Indian Institute of Technology Gandhinagar 2011 M.Tech. Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering Architectural and planning gate- - Question Paper
2011 AR
AR : ARCHITECTURE AND PLANNING
Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. Write your name and registration number in the space provided at the bottom of this page.
2. Take out the Optical Response Sheet (ORS) from this Question Booklet without breaking the seal.
3. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are asked to do so by the invigilator.
4. Write your registration number, your name and name of the examination centre at the specified locations on the right half of the ORS. Also, using HB pencil, darken the appropriate bubble under each digit of your registration number and the letters corresponding to your test paper code (AR).
5. This Question Booklet contains 16 pages including blank pages for rough work. After opening the seal at the specified time, please check all pages and report discrepancy, if any.
6. There are a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks. All these questions are of objective type. Questions must be answered on the left hand side of the ORS by darkening the appropriate bubble (marked A, B, C, D) using HB pencil against the question number. For each question darken the bubble of the correct answer. In case you wish to change an answer, erase the old answer completely. More than one answer bubbled against a question will be treated as an incorrect response.
7. Questions Q.l - Q.25 carry 1-mark each, and questions Q.26 - Q.55 carry 2-marks each.
8. Questions Q.48 - Q.51 (2 pairs) are common data questions and question pairs (Q.52, Q.53) and (Q.54, Q.55) are linked answer questions. The answer to the second question of the linked answer questions depends on the answer to the first question of the pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is unattempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated.
9. Questions Q.56 - Q.65 belong to General Aptitude (GA). Questions Q.56 - Q.60 carry 1-mark each, and questions Q.61 - Q.65 carry 2-marks each. The GA questions begin on a fresh page starting from page 10.
10. Unattempted questions will result in zero mark and wrong answers will result in NEGATIVE marks. For Q.l - Q.25 and Q.56 - Q.60, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. For Q.26 - Q.51 and Q.61 - Q.65, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. The question pairs (Q.52, Q.53), and (Q.54, Q.55) are questions with linked answers. There will be negative marks only for wrong answer to the first question of the linked answer question pair, i.e. for Q.52 and Q.54, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. There is no negative marking for Q.53 and Q.55.
11. Calculator is allowed whereas charts, graph sheets or tables are NOT allowed in the examination hall.
12. Rough work can be done on the question paper itself. Additionally, blank pages are provided at the end of the question paper for rough work.
|
Name | ||||||||
|
Registration Number |
AR | |||||||
Q. 25 carry one mark each.
Capital town of Gandhinagar has been designed by
(A) Norman Foster (B) B.V. Doshi (C) H.K. Mewada (D) Le Corbusier
Rajiv Awas Yojana of Ministry of Housing, Government of India addresses housing for
Q.l-
Q.l
Q.2
Q.3
Q.4
Q.5
Q.6
Q.7
Q.8
Q.9
Q.10
Q.ll
(A) Middle Income Group (C) High Income Group
The triangular space formed by two consecutive arches is (A) Tympanum (B) Spandrel (C) Regula
Rose Window is an iconic feature of
(D) Extrados
(D) Tone
A slab simply supported on all its edges with a ratio of longer side to shorter side greater or equal to 2.0 is designed as
The minimum road curb length required for parking 10 cars perpendicular to the road is
(A) 15 m (B) 25 m
(C) 35 m (D) 40 m
Which of the following generates heat island?
(A) Urban areas (B) Coastal areas
(C) Wetlands (D) Forest areas
The most suitable earthquake resistant built plan form is
(A) One way slab (C) Flat slab
Entablature consists of
(A) Architrave, Tenia, Cornice (C) Frieze, Comice, Triglyphs
Town planned for Motor Age refers to
(A) Toronto, Ontario (C) Radbum, New Jersey
(A) Notre Dame, Paris (C) St. Peters, Rome
Purity of colour is described by (A) Hue (B) Value
(B) Architrave, Frieze, Cornice (D) Cornice, Guttae, Tympanum
(B) Nassan Shores, Long Island (D) Green Belt, Maryland
(B) Hagia Sophia, Istanbul (D) Victoria Memorial, Kolkata
(B) Low Income Group (D) Slum Dwellers
(B) Two way slab (D) Coffered Slab
(C) Chroma
/
(A) (B) (C) (D)
Q. 12 Transfer of Development Right (TDR) is a tool used for
(B) Land development
(D) Infrastructure development
(A) Human development (C) Economic development
Q. 13 Dandaka form of settlement layout is basically a
(A) Grid Iron pattern (C) Radial pattern
(B) Ring radial pattern (D) Informal Pattern
Q. 14 Maximum horizontal angle from the speaker in a seating area of a lecture theatre should be
(B) 90
(A) 70
(C) 120
(D) 140
Q.15 U-value refers to
(A) Utility function for convective heat transfer
(B) Thermal transmittance of building components
(C) Energy transfer between thermal bridges
(D) Measure for area related heating and cooling loads
Q. 16 Consistency of cement is measured by
(A) Pycometer (B) Slump cone
(C) Universal Testing Machine (D) Vicats apparatus
Q. 17 The appropriate material for flooring of an external ramp of a building would be
(A) Polished granite (B) Wax polished marble
(C) Glazed ceramic tile (D) Rough finish sandstone
Q. 18 Which of the following is NOT a member of a Steel Truss?
(A) Gusset Plate (B) Wall Plate
(C) Fish Plate
(D) Anchor Bolts
Q. 19 Identify the odd one among the following
(A) Security deposit
(C) Performance bank guarantee
(B) Professional tax (D) Earnest money
Q.20 Weep hole is a term used to describe
(A) Perforations in the cast iron pipe used for boring
(B) Holes in retaining wall for draining water
(C) Holes in the cover plate of floor traps
(D) Holes dug in earth to recharge ground water
Q.21 Bus way, Busduct and Raceway are components of
(A) Security systems (B) Air conditioning systems
(C) Electrical systems (D) Water supply systems
Q.22 The difference between Wet Bulb Temperature and Dry Bulb Temperature is called
(A) Dry bulb depression (B) Wet bulb depression
(C) Variable depression (D) Atmospheric depression
Q.23 In India, one of the Slum Improvement initiatives is
(A) Special Residential Zone (B) Valmiki Ambedkar Malin Basti Awas Yojana
(C) Indira Awas Yojana (D) Eco Housing
Q.24 Suspended Floors is a structural system used in
(A) Lloyds Building, London (B) Jin Mao Building, Shanghai
(C) Petronas Tower, Kualalampur (D) Hongkong Shanghai Bank, Hongkong
Q.25 Residual method of valuation is used to determine
(A) Public Private Partnership Deal (B) Rent
(C) Property Tax (D) Selling Price
Q. 26 to Q. 55 carry two marks each.
Q.26 Match the buildings in Group I with their architects in Group II
P. Bibliotheca Alexandrina, Alexandria 1.1.M. Pei
Q. Institut du Monde Arab, Paris 2. Jean Nouvel
R. Bank of China, Hongkong 3. Daniel Libeskind
S. Jewish Museum, Berlin 4. Renzo Piano
5. Sn0hetta
(A) P-5, Q 2, R-l, S-4 (B) P-5, Q-4, R-l, S-3
(C) P-4, Q-2, R-5, S-3 (D) P-5, Q-2, R-1, S-3
Q.27 A room measuring 5 m x 3.5 m enclosed by brick wall has a ceiling at 3 m height. The room has a door and a window opening of 1 m x 2 m and 1 m x 1 m respectively. The quantity of plastering required for interior walls (in sqm) is
(A) 46.5 (B) 48 (C)51 (D) 68.5
Q.28 One cubic metre of Ordinary Portland Cement yields a volume of M15 concrete in the range of (A) 2 to 3 cum (B) 4 to 5 cum (C) 7 to 8 cum (D) 8 to 9 cum
Q.29 Match the CAD commands in Group I with their functions in Group II
|
Group I |
Group II |
|
P. LAYISO |
1. blends selected object to destination layer |
|
Q. LAYMCH |
2. freezes layer of selected object |
|
R. LAYMRG |
3. hides or locks layers other than those of selected objects |
|
S. LAYLCK |
4. assigns selected object to destination layer |
|
5. locks object of destination layer |
(A) P-2, Q-4, R-l, S-5 (B) P-3, Q-2, R-l, S-5
(C) P-4, Q-2, R-3, S-5 (D) P-3, Q-4, R-l, S-5
Q.30 Match the buildings in Group I with their corresponding structural forms in Group II
|
Group I P. Hall of Nations, New Delhi Q. Salvacao Church, Mumbai R. State Trading Corporation Building, New Delhi S. Matrimandir, Auroville |
Group II 1. Spherical Structure 2. Folded Plates 3. Octahedral lattice structure 4. Vierendeel girders 5. Shell roof structure |
(A) P-3, Q-5, R-4, S-l
(B) P-2, Q-5, R-4, S-l (D) P-3, Q-5, R-2, S-l
(C) P-3, Q-5, R-4, S-2
Q.31 Identify the INCORRECT statement
(A) Guggenheim, Bilbao is an example of Deconstructivism
(B) Silver Abstraction is a term used for metal clad modern high rise buildings
(C) Spiral Building in Tokyo has a curvilinear built form
(D) Free Building plan form is a concept given by Le Corbusier
Q.32 Match the terms in Group I with their descriptions in Group II
Q.34
(A) Aesthetics of form are a function of Golden Section
(B) Things are perceived as a whole
(C) Whole is greater than the sum total of its parts
(D) Elements with continuity are perceived together
Q.35 A site in a map drawn to scale of 1:16000 measures 75 sqcm. The actual area of the site in hectares is
|
Group I |
Group II |
|
P. Quoin |
1. Geometric representation of the universe |
|
Q. Stucco |
2. Small dome |
|
R. Mandala |
3. Triangular form above an opening |
|
S. Cupola |
4. Corner stone at the angle of buildings |
|
5. Plaster | |
|
(A) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-l |
(B) P-3, Q-5, R-l, S-4 |
|
(C) P-4, Q-5, R-l, S-2 |
(D) P-3, Q-l,R-5, S-4 |
|
Match the architectural styles in Group I with their features in Group II | |
|
Group I |
Group II |
|
P. West Asiatic |
1. Arches and pendentives |
|
Q. Greek |
2. Pagodas |
|
R. Byzantine |
3. Flying buttresses |
|
S. Japanese |
4. Orders and pediments |
|
5. Hanging gardens | |
|
(A) P-3, Q-2, R-l, S-4 |
(B) P-5, Q-4, R-l, S-2 |
|
(C) P-5, Q-4, R-l, S-3 |
(D) P-4, Q-3, R-5, S-2 |
|
Gestalts Laws of visual perception DO NOT relate to | |
(A) 120 (C) 192
(B) 162 (D) 256
Q.36 Identify the CORRECT CAD statements
P. SPLINE connects sequence of line segments into a single object
Q. SPLINE is a smooth curve passing through or near a given set of points
R. PLINE creates straight line segments, arc segments or both
S. PLINE can be closed only when its start and end points are coincident and tangent
T. PLINE allows adjusting the width and curvature of its multiline segments
U. SPLINE can be exploded into smaller segments
V. PLINE can be converted into a continuous curve segment
(A) P, R, S, U (B) Q, R, T, V (C) R, S, T, V (D) S, T, U, V
Q.37 Match the eminent personalities in Group I with their books and statements in Group II
P. Kevin Lynch 1. The Fountainhead
Q. Ayn Rand 2. Small is Beautiful
R. Paul D. Spreiregen 3. Site Planning
S. E. F. Schumacher 4. Urban Design : Architecture of Towns and Cities
5. Design of Cities
(A) P-4, Q-2, R-5, S-3 (B) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-5
(C) P-5, Q-l, R-4, S-2 (D) P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-2
Q.38 Match the urban forms listed in Group I with the towns listed in Group II
|
Group I |
Group II |
|
P. Grid lion |
1. New Delhi |
|
Q. Radial |
2. Washington D.C. |
|
R. Linear |
3. Copenhagen |
|
S. Finger plan |
4. Mumbai |
|
5. Canberra |
(A) P-2, Q-l, R-4, S-3 (B) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-5
(C) P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-2 (D) P-2, Q-l, R-4, S-5
Q.39 Consider the following features
1. Length finely proportional to its width
2. Statues as silhouettes against the sky above cornice lines
3. Fountains signifying fine vintage points
4. Series of different shapes connected by traditional narrow streets, column screens or arches The element of urban design which comprises the above is
(A) Vista (B) Piazza
(C) Rond Point (D) Bosque
Q.40 Match the instruments in Group I with their corresponding functions in Group II
|
Group I |
Group II |
|
P. Hygrometer |
1. Precipitation |
|
Q. Disdrometer |
2. Vapor Pressure |
|
R. Anemometer |
3. Solar Radiation |
|
S. Manometer |
4. Relative Humidity |
|
5. Velocity of Air |
(A) P-4, Q-l, R-2, S-3 (B) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-5
(C) P-l, Q-2, R-5, S-4 (D) P-4, Q-l, R-5, S-2
Match the features in Group I with the corresponding type of garden in Group II
Group I
Q.41
Group II
1. French gardens
2. English gardens
3. Chinese gardens
4. Mughal gardens
5. Japanese gardens
P. Symmetrical layout, water cascades, entombment Q. Radial layout, symmetrical sculpture, boulevards R. Occult symmetry, pontoon bridges, stepping stones S. Hierarchy of courts, hierarchy of gates, zoomorphic forms
(A) P-2, Q-l, R-4, S-3 (C) P-4, Q-3, R-5, S-l
(B) P-4, Q-l, R-5, S-3 (D) P-5, Q-l, R-2, S-3
Arrange the following sense of enclosures in a hierarchy of decreasing order
Q.42
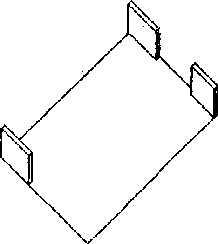
R
 |
|
T U |
(A) S>Q>U>P>T>R (C) P>Q>R>S>T>U
(B) U>S>Q>R>P>T (D) T>P>S>Q>U>R
Match the elements of Group I with their corresponding type in Group II
Q.43
|
Group I Group II P. Fire hydrant Q. Planter beds R. Letter box 1. Street Furniture 2. Street Hardware S. Traffic signs T. Lamp Posts (A) P-2, Q-l, R-l, S-2, T-2 (C) P-l, Q-l, R-2, S-2, T-2 |
(B) P-l, Q-l, R-2, S-l, T-l (D) P-2, Q-l, R-2, S-2, T-2 |
In a construction project schedule, A is the first activity. Activities B & C follow A. Activity D follows B & C. Activity E follows C. Activity F follows D & E.
Q.44
|
Activity |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
F |
|
Duration (in days) |
3 |
2 |
5 |
6 |
5 |
3 |
The critical time to complete the project will be
(A) 14 days (B) 16 days (C) 17 days (D) 20 days
The maintenance cost of a building will be Rs.2 lacs after 10 years. The annual sinking fund required for such maintenance @6% interest per annum will be
Q.45
(A) Rs. 17,200/- (B) Rs. 15,200/- (C) Rs. 13,200/- (D) Rs. 11,200/-
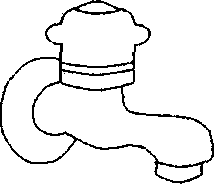
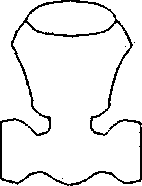
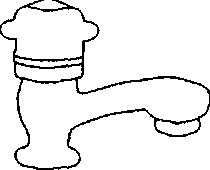
Q.46 Match the figures in Group I with the fixtures in Group II Group I
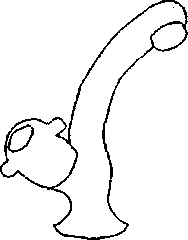
R
Group II
1. Sink Cock
2. Bib Cock
3. Pillar Cock 4. Stop Cock
(B) P-2, Q-3, R-l, S-4 (D) P-2, Q-4, R-3, S-l
(A) P-l, Q-4, R-2, S-3 (C) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-4
Q.47 Match the joints in Group I with the corresponding figures in Group II Group I
P. Butt joint Q. Rebated joint R. Table joint S. Tongue & Groove joint
Group II
1. 2. 3. 4.
(B) P-4, Q-l, R-3, S-2 (D) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l

(A) P-3, Q-4, R-l, S-2
(C) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-4
Common Data for Questions 48 and 49:
A beam of span L is simply supported at two ends. One half span of the beam weighs W and the remaining half span weighs 2W.
Q.48 Maximum shear force in the beam will be
(A) W (B) 1.25W (C) 1.75W (D) 3W
Q.49 Maximum bending moment will occur at
(A) L/16 from midpoint of the beam (B) Midpoint of the beam
(C) L/7 from midpoint of the beam (D) One of the endpoints of the beam
Common Data for Questions 50 and 51:
A building site has a plot of 500 sqm
Maximum allowable height - G+7 Area to be utilized for paved access roads - 10 %
Maximum ground coverage - 40% Runoff coefficient for paved surface - 0.9
Maximum allowable FAR - 2.0 Runoff coefficient for unpaved surface - 0.3
Q.50 If maximum allowable FAR is utilized, the minimum ground coverage would be
(A) 20 % (B) 25 % (C) 30 % (D) 35 %
Q.51 If it rains for 30 min. with an intensity of 10 cm/hr, minimum volume of rain water that can be collected will be
(A) 12.75 cum (B) 14 cum (C) 15 cum (D) 16 cum
Linked Answer Questions
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 52 and 53:
An auditorium having volume of 4500 cum and total absorption of all acoustic materials is 480 m2sabine
Q.52 The reverberation time of the auditorium is
(A) 1.0 second (B) 1.5 second (C) 2.0 second (D) 2.5 second
Q.53 To reduce reverberation time by 0.5 second, additional absorption (m2sabine) required would be
(A) 120 (B) 160 (C) 240 (D) 720
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 54 and 55:
A residential sector planned over an area of 100 hectares has been divided into various plots, each having one dwelling unit with an average household size of 5 persons. Remaining area is devoted for schools, roads, parks, shops etc.
Plot size Number 500 sqm 500 300 sqm 500 200 sqm 1000
Q.54 The gross density of the residential sector in persons per hectare would be
(A) 100 (B) 150 (C) 200 (D) 250
Q.55 Assuming 20% of the total population being higher secondary school going children and expected enrolment being 80% with per capita floor space requirement of 5.0 sqm, then minimum land required for school building with 40% ground coverage and FAR 0.5 would be
(A) 1.0 hectares (B) 1.6 hectares (C) 2.2 hectares (D) 2.8 hectares
General Aptitude (GA) Questions Q. 56 - Q. 60 carry one mark each.
Q.56 Choose the word from the options given below that is most nearly opposite in meaning to the given word:
Amalgamate
(A) merge
(B) split
(C) collect
(D) separate
Q.57 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence.
If you are trying to make a strong impression on your audience, you cannot do so by being understated, tentative or__.
(A) hyperbolic
(B) restrained
(C) argumentative
(D) indifferent
Q.58 Choose the most appropriate word(s) from the options given below to complete the following sentence.
I contemplated_Singapore for my vacation but decided against it.
(A) to visit
(B) having to visit
(C) visiting
(D) for a visit
Q.59 If Log (P) = (l/2)Log (Q) = (1/3) Log (R), then which of the following options is TRUE?
(A) P2 = Q3R2 (B) Q2 = PR (C) Q2 = R3P (D) R = P2Q2
Q.60 Which of the following options is the closest in the meaning to the word below:
Inexplicable
(A) Incomprehensible
(B) Indelible
(C) Inextricable
(D) Infallible
Q. 61 to Q. 65 carry two marks each.
Q.61 A container originally contains 10 litres of pure spirit. From this container 1 litre of spirit is replaced with 1 litre of water. Subsequently, 1 litre of the mixture is again replaced with 1 litre of water and this process is repeated one more time. How much spirit is now left in the container?
(A) 7.58 litres (B) 7.84 litres (C) 7 litres (D) 7.29 litres
Q.62 A transporter receives the same number of orders each day. Currently, he has some pending orders (backlog) to be shipped. If he uses 7 trucks, then at the end of the 4th day he can clear all the orders. Alternatively, if he uses only 3 trucks, then all the orders are cleared at the end of the 10th day. What is the minimum number of trucks required so that there will be no pending order at the end of the 5th day?
(A) 4 (B) 5 (C) 6 (D) 7
_AR
The variable cost (V) of manufacturing a product varies according to the equation V= 4q, where q is the quantity produced. The fixed cost (F) of production of same product reduces with q according to the equation F = 100/q. How many units should be produced to minimize the total cost (V+F)?
2011
Q.63
(A) 5 (B) 4 (C)7 (D) 6
P, Q, R and S are four types of dangerous microbes recently found in a human habitat. The area of each circle with its diameter printed in brackets represents the growth of a single microbe surviving human immunity system within 24 hours of entering the body. The danger to human beings varies proportionately with the toxicity, potency and growth attributed to a microbe shown in the figure below:
Q.64
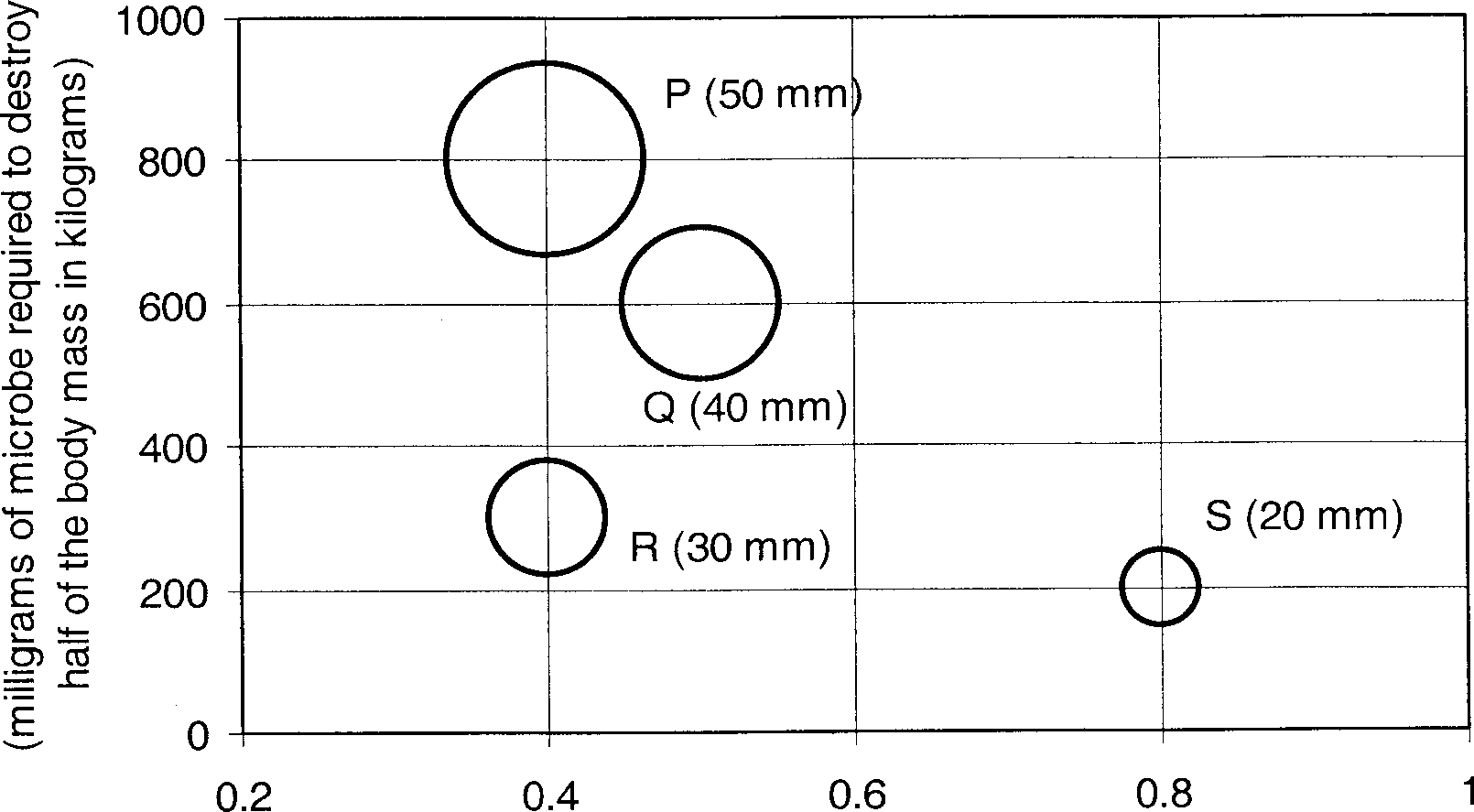
Potency
(Probability that microbe will overcome human immunity system)
A pharmaceutical company is contemplating the development of a vaccine against the most dangerous microbe. Which microbe should the company target in its first attempt?
(A) P (B) Q (C) R (D) S
Few school curricula include a unit on how to deal with bereavement and grief, and yet all students at some point in their lives suffer from losses through death and parting.
Q.65
Based on the above passage which topic would not be included in a unit on bereavement?
(A) how to write a letter of condolence
(B) what emotional stages are passed through in the healing process
(C) what the leading causes of death are
(D) how to give support to a grieving friend
AR 11/16
2010 AR
Duration: Three Hour* Maximum Marks: 100
Read the following Instructions carefully.
1. This question paper contains 16 pages including blank pages for rough work. Please check all pages and report discrepancy, if any.
2. Write your registration number, your name and name of the examination centre At the specified locations on the right half of the Optical Response Sheet (ORS).
3. Using HB pencil* darken the appropriate bubble under each digit of your registration number and the letters corresponding to your paper code.
4. All questions in this paper are of objective type.
5. Questions must be answered on the ORS by darkening the appropriate bubble (marked A, B, C, D) using HB pencil against the question number on the left hand side of the ORS. For each question darken Uk bubble of the correct answer, En case you wish to change an answer, erase the old answer completely. More than one answer bubbled against a question will be treated as an incorrect response.
6. There are a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks.
7. Questions Q. 1 - Q.25 will cany 1-mark each* and questions Q.26 - Q.55 will carry 2-marks each.
8. Questions Q.48 - Q.51 (2 pairs) are common data questions and question pairs (Q.52. Q.53) and (Q.54. Q.55) are linked answer questions. The answer to the second question of the linked answer questions depends on the answer to the first question of the pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is un-attempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated.
9 Questions Q.56 - Q.65 belong to General Aptitude (GA). Questions Q.56 - Q.60 will carry 1-mark each, and questions Q.61 - Q.65 will carry 2-marks each. The GA questions will begin on a fresh page starting from page 13.
10. Un-attempted questions will cany zero marks.
11. Wrong answers will cany NEGATIVE marks. For Q.1 - Q.25 and Q,56 - Q.60, *A mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. For Q.26 - Q.51 and Q.61 - Q.65, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. The question pairs (Q.52. Q.53). and (Q.54, Q.55) are questions with linked answers. There will be negative marks only for wrong answer to the first question of the linked answer question pair i.e. for Q.52 and Q.54, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. There is no negative marking for Q.53 and Q.55.
12. Calculator (without data connectivity) is allowed in the examination hall.
13. Charts, graph sheets or tables are NOT allowed in the examination hall.
14. Rough work can be done on the question paper itself. Additionally, blank pages are provided at the end of the question paper for rough work.
___AR_
3010
Q-i-
Q.i
Q.2
Q.3
Q.4
Q5
Q.6
Q7
Q.8
Q-9
Q.10
Q.ll
QJ2
Natural granite used for cladding in buildings belongs to the category of
(A) Igneous Rock (B) Acid Rock
(C) Sedimentary Rock (D) Metamorphic Rock
Flying Buttress' is an architectural element of
(A) Indian Architecture (B) Greek Architecture
(C) Gothic Architecture (D) Byzantine Architecture
A major hole in the Ozone layer has been identified above the
(A) Amazon Forest (B) Arctic Region (C) Savannah Grasslands (D) Sahara Desert A flat arch at the skewback should NOT have an angle less than IA)30D (B) 45 (C)60 <D)OT
Primary colours of natural light are
(A) Red, Blue, Yellow (B) Red, Green, Blue
(C) Red. Violet. Yellow (D) Red, Green, Yellow
Horizontal member of a shuiter that subdivides a window is termed as
(A)MuJlion (B) Transom (C) Reveal (D) Purlin
If the temperature of a composite bar made of copper and steel is raised, then the copper bar will be under
(A) Tension (B) Compression (O Shear (D) Torsion
H I. A. stands for
(A) East India Association (B) Environmental Impact Audit
(C) Environment Impact in Asia (D) Environmental Impact Assessment
A sieei truss with parallel upper and lower chords and inclined connecting members forming a series of equilateral triangles is known as
(A) Bowstring Truss (B) Wanen Truss
(C) Kingpost Truss (D) Scissors Truss
In water supply systems, the 'Reflux Valves' allow water to flow
(A) In one direction only (B) In both directions
(C) Through air locked joints (D) Only under low pressure
In Islamic Architecture, the circular dome was constructed over a square configuration through
(A) Grid Iron Coffered Slab
(B) Pendentives and Squ inch Arches
(C) Double Barrel Vaulls and Jack Arches
(D) Horizontal Cross Tie Members
With rcspecl to energy conservation and cost efficiency, the nature of an ideal built form should be
(A) High Rise Low Density (B) Medium Rise High Density
(C) Low Rise High Density (D) Low Rise low Density
AH
Q. 13 Two default sequences P and Q are given below :
P: Specily height ol extrusion or (Path]; 50 Specify angle of taper for extrusion <0>:
Q: Specify height of extrusion or [Path]: p Seled extrusion path or [Taper angle]:
The above mentioned sequences P and Q respectively, belong lo
(B) 2D and 3D AutoCAD
(D) 3D AutoCAD and 3D AutoCAD
(A) 2D AutoCAD and 2D AutoCAD
(C) 3D and 2D AutoCAD
Q.14 When shear stress exceeds the permissible limit in a RCC slab, then this problem is solved by
(B) Providing shear reinforcement
(D) Using thinner bars but more in number
(A) Increasing (he slab depth (C) Using high strength steel
Q. 15 Considering the totaJ heal losses from all fluorescent lamps lo be 79%, the Healing load (Btu / hr) due to office illumination with 48 ceiling mounted luminaires, each containing four 40 W fluorescent lamps and flat surface diffusers will be
(B) 15000 Blu / hr (D) 21000Btu/hr
(A) 10000 Btu / hr (C) 17500 Btu/hr
Q. 16 Prime resultant forces that develop in a structure due to an earthquake depend on
(A) Mass and Surface Area of structure
(B) Surface Area and Stiffness of structure
(C) Stiffness and Mass of structure
(D) Surface Area and Volume of structure
Q. 17 Concept of Serial Vision1 has been applied to the approach layout of
(A) Victoria Memorial Complex, Kolkaia (B) Umaid Bhawan Palace. Jodhpur
(C) Vidhan Soudha Precinct, Bangalore (D) Rashtrapati Bhawan Complex. New Delhi
Q.18 Advanced Traffic Lane Information is an important feature of
(A) Para Transit system (B) Intelligent Transportation system
(C) High Level Cable Car system (D) Pedestrian Travellator system
Q.19 A local authority can go for Urban Development through
(A) Land Acquisition (B) Land Pooling
{C) Transferable Development Rights (D) All the above
Q.20 The Planning document submitted for the selcctcd cities under JNNURM is
(A) Master Plan (B) Basic Development Plan
(C) City Development Plan (D) Outline Development Plan
Q.21 Excessive till of the Leaning Tower of Pisa has been checkcd by
(A) Pumping cement concrete mix under the dipping foundation
(B) Relocating heavier furniture to the rising side of the tower
(C) Raising the dipping side by massive Jack screws
(D) Pumping out mud and slurry from ihc foundation base of the rising side
Q.22 The Prittker Prize 2009 has been awarded to
(A) Zaha Hadid (C> Jean Nouvel
(B) Peter Zumthor (D) Norman Foster
Q 23 The age of a tree is determined by
(A) Counting the number of rings in the stem cross section
(B) Counting the number of leaves on the main branches
(C) Measuring the height of the tree from the root ball
(D) Measuring the canopy circumference of the tree
Q.24 Nakagin Capsule Tower. Tokyo famous for its spatial modular approach was designed by
(A) A rata hozaki (B) Tadao Ando
(C) Kisbo Kurokawa (D) Minoru Yamasaki
Q.2S Proportioning system used in the layout of Mughal Gardens is derived from
(A) Rational number system
(B) Constants of equilateral triangle
(C) Irrational number system
(D) Constants of right angled isosceles triangle
Q.26 - QSS carry two marks each*
Q.26 Match the cities in Group I with their form in Group IE
Group ii
P. Detroit Q.Copenhagen R. Stalingrad S. San Francisco
1 Star Form 2. Polycentrcd Net
3, Linear City
4, Ring Form
5, Galaxy
|
(A) P - l.Q-4,R-3,S-2 (C)P-5.Q- l,R-2,S-3 |
(B) P - 2, Q - 1. R - 3, S - 4 (DJP-4.Q-3.R- l.S-5 |
Q.27 Match the visionaries in Group I with their concepts in Group II
Group H
Group I
P. Clarence A, Perry Q. Constantinos Dojtiadis R. Paul Davidoff S. Walter Gropius
1. Post Modernism
2. Bauhaus
3. Advocacy Planning
4. Dynopolis
5. Neighborhood Unit
|
(A) P* 5,Q *4. R - 3. S - 2 (C) P - ),Q- 3. R - 2. S - L |
(B) P * 5. Q 4, R - 2, S -1 <D) P - 2, Q - 4, R - 2, S - 5 |
|
Group 1 Q.28 Match the trees in Group I with their botanical names in Group II P. Neem Q- Amalias R. Pipal S. Asoka (A)P- l,Q-2,R-3,S-4 (C) P - 2, Q -1* R - 4, S -5 |
Gnwpil ]. Cassia Fistula 2. Atadirachta Iodica 3. Ficus Bengalensis 4. Ficus Religiosa 5. Saraca Indica (B) P - 3, Q - 4, R - 5, S -1 (D) P-2, Q-3, R-5TS-4 |
Q.29 FolJowmg graphs represent the relationship between city size (in terms of population) on X-axis and area uDder residential use (in percent) on Y-axis. Identify the correct graph.




Q.30 Global climate change is expected to bring about a combination of the following changes. Identify the correct combination.
|
P. Increase in Biodiversity R. Loss of Biodiversity T. Sea Level Rise V. Emergence of New Islands |
Q. Emergence of New Diseases S. Loss of all Rocky Outcrops U. Extinction of Polar Bears |
(A) P. Q, R. S
(B)Q. R. T* U
(C) R,T, U, V
(D) Q, R, U, V
Q.3L Annual housing demand of a metropolitan city is estimated through the combination of the following components. Identify the correct combination.
|
P. New Entrants to the City R. New Relocated Slum Dwellers T. Unauthorized Dwelling Units V. Part of Backlog |
Q. Elderly Population Living in Cities S. Slum Squatter Dwellers U. Dilapidated Houses W. Any Other Houses |
(D) P, U, V
(B) U. S, Q
(A) Pt R. T
(C) W, Q, T
Q.32 A square pin jointed truss is subjected to a load P. acting in the direction of member US, ai joiat U. The force in member UR is

(A) 1.414 P (B) 1.000 P (C) 0.707 P (D) 0.000 P
|
Q.33 Given below is the sketch plan of a site showing contours. The broken lines show valleys and ridges. Identify the ridges and valleys. |
 |
|
(A) Ridges: P, Q, R Valleys: S, T |
(B) Ridges: T, V Valleys R. T, U
(D) Ridges; R, V, U Valleys: P.T
(Q Ridges: S. U Valleys: Q, T, V
Q.34 From the following, identify (he factors which influence the loudness of sound (o a listener in an enclosure
P. Loudness of sound at source
Q. Directivity factor
R. Length/Width ratio of the enclosure
S. Distance between sound source and listener
U Sound absorption coefficient of all enclosing surfaces
V. Surface area of enclosing surfaces
Y. Inside temperature level of the enclosure
(A) P, Q, S, Y, V (B) Q. R, S. U, Y (C) P. R. S. U, V (D) F, Q, ST U, V
Q.35 Match the lamps in Group I with their Colour Rendering index (CRI) in Group II Group I Group II
P. Mercury Vapour L 65 70
Q. Metal Halide 2. 40 - 55
R. High*pressure sodium 3, 20 - 25
S. Low-pressure sodium 4, 60 - 64
(A) P - 4, Q - 2, R - t, S - 3 (B) P - 3, Q 2, R - 4, S -1
<C) P - 2, Q -1, R - 4t S - 3 (D) P - 4, Q - 3, R - 2. S -1
Q.36 Match the terms io Group I with the architectural elements in Group II
Group I Group II
P. Tympanum L Auditorium Stage
Q. Proscenium 2. Door or Window Bands
R. Campanile 3. Circular House
S. Dymaxion 4, Church Tower
5. Horizontal Space for Services
(A) P - 1, Q - 3, R - 2, S - 4 (B) P * 2, Q - 3, R - 4, S - 1
(C) P - 2, Q - lt R - 4, S - 3 (D) F - 1, Q - 2, R - 3, S - 5
Q.37 Identify the most representative percentage distribution of landuse for a medium urban centre, according to UDPFI guidelines, where
Residential = R* Commercial = C, Transport = T, Industry = I.
(A) R = 30%, C = 20%> T = 12%, 1=10%
(B)R = 45%, C = 4%, T = 14%, 1 = 8%
(C)R = 30%, C-4%, T = 14%, 1=15%
(D) R = 45%, C = 10%, T 12%, I = 10%
Q.38 If the area of a plot is 1000 sq.m, area of its adjoining roads is 500 sq.m., maximum permissible FAR is 150 and maximum permissible Ground Coverage is 50%, then utilizing fullest ground coverage and assuming floors of equal area, (he number of storeys that can be built on the plot is
(A) 6 (B) 4 (C) 3 (D) 2
AR
Group n
t. Hasmukh C. Patel
2. Charles Correa
3. Hafeez Contractor
4. Karan Grover
5. BaJkrishna V. Doshi
JO 10_
Q.39 Mitch the buildings in Group I with their architects in Group II Group 1
P. British Council Library, New Delhi Q. Osbo Commune Campus, Pune R. C1I Sohrabji Godrej GTeen Business Centre, Hyderabad S, HM New Campus, Ahmedabad
(A)P - lfQ-2,R-3.S-4 {C)P-2, Q-3,R-5, S - J
<B) P - 2, Q - 3, R ~ 4, S - 1 <D) P-5, Q-4.R-3, S-2
Q.40 The age-sex compositions of three communities are represented by the diagrams P, Q and R as shown below,
 |
Mrte |
|
Female |
 |

Each of them implies a strong socio-economic characteristic as indicated below.
1. Aging community 3. Multi ethnic community
Identify the correct set out of the following
(A)P-4,Q 3,R 1 (C) P - 2, Q - 4, R -1
2. Economically vibrant community 4. Young community with high birth rate
(B) P - 2. Q - 4t R - 3 (D) P- 4, Q - 2, R - 3
Q.4! The conect requirements provided to seek permission from the local authority for constructing a small residential building are
P - Key Plan R - 2tonal Plan T - Power of Attorney V - Transport Plan X - Solid waste disposal plan
Q - Site Plan S - Building Plan U - Ownership Title
W - Drainage / Sewerage/ Water Supply Plan
(D) Q, S, T, V* X
(A) P, Q, R, S, W (B) P, Q, S, U, W (C) P. S, V, W, X Q.42 Two commands P and Q, in AutoCAD are given below.
P: Current saltings; Mode = TRIM. Radius = 0.0000 Sotod first object or (Potyfneffiatfus/Trim/mUKiple]:
Q: (TRIM mode) Current chamfer Dbt1 = 0.0000, Dist2 = 0.0000 Sefect first line or (Potytfne/Distance/Anglftffrirn/MethocVrnUltipte}:
The above mentioned commands are used for
(A) P: Trim and Q: Trim (C) P: Fillet and Q: Chamfer
(B) P: Fillet and Q: Trim (D) P: Trim and Q: Chamfer
Q.43 A T- beam slab is cast and cured. The shuttering has to be removed. The right sequence for removal of shuttering is
(A) Base of beam * Sides of beam * Base of slab Vertical support under beam
(B) Base of slab Sides of beam * Base of beam * Vertical support under beam
(C) Base of slab Sides of beam * Vertical support under beam * Base of beam
(D) Base of beam Base of slab * Sides of beam * Vertical support under beam
Q.44 Bioc lima tic chart developed by Victor Olgyay shows (he relationship between
(A) Temperature and Precipitation (B) Relative Humidity and Precipitation
(C) Air Movement and Temperature (D) Temperature and Relative Humidity

Q.45 In a display window of height H = S.66 m, of a retail store, a luminaire of intensity L is mounted at a distance l = 5m away from the rear. Its light beam is cast at an angle of 45 from the ceiling, as shown in the figure alongside.
The ratio of illumination at points Pj and P2 is
Q.46 Following figure shows network for a particular project consisting of four activities.

Normal duration and crash time for each activity are given below.
|
Activity |
Normal da ration |
Ciash time |
|
(in days) |
(in days) | |
|
1-2 |
3 |
2 |
|
2-3 |
4 |
2 |
|
2-4 |
5 |
4 |
|
3-4 |
7 |
5 |
The minimum time required for completion of project is
(A) 9 days (B) 13 days <C) 14 days (D) 19 days
Q.47 Pick the ODD one from the figures given below with respect to Reflection and Transmission of light.

|
Preferential Reflection and Transmission |
 |
|
Scauercd Reflection and Transmission |
(C)R
(A) P
(D)S
R
(B)Q
|
Diffused Reflection and Transmission Q |
 |
|
ConiroHed Reflection and Transmission $ |
Common Data Questions Common Data Tor Questions 48 and 49:
A simply supported beam PQ i$ subjected to a load of 100 kN through a rigid link at the centre of the beam as shown in the figure below

Q.48 Correct shear force diagram for the beam is
\ kN
1 kN 1 kN
r i
-1 kN
(B)
(A)
1 kN
_ 1 kN
<D)
(C)
Q 40 Bending moment diagram for the above beam is
10kN.m
lOkN.rn
(A)
(B)
5kNm
-Skh.m
(C)
Common Data for Questions 50 and 51:
A plot of land is io be developed as a residential neighbourhood. The key development conditions and project requirements are given below
|
Plot area : 1.25 Hectares Maximum permissible ground coverage : 30% Density of population : 800 ppHa |
Maximum permissible FAR : 350 Maximum permissible height: 45 m Average household size: 3 55 |
Building Type Percentage of Dwelling Units Total Built up Area (in sq. m)
L.I.G.
M.LG.
H.I.G,
4480
18600
14200
20
55
25
Q 50 The total number of dwelling units under L.LG,, M.LG. and H.I.G. respectively, are
|
U.G. 1 |
M.LG |
H.I.G. | |
|
p |
56 |
155 |
71 |
|
Q |
GO |
142 |
71 |
|
R |
56 |
150 |
63 |
|
S |
59 |
155 |
63 |
<A)P (B)S (C) Q (D)R
Q.51 Wjih the above data, the covered area of each flat (in sq. m) under L.I.G., M.LG. and H.I.G. respectively are
|
L.I.G. |
M.LG |
H.I.G. | |
|
P |
70 |
130 |
200 |
|
Q |
m |
120 |
200 |
|
R |
70 |
130 |
220 |
|
s |
80 |
\20 |
220 |
(A) Q (B) S (C) R (D) P
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 52 and 53:
A person has purchased an old building at a cost of Rs. 2,50,000/*, excluding the cost of land. The scrap value of the building is 10 % of (he cost of purchase and the future life of (he building is 20 years.
Q.52 The total amount of sinking fund at the end of 20 years will be
(A) Rs. 1,35,000/- (B) Rs. 1,90,000/- (C) Rs. 2.25,000/- (D) Rs. 2,30,000/-
Q.53 If the rate of interest is 7 %, then the annual installment of sinking fund will be
(A) Rs. 4,583/- (B) Rs. 4,855/- (C) Rs. 5,507/- (D) Rs. 5,640/-
SUtemeot for Linked Answer Questions 54 and 55:
A standpipe system in a 39 m tall building has a rooftop reservoir for fire fighting containing 1/2 hour water supply.
Q.54 Assuming that each floor has one hose, the delivery rate (in litre per second) of the fire hose at greatest pressure is
(A) 75 (BJ 78
(C) 81 (D) 84
Q.55 The volume of water (in cubic metre) required for (he reservoir is
(A) 105 (B) 110
(C) 120 (D) 130
General Aptitude (GA) Questions Q*56 - Q.60 carry one mark each.
Q.56 25 persons are in a room. 15 of them play hockey, 17 of them play football and 10 of them play both hockey and football. Then the number of persons playing neither hockey nor football is:
(A) 2 (B> 17 (C) 13 (D) 3
Q.57 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence:
If we manage to_our natural resources, we would leave a better planet for
our children,
(A) uphold <B) restrain
(C) cherish <D) conserve
Q.58 The question below consists of a pair of related words followed by four pairs of words. Select the pair that best expresses the relation m the original pair.
Unemployed: Worker
(A) fallow: land (B> unaware: sleeper
(C) wit: jester
(D) renovated: house
Q.59 Which of the following options is the closest in meaning to the word below;
Circuitous
(A) cyclic
(B) indirect
(C) contusing
(D) crooked
Q.60 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence:
His rather casual remarks on politics_his lack of seriousness about the subject.
(A) masked
(B) belied
(C) betrayed (O) suppressed
Q.61 - Q.65 carry two marks each.
Q.61 Hari (H), Gita (G), Man (I) and Saira <S> are siblings (i.e, brothers and sistere). All were bom on iu January. The age difference between any two successive siblings (that is bom one after another) is less than 3 years. Given the following facts:
i. Hans age + Gilas age > Irfan's age + Sairas age.
ii. The age difference between Gita and Saira is 1 year. However, Gita is not the oldest and Saira is not (he youngest.
iii. There are no twins.
In what order were they bom (oldest first)?
(A)HSIG (B)SGHI (O IGSH (D) IHSG
Q 62 5 skilled workers can build a wall in 20 days; 8 semi-skilled workers can build a wall in 25 days, JO unskilled workers can build a wall in 30 days. If a team has 2 skilled. 6 semi-skilled and 5 unskilled workers, how long will it take to build the wall?
(A) 20 days
(B) 18 days
(D) 15 days
(C) J 6 days
Q.63 Modem warfare has changed from large scale clashes of armies to suppression of civilian populations. Chcmical agents that do their work silently appear to be suited to such warfare; and regretfully, there exist people in military establishments who think that chemical agents are useful tools for their cause.
Which of the following statements best sums up the meaning of the above passage:
(A) Modem warfare has resulted in civil strife.
(B) Chemical agents are useful in modem warfare.
(C) Use of chemical agents in warfare would be undesirable.
<D) People in military establishments like to use chemical agents in war.
Q.64 Given digits 2, 2, 3. 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4 how many distinct 4 digit numbers greater than 3000 can be
formed?
(A) 50
<B)51
(C) 52
(D) 54
Q65 If 137 + 276 = 435 how much is 731 + 672?
(A) 534
<B)1403
CD) 1513
(C) 1623
MlO_____AK
Space for Rough Work
Space for Rough Work
SEAL
AR l6/\6
2009 AR
AR : ARCHITECTURE AND PLANNING
Duration : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. This question paper contains 16 printed pages including pages for rough work. Please check all pages and report discrepancy, if any.
2. Write your registration number, your name and name of the examination centre at the specified locations on the right half of the Optical Response Sheet (ORS).
3. Using HB pencil, darken the appropriate bubble under each digit of your registration number and the letters corresponding to your paper code.
4. All questions in this paper are of objective type.
5. Questions must be answered on Optical Response Sheet (ORS) by darkening the appropriate bubble (marked A, B, C, D) using HB pencil against the question number on the left hand side of the ORS. Each question has only one correct answer. In case you wish to change an answer, erase the old answer completely. More than one answer bubbled against a question will be treated as an incorrect response.
6. There are a total of 60 questions carrying 100 marks. Questions 1 through 20 are 1-mark questions, questions 21 through 60 are 2-mark questions.
7. Questions 51 through 56 (3 pairs) are common data questions and question pairs (57, 58) and (59, 60) are linked answer questions. The answer to the second question of the above 2 pairs depends on the answer to the first question of the pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is un-attempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated.
8. Un-attempted questions will carry zero marks.
9. Wrong answers will carry NEGATIVE marks. For Q.l to Q.20, lA mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. For Q. 21 to Q. 56, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. The question pairs (Q.57, Q.58), and (Q.59, Q.60) are questions with linked answers. There will be negative marks only for wrong answer to the first question of the linked answer question pair i.e. for Q.57 and Q.59, 2A mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. There is no negative marking for Q.58 and Q.60.
10. Calculator (without data connectivity) is allowed in the examination hall.
11. Charts, graph sheets or tables are NOT allowed in the examination hall.
12. Rough work can be done on the question paper itself. Additionally, blank pages are given at the end of the question paper for rough work.
Q. 1 - Q. 20 carry one mark each.
Q. 1 The essential difference between CPM and PERT is
(A) Critical Path vs. Critical Activity
(B) Arrow notation vs. Precedence notation
(C) Deterministic approach vs. Probabilistic approach
(D) Project Management vs. Network Analysis
Q.2 The minimum thickness of a wall where single Flemish bond can be used is
(A) Half-brick thick
(B) One-brick thick
(C) One-and-half-brick thick
(D) Two-brick thick
Q.3 On the colour wheel, the combination of Violet-Yellow or Orange-Blue are best described as (A) Complementary (B) Supplementary (C) Analogous (D) Monochromatic
Q.4 The sudden stoppage in the flow of water in a closed conduit results in a phenomenon called
(A) Cavitation (B) Hydraulic gradient
(C) Stack pressure (D) Water hammer
Q.5 The number of intersecting arches that support Bijapurs Gol Gumbaz is
(A) 4 (B) 8 (C) 12 (D) 16
Q.6 The 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments pertain to
(A) Abolishing the Urban Land Ceiling Act
(B) Providing restricted role to local courts to settle rural disputes
(C) Providing more responsibility to municipal and local bodies for planning and development
(D) Providing right to information for the general public
Q.7 A simply supported beam of length L carries a concentrated load of intensity P at its centre. The bending moment at the centre of the beam will be
(A) PL/2 (B) PL/4 (C) PL/6 (D) PL/8
Q.8 Desire lines are associated with
(A) Origin - Destination analysis in transportation planning
(B) Income - Expenditure analysis in personal finance management
(C) Cut - Fill analysis in landscape planning
(D) Demand - Supply analysis in economic planning
Q.9 GRIHA is a rating for Green Buildings given by
(A) The Energy Research Institute (
(B) Development Alternatives (D) Ministry of Power
(C) Bureau of Energy Efficiency (
Q.10 A cul-de-sac is a street where
(A) Only two-wheelers are permitted
(B) Through traffic is discouraged
(C) Pedestrians are not permitted
(D) Vehicles are permitted to move in one direction only
Q.11 Usonian houses were designed by
(A) Mies van der Rohe (B) Alvar Aalto
(C) Frank Lloyd Wright (D) Le Corbusier
Q.12 Increase in the volume of fine aggregate due to the presence of moisture is called
(A) Bulking (B) Buckling (C) Bending (D) Twisting
Q. 13 The Pattern Language theory was propounded by
(A) Christopher Alexander (B) Patrick Geddes
(C) John Ruskin (D) Amos Rapoport
Q. 14 As per IS:456-2000, the maximum area of tension reinforcement in a RCC beam shall not exceed x% of its cross-sectional area, where x is equal to
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 8
|
Q.15 No-cut no-filF lines are mostly used in (A) Land use planning (C) Earthwork computation |
(B) Interpretation of stereo-vision photographs (D) Interpretation of remotely sensed images |
Q. 16 The property of concrete measured by the Slump Test is
(A) Durability (B) Hardness (C) Strength
(D) Workability
Q.17 The Remote Sensing satellite that gives the highest spatial resolution is
(A) IKONOS 2 (B) IRS 1C/1D (C) Quickbird 2 (D) SPOT 5
Q.18 Development that meets the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs is termed by UNDP as
|
(A) Comprehensive Development (C) Human Development |
(B) Equitable Development (D) Sustainable Development |
Q.l9 The parameter that does NOT appear in a Psychrometric Chart is
(A) Wind speed (B) Dry bulb temperature
(C) Wet bulb temperature (D) Relative humidity
Q.20 Allowable stress in the design of a tension member in a steel truss is a function of
(A) Cross-sectional area of the member
(B) Yield stress of the material
(C) Slenderness ratio of the member
(D) Moment of inertia of the members cross-section
Q. 21 to Q. 60 carry two marks each.
Q.21 The parameters for determining Human Development Index are:
P. Educational Attainment
Q. Per capita Gross Agricultural Produce
R. Life Expectancy
S. Per capita Gross Domestic Product
T. Per capita State Domestic Product
(A) P, Q, S (B) P, Q, S, T (C) P, R, S (D) R, S, T
Q.22 Match the individuals in Group I with the works in Group II:
Group I
P. Hippodamus Q. Vitruvius R. Michelangelo S. Constantine
Group II
1. Aqueducts
2. Campidoglio
3. Hagia Sophia
4. Agora
5. Hanging Gardens
(A) P-4, Q-l, R-2, S-3 (B) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-5
(C) P-4, Q-5, R-l, S-3 (D) P-3, Q-4, R-l, S-2
Q.23 If the height of the facade = h, and the distance of the observer from the building = d, then match the enclosure types in Group I with their corresponding h/d ratio in Group II:
|
Group I Group II | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-4 (C) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-l
(B) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-l (D) P-5, Q-l, R-2, S-4
Q.24 The correct sequence of activities in Solid Waste Management is
(A) Collection -> Transportation -> Treatment -> Segregation
(B) Segregation Collection -> Transportation Treatment
(C) Collection -> Segregation Treatment Transportation
(D) Treatment Collection Transportation -> Segregation
Q.25 The principles of Universal Design include:
P. Flexibility in use Q. Tolerance for error R. Energy efficiency S. Low physical effort
(A) P, Q, R (B) Q, R, S (C) P, R, S (D) P, Q, S
Q.26 Match the urban design elements in Group I with their descriptions in Group II:
Group II
Group I
P. District Q. Landmark R. Node S. Pathway
1. Recognizable as having some common identifying character
2. Centre of activity
3. Network of major and minor routes
4. Prominent visual feature of the city
(A) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l (C) P-l, Q-2, R-4, S-3
(B) P-l, Q-4, R-2, S-3 (D) P-2, Q-4, R-l, S-3
Q.27 A commercial plot measures 100 m x 80 m. If the permissible Floor Space Index (FSI) is 3.0, and 50% of the ground is covered, then the maximum number of floors that can be built is
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 6
(D) 12
Q.28 Match the elements of a Buddhist Stupa in Group I with their traditional names in Group II:
Group I
P. Hemispherical Dome Q. Peripheral Railing R. Entrance Gateway S. Portion above dome
Group II
1. Vedika
2. Anda
3. Harmika
4. Nagara
5. Chaitya
6. Torana
(B) P-2, Q-6, R-4, S-3 (D) P-5, Q-6, R-l, S-2
(A) P-2, Q-l, R-6, S-3 (C) P-3, Q-l, R-5, S-2
Q.29 A microwave oven of 3 kW rating is operated for 30 minutes, a hot water geyser of 1 kW rating is operated for 15 minutes, and 5 fluorescent lamps of 60 W are operated for 6 hours. The total power consumed (in kWh) will be
(A) 1.80 (B) 3.55 (C) 18.01 (D) 35.50
Q.30 Match the building projects in Group I with their architects in Group II:
Group II
Group I
P. National Olympic Stadium, Beijing Q. Glass Pyramid, the Louvre, Paris R. Millennium Dome, London
1. Rem Koolhaas
2. Richard Rogers
3. Renzo Piano
S. Kansai Airport, Osaka
4. Tadao Ando
5. I. M. Pei
6. Herzog & de Meuron
(B) P-l, Q-6, R-2, S-4 (D) P-2, Q-5, R-l, S-3
(A) P-6, Q-2, R-3, S-4 (C) P-6, Q-5, R-2, S-3
Q.31 Identify the pre-historic structures in the following: P. Mastaba Q. Dolmen R. Menhir S. Pylon T. Stonehenge U. Thermae
(C) Q, S, T
(D) Q, R, T
(A) P, Q, R
(B) R, T, U
Q.32 Match the figures of cut bricks in Group I with their terms in Group II: Group 1
P Q
|
R U |
 |
|
MJ |



Group II
1. King Closer
(A) P-2, Q-3, R-l, S-4 (C) P-l, Q-2, R-4, S-3
4. Three Quarter Bat
3. Half Bat
(B) P-2, Q-l, R-3, S-4 (D) P-3, Q-4, R-l, S-2
2. Queen Closer
Q.33 A site has 6 contour lines and the length of the line joining the midpoints of the highest contour and lowest contour is 300 m. If the slope of the line is 1 in 10, then the contour interval (in m) is
(C) 50
(A) 5
(B) 6
(D) 60
Q.34 Match the plant types in Group I with their corresponding examples in Group II:
Group I
P. Climber Q. Shrub R. Tree S. Hedge
(A) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-4 (C) P-4, Q-l, R-2, S-3
Group II
1. Croton
2. Shirish
3. Duranta
4. Bougainvillea
(B) P-2, Q-4, R-l, S-3 (D) P-4, Q-3, R-l, S-2
Q.35
A neighbourhood with a total area of 200 hectares has a gross density of 300 persons per hectare (pph). If the residential area is 60% of the total area, then net density (in pph) of the neighbourhood is
(A) 300
(B) 450
(C) 500
(D) 750
Q.36 Identify the parameters used in the Hazen & Williams nomogram to calculate pipe diameter for water supply:
P. Flow rate in lit/sec Q. Pipe diameter in mm R. Population to be served S. Head loss in m/m T. Velocity in m/sec
(A) P, Q, S
(B) R, S, T
(C) P, R, S
(D) P, S, T
Q.37 Match the domes in Group I with their examples in Group II:
Group I
P. Dome with a huge central cut-out at the top Q. Dome with slit windows at the springing level R. Dome with an elliptical base S. Dome on a drum with a lantern on top
Group II
1. Pisa Cathedral
2. St. Peters Cathedral
3. Pantheon
4. Hagia Sophia
(A) P-2, Q-l, R-3, S-4 (C) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l
(B) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-4 (D) P-3, Q-4, R-l, S-2
Q.38 Match the Institutions in Group I with their Architects in Group II:
Group I
P. National Dairy Development Board, New Delhi Q. National Institute of Immunology, New Delhi R. Indian Institute of Management, Bangalore S. Jodhpur University, Jodhpur
Group II
1. B.V.Doshi
2. Charles Correa
3. A.P. Kanvinde
4. J.A. Stein
5. Raj Rewal
6. U.C. Jain
(A) P-3, Q-5, R-l, S-6 (C) P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-6
(B) P-6, Q-3, R-4, S-l (D) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-6
Q.39 Identify the urban functions that are included under Social Infrastructure:
P. Schools and colleges Q. Hospitals and clinics R. Roads and footpaths S. Parks and plazas T. Malls and markets U. Community centres
(A) P, Q, S, U (B) P, Q, S. T (C) P, R, S, U (D) Q, S, T, U
Q.40 Match the tombs in Group I with their architectural characteristics in Group II:
|
Group I Group II | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Q.41 Match the high-rise tube structural systems in Group I with their corresponding terms in Group II: Group I

P Q R S
1. Framed tube 2. Bundled tubes 3. Braced tube 4. Perforated shell tube
(A) P-l, Q-3, R-2, S-4 (B) P-4, Q-l, R-3, S-2
(C) P-4, Q-l, R-2, S-3 (D) P-l, Q-4, R-3, S-2
Q.42 A town with a population of 50000 has an average household size of 5.0. The number of occupied dwelling units is 8400 of which 10% are in dilapidated condition. The housing demand of the town is
(A) 760 (B) 1600 (C) 2440
(D) 10840.
Q.43 Match the items in Group I with those in Group H:
Group I
P. Hypostyle hall Q. Ziggurat R. Acropolis S. Triumphal arch
(A) P-l, Q-3, R-4, S-2 (C) P-l, Q-4, R-2, S-3
Group U
1. Roman architecture
2. Egyptian architecture
3. Assyrian architecture
4. Greek architecture
(B) P-2, Q-3, R-l, S-4 (D) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-l
Q.44 Match the Planning Models in Group I with their proponents in Group II: Group I
P Q R



Group U
1. Homer Hoyt 2. Ernest Burgess 3. V5n Thunen 4. Harris & Ullman 5. William Reilley
(A) P-l, Q-4, R-5 (C) P-4, Q-l, R-2
(B) P-2, Q-l, R-4 (D) P-3, Q-2, R-l
Q.45 The correct sequence in the four-stage model used for transportation planning is
(A) Trip generation Trip distribution -> Modal split Trip assignment
(B) Trip generation Trip assignment Modal split Trip distribution
(C) Trip distribution -> Modal split -> Trip assignment Trip generation
(D) Trip generation -> Trip distribution -> Trip assignment -> Modal split
>
m
Q.46 Identify the objects with which the EXPLODE command in AutoCAD can be used :
P. Polyline Q. Block R. Multi-line text
S. Arc T. 3D solid
(A) P, Q, R, T (B) P, R, S, T (C) P, Q, S (D) P, Q, S, T
Q.47 Match the planning terms in Group I with their descriptions in Group II:
|
Group I P. Eminent Domain Q. Police Power R. Transfer of Development Rights |
Group II 1. Protecting land by reassigning the rights to develop from one area to another 2. Regulating behaviour and enforcing order within the state territory 3. Protecting the individual development rights of a citizen by seeking state protection 4. Inherent power of state to seize private property without the owners consent |
(A) P-4, Q-l, R-2 (C) P-l, Q-3, R-2
(B) P-2, Q-3, R (D) P-4, Q-2, R-l
Q.48 A building has a rooftop area of 300 sq.m. If the average annual rainfall in the region is 700 mm and the Runoff Coefficient of the rooftop is 0.8, then the maximum amount of rainfall that can be harvested from the rooftop (in litres) is
(A) 168 . (B) 262
(C) 168000 (D) 262500
Q.49 Identify Pozzolana from the following materials:
P. Cement Q. Fly-ash R. Sand
S. Surkhi
(A) Q, S (C) P, Q, S
(B) P, R, S (D) P, R
|
Q.50 Match the notations in the given figure in Group I with corresponding names in Group II: Group I |
 |
Group II
1. Intrados 2. Extrados 3. Archivolt 4. Spring 5. Rise 6. Keystone
(A) P-6, Q-4, R-l, S-2, T-5
(B) P-6, Q-5, R-2, S-l, T-4
(C) P-6, Q-3, R-2, S-l, T-5
(D) P-6, Q-3, R-l, S-2, T-4
Common Data for Questions 51 and 52 :
A construction project has the following data:
Activity Duration (days) Predecessors
P 4
Q 3 P
R 7 P
S 2 P
T 4 Q
U 6 S
V 4 R, T, U
Q.51 The normal project duration (in days) is
(A) 14 (B) 15 (C) 16 (D) 17
Q.52 The critical activities of the project are
(A) P, Q, R, V (B) P, R, S, U (C) P, Q, T, V (D) P, S, U, V
Common Data for Questions 53 and 54:
A seminar hall has a volume of 2000 cu.m, and the total absorption of all acoustic materials without any audience is 80 m2-sabines.
Q.53 The reverberation time of the empty hall (in seconds) will be
(A) 1.0 (B) 4.0 (C) 8.0 (D) 12.0
Q.54 When the same seminar hall is filled with audience, the reverberation time is recorded as 2.0 seconds. Then the total absorption of all acoustic materials (in m2-sabines) will be
(A) 40 (B) 80 (C) 160 (D) 320
Common Data for Questions 55 and 56:
An office has an area of 60 sq.m with floor height of 3 m and occupancy of 5 persons. The external wall area is 40 sq.m which includes 4 sq.m of double glazed windows. The thermal transmittance rate (U) of external wall is 0.35 and window is 2.00. External and internal design temperatures are 34 C and 22 C respectively.
Q.55 The heat gain through the external walls and windows (in watts) will be
(A) 151.2 (B) 168.0 (C) 247.2 (D) 264.0
Q.56 If 20 lit/sec/person of air is extracted from the office, calculate the ventilation rate in terms of air changes/hour.
(A) 0.4 (B) 2.0 (C) 4.0 (D) 20.0
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 57 and 58:
A cantilever beam XY of 2.5 m span is supported at P and is subjected to 40 kN point load at free end Y.
Q.57 If self-weight of the beam is neglected, bending moment developed at the fixed end (in kN-m) is (A) 50 (B) 100 (C) 150 (D) 200
Q.58 A uniformly distributed load (in kN/m) that will result in the same value of bending moment at the fixed end is
(A) 12 (B) 22 (C) 32 (D) 42
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 59 and 60:
A semi-circular stone arch of thickness 30 cm is provided over an opening in a brick wall. The wall has length 3.0 m, width 30 cm and height 3.0 m. The opening has span 1.0 m and height 2.0 m.
Q.59 The quantity of stone work in the semi-circular arch (in cu.m) is
(A) 0.141 (B) 0.184 (C) 0.325 (D) 0.613
Q.60 The quantity of brickwork in the wall (in cu.m) is
(A) 1.369 (B) 1.445 (C) 1.629 (D) 1.798
13/16
2008 MAIN PAPER-AR
AR : ARCHITECTURE AND PLANNING
Duration : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 150
Read the following instructions carefully
1. This question paper contains 20 printed pages including pages for rough work. Please check all pages and report discrepancy, if any.
2. Write your registration number, your name and name of the examination centre at the specified locations on the right half of the ORS.
3. Using HB pencil, darken the appropriate bubble under each digit of your registration number and the letters corresponding to your paper code.
4. All the questions in this question paper are of objective type.
5. Questions must be answered on Objective Response Sheet (ORS) by darkening the appropriate bubble (marked A, B, C, D) using HB pencil against the question number on the left hand side of the ORS. Each question has only one correct answer. In case you wish to change an answer, erase the old answer completely. More than one answer bubbled against a question will be treated as a wrong answer.
6. Questions 1 through 20 are 1-mark questions and questions 21 through 85 are 2-mark questions.
7. Questions 71 through 73 is one set of common data questions, questions 74 and 75 is another pair of common data questions. The question pairs (76, 77), (78, 79), (80, 81), (82, 83) and (84, 85) are questions with linked answers. The answer to the second question of the above pairs will depend on the answer to the first question of the pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is un-attempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated.
8. Un-attempted questions will carry zero marks.
9. NEGATIVE MARKING: For Q.l to Q.20, 0.25 mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. For Q.21 to Q.75, 0.5 mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. For the pairs of questions with linked answers, there will be negative marks only for wrong answer to the first question, i.e. for Q.76, Q.78, Q.80, Q.82 and Q.84, 0.5 mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. There is no negative marking forQ.77, Q.79, Q.81, Q.83 and Q.85.
10. Calculator without data connectivity is allowed in the examination hall.
11. Charts, graph sheets and tables are NOT allowed in the examination hall.
12. Rough work can be done on the question paper itself. Additional blank pages are given at the end of the question paper for rough work.
Q. 1 - Q. 20 carry one mark each.
Q. 1 Function of Air Handling Unit in a building is to
(A) purify and re-circulate the cool air.
(B) supply purified bulk of air from outside to the window air-conditioner.
(C) collect the stale air from the room and throw it outside the building.
(D) act as a container in which air is carried from one place to the other.
Q.2 The KYOTO Protocol - 2003 addressed the issue of
(A) Bio-diversity
(B) Green House Gases
(C) Wetlands
(D) Rainwater Harvesting
Q.3 The principle of Solid Waste Management involves
(A) Reproduce, Reuse, Recycle.
(B) Recycle, Replenish, Reuse.
(C) Reduce, Reuse, Reproduce.
(D) Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.
Q.4 The correct diagram for a Mirror Stereoscope is



(C)
Q.5 Which of the following is not included in the UDPFI Guidelines for urban development ?
(A) Perspective Plans (B) Development Plans
(C) City Development Plans (D) Annual Plans
Q.6 A system of art-appreciation characterized by an unorthodox experimental approach to appreciate visual, literary and musical aspects of a design process, is called
(A) Avant-garde. (B) Post-modernism.
(C) Neo-impressionism. (D) Proto-Deconstruction.
Q.l An applied science of design concerning universal human characters and configurations aiming at effective utility and safety is called
(A) Anthropometry. (B) Cognitive behavioural mapping.
(C) Universal design. (D) Ergonomics.
Q.8 'Entasis is a visual correction for end columns by providing
(A) a slight convexity to the columns.
(B) a slight concavity to the columns.
(C) a major convexity to the columns.
(D) a major concavity to the columns.
Q.9 The first group of people to influence the architecture of South-east Asia and the Amaravati School of Art was
(A) Sakas and Palas. (B) Satavahanas and Pandyans.
(C) Pallavas and Guptas. (D) Rashtrakutas and Chalukyans.
Q.10 A linear regression model involving one independent and one dependent variable requires at least
(A) One pair of data. (B) Two pairs of data.
(C) Three pairs of data. (D) Four pairs of data.
Q. 11 Identify the FALSE statement.
(A) Susceptibility to non-structural elements damage in any building would be high even in a moderate level earthquake.
(B) For important non-structural elements, no structural analysis is required to assess vulnerability.
(C) Earthquake damage to non-structural elements results in loss of critical functions.
(D) The non-structural elements can be retrofitted appropriately.
Q.12 Under which category the percentage of land use decreases with an increase in city size ?
(A) Residential (B) Commercial
(C) Recreational (D) Transportation and Communication
Q.l3 The instrument that provides standards for land development by indicating lot sizes and layouts is
(A) Zoning regulations. (B) Land use control.
(C) Building bylaws. (D) Subdivision regulations.
Q.l4 Identify the group containing only GIS packages.
P. Total Station
Q. SatGuide
R. GPS
S. ILWIS
T. CorelDraw
U. GeoMedia
V. Arclnfo
(A) P, Q, U (B) Q, R, V (C) S, U, V (D) R, T, V
Q. 15 Organizations namely STACO, UNSCC and ISO are associated with:
(A) Environmental planning (B) Landscape architecture
(C) Modular coordination (D) Urban design
Q.16 Inflorescence in a tree-structure refers to
(B) Fragrance of the flowers. (D) Depth of the root structure.
(A) Flowering character.
(C) Spread characteristics of the branches.
Q. 17 Income inequalities across population is expressed through
(A) Cohort pyramid. (C) Indifference curve.
(B) Lorenz curve.
(D) Inverted U-curve.
Q.18 The Columbian Exposition in North America is synonymous with
(A) City Beautiful Movement. (B) Urbana Lake front development.
(C) CIAM. (D) Broad-acre City.
Q.19 The ideal cross-section of a combined sewerage system for significant variation in flow is
(A) Circular. (B) Egg-shaped.
(C) Semi-elliptical. (D) Horse-shoe-shaped.
Q.20 The international guideline for conservation and restoration of monuments and sites recommended by ICOMOS, is known as
(B) Amsterdam Declaration. (D) Burra Charter.
(A) Venice Charter.
(C) Granada Convention.
Q. 21 to Q.75 carry two marks each.
Q.21 Heating, cooling and ventilation in passive system designs are dependent on
(A) differences in standards of active energy systems and amount of sunlight.
(B) quality of insulation and quantity of glazing.
(C) mechanical ventilation and the floor height of the building.
(D) daylight factor and energy from mechanical systems.
Q.22 Which pair, out of the following options, is used in more than one computer languages listed below?
C, AutoLISP, Basic, Pascal
(D)
(A) ; /n
(C) ? /n
(B) ,
Q.23 Match labels in the diagram with items in the table :
|
P R |
 |
Q
1 Activity
2 Dummy activity
3 Duration
4 Event starting/ finishing
(B) P-4, Q-l, R-3, S-2 (D) P-l, Q-3, R-4, S-2
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-4, S-3 (C) P-3, Q-2, R-l, S-4
Q.24 Select the valid combination of shear force and bending moment diagrams for the loading shown below.
W tons per meter run
i
|
JSL , 1( |
i |
I | |
|
p | |||
|
Ik........A |
2 Bliirmr, | ||
|
il Q | |||
|
.....1 |
w~ |
3 | |
|
R | |||
|
uimi |
4 II | ||
|
U|| s |
fr |
..........1 |
luuiiiiiii |
(A) P-3 (B) Q-2 (C) R-l (D) S-4
Q.25 Recommended temperature and fresh air flow for HVAC systems in office buildings in India are
(A) 21C with maximum of 30C in summer and 25C in winter, with fresh air provisions of 18-22 litres per second per person.
(B) 29C with maximum of 32C in summer and 36C in winter, with fresh air provisions of 28-32 litres per second per person.
(C) 30C with maximum of 36C in summer and 32C in winter, with fresh air provisions of 38-42 litres per second per person.
(D) 21C with maximum of 24C in summer and 22C in winter, with fresh air provisions of 8-12 litres per second per person.
Q.26 Match the architects / city planners from Group I with the design movements listed in Group II
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
P. |
Viollet-le-Duc |
1 |
Post Modernism |
|
Q. |
William Morris |
2 |
Arts & Crafts Movement |
|
R. |
Robert Venturi |
3 |
Ekistics |
|
S. |
C.A. Doxiadis |
4 |
French Rationalism |
|
P-4, |
Q-2, R-l, S-3 |
(B) |
P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-2 |
|
P-2, |
Q-3, R-l, S-4 |
(D) |
P-l, Q-4, R-2, S-3 |
(A)
(C)
Q.27 Structural adjustment between two regions with respect to supply and demand of labourers and their wages is explained by
(A) Input-Output Analyses by W. Leontiff.
(B) Export-Base Model by Douglas C. North.
(C) Backwash effect based Economic Growth Model by Gunner Myrdal.
(D) Economic Base Theory by Hans Blumenfield.
Q.28 Match the surfaces in Group -1 with their respective range of albedo values in Group - II
|
Group -1 |
Group - II | |||
|
P |
Close ground crops |
1 |
0.45 - 0.95 | |
|
Q |
Bare lands |
2 |
0.05 - 0.055 | |
|
R |
Water surface |
3 |
0.05 - 0.45 | |
|
S |
Snow |
4 |
0.15-0.25 | |
|
(A) |
P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l |
(B) P-4, |
Q-3, | |
|
(C) |
P-4, Q-3, R-l, S-2 |
(D) P-4, |
Q-2, | |
|
Which of the following is NOT a criterion for defining urban |
areas in | |||
Q.29
(A) Population size.
(B) Percentage of male working population engaged in non-agricultural pursuits.
(C) Density of population.
(D) Percentage of pucca houses.
Q.30 Signal phasing in transportation system refers to
(A) the number of combinations of traffic movements served through a signalized intersection.
(B) the distance between signalised intersections.
(C) phase of electric power required to make the signals operational.
(D) relative placements of red, green and amber lights on a signal post.
Q.31 Pair the groups correctly:
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
p |
Solar constant |
1 |
W/m deg C |
|
Q |
Air to air transmittance, U-value |
2 |
1.4 kW/ m2 |
|
R |
Volumetric specific heat |
3 |
W/ m2 deg C |
|
S |
Conductivity, k-value |
4 |
K Cal/m3 deg C |
|
(A) |
P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-l |
(B) |
P-2, Q-l, R-4, |
|
(C) |
P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-4 |
(D) |
P-4, Q-3, R-l, |
Q.32 Identify the right network representing the following statement,
S controls X, Y & Z; T controls Y & Z; and U controls Y\
|
(A) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
(B)
*6*o
a
(D)
oo
o-L-<W>
u * z
o>*o
Q.33 Architectural projects designed by Laurie Baker are generally characterised by P. Appropriate technology Q. Human scale
R. Interpretation of nine-square model
S. Use of locally available materials
(A) P, R, S (B) P,Q,S (C) Q,R,S (D) P, Q, R
Q.34 Match the glasses listed in Group I, with the appropriate descriptions in Group II
|
Group I P Liquid crystal laminated glass 1 Q Electro-chromic glass 2 R Coated glass 3 S Tinted glass 4 |
Group II Promotes absorption of both visible light and infrared radiation. Improves thermal performance of the glass by reflecting visible light and infrared radiation. Requires continuous supply of electricity to change from translucent to transparent state Requires electrical pulses to change from transparent to opaque state |
|
(A) P-4, Q-l, R-3, S-2 (C) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l |
(B) P-l, Q-3, R-2, S-4 (D) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-l |
Q.35 Which of the following commands in AutoCad is used to extract one or more elements from a list?
(A) Filter (B) Boundary (C) Explode (D) Eattext
Q.36 Identify the satellites that provide useful information for physical planning.
P. IKONOS Q. IRS-ID R. CartoSAT S. INSAT-IB
T. PSLV U. Google Earth V. Apple W. Quick Bird
(A) P, Q, R, W (B) R, S, T, V (C) P, Q, R, S (D) S, T, U, V
Q.37 Stack effect is
(A) the process of supplying fresh air by electro-mechanical means both vertically and horizontally.
(B) the tendency of hot air in a shaft to rise and create a draft of cool air intake.
(C) the air-supply to a motor-driven louvered opening in basement.
(D) the circulation of fresh air through windows from the plenum level.
Q.38 Match the equipments with their use.
|
P. |
Power shovel |
1. |
Spreading and Levelling |
|
Q. |
Front end loader |
2. |
Drilling |
|
R. |
Drop hammer |
3. |
Excavation |
|
S. |
Earth-auger |
4. |
Piling |
|
(A) |
P-l, Q-3, R-2, S-4 |
(B) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-l | |
|
(C) |
P-4, Q-2, R-l, S-3 |
(D) P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-2 |
Q.39 Contemporary architecture has made a shift from machine-based modernist approach to passive energy-sensitive approach.
Which of the following groups of architects best represent this shift?
(A) Paul Rudolph, Mies van der Rohe, Arato Isozaki
(B) Norman Foster, James Carpenter, Richard Rogers
(C) James Sterling, Philip Johnson, Ralph Rapson
(D) Arthur Erikson, Frei Otto, Rem Koolhass
Q.40 Park le de Villete, Paris designed by Bernard Tschumi, is characterised by
(A) continuous sequence along a zigzag line.
(B) beast like benches embedded with fragments of coloured tiles and stepped terraces.
(C) point grid, superimposition and agglomeration of activities.
(D) semi underground cave-like gallery for the display of artworks.
Q.41 The predominant characteristics of spatial organizational principles found in the works of Le Corbusier and Frank Lloyd Wright are characterized respectively by
(A) Grid organization and Linear-planar organization.
(B) Centralized-clustered organization and Grid organization.
(C) Radial organization and Grid-radial organization.
(D) Centralized organization and Multi-grid organization.
Q.42 The ratios presented by the two-number series 70:113:183 and 86:140:226 stand respectively for
(A) the blue and the red series of Le Modular.
(B) the vertical and horizontal proportions found in Leonardo da Vincis Pentagram.
(C) the horizontal and vertical proportions found in Leonardo da Vincis Pentagram.
(D) the red and the blue series of Le Modular.
Q.43 The difference between an axonometric projection and an isometric projection of an object with respect to a picture plane is in terms of
(A) height or breadth of cross-sectional views generated by the picture plane.
(B) measurements in the angle of faces with respect to the aspect ratio.
(C) obliqueness in projection of faces of the object on the vertical plane.
(D) foreshortened angular measurements in the three principal axes.
Q.44 A squinch system is a method of constructing an arch across a square base by erecting
(A) Pendentives and Cul-de-four. (B) Intra-domes and Tension ring.
(C) Saucer-domes and Traverse vaults. (D) Cross-bandages and Hoop lines.
Q.45 Match the following:

|
P. |
Nile Valley Civilization |
1. |
Shang | |
|
Q. |
Indus Valley Civilization |
2. |
Harappa | |
|
R. |
Euphrates and Tigris Valley Civilization |
3. |
Akhetaton | |
|
S. |
Yellow River Civilization |
4. |
Babylon | |
|
(A) |
P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-4 |
(B) |
P-3, |
Q-2, R-4, |
|
(C) |
P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-l |
(D) |
P-4, |
Q-2, R-3, |
|
Q.46 Match the appropriate arches with types listed below. |
 |

1. Equilateral Arch
2. Lancet Arch 5. Tudor Arch
3. Drop Arch 6. Roman Arch
4. Surbased Arch
(B)
(D)
R-3,
R-5,
S-5
S-3
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-5, S-3 (C) P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-4
P-l, Q-2, P-6, Q-2,
Q.47 The study of varying population sizes of urban centers in a region is assessed by
(A) Multiplier effect. (B) Rank-size Rule.
(C) Shift-share analysis (D) Bulk share of workforce.
Q.48 Identify the correct hierarchy of traditional Indian settlements expressed in an ascending order.
(A) Kharvata Khetaka Nagara Durga
(B) Durga - Vidambaka - Pura - Rajdhani
(C) Grama Khetaka Kharvata Nagara
(D) Nigama - Agrahara - Pura - Kharvata
Q.49 Formal regions and Functional regions are determined respectively by their
(A) Natural resources; physiography and Economic linkages.
(B) Economic linkages and Natural resources; physiography.
(C) Industrial location and Transportation; communication.
(D) Transportation; communication and Industrial location.
Q.50 Nagar Panchayats and District Planning Committees in India were introduced as a result of
(A) National Urbanisation Policy
(B) Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission
(C) Electoral reforms
(D) Constitution (73rd and 74th Amendment) Acts Q.51 The concept of Slum-networking aims to promote
P social and physical improvement of slums.
Q holistic development in conformity with the infrastructure of the entire city.
R improvement of physical networks only within the slum areas.
S rehabilitation of slum dwellers.
(A) P, Q (B) P, Q, R (C) P, R (D) Q, R, S
Q.52 Shells and Space Frames are examples of
(A) modular Bulk-active and Form-active systems respectively.
(B) modular Surface-active and Vector-active systems respectively.
(C) modular Vector-active and Form-active systems respectively.
(D) modular Bulk-active and Surface-active systems respectively.
Q.53 The Law of vicinity states that
(A) the objects of similar form situated close enough together are perceived as one.
(B) the objects of similar form situated at a distance are perceived as one.
(C) the objects of different forms situated close enough together are perceived as one.
(D) the objects situated close enough together are perceived as confusing.
Q.54 Luminaire efficiency is defined as the
(A) sum of the light outputs of the lamps operating inside the luminaire to the ratio of the sum of the light output of the luminaire operating outside the luminaire.
(B) sum of the individual light outputs of the lamps operating outside the luminaire to the ratio of the light output of the luminaire.
(C) ratio of the light output of the luminaire to the sum of the individual light outputs of the lamps operating outside the luminaire.
(D) ratio of the light output of the luminaire to the individual light output of the lamp operating outside the luminaire.
Q.55 Match the following:
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
p |
Dumbwaiter |
1 |
Opening |
|
Q |
Comb-plate |
2 |
Escalator |
|
R |
Co-axial cable |
3 |
Elevator |
|
S |
Transom |
4 |
Data Signal |
|
(A) |
P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-4 |
(B) P-3, Q-2, R-4, S-l | |
|
(C) |
P-2, Q-l, R-4, S-3 |
(D) P-4, Q-3, R-l, S-2 |
Q.56 Negative and positive correlations between Price and Quantity of a commodity are respectively represented by
(A) Demand and supply curves.
(B) Supply and demand curves.
(C) Indifference curves and scattered matrix.
(D) Scattered matrix and indifference curves.
Q.57 Traditional Indian settlement patterns, based on orthogonal grid are represented by:
(A) Padmaka, Kurmaka and Swastika
(B) Mandala, Kurmaka and Angula
(C) Dandaka, Vidambaka and Dhanurmusti
(D) Sarvatabhadra, Prastara and Chaturmukha
Q.58 .Plans of Mohenjodaro and medieval Jaipur are based on:
(A) grid pattern and sectoral allocation of zoning.
(B) radial pattern and grid allocation of zoning.
(C) clustered pattern and segregated allocation of zoning.
(D) centralized pattern and composite allocation of zoning.
|
Q.59 Match the following: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Q.60 The most appropriate criteria to be considered for delineating backward regions are |
|
P density of population. R infant mortality. |
Q amount of sales tax collection. S per capita income and its distribution. |
(A) P, R (B) R, S (C) P, S (D) P, Q
Q.61 The relationship between headway (h) and flow (q) in a traffic stream is represented by:
(A) h = q1 (B) h = q (C) h = 1 / q2 (D) h = 1 / q
Q.62 Match the diagrams of Age-Sex pyramids from the descriptions of the population growth, given below:
 |
Female Mai |
 |
Female Mal< |
 |
Female |
 |
Male |
Afcj0-I4 CD Ages 15 - 44 S9 Ages 43 -8S*
P Q R
1. Rapid Growth
4. Negative Growth
|
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-4 (C) P-3, Q-2, R-4, S-l |
(B) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-l (D) P-l, Q-2, R-4, S-3 |
Q.63 'Ecological Footprint corresponds to
(A) the land area required to preserve as forests to ensure sufficient levels of oxygen for a community.
(B) the land area necessary to supply natural resources to a community and disposal of its wastes.
(C) the land area required to take care of solid wastes and sewerage of a community.
(D) the land area per person per year, from which forests are cut.
Q.64 Match the following with their area of application
P Potometer 1 Area measurement
Q Histogram 2 Soil moisture measurement
R Electrostatic precipitator 3 Transpiration
S Planimeter 4 Suspended particles
T Potentiometer 5 Statistics
(A) P-l, Q-l, R-2, S-3, T-l
(B) P-4, Q-5, R-5, S-4, T-l
(C) P-3, Q-5, R-4, S-l, T-2
(D) P-2, Q-3, R-2, S-5, T-5
Q.65 Select the appropriate word from the list given below that fits in ALL the blanks:
1. The aim of conservation is to retain or recover the_significance of a place.
2. Preservation is appropriate where the existing state of the fabric itself constitutes of specific _significance.
3. Restoration is appropriate only if there is sufficient evidence of an earlier state of the fabric
and only if returning the fabric to that state recovers the_significance of the
place.
4. Reconstruction is appropriate where a place is incomplete through damage or alteration and
where it is necessary for its survival, or where it recovers the_significance of
the place as a whole.
(A) historical (B) cultural (C) architectural (D) aesthetic
Q.66 The rule for generating a Fibonacci series is:
(A) Fj= Fj-i+2 for i>l given Fj and Fo
(B) F, Fj-i+1 for i>l given Fj and F0
(C) F;= Fj-i+Fj-2 for i>l given Fj and F0
(D) Fj= (Fj.|)2 for i>l given Fj and Fo
Q.61 Two names associated with the planning of Paris and Philadelphia are respectively:
(A) Georges-Eugene Hausmann and William Penn
(B) Patrick Geddess and Louis Wirth
(C) Albert Perry and Oswald Spangler
(D) Le Corbusier and John Friedman
Q.68 Which of the following statements is valid for a saddle surfaced shell structure?
P regions of downward curvature exhibit arch like action R regions of upward curvature behave as a cable structure
(A) P is true and R is false (B) R is true and P is false
(C) Both P & R are true (D) Both P and R are false
Q.69 Which of the following statements describes the advantage of A.C. supply over D.C supply?
(A) Electroplating process
(B) Noise reduction in motors
(C) Facility of transforming from one voltage to another
(D) Charging of storage batteries
Q.70 For which application software the following expression is valid?
( 2.5 (+ (/ a 2) (- 5 x)))
(A) Qbasic (B) AutoLISP (C) Java (D) C++
Common Data Questions
Common Data for Questions 71,72 and 73:
For a building, the gross rent fetched is Rs. 22,500/- per month; municipal tax is Rs. 8,000/ per quarter; repair and maintenance charges are @ 10% of gross rent and other expenses borne by owner are Rs. 16,000/- per annum.
Q.71 What would be the total outgoings in Rs. ?
(A) 60,000/- (B) 70,000/- (C) 75,000/- (D) 80,000/-
Q.72 What would be the net annual rent in Rs. ?
(A) 1,90,000/- (B) 1,95,000/- (C) 2,00,000/- (D) 2,05,000/-
Q.73 If the Years Purchase in perpetuity comes out to be 12.5, what would be the capitalized value, in Rs. of the above building?
(A) 24,00,000/- (B) 24,37,000/- (C) 24,37,500/- (D) 25,00,000/-
Common Data for Questions 74 and 75:
The following table provides total population and urban population of India in various years.
|
Year |
Total Population (millions) |
Urban Population (millions) |
|
1901 |
238.40 |
25.85 |
|
1911 |
252.09 |
25.94 |
|
1921 |
251.32 |
28.09 |
|
1931 |
278.98 |
33.46 |
Q.74 Level of Urbanisation in the year 1921 was:
(A) 10.29 (B) 10.84 (C) 11.18 (D) 11.99
Q.75 As per the table given in Q. No. 74 the Annual Growth Rate of urban population of India during 1921 - 31 was:
(A) 0.03 (B) 0.79 (C) 1.76 (D) 1.91
f
Linked Answer Questions: Q.76 to Q.85 carry two marks each Linked Answer Questions 76 and 77:
Q.76 In professional practice, when there are disputes among the architects, clients and contractors regarding the building constructions or contract, then to resolve the issues the Expert / Experts appointed for the same is / are termed as
(A) Arbitrator (B) Lawyer (C) Solicitor (D) Valuer
Q.77 When there is dispute among the above Experts then another expert is appointed to resolve the issues, who is known as
(A) Mediator (B) Referee (C) Judge (D) Umpire
Linked Answer Questions 78 and 79:
Q.78 Identify the formula for calculating the reverberation time (t) of a hall of volume V cu.m., where S represents sound absorption area.
(A) t = 16V/ S (B) t = 0.16V2/S (C) t = 0.16V/S (D) t = 16V/S2
Q.79 A school auditorium has a capacity of 800 persons. Considering 3.5 cu.m. of volume per person and reverberation time of 1.25 sec, the total sound absorption area required would be:
(A) 348 sq.m. (B) 358 sq.m. (C) 368 sq.m. (D) 378 sq.m.
Linked Answer Questions 80 and 81:
Q.80 If a bedroom of 3m x 3m x 3m requires 3 air-changes per hour, and difference in temperature between inside and outside (AT) = 12 deg C, then Ventilation Heat Flow Rate (Qv) will be:
(A) 0.12 kW (B) 0.35 kW (C) 0.70 kW (D) 1.17 kW
Q.81 For a given air velocity of 2m/s, the necessary cross-sectional area of supply-duct will be:
(A) 0.0375 sq.m. (B) 0.0225 sq.m. (C) 0.0113 sq.m. (D) 0.0037 sq.m.
Linked Answer Questions 82 and 83:
Q.82 The number of Senior Secondary schools required for a city of population of 1,00,000 persons is:
(A) 8-10 (B) 14-15 (C) 18-20 (D) 25-28
Q.83 The total land requirement for Senior Secondary schools for a city of population of 1,00,000 persons is about:
(A) 8 ha (B) 15 ha (C) 25 ha (D) 40 ha
Linked Answer Questions 84 and 85:
Q.84 Identify the relationship governing the cost of land (C) based on the following factors:
Net density in plots per hectare = p
Land use percentage allocation in net housing = q Price of land in Rs. per sq m =s
(A) C = (10,000/p x 100/?) 5 (B) C = (10,000/p x ?/100)s
(C) C= (10,000/p x 100/s)? (D) C = (10,000/s x 100/?)/?
Q.85 If for a housing development, p = 30, ? = 45 and s = 500, then the cost of land per dwelling unit is:
(A) Rs. 1,333/- (B) Rs. 3,000/- (C) Rs. 75,000/- (D) Rs. 3,70,370/-
Slow Growth 3. Zero Growth
2007
Duration : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 150
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. This question paper contains 85 objective type questions. Q.l to Q.20 carry one mark each and Q.21 to Q.85 carry two marks each.
2. Attempt all the questions.
3. Questions must be answered on Objective Response Sheet (ORS) by darkening the appropriate bubble (marked A, B, C, D) using HB pencil against the question number on the left hand side of the ORS. Each question has only one correct answer. In case you wish to change an answer, erase the old answer completely.
4. Wrong answers will carry NEGATIVE marks. In Q.l to Q.20, 0.25 mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. In Q.21 to Q.76, Q.78, Q.80, Q.82 and in Q.84, 0.5 mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. However, there is no negative marking in Q.77, Q.79, Q.81, Q.83 and in Q.85. More than one answer bubbled against a question will be taken as an incorrect response. Unattempted questions will not carry any marks.
5. Write your registration number, your name and name of the examination centre at the specified locations on the right half of the ORS.
6. Using HB pencil, darken the appropriate bubble under each digit of your registration number and the letters corresponding to your paper code.
7. Calculator is allowed in the examination hall.
8. Charts, graph sheets or tables are NOT allowed in the examination hall.
9. Rough work can be done on the question paper itself. Additionally blank pages are given at the end of the question paper for rough work.
10. This question paper contains 20 printed pages including pages for rough work. Please check all pages and report, if there is any discrepancy.
AR 1/20
S/121 Food/06-AR-1 A
Q. 1 - Q. 20 carry one mark each.
Q.l Ramsar list is related to
(A) Wetlands
(B) Heritage buildings
(C) Seismic zones
(D) Special Economic Zones
Q.2 Hazens-Williams nomogram is used to calculate
(A) size of sanitary pipe lines
(B) size of water supply pipe lines
(C) capacity of overhead water reservoir
(D) capacity of water required for fire fighting
Q.3 Awoonerfisa
(A) pavement pattern (B) sanitation system element
(C) speed reducing element (D) furniture detail
Q.4 In urban planning, cohort refers to
(A) age and sex classification of population
(B) contour levels in slope analysis
(C) land use classification of public and semi-public spaces
(D) soil layer classification
Q.5 The project Habitat, Montreal, designed by Moshe Safdie is an example of
(A) high rise apartments
(B) low rise detached dwellings
(C) organic architecture
(D) prefabricated housing
Q.6 The degree of freedom of a joint in a plane truss is
(A) two (B) three (C) four (D) six
Q.l A brick cut lengthwise into two pieces so that each piece is half as wide as the full brick is called a
(A) King closer (B) Frog (C) Quoin brick (D) Queen closer
Q.8 The strength of concrete increases with
(A) increase in water cement ratio
(B) decrease in water cement ratio
(C) increase of workability
(D) decrease in cement aggregate ratio
The point of contraflexure is the point where the
(A) shear force changes its sign (B) deflection is zero
Q.9
Q.10
Q.ll
Q.12
Q.13
Q.14
Q.15
Q.16
Q.17
(C) bending moment changes its sign (D) torque is zero
When wind loads are accounted for in the design of structures, the permissible stresses in the material are increased by
(A) 10% (B) 16.33% (C) 33.33 % (D)50%
The term coined by Paolo Soleri that combines ecology with architecture and deals with habitats maintaining an extremely high population density is
(A) Archaeology (B) Proxemics
(C) Arcology (D) Utopia
A dislocation of continuity in rock strata as a result of cracking of the earths crust is called
(A) Fissure (B) Fault (C) Eluvium (D) Drift
LEED is the internationally accepted rating system for
(A) Green buildings (B) Fire resistant buildings
(C) Intelligent buildings (D) Tall buildings
An architect of the Chicago School movement is
(A) Richard Boyle (B) Louis Sullivan
(C) Hector Guimard (D) William Morris
Surkhi is obtained by grinding
(A) well burnt clay bricks (B) slag from industry
(C) stone aggregate (D) rice husk
Hemadpanthi style of temples belongs to
(A) Himalaya (B) Deccan (C) Orissa (D) Kerala
A building in which the roof is perfectly hemispherical on the inside and a shallow dome on the outside is
(A) Hagia Sophia (B) Pantheon
(C) Parthenon (D) Gol Gumbaz
National Science Centre at Pragati Maidan, New Delhi, is designed by
(A) J.A. Stein (B) Anant Raje (C) Raj Rewal (D) A.P. Kanvinde
Q.19 In Islamic architecture, the device used for placing a perfect circular dome over a square plan is called a
(A) Mehrab (B) Scroll (C) Mastaba (D) Squinch
Q.20 Parallel sound rays incident on a convex surface of a fibre-board will )lVi-
1 * c
(A) converge and reduce in intensity
(B) converge and increase in intensity
(C) disperse and reduce in intensity
(D) disperse and increase in intensity
Q. 21 to Q. 75 carry two marks each.
Q.21 Match the architect-Mlanners in Group I with their contributions in Group II.
Group II
Group I
P. Hippodamus Q. Michelangelo R. Leon Battista Alberti S. Daniel Burnham
(A) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l (C) P-4, Q-l, R-5, S-3
1. City Beautiful
2. Star-shaped plan
3. Grid iron plan
4. Campidoglio
5. St. Peters Square
(B) P-3, Q-5, R-2, S-4
(D) P-3, Q-2, R-l, S-5
|
Q.22 The characteristics of Japanese gardens are P. Stepping stones Q. Stone lanterns R. Octagonal geometry (A) P, Q, S, T (C) R, S, T |
S. Miniature symbolic elements T. Stone water basins U. Monumental scale (B) P, Q, U (D) Q, R, S, T |
Q.23 Match the styles of architecture in Group I with the elements in Group II.
Group 1 P. Khajuraho Q. Dravidian R. Hoysala S. Himalayan
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-4, S-3 (C) P-2, Q-4, R-3, S-l
Group II
4. Urushringa
(B) P-4, Q-2, R-l, S-3
Q.24 A site has a uniform slope of 6 %. The site map has seven contour lines with the elevation of the highest contour as +53 metres. If the distance between the midpoints of the highest and the lowest contours is 700 metres, then the contour interval in metres is
(A) 6 (B) 7 (C) 11 (D) 42
Q.25 Match the statements about thermal comfort in Group 1 with True/False in Group
II.
Group I Group II
P. Low capacitance materials should be used to store heat gain 1. True Q. Stack effect depends on temperature difference between 2. False
indoor and outdoor air R. Venturi effect is a passive cooling technique S. Wind breaks are used to maximize winter wind turbulence
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-2, S-2 (B) P-l, Q-2, R-2, S-l
(C) P-2, Q-l, R-l, S-2 (D) P-2, Q-l, R-l, S-l
Q.26 A person standing at a point in a public plaza is observing'a fa9ade of height 40 metres from a distance of 120 metres. The sense of enclosure experienced by the person is equivalent to the limits of
(A) Loss of enclosure (B) Minimal enclosure
(C) Full enclosure (D) Threshold of enclosure
Q.27 Match the Urban Planning Theories in Group I with their proponents in Group II.
Group I
Group II
1. Walter Christaller
2. Clarence Perry
3. Ebenezer Howard
4. Harris & Ullman
5. Homer Hoyt
P. Sector Theory Q. Multiple Nuclei Theory R. Neighbourhood Theory
S. Central Place Theory
(A) P-l, Q-4, R-5, S-3 (C) P-5, Q-l, R-2, S-3
(B) P-4, Q-2, R-3, S-l (D) P-5, Q-4, R-2, S-l
Q.28 The plan of a residential area with small houses on small plots has an urban fabric with
(A) fine grain and uniform texture
(B) coarse grain and uniform texture
(C) fine grain and uneven texture
(D) coarse grain and uneven texture
Group I Group II
P. Elev 1. Changes the dashed line to a non-dashed line
Q. LType 2. Changes the size and spacing of the dashes
R. Thickness 3. Changes the position along the Z axis
S. LtScale 4. Changes the width of the line on the screen
5. Changes the height along the Z axis
6. Changes the position along the Y axis
(A) P-6, Q-l, R-4, S-2 (B) P-5, Q-2, R-6, S-4
(C) P-3, Q-l, R-5, S-2 (D) P-6, Q-4, R-3, S-l
Q.30 Match the statements on intelligent buildings in Group I with True/False in Group
II.
Group I
Group II
1. True
2. False
P. All intelligent buildings are examples of high-tech architecture
Q. An intelligent building is synonymous with a smart building
R. An intelligent building need not deploy a building automation system
S. High-tech architecture always results in intelligent buildings
(A) P-l, Q-l, R-2, S-2 (B) P-l, Q-2, R-2, S-2
(C) P-2, Q-2, R-1, S-1 (D) P-2, Q-1, R-1, S-1
Q.31 The correct sequence of various components of a house water connection from the
municipal water main is
(A) Stop cock Water meter -> Goose neck Service pipe Ferrule connection
(B) Ferrule connection -> Stop cock Goose neck -> Service pipe Water meter
(C) Goose neck Ferrule connection Service pipe Water meter Stop cock
(D) Ferrule connection -> Goose neck -> Service Pipe Stop cock Water meter
Q.32 The figure that will be generated by the following sequence of commands in
AutoCAD is
Command: pline Specify starL point: 0,0 Specify next point: @50,0 Specify next point: @0,-25 Specify next point: @25<180 Specify next point: c
Q.33 A sector has a gross density of 250 persons per hectare and a net density of 400 persons per hectare. If the area of the sector is 120 hectares, then the percentage of non-residential area is
(D) 40
(B) 35.5
(A) 30
(C) 37.5
Q.34 Match the systems of plumbing for building drainage in Group I with their descriptions in Group II.
Group II
Group I
P. One-pipe system Q. Two-pipe system R. Single stack system
1. Minimum two pipes, one for soil and the other for suliage
2. Single pipe for soil and suliage, and serving as vent for all traps
3. Minimum two pipes, one for soil and suliage and the other for vent
4. Single pipe for soil and suliage, and serving as vent for soil traps only
(B) P-3, Q-2, R-l
(A) P-4, Q-3, R-2 (C) P-2, Q-3, R-4
(D) P-3, Q-l, R-2'
Q.35 In a plane truss, the equation in terms of m and j is used to check its determinacy and stability, where m = number of members and j = number of joints. The truss is deficient and unstable when
(A) m < 2j - 3
(B) m = 2j - 3
(C) m > 2j - 3
(D) both (A) and (B) are correct
Q.36 Match the functions in Group I with the numbers shown in the given figure of Concentric Zone Theory by Burgess.

Group I
P. Central Business District Q. Commuters Zone R. Workingmens Homes S. Zone of Better residences T. Zone of Transition
|
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-5, S-4, T-3 (C) P-2, Q-4, R-5, S-3, T-l |
(B) P-l, Q-5, R-3, S-4, T-2 (D) P-3, Q-5, R-l, S-4, T-2 |
Q.37 For a PERT activity, the optimistic time, most likely time and pessimistic time are 1, 2 and 9 days respectively. The expected time for the activity (in days) is
Q.38 Zoning regulations deal with
P. Density S. Minimum areas of rooms
Q. Land use T. Height
R. Building materials U. Reserved land areas
(A) P, 0, T (B) P,Q, R,U (C) Q, S, U (D) Q, R, S, T
Q.39 Match the temples in Group I with their distinguishing features in Group II.
Group I Group II
P. Konark 1. Golden Lily Pond
Q. Madurai 2. Sculpted Marble Ceiling
R. Dilwara 3. Twin Vimanas
S. Mamallapuram 4. Chariot
5. Torana
(A) P-3, Q-1, R-2, S-5 (B) P-4, Q-1, R-2, S-3
(C) P-2, Q-3, R-5, S-l (D) P-3, Q-4, R-l, S-2
Q.40 The correct sequence of generic elements in a Classical Order arranged from top to bottom is
(A) Architrave -> Frieze Capital Cornice -> Shaft -> Pedestal -> Base
(B) Architrave -> Capital -> Cornice -> Frieze -> Base -> Shaft -> Pedestal
(C) Cornice -> Frieze -> Architrave -> Capital -> Shaft Base -> Pedestal
(D) Cornice -> Capital -> Frieze Architrave -> Shaft -> Pedestal -> Base
Q.41 Match the tree forms in Group I with their common examples in Group II.
Group I Group II
P. Broad 1. False Acacia
Q. Tapering 2. Holly
R. Conical 3. Lombardy Poplar
S. Columnar 4. Oak
5. Silver Maple
(A) P-l, Q-5, R-4, S-2 (B) P-l, Q-3, R-4, S-5
(C) P-4, Q-l, R-2, S-3 (D) P-4, Q-5, R-2, S-l
Q.42 A town has 16,000 existing dwelling units of which 10 % are dilapidated. If the housing need is 8,700 dwellings units and the average household size is 4.5, then the population of the town is
(A) 64,800 (B) 1,03,950 (C) 1,11,150 (D) 1,18,350
|
Group I Group II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(A) P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-5 (B) P-l, Q-5, R-4, S-6
(C) P-4, Q-2, R-3, S-l (D) P-4, Q-5, R-3, S-6
Q.44 Match the city plans in Group I with their designers in Group II.
|
Group I |
Group II |
|
P. London |
I. Eliel Saarinen |
|
Q. Berlin |
2. Kenzo Tange |
|
R. Helsinki |
3. Alvar Aalto |
|
S. Tokyo |
4. Tadao Ando |
|
5. Martin Machler | |
|
6. Patrick Abercrombie |
(A) P-6, Q-5, R-1, S-2 (B) P-1, Q-3, R-5, S-2
(C) P-6, Q-3, R-1, S-4 (D) P-5, Q-6, R-3, S-4
Q.45 On a door opening with effective span L, the total weight (W) of an equilateral triangle on the base L is considered as a uniformly distributed load over the span. The bending moment for the door opening is given by
(A) WL / 2 (B) WL / 4 (C)WL/6 (D) WL / 8
Q.46 Match the descriptions in Group I with the traffic terminology in Group II.
Group I Group II
P. The length of a road ahead of the vehicle 1.
Visibility distance Sighting distance Overtaking sight distance Cross over distance Stopping distance
which should be visible to enable a driver to 2. stop in case of an obstruction on the road 3.
Q. Distance covered by a vehicle from the instant 4. a driver sees an obstruction ahead and brings 5. the vehicle to a stop R. Distance required for a vehicle to overtake and safely pass another vehicle moving in the same direction but at a lower speed
Group II
1. Jamb
|
Group I | |
 |
0 R S |
2. Muntin
3. Panel
4. Rail
5. Saddle
6. Stile
|
(A) P-1, Q-6, R-5, S-4, T-2 (C) P-5, Q-3, R-l, S-6, T-2 |
(B) P-l, Q-6, R-2, S-4, T-3 (D) P-5, Q-6, R-l, S-4, T-3 |
Q.48 A house was constructed 20 years ago at a cost of Rs. 1,00,000. The estimated life of the building is 50 years, at the end of which it will have a 15 % scrap value of its cost of construction. Its present value in Rupees is
(A) 36,000 (B) 66,000 (C) 75,000 (D) 85,000
Q.49 A typical roof top Rainwater Harvesting System essentially comprises of
P. Roof catchment Q. Down pipes R. Rain gauge
S. Filter chamber
(A) P,R (B) P,R,S (C) Q,R,S
(D) P,Q,S
Q.50 Match the architects in Group I with their works in Group II.
Group I
P. Norman Foster Q. Cesar Pelli R. Richard Meier S. Renzo Piano
Group II
1. Petronas Towers
2. Kansai Airport
3. HSBC, Hongkong
4. The Atheneum
5. Sydney Opera House
Q.51 A single room of 3 metres x 5 metres enclosed by 20 cm thick walls has to be constructed. The required foundation trench is 80 cm wide and 80 cm deep. The quantity of earthwork in excavation in cubic metres is
(A) 10.75 (B) 12.80 (C) 18.70 (D) 20.24
Q.52 Match the parts of a tree log in Group I with their descriptions in Group II.
Group II
Group I P. Heartwood Q. Sapwood R. Cambium Layer S. Medullary Rays
(A) P-4, Q-2, R-5, S-3 (C) P-4, Q-l, R-5, S-2
1. Outer annual rings of the tree
2. Thin horizontal veins radiating from the pith towards the bark
3. Outermost protective covering of the log
4. Innermost rings surrounding the pith
5. Outermost one ring between the bark and sapwood
(B) P-3, Q-5, R-4, S-l
(D) P-5, Q-l, R-4, S-2
Q.53 The quantity of plastering in sq.m required for both sides of a wall 5.0 m x 0.30 m x
3.0 m (L x B x H) with a window opening 2.0 m x 0.30 m x 1.2,m is
(A) 25.2 (B) 27.6 (C) 30.0 (D) 34.8
Q.54 Match the urban theorists in Group I with the planning concepts in Group II.
|
Group I P. Patrick Geddes Q. Charles Abrams R. Constantine Doxiadis S. Lewis Mumford |
Group II 1. Cities in evolution and their relationship with man 2. Judicious use of technological power 3. Role of housing in urban development 4. The science of human settlements called Ekistics |
(A) P-l, Q-3, R-4, S-2 (B) P-4, Q-2, R-3, S-l
(C) P-3, Q-4, R-1, S-2 (D) P-2, Q-1, R-4, S-3
Q.55 If the reinforcement steel provided for a RCC slab of volume 15.0 cu.m. is @ 1%, then the quantity of steel required in kilograms is
(A) 655.5 (B) 1,000.0
(C) 1,177.5 (D) 1,500.0
Q.56 The Prairie House design of Frank Lloyd Wright is characterised by
P. Horizontal planes Q. Extended roofs R. Focal fire place
S. Steel columns T. Vertical screen windows
(A) P, R, S (B) P, Q, S (C) Q, R, S, T (D) P, Q, R, T
Group II
1. Horizontal louvers pivoting simultaneously in a common frame
Group I
P. Bay window Q. Pivoted window R. Dormer window
2. A sash that rotates 90 or 180 about a vertical or horizontal axis at or near its centre
3. Projecting outward from the main wall of a building, forming an alcove within a room
4. Vertical window projecting out of a sloping roof
(A) P-3, Q-2, R-4 (C) P-l, Q-4, R-2
(B) P-2, Q-3, R-l (D) P-4, Q-2, R-3
Q.58 Match the housing projects in Group I with the architects in Group II.
Group II
1. Balkrishna Doshi
2. Charles Correa
3. Hasmukh Patel
4. Kuldip Singh
5. Laurie Baker *
6. Raj Rewal
Group I
P. Tara Group Housing, New Delhi Q. Marine Front Housing, Cochin R. Aranya Community Housing, Indore
S. Asiad Village, New Delhi
(A) P-2, Q-4, R-l, S-6 (C) P-2, Q-5, R-6, S-l
(B) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-6 (D) P-l, Q-5, R-3, S-6
Q.59 A beam of 50 mm diameter is simply supported at both ends and has an effective span of 6 metres. It carries two loads of 50 kN each at one-third span. The section modulus (in cm3) of the beam at the quarter span is
(A) 11.17 (B) 12.27 (C) 13.37 (D) 14.47
Q.60 Match the Earthquake related terms in Group I with their definitions in Group II.
Group II
Group I P. Focus Q. Epicentre R. Centre of Mass S. Centre of Stiffness
1. The geographical point on the earth surface vertically above the originating source
2. The originating source of the seismic waves inside the earth
3. The point corresponding to the centre of gravity of a structural system
4. The point through which the resultant of the restoring forces of a structural system act
Group I Group II
P. Greek 1. Semi-circular arch
Q. Roman 2. Trabeation
R. Indian 3. Corbelling
S. Gothic 4. Pointed arch
(A) P-2, Q-4, R-3, S-l (B) P-l, Q-2, R-4, S-3
(C) P-2, Q-1, R-3, S-4 (D) P-3, Q-1, R-2, S-4
Q.62 For incandescent lamps the distribution of total energy emission is
(A) 5 % light & 95 % heat
(B) 25 % light & 75 % heat
(C) 50 % light & 50 % heat
(D) 75 % light & 25 % heat
Q.63 Match the characteristics in Group I with the climate types in Group II.
Group I Group II,
P. High humidity accelerates rusting and rotting 1. Composite or monsoon
Q. High daytime temperature and rapid cooling at 2. Hot dry desert
night cause materials to crack 3. Hot dry maritime
R. Seasonal changes in relative humidity cause 4. Tropical Upland
rapid weakening of building materials 5. Warm humid
(A) P-5, Q-2, R-l (B) P-4, Q-1, R-3
C) P-5, Q-3, R-4 (D) P-4, Q-3, R-5
Q.64 The architectural projects of the International Style are
P. Aurora House by Aldo Rossi Q. Schroder House by Gerrit Reitveld R. Thematic House by Jencks & Farrell
S. Tugendhat House by Mies van der Rohe T. Villa Savoye by Le Corbusier
(A) P, Q, R, T (B) P, S (C)Q,S,T (D) Q, R, T
Q.65 Tactile flooring with guiding blocks, an element of Barrier Free Design, is used to aid
P. ambulant disabled Q. non-ambulant disabled R. partially sighted
S. totally blind
(A) P, Q, S (B) P, Q, R (C) R, S (D) Q, S
|
Q.66 Match the characteristics of vaults in Group I with their names in Group II. Group I Group II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
(A) P-1, Q-6, R-5, S-2 (B) P-6, Q-3, R-4, S-2
(C) P-4, Q-5, R-2, S-6 (D) P-l, Q-3, R-4, S-2
Q.67 A 60 segmental arch is provided over a door of 1.0 m width. The wall thickness is 30 cm and the arch thickness is 20 cm. The mean length of the arch in metres is
(A) 1.00 (B) 1.15 (C) 1.20
(D) 1.30
with True/False in
Q.68 Match the statements about elevators & escalators in Group 1 Group II.
Group I
Group II
1. True
2. False
P. Handling capacity of elevators for residential buildings as per Indian standards is 7.5 %
Q. Minimum height from the top floor to the bottom of the lift machine room should be 3,000 mm R. Minimum width for escalators as per Indian standards is
1,000 mm
S. Recommended angle with the horizontal for escalators is 30
(A) P-1, Q-2, R-1, S-2 (B) P-2, Q-2, R-2, S-
1
1
(C) P-2, Q-l, R-l, S-l (D) P-l, Q-2, R-2, S-
Q.69 The slenderness ratio for a cantilever prismatic column of length L with a circular cross section having radius r is
(A) L / r (B) 2L / r (C) 3L / r (D) 4L / r
Q.70 Match the designers in Group I with the terms in Group II
Group I Group II
P. Max Dubois 1. Prefabrication
Q. Joseph Paxton 2. Domino System
R. Victor Horta 3. Minimalism
4. Vegetal Ornamentation
(A) P-2, Q-1, R-4 (B) P-4, Q-1, R-3
(C) P-2, Q-4, R-3 (D) P-l, Q-3, R-4
Common Data Questions Common Data for Questions 71,72,73:
The continuous utility data for a construction project is as follows:
Activity Duration (days) Immediate
Normal Crash Predecessors
P 3 3
Q 44 P
R 2 I P
S 3 3 P
T 0 0 Q
U 6 5 R, T
V 4 2 S
Q.71 The normal project time for the given network is
(A) 11 (B) 12 (C) 13 (D) 14
Q.72 For the all-normal solution, the total float and free float for the activity S are (A) 1,1 (B) 0, 3 (C)3,3 (D) 3, 0
Q.73 While crashing the project, the first step cf compression would involve the activity (A) R (B) U (C) T (D) V
Common Data for Questions 74, 75:
A room measuring 10 m x 10 m has to be illuminated to a level of 200 lux by a single electrical lamp. The coefficient of utilization is 0.75 and the maintenance factor is 0.8.
Q.74 The lumen output required for the above lamp is
(A) 12,000 (B) 16,666 (C) 30,000 (D) 33,333
Q.75 The depreciation factor for the above lamp is
(A) 0.6 (B) 1.25 (C) 1.33 (D) 1.66
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 76 & 77:
The following data is related to the design of a septic tank for a housing complex:
Population of housing complex = 150
Water supply / person / day = 130 litres
Waste water flow = 80 % of water supply
Detention period = 1 day
Sludge production = 0.045 cu.m / person / year
Storage capacity for sludge = l/3rd of septic tank capacity
Q.76 Total capacity of septic tank in cubic metres is
(A) 31.70 (B) 23.40 (C) 20.80 (D) 15.60
Q.77 De-sludging interval (to the nearest year) is
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 78 & 79:
A residential plot measuring 12 metres x 15 metres abuts a road on its smaller side. Permissible ground coverage = 50 %, Floor Space Index (FSI) = 2.5 and maximum permissible floors = 4.
Q.78 Maximum total buildable area in sq.m is
(A) 180 (B) 225 (C) 360 (D)450
Q.79 As per revised building bye-laws, if the required setbacks are - Front 3 metres, each Side 2 metres and Rear 2 metres, then the maximum total buildable area will
(A) increase by 248 sq.m (B) increase by 40 sq.m
(C) decrease by 30 sq.m (D) decrease by 40 sq.m
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 80 & 81:
An aerial photograph is taken from a plane with a camera lens of focal length 305 mm. The desired scale of the photograph is 1: 25,000 and the height of the terrain above mean sea level is 300 metres.
Q.80 The flying height of the plane above mean sea level is
(A) 7,625 (B) 7,925 (C) 8,562 (D) 8,965
Q.81 If the above photograph is taken by a camera lens of focal length 210 mm from the same flying height, then the scale of the photograph will be
(A) 1 : 45,000 (B) 1 : 37,740 (C) 1: 36,310 (D) 1 : 19,050
A beam of cross section 300 mm x 400 mm has overhangs at both ends. The beam has a simple support of 10 metres and an overhang of 5 metres each at both ends and carrying a load of 10 kN on both the free ends.
Q.82 The maximum values of shear force and bending moment in the beam are
(A) 5 kN, 50 kN-m (B)20kN, 80 kN-m
(C) 15 kN, 45 kN-m (D) 10 kN, 50 kN-m
Q.83 The maximum values of bending stress and shear stress developed in the beam in N/mm2 are
(A) 5.15, 0.1 (B) 6.25, 0.125 (C) 7.35, 0.15 (D) 8.45, 0.175
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 84 & 85:
An auditorium has a volume of 3000 m3 with optimum reverberation time of 0.8 seconds.
Q.84 The sound absorption power required in the auditorium in m2-sabins is approximately
(A) 250 (B) 400 (C) 600 (D) 800
Q.85 During a convocation programme in the same auditorium, the absorption power increases by 200 m2-sabins. The reverberation time in seconds will now be
(A) 0.4 (B) 0.6 (C) 0.8 (D) 1.2
AR 17/20
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
