Institute of Actuaries of India 2010 CT-5 Contingencies Core Technical ( ) - Question Paper
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
EXAMINATIONS 16th November 2010 Subject CT5 - General Insurance, Life and Health Contingencies
Time allowed: Three Hours (10.00 - 13.00 Hrs)
Total Marks: 100
INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES
1) Please read the instructions on the front page of answer booklet and instructions to examinees sent along with hall ticket carefully and follow without exception
2) Mark allocations are shown in brackets.
3) Attempt all questions, beginning your answer to each question on a separate sheet. However, answers to objective type questions could be written on the same sheet.
4) In addition to this paper you will be provided with graph paper, if required.
Q. 1) Explain why life insurers set up reserves for the endowment assurance policies.
Q. 2) i) Calculate the value of the following benefits:
[4]
a) Term assurance of Re 1 on a life aged 40 and term of 20 years.
b) Endowment assurance of Re 1 on a life aged 40 and term of 20 years.
(5)
Basis: Ix = (120 - x) (for x < 120); Interest Rate: 4% per annum.
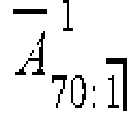
consecutive integer ages.
(5)
[10]
Basis: Mortality: ELT15 (Males); Interest rate: 7.5% per annum
Q. 3) A large industrial company recruits a constant number of school leavers aged exactly 18 years on 1st July each year.
Upon joining, workers undergo training for one year. Of those who complete this period of training, ten percent fail a final test of competence and are dismissed. Employees may also leave service voluntarily at any time. The independent rate of voluntary withdrawal from service is 0.15 for trainees and 0.10 at each age for fully trained employees.
The occupation is hazardous and all workers, including trainees, are exposed to the risk of injury. The independent rate of injury is 0.05122 at age 18 and 0.05003 at ages 19 and above.
An employee who is injured is transferred to alternate work with a subsidiary company, at a relocation cost of Rs 1000.
The independent mortality rate for all employees aged 18 is 0.00112, for aged 19 is 0.00117 and for aged 20 is 0.00119.
The number of employees attaining age 21 each year is 500.
(1) Construct a service table covering the first 3 years of employment with the original company, distinguishing between those about to take the final test of competence and those who pass it. [Note: Regard failing the test as a special mode of decrement] (9)
(2) How many people are recruited on each 1st July? (1)
Q. 4) i) Write down in the form of symbols, and also explain in words, the expressions Death Strain at Risk, Expected Death Strain and Actual Death Strain.
(3)
ii) A life insurer issues the following policies:
15-year term assurances with a sum assured of Rs.3,00,000 where the death benefit is payable at the end of the year of death and premiums are payable annually in advance.
15-year pure endowment assurances with a sum assured of Rs.1,50,000 and premiums are payable annually in advance.
5-year single premium temporary immediate annuities of Rs. 50,000 per annum.
On 1 January 2007, the company sold 5,000 term assurance policies and 2,000 pure endowment policies to male lives aged 45 exact and 1,000 temporary immediate annuity policies to male lives aged 55 exact. During the first two years 2007 & 2008, there were fifteen actual deaths from the term assurance portfolio, five each from pure endowment assurance & immediate annuity portfolios.
During the calendar year 2009, there were eight actual deaths from the term assurance portfolio and one actual death from each of the other two portfolios. Calculate the total mortality profit or loss to the life insurer in the year 2009.
Basis:
Interest Rate: 4% per annum
Mortality: AM92 Ultimate for term assurances and pure endowments; PMA92C20 for annuities (13)
[16]
Q. 5) (i) Describe three types of reversionary bonuses that may be given to a with profits contract. (4)
(ii) A life insurance company issues a 25-year with profits endowment assurance policy to a male life aged 40 exact. The sum assured of Rs.100,000 plus declared reversionary bonuses are payable on survival to the end of the term or immediately on death, if earlier. Calculate the monthly premium payable in advance throughout the term of the policy if the company assumes that future reversionary bonuses will be declared at a rate of 1.92308% of the sum assured, compounded and vesting at the end of each policy year.
Basis:
Interest 6% per annum
Mortality AM92 Select
Initial commission 87.5% of the total annual premium
Initial expenses Rs. 175 paid at policy commencement date
Renewal commission 2.5% of each monthly premium from the start of the second policy year
Renewal expenses Rs. 65 at the start of the second and subsequent policy years
Claim expense 2.5% of the claim amount (10)
[14]
(i) State the conditions necessary for gross premium retrospective and prospective reserves
to be equal. (3)
Q. 6)
(ii) Demonstrate the equality of gross premium retrospective and prospective reserves for a whole life policy, given the conditions necessary for equality. (4)
(i) Identify three classes of pensioners in receipt of a benefit from a pension scheme. (3)
Q. 7)
(ii) State, with examples, three distinct types of selection in the membership of a pension scheme. (3)
A life insurer issues 4-year unit linked endowment assurance contract to a male life aged 40 exact under which level premiums of Rs 10,000 per annum are payable in advance.
Q. 8)
In the first policy year, 45% of the premium is allocated to units and 100% in the subsequent years. The fund management charge is 1.0% p.a. and is deducted at the end of each year.
If the policyholder dies during the term of the policy, the death benefit of 10 times the annual premium or the bid value of units after deduction of fund management charge, whichever is higher, is payable at the end of the year of death. On surrender or on survival to the end of the term, the bid value of the units is payable at the end of the year of exit.
The company uses the following assumptions in its profit test of this contract:
Independent rates of Mortality: 80% of AM92 Select
Independent rates of withdrawal: 20% p.a. in the first policy year;
10% p.a. in subsequent years.
Rate of growth of unit fund: 10% per annum
Rate of interest on non unit fund: 5% per annum
Initial Commission: 15% of first year premium.
Renewal Commission: 3% of subsequent premium.
Initial Expenses: 20% of first year premium.
Renewal Expenses: 2% of subsequent premium.
Risk Discount Rate: 15% per annum.
(i) Calculate the profit margin on the assumption that the insurer does not zeroise future negative cashflows and those decrements are uniformly distributed over the year. (14)
(ii) Calculate the profit margin if the insurer zeroise future negative cashflows by setting up expected provisions that must be set up at the end of each year, per policy in force at the start of the year. (5)
|
(iii) The Regulator recently issued guidelines on unit linked contracts that the allocation to units in any year cannot be less than 90% of the premium. What are the risks to the insurance company because of the new regulations in case the insurance companies decided to set allocation charges as the maximum allowed by the regulations without |
 |
Q. 9) (i) Express in terms of ax , axx and the rate of interest.
(2)
(ii) Amit and Vijay are both aged 60. A life office has been asked to issue a special joint-life assurance policy providing Rs 1, 00,000 at the end of the year of death of the first to die of these two lives. In addition, if Amit is the second to die, a further Rs 50,000 will be payable at the end of the year if his death. The policy is to have annual premiums payable during the joint lifetime of Amit and Vijay.
Write down (but do not evaluate) the formulae to calculate the annual premium assuming expenses are 5% of all premiums, with an additional initial expense of Rs 1,000, in terms of ax , axx and the rate of interest. (4)
(iii) Write down (but do not evaluate) formulae for the reserve at duration 10 years (immediately before the payment of the premium then due) on the premium basis, if
(a) Both Amit and Vijay are alive; and
(b) Vijay has died but Amit is alive. (2)
Page 5 of 5
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
