Institute of Actuaries of India 2010 ST2 Life Insurance Specialist Technical ( ) - Question Paper
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
EXAMINATIONS 11th November 2010 Subject ST2 Life Insurance
Time allowed: Three hours (14.45* - 18.00 Hrs) Total Marks: 100 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE CANDIDATES
1. Please read the instructions on the front page of answer booklet and instructions to examinees sent along with hall ticket carefully and follow without exception
2. * You have 15 minutes at the start of the examination in which to read the questions. You are strongly encouraged to use this time for reading only, but notes may be made. You then have three hours to complete the paper.
3. You must not start writing your answers in the answer sheet until instructed to do so by the supervisor
Q. 1) With regards to a unit-linked insurance product:
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
i) Describe the difference between a bid pricing basis and offer pricing basis. (2)
ii) Explain why it might be advantageous, ignoring the performance of individual investments, for a policyholder to invest through a unit-linked life insurance product instead of directly in investment markets. (3)
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
[5]
Q. 2) With regard to asset share calculations
i) List the components used in calculation of asset shares (4)
ii) State the two most important applications of asset shares in life insurance business (1)
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
[5]
Q. 3) A new CEO has recently joined a life insurance company. She has a mandate from the Board of the company to simplify existing products from an administrative perspective; make products easier for customers to understand; and to suggest ways to make products more attractive. She has come up with the following ideas. Discuss the issues that may arise for each of the following suggestions
i) The insurance company sells a lot of one year renewable group term business and charged its clients employee age dependent rates. The CEO has suggested that based on risk profile of a particular client company, they should offer a single age independent rate to be applicable for all business during the next year. This rate would
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
not be guaranteed for future years. (3)
ii) The insurance company sells participating endowment business with bonuses being declared as addition to benefits. The company declares both reversionary and terminal bonuses. The CEO has suggested that the surplus that is being generated (that is eventually used towards addition to benefits) could instead be paid out as regular cash dividends. Additionally, the sales force can position this cash as a premium offset option where policyholders would not be required to pay in their premiums once there
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
is enough cash to support premiums. (6)
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
[9]
Q. 4) You have joined a small life insurance company in India. The company has been in existence for 5 years and sells only term assurance (mortality related) products.
You have been asked to examine the adequacy of the reinsurance arrangements of the company. You discover that the company retains only 10% of each risk, up to a maximum of Rs5 lakh, and reinsures the rest with one specific reinsurer. You questioned the CEO as to the reason for this and she informed you that it was because the company was small, had little actuarial experience and expertise when it started up, and its capital was limited. However the company has since gained actuarial experience and has more capital and hence the CEO is happy for you to recommend a change in the reinsurance strategy.
i) Describe how you could go about deciding what level of retention your company
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
should have in the future. (8)
ii) Outline briefly the factors you would consider in choosing which re-insurer(s) to work
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
with in the future. (6)
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
[14]
Q. 5) i) List the principles that an actuary should consider when determining the surrender value
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
basis for whole life and endowment assurance policies. (6)
ii) List reasons why a policyholder might wish to make his policy paid-up, and reasons
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
why an insurance company might prefer this to a surrender. (3)
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
[9]
Q. 6) An insurance company has a partnership agreement with a bank that sells large volumes of home mortgages with an average term of 20 years. The bank wants to cover its home loan portfolio against mortality of its borrowers. The insurance company offers a single premium term insurance to the bank that in turn offers this assurance to its borrowers on a voluntary basis. This contract would be sold under a group version and the insurance company would not be carrying out any medical underwriting.
i) Highlight the risks to the insurance company under this contract. (2)
ii) The products team of the insurer has come up with a proposal where the bank will offer a home mortgage loan to its borrowers bundled with a participating endowment policy. Mortgage customers of the bank would be required to pay regular premiums into a participating endowment policy offered by the insurer. The point-of-sale illustrations show that the maturity proceeds from the policy should cover the capital sum borrowed based on current investment returns. The home loan borrowers would continue to pay the interest payments (only) to the bank.
Highlight the benefits and risks under this product proposal to the loan borrowers, the bank and the insurance company. (10)
iii) Suggest ways in which some of these risks can be mitigated along with pros and cons
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
of the stated mitigants (5)
INSTITUTE OF ACTUARIES OF INDIA
[17]
Q. 7) An insurance company in a country sells unit linked endowment assurance business and participating endowment assurance business.
For unit linked business, the regulations governing reserving in this country mandate use of a unit reserve plus a non unit reserving approach where non unit reserves are floored to zero at each contract level. The company chooses an asset strategy where-in the unit reserves are matched exactly and non unit reserves are kept in secure government bonds.
For participating business, reserving is based on a gross premium basis where reserves are floored to surrender values at a contract level. The asset strategy for this set of business is to invest in secure government bonds and any surplus has to be distributed in ratio of 90:10 to policyholders and shareholders by legislation
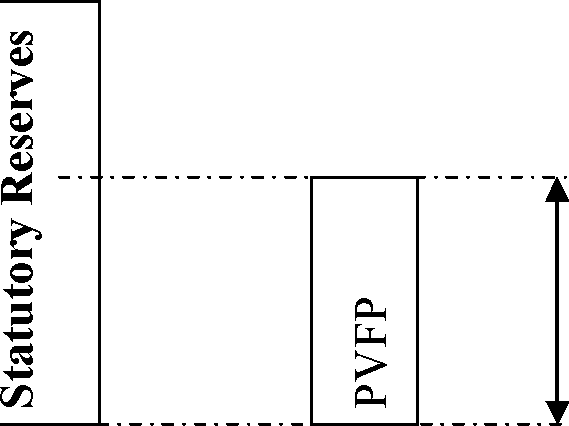
The company is presenting to its Board some key matrices and you see the following slide
Present Value of future profits are as much as 50% of statutory reserves
i) Briefly outline the reasons that could constitute the difference between statutory reserves and PVFP for this company. (3)
ii) The country has a simple factor based solvency regime based on reserves under the contract and Sum at Risk although the factors do vary by product line. Briefly list the merits and demerits of such a solvency approach for this company. (4)
iii) Because of the statutory prudence in reserving, the insurer is not able to free up its capital and hence it is contemplating taking out financial reinsurance. Outline the factors that the following stakeholders should consider when assessing this proposal.
Insurance Company (4)
Reinsurance Company (3)
Regulatory authority (3)
[17]
Q. 8) In an Asian developing country group farming is a major industry. The large group farms are located far away from the major cities. The farmers live in relatively isolated communities close to the group farms. The high-density housing area in which they live is owned by the company that owns the farms.
The insurance for this farm worker community has been neglected by the insurance industry. The company that owns the farms has approached an insurer to provide the employees with level regular premium term assurance policies. The contracts offered will have a decreasing sum assured. The cover starts at 3 times the annual salary and reduces to a level equaling the employees annual salary at the retirement age of 60 (which would be the end of the policy term).
The policies are to be sold through insurance agents employed by the insurer who will collect premiums on a weekly basis from the employees (who are paid in cash on a weekly basis). The only evidence of good health required to issue a policy will be that the employee is actively at work at the time of the application.
The farming company will provide the agents with office space and opportunities to market contracts to its employees.
i) Outline briefly the various aspects of insurance distribution or design which the countrys regulator may control? (4)
ii) Explain why the contracts are unlikely to offer withdrawal benefits? (2)
iii) Outline the risk the insurance company would face in respect of the items below if it goes ahead with the proposal:
a) mortality
b) expenses
c) withdrawals
The future possibilities of this market is very attractive to the insurance company as it has been losing market share over the last 5 years in the term assurance market. (8)
iv) Outline the reasons why the company may have been losing market share. (5)
v) Outline various actions the insurance company could take to reverse the trend of its failing market share in the term assurance market. (5)
[24]
Page 5 of 5
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
