thick leather belt required to transmit 15 kW from a motor running at 900 r.p.m. The diameter of the driving pulley of the motor is 300 mm. The driven pulley runs at 300 r.p.m. and the distance between the centre of two pulleys is 3 meters. The density of leather is 1000 kg/m3. The maximum allowable stress in the leather is 2.5 MPa. The coefficient of friction between the leather and pulley is 0.3. Assume open belt drive and neglect the sag and slip of the belt. [16]
4. A hemisphere of diameter 30 cm is symmetrically placed on top of a circular cylinder of diameter 20 cm and height 30 cm. locate the center of gravity of the composite volume. [16]
5. (a) Starting from the first principles determine the moment of inertia of a triangle
with respect to its base.
(b) Determine the radius of gyration for rectangle
i. about x axis and
ii. about its base. [8+8]
6. The horizontal component of velocity of a projectile is twice its vertical component. Find the range on the horizontal plane through the plane of projection if the projectile passes through a point 18 m horizontally and 3 m vertically above the point of projection. Determine also initial velocity of the projectile. [16]
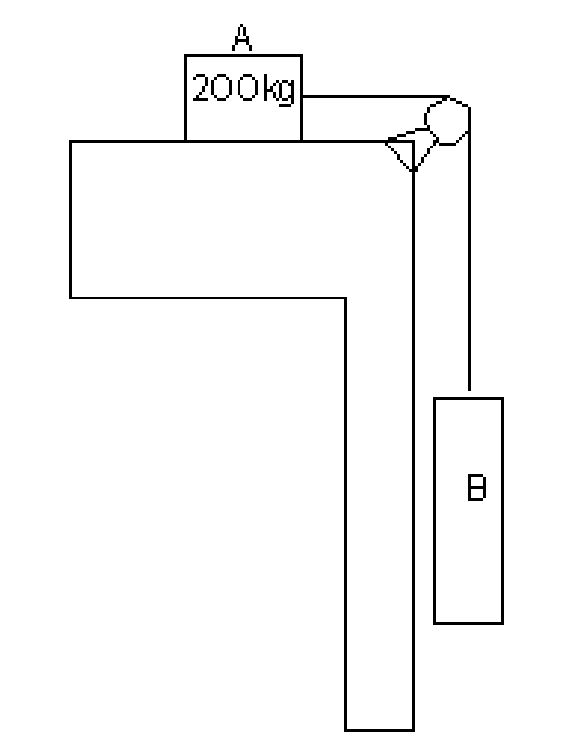
7. Two blocks are joined by an inextensible cable as shown in figure 7. If the system is released from rest, determine the velocity of block A after it has moved 2 m. Assume that i equals to 0.25 between block A and the plane and that the pulley is weightless and frictionless. [16]
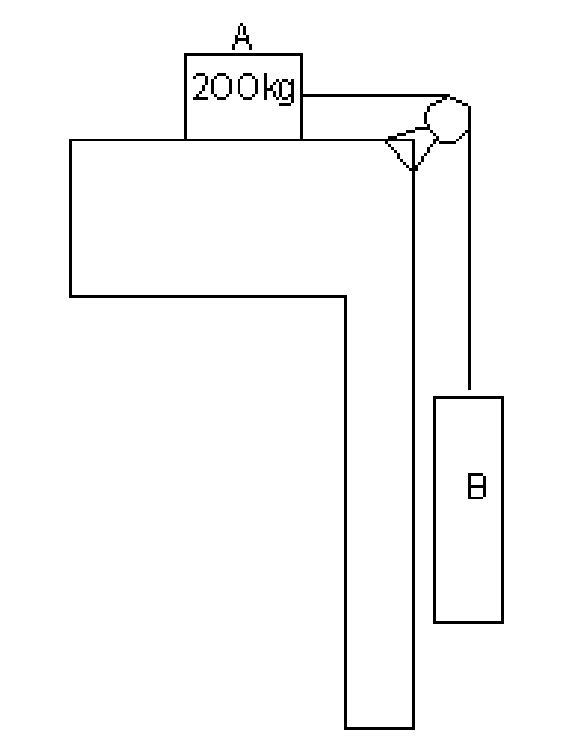 |
|
Figure 7 |
8. A shaft 1.5 m long is supported in flexible bearings at the ends and carries two wheels each of 50 kg mass. One wheel is situated at the center of the shaft and the other at the distance of 0.4 m from the towards right. The shaft is hollow of external diameter 75 mm and inner diameter 37.5 mm. The density of the shaft
material is 8000 kg/m2. The Youngs modulus for the shaft material is 200 GN/m2. Find the frequency of transverse vibration. [16]
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 ENGINEERING MECHANICS
( Common to Metallurgy & Material Technology and Aeronautical
Engineering)
Max Marks: 80
Time: 3 hours
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Two forces are acting at a point O as shown in figure 1a. Determine the resultant in magnitude and direction.
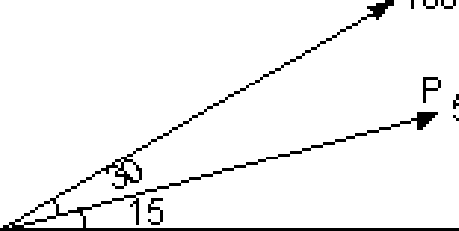
0
|
Figure 1a (b) Three forces of magnitude 40 KN, 15 KN and 20 KN are acting at a point O as shown in figure 1b. The angles made by 40 KN, 15 KN and 20 KN forces |
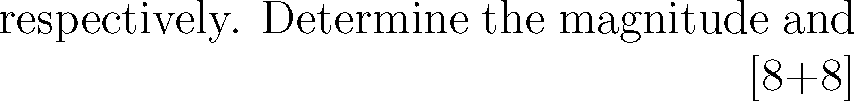 |
with X-axis are 600, 1200 and 2400
direction of the resultant force.
|
y 1SKN | |
 |
-K |
Figure 1b
2. (a) A wooden block weighing 30 N is placed on a horizontal plane. A horizontal
force of 12 N is applied and the block is on the point of moving. Find
i. Coefficient of friction
ii. Angle of friction and
iii. The resultant reaction.
(b) A block of weight 80 N is placed on a horizontal plane where the coefficient of friction is 0.25. Find the force that should be applied to the block at an angle of 300 with the horizontal to attain the condition of limiting equilibrium.[8+8]
larger pulley (driver) is 220 r.p.m. The permissible load on the belt is 25 N/mm, width of the belt is 5 mm thick. The coefficient of friction between the smaller pulley surface and the belt is 0.35. Determine necessary length of the belt, width of the belt and necessary initial tension in the belt. [16]
4. Find the centroid of the shaded area shown in figure 4. All dimensions are in mm.
[16]
27 i 35 j
H-
35 }
Figure 4
5. (a) Starting from the first principles determine the moment of inertia of a triangle
with respect to its base.
(b) Determine the radius of gyration for rectangle
i. about x axis and
ii. about its base. [8+8]
6. A bus starts from rest at point A and accelerates at the rate of 0.9 m/s2 until is reaches a speed of 7.2 m/s. It then proceeds with the same speed until the brakes are applied. It comes to rest, at point B, 18 m beyond the point where the brakes are applied. Assuming uniform acceleration, determine the time required for the bus to travel from A to B. Distance AB = 90 m. [16]
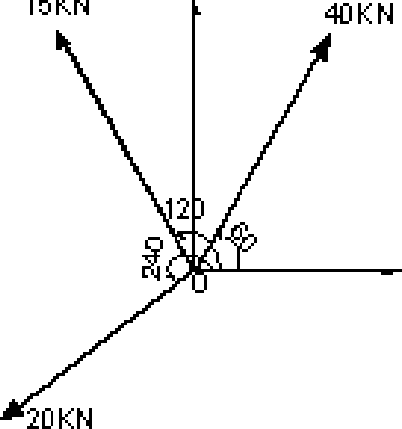
7. A spring is used to stop a 60 kg package which is sliding on a horizontal surface. The spring has a constant k = 20 kN/m and is held by cables so that initially it is compressed to 120 mm. Knowing that the package has a velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown in the figure 7 and that the maximum additional deflection of the spring is 40 mm, determine.
(a) The coefficient of kinetic friction between the package and the surface.
 |
|
Figure 7 |
(b) The velocity of the package as it passes again through the position shown. [16]
8. A shaft 1.5 m long supported in flexible bearings at the ends carries two wheels each of 50 kg mass. One wheel is situated at the centre of the shaft and the other at a distance of 375 mm from the centre towards left. The shaft is hollow of external diameter 75 mm and the internal diameter 40 mm. The density of shaft material is 7700 kg/m3 and its modulus of elasticity is 200 GN/m2. Find the lowest whirling speed of the shaft, taking into account the mass of the shaft. [16]
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 ENGINEERING MECHANICS ( Common to Metallurgy & Material Technology and Aeronautical
Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
k k k k k
|
1. A 300 N vertical force is applied at the end of a lever which is attached to shaft at O as shown in figure 1. Determine |
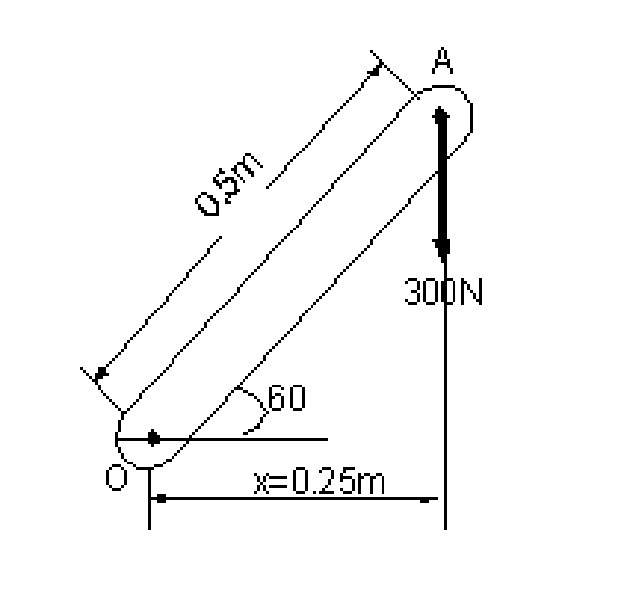 |
|
Figure 1 |
(a) The moment of the 300 N force about O.
(b) The magnitude of the horizontal force applied at A which creates the same moment about O.
(c) The smallest force applied at A which creates the same moment about O. [16]
2. (a) A wooden block weighing 30 N is placed on a horizontal plane. A horizontal
force of 12 N is applied and the block is on the point of moving. Find
i. Coefficient of friction
ii. Angle of friction and
iii. The resultant reaction.
(b) A block of weight 80 N is placed on a horizontal plane where the coefficient of friction is 0.25. Find the force that should be applied to the block at an angle of 300 with the horizontal to attain the condition of limiting equilibrium.[8+8]
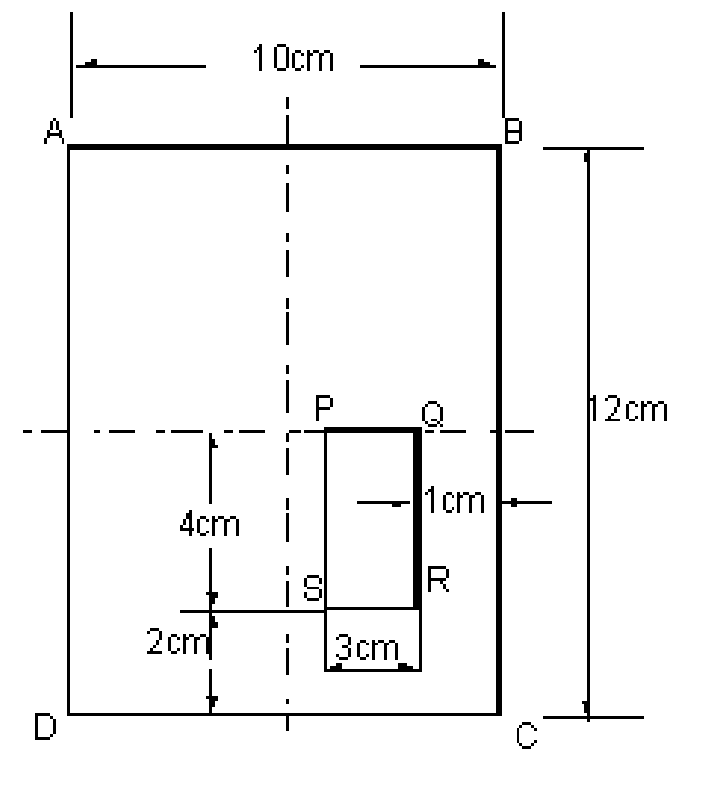
4. In a rectangular plate 10 cm x 12 cm, as shown in figure 4 a rectangular opening PQRS 3 cm x 12 cm, is made. Find the centroid of the plate after the opening is made. [16]
 |
|
Figure 4 |
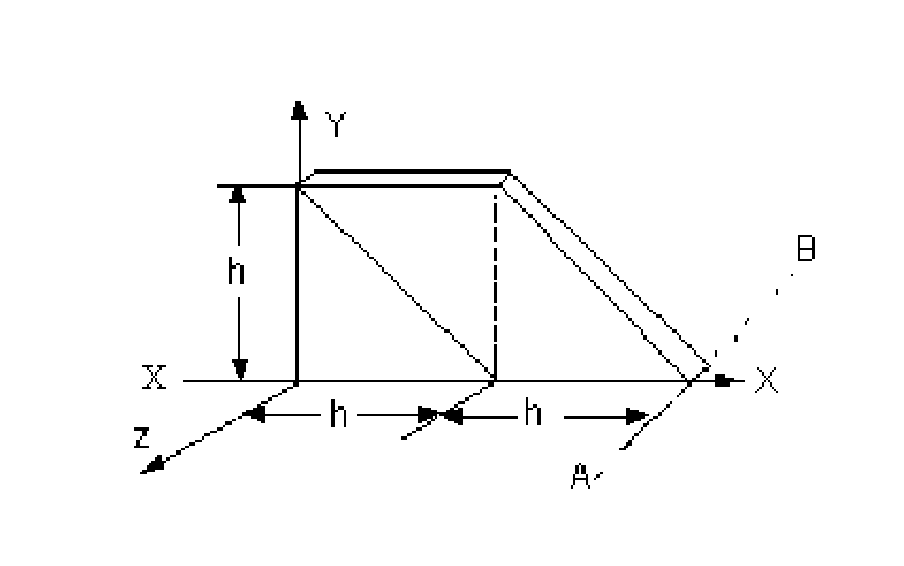
5. Calculate the mass moment of inertia of thin plate shown in figure 5 with respect to the axis X-X.Take mass of the plate as m. [16]
 |
|
Figure 5 |
6. A bus starts from rest at point A and accelerates at the rate of 0.9 m/s2 until is reaches a speed of 7.2 m/s. It then proceeds with the same speed until the brakes are applied. It comes to rest, at point B, 18 m beyond the point where the brakes are applied. Assuming uniform acceleration, determine the time required for the bus to travel from A to B. Distance AB = 90 m. [16]
7. Two blocks are joined by an inextensible cable as shown in figure 7. If the system is released from rest, determine the velocity of block A after it has moved 2 m. Assume that i equals to 0.25 between block A and the plane and that the pulley is weightless and frictionless. [16]
 |
|
Figure 7 |
8. A cantilever shaft 50 mm diameter and 300 mm long has a disc mass 100 kg at its free end. The young?s modulus for the shaft material is 200 GN/m2. Determine the frequency of longitudinal and transverse vibrations of the shaft. [16]
'k 'k 'k 'k 'k
I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, November 2009 ENGINEERING MECHANICS ( Common to Metallurgy & Material Technology and Aeronautical
Engineering)
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80
Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
[16]
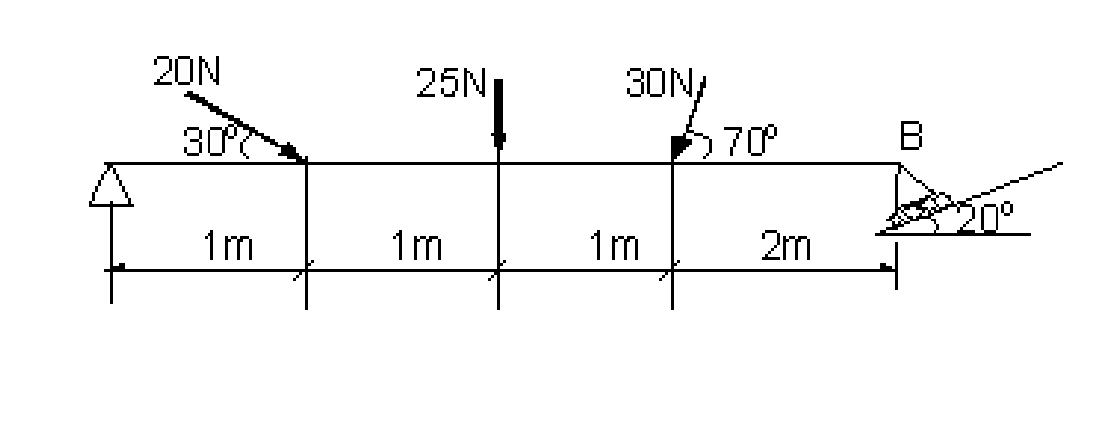
1. Find the reaction at the supports A, B of the beam shown in figure 1.
 |
|
Figure 1 |
2. The cutter of a broaching machine is pulled by square threaded screw of 55 mm external diameter and 10 mm pitch. The operating nut takes the axial load of 400 N on a flat surface of 60 mm internal diameter and 90 mm external diameter. If the coefficient of friction is 0.15 for all contact surfaces on the nut, determine the power required to rotate the operating nut, when the cutting speed is 6 m/min.
[16]
3. An open belt running over two pulleys 240 mm and 600 mm diameter connects two parallel shafts 3 metres apart and transmits 4 kW from the smaller pulley that rotates at 300 r.p.m. Coefficient of friction between the belt and pulley is 0.3 and the safe working tension is 10 N per mm width. Determine the minimum width of the belt, initial belt tension and length of the belt required.
[16]
[16]
4. Determine the centroid of the section shown in figure 4.
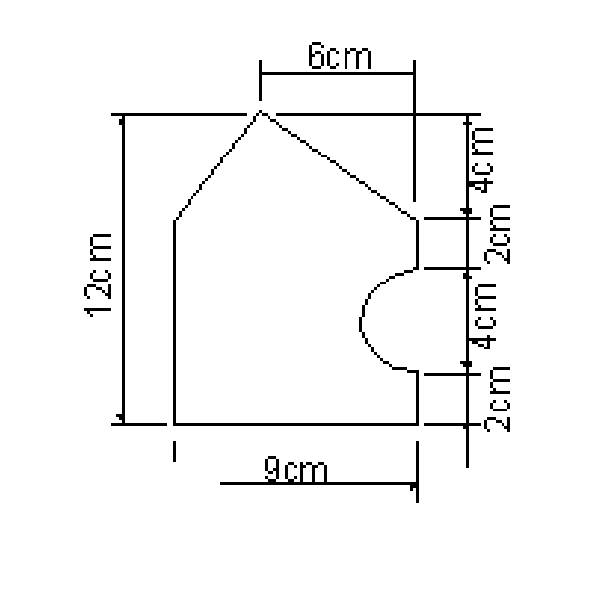
5. (a) Starting from the first principles determine the moment of inertia of a triangle
with respect to its base.
(b) Determine the radius of gyration for rectangle
i. about x axis and
ii. about its base. [8+8]
6. A bus starts from rest at point A and accelerates at the rate of 0.9 m/s2 until is reaches a speed of 7.2 m/s. It then proceeds with the same speed until the brakes are applied. It comes to rest, at point B, 18 m beyond the point where the brakes are applied. Assuming uniform acceleration, determine the time required for the bus to travel from A to B. Distance AB = 90 m. [16]
7. A spring is used to stop a 60 kg package which is sliding on a horizontal surface. The spring has a constant k = 20 kN/m and is held by cables so that initially it is compressed to 120 mm. Knowing that the package has a velocity of 2.5 m/s in the position shown in the figure 7 and that the maximum additional deflection of the spring is 40 mm, determine.
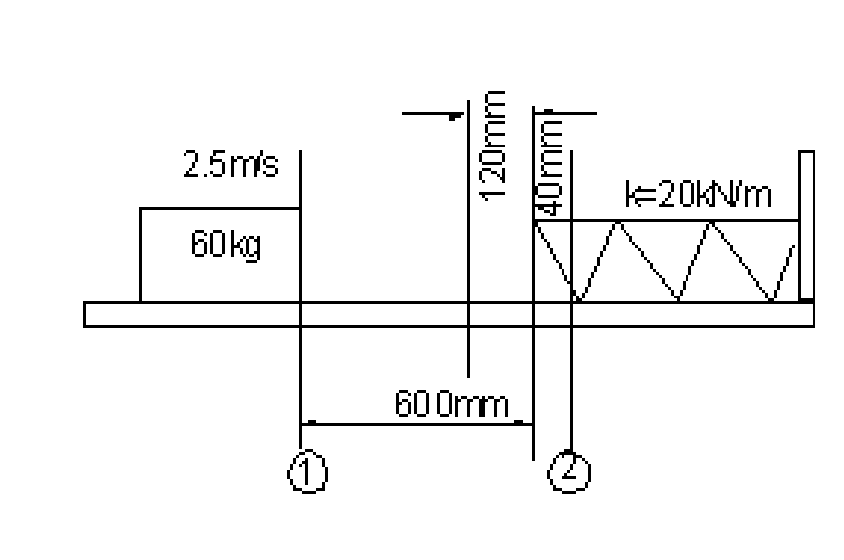 |
|
Figure 7 |
(a) The coefficient of kinetic friction between the package and the surface.
(b) The velocity of the package as it passes again through the position shown. [16]
8. Determine the natural frequency of the free longitudinal vibrations of a contilevel beam by equilibrium method and Rayleighs method. [16]
2 of 2
(a) Find the eigen values and eigen vectors of the matrix A
The power transmitted between two shafts 3.5 metres apart by a cross belt dive round the two pulleys 600 mm and 300 mm in diameters, is 6 kW. The speed of the
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
