K L University 2009 B.Tech Civil Engineering University board,engineering mathematics-3,engineering maths - Question Paper
KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
II/IV B. Tech I SEMESTER / DECEMBER
(REGULAR)
MATHEMATICS-IV CE-211
Time: three Hrs Max. Marks: 60
ans 1 ques. from every unit
ans All Units
UNIT – I
I. (a) find a Fourier Series for f (x) = x sin x, 0 < x < 2p
(b) If f (x) = p x, 0 = x = 1
= p (2-x), one = x = 2, show that in the interval (0,2),
(OR)
(c) find Fourier Series for the function f (x) provided by ,
,
Hence deduce that
(d) find a half range sine series for f (x) = x- x2 in (0,1).
UNIT – II
II. (a) obtain the Fourier Transform of f(x)= 1-x2, 1x1= 1
0, 1x1 > 1
Hence evaluate
(b) Express the function f (x) = 1, for 1x1 = 1
0, for 1x1 > 1, as a Fourier ritegral
Hence evaluate
(OR)
(c) find the constant term and the coefficients of the 1st sine & cosine terms in Fourier Expansion of "y" as provided in the subsequent table
x: 0 1 2 3 4 5
y: 9 18 24 28 26 20
(d) obtain the Fourier Cosine transform of f (x)= e-ax, (a>0)
UNIT – III
III. (a) obtain the 1st and 2nd derivatives of f(x) at x = 1.5 of
x: 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
y: 3.375 7.000 13.625 24.000 38.875 59.000
(b) obtain an approximate value of log e five by calculating to four decimal places, by Simpson's Rule dividing the range into 10 equal parts.
(OR)
(c) Using Range Kutta Method of fourth order calculate y (2) and y (4) from , taking h = 0.1
(d) Apply Euler's method to solve y1 = x + y, y (0) = 0, choosing the step length h = 0.2 (carry out six steps)
UNIT – IV
IV. (a) obtain by Taylor's series method, the value of y at x = 0.1 & x = 0.2 to 5 places of decimals from
(b) obtain the value of y for x = 0.1, by picard's method, provided that
(OR)
(c) Solve the formula y11=x+y, with the boundary conditions y (0) = y (1) = 0.
(d) Determine the value of y at the pivotal points of the interval (0,1) of y satisfies the
boundary value issue
UNIT – V
V. (a) obtain K so that the subsequent can serve as the probability density of a random variable
f(x) = 0, x = 0
(b) If the amount of cosmic radiation to which a person is exposed while flying by jet across the united states is a random variable having the normal distributions with Mean = 4.35 mrem and s = 0.59 mrem, obtain the probabilities that the amount of cosmic radiation to which a person will be exposed on such a flight is (i) ranging from 4.00 & 5.00 mrem (ii) at lowest 5.50 mrem
(OR)
(c) If 20 % of the memory chips made in a certain plant are defective, elaborate the probabilities that in a lot of 100 randomly chosen for inspection
(i) at most 15 will be defective
(ii) Exactly 15 will be defective
(d) In a certain country, the proportion of highway parts requiring repairs in any provided year is a random variable having the beta distribution with a = 3, ß = 2
(i) On the avg. what percentage of the highway parts require repairs in any provided year
(ii) Find the probability that at most half of the highway parts will require repairs in any provided year.
 KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
II/IV B. Tech I SEMESTER / DECEMBER
(REGULAR)
MATHEMATICS-IV CE-211
Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 60
Answer One Question from each unit
Answer All Units
UNIT I
I. (a) Obtain a Fourier Series for f (x) = x sin x, 0 < x < 2π
(b) If f (x) = π x, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1
= π (2-x), 1 ≤ x ≤ 2, show that in the interval (0,2),
![]()
(OR)
(c) Obtain Fourier Series for the function f (x)
given by ![]() ,
, ![]()
![]() ,
, ![]()
Hence deduce that ![]()
(d) Obtain a half range sine series for f (x) = x- x2 in (0,1).
UNIT II
II. (a) Find the Fourier Transform of f(x)= 1-x2, 1x1≤ 1
0, 1x1 > 1
Hence evaluate ![]()
(b) Express the function f (x) = 1, for 1x1 ≤ 1
0, for 1x1 > 1, as a Fourier ritegral
Hence evaluate ![]()
(OR)
(c) Obtain the constant term and the coefficients of the first sine & cosine terms in Fourier Expansion of y as given in the following table
x: 0 1 2 3 4 5
y: 9 18 24 28 26 20
(d) Find the Fourier Cosine transform of f (x)= e-ax, (a>0)
UNIT III
III. (a) Find the first and second derivatives of f(x) at x = 1.5 of
x: 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
y: 3.375 7.000 13.625 24.000 38.875 59.000
(b) Find an approximate value of log e 5 by calculating to 4 decimal places, by
Simpsons ![]() Rule
Rule
![]() dividing the
range into 10 equal parts.
dividing the
range into 10 equal parts.
(OR)
(c) Using Range Kutta Method of 4th order
compute y (2) and y (4) from ![]() , taking h =
0.1
, taking h =
0.1
(d) Apply Eulers method to solve y1 = x + y, y (0) = 0, choosing the step length h = 0.2 (carry out 6 steps)
UNIT IV
IV. (a) Find by Taylors series method, the value of y
at x = 0.1 & x = 0.2 to five places of decimals
from ![]()
(b) Find the value of y for x = 0.1, by
picards method, given that ![]()
(OR)
(c) Solve the equation y11=x+y, with the boundary conditions y (0) = y (1) = 0.
(d) Determine the value of y at the pivotal points of the interval (0,1) of y satisfies the
boundary value problem ![]()
UNIT V
V. (a) Find K so that the following can serve as the probability density of a random variable
f(x) = 0, x ≤ 0
![]()
(b) If the amount of cosmic radiation to which a person is exposed while flying by jet across the united states is a random variable having the normal distributions with Mean = 4.35 mrem and σ = 0.59 mrem, find the probabilities that the amount of cosmic radiation to which a person will be exposed on such a flight is (i) between 4.00 & 5.00 mrem (ii) at least 5.50 mrem
(OR)
(c) If 20 % of the memory chips made in a certain plant are defective, what are the probabilities that in a lot of 100 randomly chosen for inspection
(i) at most 15 will be defective
(ii) Exactly 15 will be defective
(d) In a certain country, the proportion of highway sections requiring repairs in any given year is a random variable having the beta distribution with α = 3, β = 2
(i) On the average what percentage of the highway sections require repairs in any given year
(ii) Find the probability that at most half of the highway sections will require repairs in any given year.
 KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
II/IV B. Tech I SEMESTER / DECEMBER
(REGULAR)
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY CE-216
Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 60
Answer One Question from each unit
Answer All Units
UNIT I
1. (a) Define Geology ? Explain various branches of Geology. 8 M
(b) Give importance of geology from Civil Engineering point of view. 4 M
(OR)
2. (a) Describe in-detail the weathering process of rocks and its importance in Civil Engineering. 12 M
UNIT II
3. (a) Describe the physical properties, Chemical composition crystal system, uses and distribution of the following minerals. 4 x 3 = 12 M
1. Microcline
2. Quartz
3. Calcite
4. Bauxite
(OR)
4. (a) How Igneous Rocks are formed and classified? Describe the characteristics features of each group with suitable examples. 6 M
(b) Differentiate between the following 3 x 2 = 6 M
(i) Granite and Granite Gneiss
(ii) Limestone and Marble
(iii) Vesicular and Amygdaloidal structures
UNIT III
5. (a) What is a Fold? and lable the parts of a Fold with neat sketch 3 M
(b) Explain the types of Folds with neat sketches and give importance of folds in Civil Engineering Projects. 9 M
(OR)
6. (a) Explain the causes and effects of Earthquakes. 8 M
(b) Explain Seismic Belts. 4 M
UNIT IV
7. (a) What is Geo-Physical prospecting? and mention various geophysical methods. 3 M
(b) Explain the importance of Seismic Method in Civil Engineering Structures. 9 M
(OR)
8. Explain the following
(i) Remote Sensing 6 M
(ii) Occurrence of water in various lithological formations. 6 M
UNIT V
9. (a) What is a Multipurpose Dam? Explain the geological considerations for selection of a Dam site. 12 M
(OR)
10. Explain the following 4 x 3 = 12 M
(i) Over Break
(ii) Purpose of tunneling
(iii) Srisailam Dam
 KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
II/IV B. Tech I SEMESTER / DECEMBER
(REGULAR)
BUILDING MATERIALS & CONSTRUCTION CE-213
Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 60
Answer One Question from each unit
Answer All Units
UNIT I
1. (a) Discuss the qualities of good Building Stones - 8 M
(b) Explain Dressing of Stones - 4 M
(OR)
2. (a) Explain the method of manufacturing of bricks through clamp burning - 6 M
(b) Explain the composition of good brick earth and harmful ingredients - 6 M
UNIT II
3. (a) Comparison between Fat Lime and Hydraulic Lime 6 M
(b) Explain seasoning of Timber. 6 M
(OR)
4. (a) Briefly explain various defects of Timber. 8 M
(b) Explain Indian Timber trees. 4 M
UNIT III
5. (a) Describe the Open Hearth process of manufacturing of steel 8 M
(b) Explain Varnishing. 4 M
(OR)
6. (a) Explain sound absorbing materials. 6 M
(b) Properties of Mild Steel. 6 M
UNIT IV
7. (a) Explain what are the various types of Foundations adopted to transfer the
loads to the soil with neat sketches. 12 M
(OR)
8. (a) Explain the types of stone masonry with neat sketches. 6 M
(b) Explain the following. 3 x 2 = 6M
(i) Distinguish between English Bond and Flemish Bond.
(ii) Explain cavity walls.
UNIT V
9. (a) Explain with illustrations, the methods of providing DPC under different
situations 9M
(b) Discuss the Terrazzo flooring. 3 M
(OR)
10 (a) Explain the classification of Roofs with neat sketches. 6 M
(b) What is meant by Underpinning? Explain various methods of underpinning. 6 M
 KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
II/IV B. Tech I SEMESTER / DECEMBER
(REGULAR)
FLUID MECHANICS CE-214
Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 60
Answer One Question from each unit
Answer All Units
UNIT I
- a) Enunciate Newtons Law of Viscosity and distinguish between Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids. (6 M)
b) A cylinder of 150 mm radius rotates concentrically inside a fixed cylinder of 155 mm radius. Both cylinders are 300 mm long. Determine the viscosity of the liquid, which fills the space between the cylinders if a torque of 0.98 N-m is required to maintain an angular velocity of 60 r.p.m. (6 M)
(OR)
- a) The right limb of a simple U-tube manometer containing mercury is open to the atmosphere while the left limb is connected to a pipe in which a fluid of specific gravity 0.9 is flowing. The centre of the pipe is 12 cm below the level of mercury in the right limb. Find the pressure of fluid in the pipe if the difference of mercury level in the two limbs is 20 cm. (6 M)
b) Derive an expression for the depth of centre of pressure from free surface of liquid of an vertical plane surface submerged in the liquid (6 M)
UNIT II
- a) What is Buoyancy? Explain the terms centre of buoyancy and metacentre. (6 M)
b) What are the conditions of equilibrium of a floating body and a submerged body?
(6 M)
(OR)
- a) If for a two-dimensional potential flow, the velocity potential is given by
![]() = x
(2y 1)
= x
(2y 1)
Determine
the velocity at the point P (4,5). Determine also the value of stream function
![]() at the
point P. (6
M)
at the
point P. (6
M)
b) An open circular cylinder of 15 cm diameter and 100 cm long contains water up to a height of 80 cm. Find the maximum speed at which the cylinder is to be rotated about its vertical axis so that no water spills. (6 M)
UNIT III
- a) Derive the Bernoullis equation from fundamentals.
![]()
![]() = constant
= constant
State the assumptions made in the derivation of equation. (6M)
b) An oil of specific gravity 0.8 is flowing through a venturimeter having inlet diameter 20 cm and throat diameter 10 cm. The oil-mercury differential manometer shows a reading of 25 cm. Calculate the discharge of oil through the horizontal venturimeter. Take Cd = 0.98 (6 M)
(OR)
- a) Define displacement thickness. Derive an expression for the displacement thickness (6 M)
b) Find the displacement thickness, the momentum thickness and energy thickness for the velocity distribution in the boundary layer given by
![]() (6
M)
(6
M)
UNIT IV
- a) What are the different types of coefficients of orifice and explain them. (6 M)
b) Water discharge at the rate of 98.2 litres/sec through a 120 mm diameter vertical sharp-edged orifice placed under a constant head of 10 meters. A point, on the jet, measured from the vena-contracta of the jet has co-ordinates 4.5 meters horizontal and 0.54 meters vertical. Find the coefficients Cv, Cc and Cd of the orifice. (6 M)
(OR)
8. a) Explain the classification of Notches and Weirs. (6 M)
b) Find the discharge of water flowing over rectangular notch of 3 m length when the constant head of water over the notch is 40 cm. Take Cd = 0.6. (6 M)
UNIT V
9. a) Derive the Darcy-Weisbach equation
![]()
for computing loss of head due to friction in pipes (6 M)
b) Explain the classification of loss of energy in pipes. (6 M)
(OR)
10. a) What is Hagen Poiseuilles formula? Derive an expression for Hagen Poiseuilles formula. (6 M)
b) Water is flowing through a rough pipe of diameter 500 mm and length 4000 m at the rate of 0.5 m3/s. Find the power required to maintain this flow. Take the average height of roughness as k = 0.4 mm. (6 M)
*********
 KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
II/IV B. Tech I SEMESTER / DECEMBER
(REGULAR)
SOLID MECHANICS CE-212
Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 60
Answer One Question from each unit
Answer All Units
UNIT I
1. a) Draw Shear force Diagram for the Beam shown in fig. 1 (6 M)
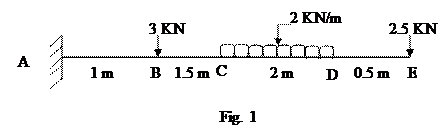 |
 b) Draw
Bending Moment Diagram for the frame shown in fig.2 (6
M)
b) Draw
Bending Moment Diagram for the frame shown in fig.2 (6
M)
(OR)
2. a) A simply supported beam of length 6 m carries a triangular load whose intensity varies uniformly from zero at the left end to 60 KN/m at the right end. It has one support at 1.5m from the left and the other support at the right end. Draw bending moment diagram for the beam. (6 M)
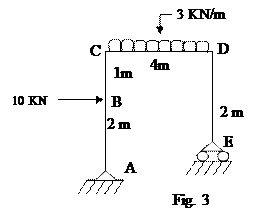 b) Draw
shear force diagram for the frame shown in fig.3. (6
M)
b) Draw
shear force diagram for the frame shown in fig.3. (6
M)
UNIT II
3. a) A cast iron test beam 20mm x 20mm in section and 1 m long and supported at the ends fails when a central load of 640 N is applied. What uniformly distributed load will break a cantilever of the same material with 50 mm wide, 100 mm deep and 2 m long? (6 M)
b) Calculate the moment of inertia about the centraidal axis of the I section shown in fig.4 (6 M)
 |
(OR)
4. a) A castiron pipe of external diameter 60 mm and 10 mm thickness and 5 m long is supported at its ends. The pipe carries a point load of 100 N at its centre. Calculate the maximum flexural stress induced? (6 M)
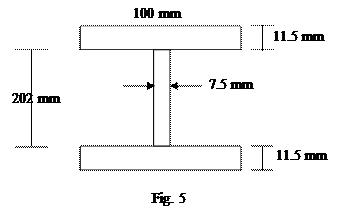
b) An I-section beam shown in Fig.5 is simply supported over a span of 10 m. If the maximum permissible bending stress is 80 N/mm2. What concentrated load can be carried at a distance of 3.5 m from one support? (6 M)
 |
UNIT III
5. a) A timber beam 100 mm wide and 150 mm deep supports a uniformly distributed load over a span of 2m. If the safe stresses are 28 N/mm2 in bending and 2 N/mm2 in shear. Calculate the maximum load which can be supported by the beam? (6 M)
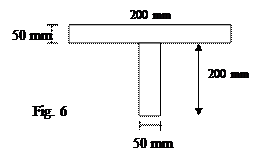 b) A
T- shaped cross section of a beam as shown in Fig.6 is subjected to a vertical
shear force of 100 KN. Calculate the shear stress at the neutral axis
and at the junction of web and flange. Moment of inertia about the horizontal
neutral axis is 1.134 x 108 mm4. (6 M)
b) A
T- shaped cross section of a beam as shown in Fig.6 is subjected to a vertical
shear force of 100 KN. Calculate the shear stress at the neutral axis
and at the junction of web and flange. Moment of inertia about the horizontal
neutral axis is 1.134 x 108 mm4. (6 M)
(OR)
6. a) Locate the shear centre for the section shown in fig. (6 M)
 |
b) A simply supported wooden
beam of span 1.3 m having a cross section of 150 mm wide and 250 mm deep.
It carries a concentrated load of W at the centre. Allowable working
stresses are ![]() = 7 N/mm2
(bending);
= 7 N/mm2
(bending); ![]() q = 1 N/mm2
(Shear). What is the safe load? (6 M)
q = 1 N/mm2
(Shear). What is the safe load? (6 M)
UNIT IV
7. a) Write the assumptions made in the theory of pure torsion? (6 M)
b) Determine the diameter of a solid circular shaft which will transmit 90 KW at 160 rpm if the shear stress in the shaft is limited to 60 N/mm2. Find also the length of the shaft, if the twist not exceed 1 degree over the entire length. Take G = 8 x 104 N/mm2. (6M)
(OR)
8. a) A solid circular shaft is to transmit 300 KW at 100 rpm. If the shear stress is not to exceed 80 N/mm2. Find the diameter of the shaft. What percentage saving in weight would be obtained if this shaft is replaced by a hollow one whose internal diameter equal to 0.6 times of the external diameter. The length, the material and the max shear stress are equal. (6 M)
b) A solid shaft of 200 mm diameter has the same cross sectional area as that of a hallow shaft of the same material with inside diameter 150 mm. Find the ratio of power transmitted by the two shafts at the same speed. (6 M)
UNIT V
9. a) A close coiled helical spring is to have a stiffness of 1 N/mm of compression under a max.load of 45 N and a Shear stress of 126 N/mm2. The solid length of the spring (when the coils are touching) is to be 45 mm. The diameter of the wire and the number of coils required. Take modular of rigidity, C = 4.2 x 104 N/mm2. (6 M)
b) A laminated spring 1 m long is made up of plates each 50 mm wide and 10 mm thick. If the bending stress in the plates is limited to 100 N/mm2, how many plates will be required to enable the spring to carry a central point load of 2000 N. If E = 2.1 x 105 N/mm2, what is the deflection under the given load of 2000 N. (6 M)
(OR)
10. a) A helical spring is made of 12 mm diameter steel wire by winding it on a 120 mm diameter mandrel. If there are 10 active turns, what is the spring constant. Take C = 8.2 x 104 N/mm2 what force must be applied to the spring to elongate it by 40mm?
b) A leaf spring is to be made of seven steel plates of 65 mm wide and 6.3 mm thick. Calculate the length of the spring so that it may carry a central load of 2750 N the stress being limited to 160 N/mm2. Calculate also the deflection at the centre of spring, Take E = 2.1 x 105 N/mm2. (6 M)
 KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
KONERU LAKSHMAIAH COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
II/IV B. Tech I SEMESTER / DECEMBER
(REGULAR)
SURVEYING I CE-215
Time: 3 Hrs Max. Marks: 60
Answer One Question from each unit
Answer All Units
UNIT I
1. (a) Define Surveying. What are the principles of surveying? Explain them briefly. - 4M
(b) In brief explain the various classifications of surveying. - 8M
(OR)
2. (a) Differentiate between accuracy & precision with an example. - 4M
(b) What are the different types & sources of error in surveying? - 8M
UNIT II
3. (a) What are the different methods of ranging? - 4M
(b) Explain how chaining is employed on flat and sloping ground with an example - 8M
(OR)
4. (a) A line was measured with a steel tape 30 m long, standardized at 150 C, with a poll of 100 N. Find the correction per tape length, if the temperature at the time of measurement was 200 C and the pull extended was 160 N
Weight of 1 cm3 steel = 0.0789 N
Weight of Tape = 8 N
Modulus of Elasticity = 2.10 x 105 N/mm2
Coefficient of Expansion of type 10 C = 7.1 x 10-7 - 6M
(b) Explain the various obstacles in ranging. - 6M
UNIT III
5. (a) Sketch & describe the salient features of prismatic compass. - 8M
(b) What is meant by local attraction? How is it detected? - 4M
(OR)
6. (a) A closed compass traverse ABCD was conducted round a lake and the following bearing were obtained. Determine which of the stations are suffering from local attractions and give the values of the corrected bearing. - 8M
Line FB BB
AB 740201 256001
BC 1070201 2860201
CD 2240501 440501
DE 3060401 126001
(b) What is resection? Explain resections by trial & error method. - 4M
UNIT IV
7. (a) Draw a neat sketch of a verneir theodolite and explain the function of the various parts
- 8M
(b) Explain the working principle of Box Sextant. - 4M
(OR)
8. (a) Explain the temporary adjustments and source of error in verneir theodolite. - 6M
(b) Explain the basic methods of horizontal angle measurement in verneir theodolite - 6M
UNIT V
9. (a) The following consecutive reading were taken with dumpy level at 4 m leveling staff on continuously sloping ground at 30 mt intervals. - 8M
0.680, 1.455, 1.855, 2.330, 2.885, 3.380, 1.055, 1.860, 2.265, 3.540, 0.835, 0.945, 1.530, 2.250
The R.L. of the starting point was 80.750
(a) Rule out a page of level book and enter the above readings
(b) Apply the arithmetic check including the check in I.S.
(c) Carry out reductions of its by rise and fall method
(d) Determine the gradients of the line joining the first & last point
(b) Explain in brief the terms - 4M
(i) Curvature
(ii) Refractions
(OR)
10. (a) What do you mean by contour and contour interval? - 4M
(b) Explain the characteristics of cantors with neat sketches. - 8M
| Earning: Approval pending. |
