Centre for Development of Advanced Computing(C-DAC) 2006 M.C.A Computer Aplications 2 - DataStructure - - Question Paper
(Please write your Roll No. immediately) Roll No.
Second Semester [MCA] - MAY-JUNE 2006
Paper Code: MCA-102 Subject: Data Structure
Time: 3 Hours_Maximum Marks: 60
Note: Question 1. is compulsory and is of 20 marks. Attempt one out of two questions from remaining four units. All questions in units are of 10 marks each.
Q. 1 (a) Differentiate between the terms variable and parameter.
(b) Determine the length and number of substring of string THREAD.
A* (B + C) * D/E .
(c) Find the number of elements in the array A (1:8, -5:5, -10:5). Which will be the first and the last element of this array
(d) When is a link list better than arrays.
(e) Why infix expressions are converted into postfix expressions.
(f) Circular Queues is better than linear queues. Justify the statement.
(g) A given binary search tree is to be sorted. Which traversal method should be applied?
(h) Why searching is easier in sorted list.
(i) Discuss any one hash function.
(j) What is a B-tree?
Q. 2 (a) Given a linear sorted array having N elements and that it can store MAX elements. Write an algorithm to insert the contents of ITEM into it.
(b) Consider a linked list defined by START. It has a node with address P. Write an algorithm to split it into two link lists one starting with START and second has P as into first node.
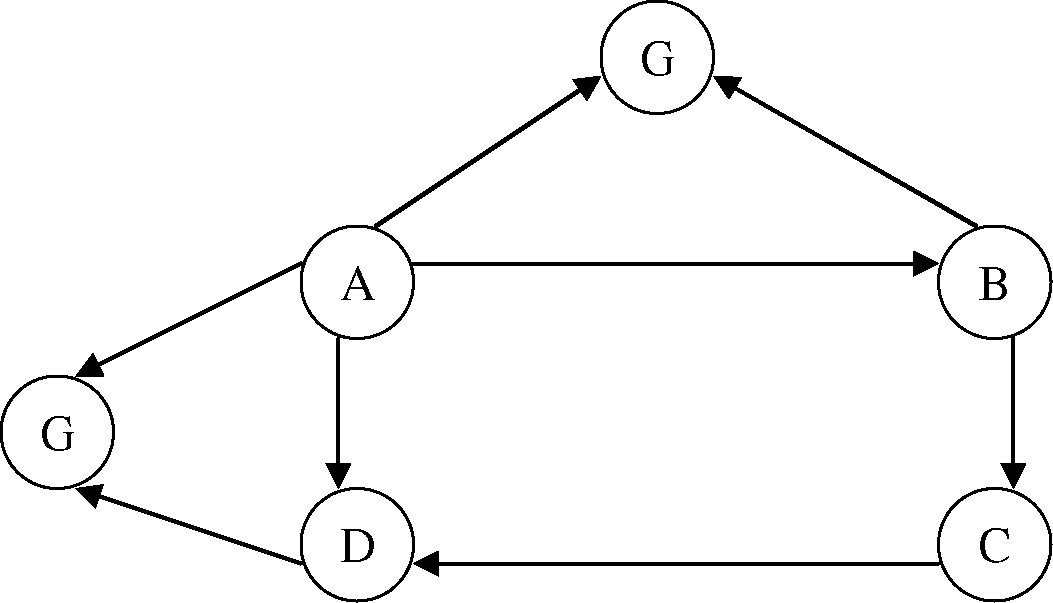
Q. 3 (a) The element of a binary tree.
- A
B C v
G
Have to be stored in an array. Write the desired algorithm. Te output should also indicate number of elements in the tree.
Q. 4 (a) Given list of numbers arranged in the form of linear array 44, 33, 11, 51, 77, 90, 99, 22. Using quick sort algorithm find the element of the array when 44 is set it position. Also discuss the status of STACK.
(b) Given the sorted list in the form of linear arrays having N and M elements. Write an algorithm to MERGE these lists into a single sorted list. The name of the elements these are repeated is to be enumerated.
Q. 5 (a) What is file organization? Why it is needed. Discuss in detail sequential file
organization with its MERITS and DEMERITS.
Q. 6 Write an algorithm to convert a given infix expression into an equivalent portfolio
expression. Illustrate the working of the algorithm on the following infix expression.
((8*7) + 4) * (7+9)/6-10
Q. 7 Describe any two of the following algorithms:
(a) Kruskals Algorithm
(b) Shell Sort
(c) Polyphone Merge sort
Second Semester [MCA] - MAY 2005
Paper Code: MCA-102 Subject: Data Structure
Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 60
Note: Question 1. is compulsory and is of 20 marks. Attempt one out of two questions from remaining four units. All questions in units are of 10 marks each.
Q. 1 (a) Define B-Tree
(b) Convert following infix expression into prefix and postfix
A* (B + C) * D/E .
(c) Give the difference between external and internal sorting. Give names of some external sorting techniques.
(d) Define stack and give some application s of stacks.
(e) How many nodes are there on level I of a binary tree? Prove the answer.
(f) Define transitive closure of a graph.
(g) Define inverted files.
(h) Describe adjacency list representation of graph with the help of an example.
(i) Give two examples of Hash function.
(j) Give difference between complete and full binary tree.
Q. 2 How polynomial are represented using linked list. Write program for addition of two polynomials represented using linked list.
Q. 3 Explain with the help of algorithm how infix expression converted to postfix
expression using stack.
Q. 4 Write Prims algorithm for finding minimum cost spanning tree. Show its
working on a graph.
Q. 5 Explain how trees can used for representation of disjoint sets. Explain Union of
find operations on these sets.
Q. 6 Explain Merge sort algorithm and show its working on following members
4, 10, 2, 6, 8, 12, 5, 7
Q. 7 What is hashing? What are various types of Hash functions? What are various methods of collision resolution?
Q. 8 What do you mean by file organization? Explain various file organization
techniques.
Q. 9 Write short notes on any two of the following Index techniques -
(d) Cylinder surface indexing
(e) Hashed Indexes
(f) Tree indexing.
|
Second Semester [MCA] - MAY 2004 | ||||||
| ||||||
Q. 1 (a) What is difference between Big-O and Small-O notation. Define them. 4
(b) Give an example of algorithm that has following complexity (in terms of Big-O). 4
(i) O (1) (ii) O(N)
(iii) O (N2) (iv) O (n log n)
(c) Algorithm 1 does a particular task in time N where N is no. of elements processed. Algorithm 2 does same task in time 3N + 1000. 4
(i) What are Big-O requirement of each algorithm.
(ii) Under what conditions, if any, would the less efficient algorithm executes more quickly than more efficient algorithm?
Q. 2 (a) Write a procedure to print elements of a singly linked list in reverse order while traversing it only once. 6
(b) Let a queue be implemented as a circular linked structure with an external pointer accessing the rear element: 6
(i) Draw a sketch of such a queue with one node.
(ii) Write a algorithm for insertion and deletion.
Q. 3 (a) Write an algorithm to implement selection sort. 7
(b) Sort the following numbers (Showing each iteration) using 5
Quick Sort :- 57, 73, 43, 77, 83, 63, 87.
Q. 4 Write a algorithm to convert infix expression to postfix expression using stack.
Also, write an algorithm to evaluate postfix expression. 12
Q. 5 Define sparse matrix. Implement sparse matrix as an array. Give an algorithm to transpose a sparse matrix for this implementation. 12
Q. 6 (a) What do you mean by file organization? Differentiate between sequential, hashed and random file organization. 6
(b) What is aim of hashing? What are different hashing techniques? What are the problems encountered in them and how to overcome them. 6
Q. 7 (a) Write a algorithm for topological sort of a graph. 7
(b) Taking an example of a graph. Show how breadth first search operates on this graph. 5
Q. 8 Write short notes on any three of the following :- 3 x 4
(a) Balanced Merge sort
(b) Critical path
(c) B+ tree
(d) B-tree
|
Second Semester [MCA] - MAY 2003 | ||||||
| ||||||
Q. 1 (a) Explain why there might be tradeoffs between saving computer (Execution)
time and saving programming time. 3
(b) Explain the difference between sequential array based representation and linked representation of a list with examples. 4
(c) Explain the difference between internal and external sorting with example. 3
(d) Define Big-O notation. 2
Q. 2 (a) Write a procedure in C/C++ to add two single variable polynomial using linked list. 7
(b) Write an algorithm that implement insertion and deletion operation on circular queue. 5
Q. 3 (a) Formulate an algorithm to implement insertion sort. 6
(b) Derive time complexities for insertion sort, quick sort, and selection sort.
6
Q. 4 (a) Define B-Tree. What is the difference B-Tree and B+ -Tree. 5
(b) Construct an AVL tree in which element are inserted in following order :
72, 44, 100, 200, 30, 57, 10 5
(c) What is difference between tree, binary tree and a graph? 2
Q. 5 Write a non-recursive algorithm for preorder traversal of a tree. Give example also. 12
Q. 6 (a) Write an algorithm to implement breadth first search for a graph. 6
(b) Taking an example of graph, show how depth first search operates on the graph. 12
Q. 7 What is sparse matrix? Implement sparse matrix as an array. Give an algorithm to add and subtract two sparse matrices for this implementation. 6
Q. 8 Write short notes on any three of the following :- 12
(a) Polyphase mergesort.
(b) Search Tree
(c) Inverted Tree
(d) Hashing
|
Second Semester [MCA] - JUNE 2001 | ||||||
| ||||||
Q. 1 (a) Write a routine, which reads the matrix, If non-zero elements are less than
25% of total elements, it converts this matrix to SPARSE matrix representation.
7
(b) What is advantage of circular queues over queues? Write add & delete routine for it. 7
Q. 2 (a) Differentiate between tree and binary tree. 4
(b) Write a module for insertion of node t as right child of s in threaded binary tree. Clearly explain its working using a suitable binary tree. 10
Q. 3 (a) Write a routine for traversal of singly linked list without using any additional
node. 9
(b) What do you mean by dynamic memory allocation? In which cases, it is used.
5
Q. 4 (a) Write PUSH & POP routines for linked stack. 6
(b) How do you determine run-time of algorithms? Give an example of O (n log n). 5
(c) Define generalized lists. 3
Q. 5 (a) Assume that we have a sorted array of elements in descending order. Can
binary search algorithm still be implemented on it? If yes, write the modified algorithm. If not, justify why not? 7
(b) If a list is already sorted in descending order, how fast will be insertion sort for ascending? Clearly explain. 7
Q. 6 (a) For an undirected graph G with n vertices & e edges, show that 6
n
d1 = 2 e where d1 = degree of vertex i. i =1
(b ) By considering the complete graph with n vertices, show that no. of spanning trees is atleast 2n-1 - 1. 8
Q. 7 (a) Write an algorithm to insert a new key value X into a tree in which the keys
are sampled from left to right, one character at a time. 7
(b) Define and explain inverted files. 7
Q. 8 (a) How overflow is handled in hashing. 10
(b) Define and explain cellular partitioning. 4
|
Second Semester [MCA] - AUGUST 2000 | ||||||
| ||||||
Q. 1 (a) What do you mean by data structure? Explain with the help of two examples. 3
(b) What do you mean by complexity of an algorithm? Explain with an example.3
(c) Define a Binary Search tree. Draw the expression tree for the following:
x : = (a<b) or (e < f) 3
(d) Determine the order in which the vertices of following binary tree will be
3
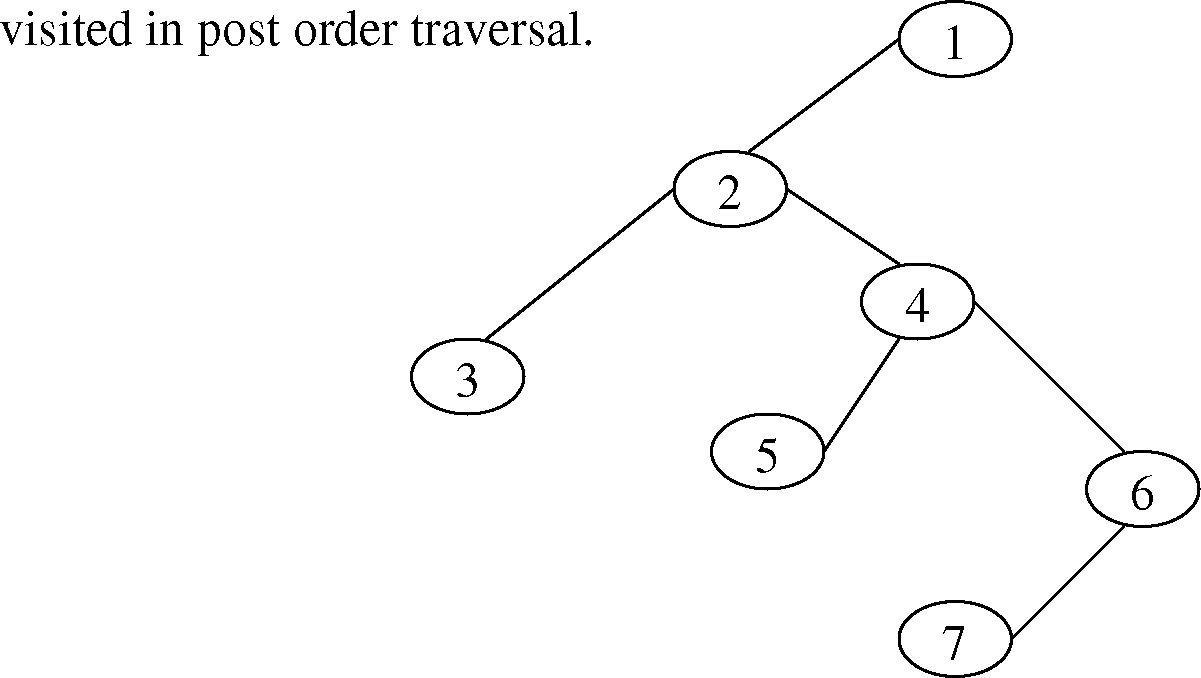 |
|
(e) Write a function in C that will count the number of nodes in linked binary tree. 5 |
(f) Convert following INFIX expression to POSTFIX expression
A+ (B*C) * (D + E) * F 2
(g) Give the average case and worst case complexity for the following algorithm
(i) Selection Sort (ii) Quick Sort 4
(h) Define AVL tree. Convert the following into an AVL tree. 4
(ii)
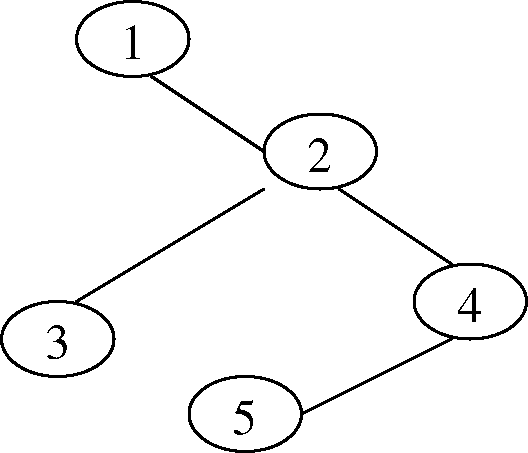
|
(i) |
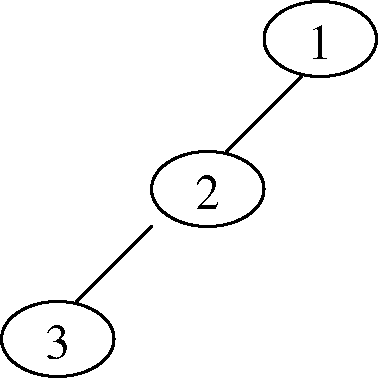 |
(i) Describe briefly sequential file organization with an example. 3
(j) What is the difference between internal and external sort. 2 (k) Write a function in C to delete a node, different from first and last node, from
a linked list. 4 (l) Give the node structure of a binary search tree. Using it write a recursive
function to traverse a tree in preorder. 4
Q. 2 Give the array implementation of the stack. Write function for pushing and
poping elements from a stack. 10
Q. 3 Draw a binary search tree when the keys arrive in the given order. 10 p, x, b, e, a, c, f, y, q, r
Delete the nodes containing the keys in the following order a, e, x
Q. 4 Describe the heap sort method for sorting the following list 10 15, 16, 13, 19, 5, 7, 4, 18 Show the result of the intermediate steps also.
Q. 5 (a) For the following digraph 7
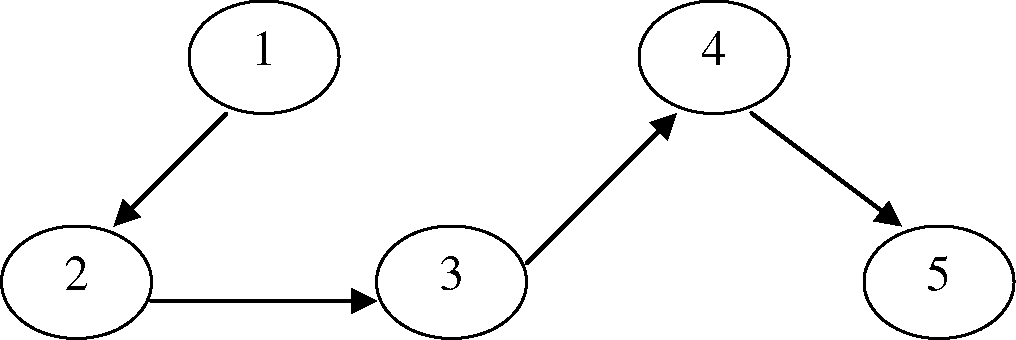
Obtain the transitive closure. Give the steps for finding the transitive closure.
(b) Write a recurrence relation for obtaining nth terms of the Fibonacci series.
3
Q. 6 Write a program in C to implement depth-first traversal of a graph. 10
Q. 7 Define a B-tree. Draw a B-tree of order 5 when the keys arrive in the following order.
a, f, g, b, h, d, j, m, s, e, r, i, e, x, n, l, u, t, p
and then delete the keys in the reverse order of arrival. 10
Give the array implementation of a circular queue. Write functions in C to insert and delete an element from circular queue. 10
Q. 8
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
