Army Institute of Fashion & Design 2010 Gate s - Question Paper
I ME | GATE 2010 www.2ateforum.com

Q. No. 1 - 25 Carry One Mark Each
1. The parabolic arc y = Vx, 1 < x < 2 is revolved around the x-axis. The volume of the solid of revolution is
(A) 4 (B) 22 (C) 34n (D) *
-> Th Dl 4-- d3f f d2f
2. The Blasius equation,- +--- = 0 is a
dn3 2 dn2
(A) Second order nonlinear ordinary differential equation
(B) Third order nonlinear ordinary differential equation
(C) Third order linear ordinary differential equation
(D) Mixed order nonlinear ordinary differential equation
30
3. The value of the integral f dx. is
J 1 + x2
4. The modulus of the complex number (y+4') is
(A) 5 (B) V5 (C) (D)5
5. The function y = |2 - 3x|
(A) is continuous Vx e R and differentiable Vx e R
(B) is continuous Vx e R and differentiable Vx e R except at x=3/2
(C) is continuous Vx e R and differentiable Vx e R except at x=2/3
(D) is continuous Vx e R except at x=3 and differentiable Vx e R
6. Mobility of a statically indeterminate structure is
(A) <-1 (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) > 2
7. There are two points P and Q on a planar rigid body. The relative velocity between the two points
(A) should always be along PQ
(B) Can be oriented along any direction
(C) should always be perpendicular to PQ
(D) should be along QP when the body undergoes pure translation

8. The state of plane-stress at a point is given by ctx = -200MPa, CTy = 100MPa and Txy = 100MPa. The maximum shear stress in MPa
is
(A) 111.8 (B) 150.1 (C) 180.3 (D) 223.6
9. Which of the following statements is INCORRECT?
(A) Grashof's rule states that for a planar crank-rocker four bar mechanism, the sum of the shortest and longest link lengths cannot be less than the sum of the remaining two link lengths.
(B) Inversions of a mechanism are created by fixing different links one at a time.
(C) Geneva mechanism is an intermittent motion device
(D) Gruebler's criterion assumes mobility of a planar mechanism to be one.
10. The natural frequency of a spring-mass system on earth is on. The natural frequency of this system on the moon (gmoon = gearth /6) is
(A) ran (B)0.408ran (C) 0.204ran (D) 0.167ran
11. Tooth interference in an external involute spur gear pair can be reduced by
(A) decreasing center distance between gear pair
(B) decreasing module
(C) decreasing pressure angle
(D) increasing number of gear teeth
12. For the stability of a floating body, under the influence of gravity alone, which of the following is TRUE?
(A) Metacentre should be below centre of gravity
(B) Metacentre should be above centre of gravity
(C) Metacentre and centre of gravity must lie on the same horizontal line
(D) Metacentre and centre of gravity must lie on the same vertical line
13. The maximum velocity of a one-dimensional incompressible fully developed viscous flow, between two fixed parallel plates, is 6ms-1. The mean velocity (in ms-1) of the flow is
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5
14. A phenomenon is modeled using n dimensional variables with k primary dimensions. The number of non-dimensional variables is
(A) k (B) n (C) n-k (D) n+k

15. A turbo-charged four-stroke direct injection diesel engine has a displacement volume of 0.0259m3 (25.9litres). The engine has an output of 950kW at 2200rpm. The mean effective pressure in MPa is closest to
(A) 2 (B) 1 (C) 0.2 (D) 0.1
16. One kilogram of water at room temperature is brought into contact with a high temperature thermal reservoir. The entropy change of the universe is
(A) equal to entropy change of the reservoir
(B) equal to entropy change of water
(C) equal to zero
(D) always positive
17. A hydraulic turbine develops 1000kW power for a head of 40m. If the head is reduced to 20m, the power developed (in kW) is
(A) 177 (B) 354 (C) 500 (D) 707
18. The material property which depends only on the basic crystal structure is
(A) fatigue strength (B) work hardening
(C) fracture strength (D) elastic constant
19. In a gating system, the ratio 1:2:4 represents
(A) sprue base area: runner area: ingate area
(B) pouring basin area: ingate area: runner area
(C) sprue base area: ingate area: casting area
(D) runner area: ingate area: casting area
-0.009
20. A shaft has a dimension, 35-0025. The respective values of fundamental deviation and tolerance are
(A) -0.025, 0.008 (B) -0.025,0.016
(C) -0.009, 0.008 (D) -0.009,0.016
21. In a CNC program block, N002 G02 G91 X40 Z40..., G02 AND G91 refer to
(A) circular interpolation in counterclockwise direction and incremental dimension
(B) circular interpolation in counterclockwise direction and absolute dimension
(C) circular interpolation in clockwise direction and incremental dimension
(D) circular interpolation in clockwise direction and absolute dimension
uhi crunum i i
EngineeringSuccess )ME| QATE2010 WWW.2ateforUm.com
22. The demand and forecast for February are 12000 and 10275, respectively. Using single exponential smoothening method (smoothening coefficient = 0.25), forecast for the month of March is
(A) 431 (B) 9587 (C) 10706 (D) 11000
23. Little's law is relationship between
(A) stock level and lead time in an inventory system
(B) waiting time and length of the queue in a queuing system
(C) number of machines and job due dates in a scheduling problem
(D) uncertainty in the activity time and project completion time
24. Vehicle manufacturing assembly line is an example of
(A) product layout (B) process layout (C) manual layout (D) fixed layout
25. Simplex method of solving linear programming problem uses
(A) all the points in the feasible region
(B) only the corner points of the feasible region
(C) intermediate points within the infeasible region
(D) only the interior points in the feasible region.
/ ~
1 Q. No. 26 - 51 Carry Two Marks Each
Note: All length dimensions shown in the figures are in mm unless otherwise specified. Figures are not drawn to scale.
26. Torque exerted on a flywheel over a cycle is listed in the table. Flywheel energy (in J per unit cycle) using Simpson's rule is
|
Angle (degree) |
0 |
60 |
120 |
180 |
240 |
300 |
360 |
|
Torque (Nm) |
0 |
1066 |
-323 |
0 |
323 |
-355 |
0 |
(A) 542
(B) 993
(C) 1444
(D) 1986
2 2 1 3
(C)
27. One of the eigen vectors of the matrix A =
is
4
2
(A)
(B)
(D)
-1
-1

28. Velocity vector of a flow field is given as V = 2xyi - x2zj. the velocity vector at (1,1,1) is
(A) 4 - j (B) 4 -k (C) i - 4j (D) i - 4k
29. The Laplace Transform of a functionf (t) = 1-. The f (t) is
W s2 (s + 1) W
(A) t -1 + e-t (B) t +1 + e-t (C) -1 + e-t (D) 2t + e
30. A box contains 2 washers, 3 nuts and 4 bolts. Items are drawn from the box at random one at a time without replacement. The probability of drawing 2 washers first followed by 3 nuts and subsequently the 4 bolts is
(A) 2/315 (B) 1/630 (C) 1/1260 (D) 1/2520
31. A band brake having band-width of 80mm, drum diameter of 250mm, coefficient of friction of 0.25 and angle of wrap of 270 degrees is required to exert a friction torque of 1000N-m. The maximum tension (in kN) developed in the band is
(A) 1.88 (B) 3.56 (C) 6.12 (D) 11.56
|
32. A bracket (shown in figure) is rigidly mounted on wall using four rivets. Each rivet is 6mm in diameter and has an effective length of 12mm. |
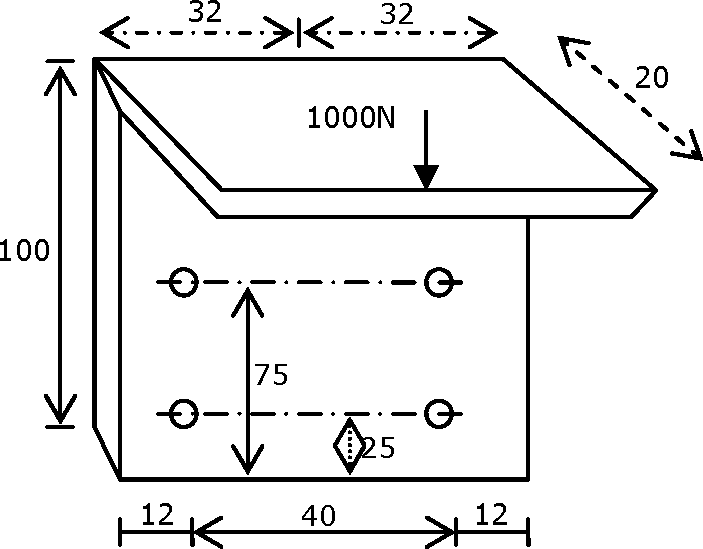 |
Direct shear stress (in MPa) in the most heavily loaded rivet is
(A) 4.4 (B) 8.8 (C) 17.6 (D) 35.2
33. A mass m attached to a spring is subjected to a harmonic force as shown in figure. The amplitude of the forced motion is observed to be 50mm. the value of m (in kg) is
k = 3000Nm
F (t) = 100 cos (100t) N
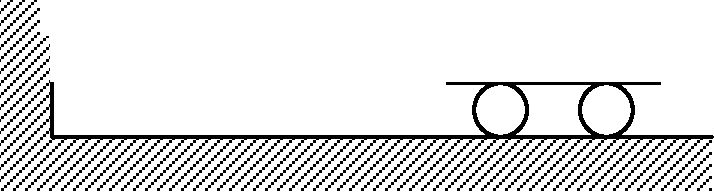

(A) 0.1
(C) 0.3
(D)0.5
(B) 1.0
34. For the epicyclic gear arrangement shown in the figure, o2 = 100rad/s clockwise
= 80rad/s counter clockwise (CCW). The angular velocity
(CW) and raa ra5(in rad/s) is
Ni = Number of teeth for gear i N2 = 20 N3 = 24 N4 = 32 N5 = 80
2
Shaft axis
arm
(A) 0
(B) 70CW
(C) 140CCW
(D) 140CW
35. A lightly loaded full journal bearing has a journal of 50mm, bush bore of 50.05mm and bush length of 20mm. if rotational speed of journal is 1200rpm and average viscosity of liquid lubricant is 0.03 Pa s, the power loss (in W) will be (A) 37 (B) 74 (C) 118 (D) 237
36. For the configuration shown, the angular velocity of link AB is 10 rad/s counterclockwise. The magnitude of the relative sliding velocity (in ms-1) of slider B with respect to rigid link CD is
D*
AB = 250 BC = 250
AC = 500
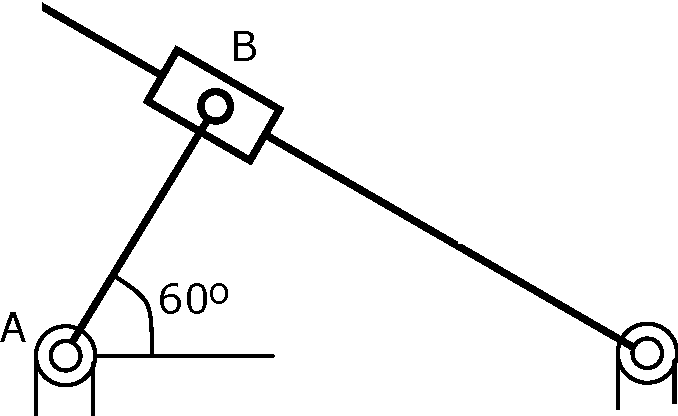 |
|
(B) 0.86 |
C
(C) 1.25
(A) 0
(D) 2.5
37. A smooth pipe of diameter 200mm carries water. The pressure in the pipe at section S1 (elevation: 10m) is 50kPa. At Section S2 (elevation: 12m) the pressure is 20kPa and velocity is 2ms-1. Density of water is 1000kgm-3 and acceleration due to gravity is 9.8ms-2. Which of the following is TRUE?
(A) flow from S1 to S2 and head loss is 0.53m
(B) flow from S2 to S1 and head loss is 0.53m

(C) flow from S1 to S2 and head loss is 1.06m
(D) flow from S2 to S1 and head loss is 1.06m
38. Match the following
|
P:Compressible flow |
U: Reynolds number |
|
Q: Free surface flow |
V: Nusselt number |
|
R: Boundary layer flow |
W: Weber number |
|
S: Pipe flow |
X: Froude number |
|
T: Heat convection |
Y: Mach number |
|
Z: Skin friction coefficient |
(A) P-U; Q-X; R-V; S-Z; T-W (B) P-W; Q-X; R-Z; S-U; T-V
(C) P-Y; Q-W; R-Z; S-U; T-X (D) P-Y; Q-W; R-Z; S-U; T-V
39. A mono-atomic ideal gas (y = 1.67, molecular weight = 40) is compressed adiabatically from 0.1MPa, 300K to 0.2MPa. The universal gas constant is 8.314kJkmol-1K-1. The work of compression of the gas (in kJ kg-1) is
(A) 29.7 ~ (B) 19.9 (C) 13.3 (D) 0
40. Consider the following two processes:
a. A heat source at 1200K loses 2500kJ of heat to sink at 800K
b. A heat source at 800K loses 2000kJ of heat to sink at 500K Which of the following statements is TRUE?
(A) Process I is more irreversible than Process II
(B) Process II is more irreversible than Process I
(C) Irreversibility associated in both the processes is equal
(D) Both the processes are reversible
41. A fin has 5mm diameter and 100mm length. The thermal conductivity of fin material is 400Wm-1K-1. One end of the fin is maintained at 130C and its remaining surface is exposed to ambient air at 30C. if the convective heat transfer coefficient is 40Wm-2K-1, the heat loss (in W) from the fin is
(A) 0.08 (B) 5.0 (C) 7.0 (D) 7.8
42. A moist air sample has dry bulb temperature of 30C and specific humidity of
11.5g water vapour per kg dry air. Assume molecular weight of air as 28.93. If the saturation vapour pressure of water at 30C is 4.24kPa and the total pressure is 90kPa, then the relative humidity (in %) of air sample is
(A) 50.5 (B) 38.5 (C) 56.5 (D) 68.5

43. Two pipes of inner diameter 100mm and outer diameter 110mm each joined by flash butt welding using 30V power supply. At the interface, 1mm of material melts from each pipe which has a resistance of 42.4Q. If the unit melt energy is 64.4MJm-3, then time required for welding in seconds is
(A) 1 (B) 5 (C) 10 (D) 20
44. For tool A, Taylor's tool life exponent (n) is 0.45 and constant (K) is 90. Similarly for tool B, n=0.3 and K=60. The cutting speed (in m/min) above which tool A will have a higher tool life than tool B is
(A) 26.7 (B) 42.5 (C) 80.7 (D) 142.9
45. A taper hole is inspected using a CMM, with a probe of 2mm diameter. At a height, Z=10mm from the bottom, 5 points are touched and a diameter of circle (not compensated for probe size) is obtained as 20mm. similarly, a 40mm diameter is obtained at a height Z=40mm. the smaller diameter (in mm) of hole at Z=0 is
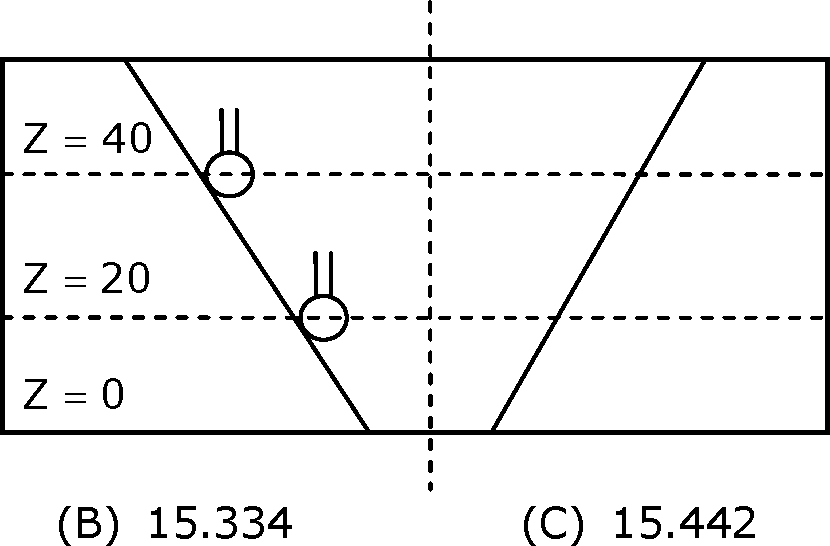
(A) 13.334
(D) 15.542
46. Annual demand for window frames is 10000. Each frame costs Rs. 200 and ordering cost is Rs. 300 per order. Inventory holding cost is Rs. 40 per frame per year. The supplier is willing to offer 2% discount if the order quantity is 1000 or more, and 4% if order quantity is 2000 or more. If the total cost is to be minimized, the retailer should
(A) order 200 frames every time (B) accept 2% discount
(C) accept 4% discount (D) order Economic Order Quantity
|
47. The project activities, precedence relationships and durations are described in the table. The critical path of the project is | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(A) P-R-T-V (B) Q-S-T-V (C) P-R-U-W (D) Q-S-U-W |

Common Data Questions: 48 & 49
In a steam power plant operating on the Rankine cycle, steam enters the turbine at 4MPa, 350C and exits at a pressure of 15kPa. Then it enters the condenser and exits as saturated water. Next, a pump feeds back the water to the boiler. The adiabatic efficiency of the turbine is 90%. The thermodynamic states of water and steam are given in the table.
|
State |
h(kJ kg-1) |
s(kJ kg 1K 1) |
v (kg 1) | |||
|
Steam: 4MPa, 350C |
3092.5 |
6.5821 |
0.06645 | |||
|
Water: 15kPa |
hf |
hg |
sf |
sg |
vf |
vg |
|
225.94 |
2599.1 |
0.7549 |
8.0085 |
0.001014 |
10.02 | |
h is specific enthalpy, s is specific entropy and v the specific volume; subscripts f and g denote saturated liquid state and saturated vapour state.
48. The net work output ( kg-1) of the cycle is
(A) 498 ~ (B) 775 (C) 860
(D)957
49. Heat supplied ( kg-1 )othe cycle is
(A) 2372 (B) 2576 (C) 2863
(D)3092
Common Data Questions: 50 & 51
Four jobs are to be processed on a machine as per data listed in the table.
|
Job |
Processing time (in days) |
Due date |
|
1 |
4 |
6 |
|
2 |
7 |
9 |
|
3 |
2 |
19 |
|
4 |
8 |
17 |
50. If the Earliest Due Date (EDD) rule is used to sequence the jobs, the number of jobs delayed is
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4

51. Using the Shortest Processing Time (SPT) rule, total tardiness is
(A) 0 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Linked Answer Questions: Q.52 to Q.55 Carry Two Marks Each
Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 52 & 53
A massless beam has a loading pattern as shown in the figure. The beam is of rectangular cross-section with a width of 30mm and height of 100mm.
3000Nm-1
I
C
2000
The maximum bending moment occurs at
52.
(A) Location B
(B) 2675mm to the right of A
(C) 2500mm to the right of A
(D) 3225mm to the right of A
53. The maximum magnitude of bending stress (in MPa) is given by
(A) 60.0 (B) 67.5 (C) 200.0 (D) 225.0
Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 54 & 55
In a shear cutting operation, a sheet of 5mm thickness is cut along a length of 200mm. The cutting blade is 400mm long and zero-shear (S=0) is provided on the edge. The ultimate shear strength of the sheet is 100MPa and penetration to thickness ratio is 0.2. Neglect friction.
400
I*----------------------------!
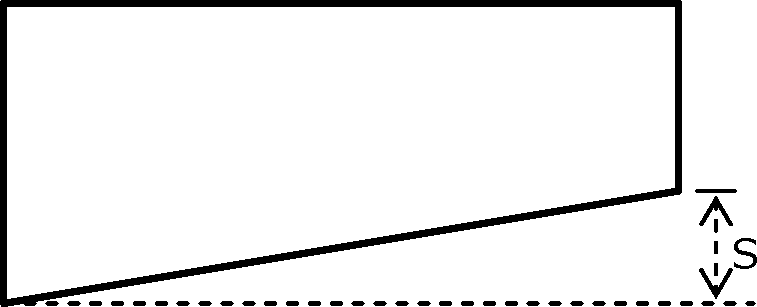
54. Assuming force vs displacement curve to be rectangular, the work done (in J) is (A) 100 (B) 200 (C) 250 (D) 300

55. A shear of 20mm (S=20mm) is now provided on the blade. Assuming force vs displacement curve to be trapezoidal, the maximum force (in kN) exerted is
(A) 5 (B) 10 (C) 20 (D) 40
Q. No. 56 - 60 Carry One Mark Each
56. 25 persons are in a room. 15 of them play hockey, 17 of them play football and
10 of them play both hockey and football. Then the number of persons playing neither hockey nor football is:
(A) 2 (B) 17 (C)13 (D) 3
57. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence:
If we manage to_our natural resources, we would leave a
better planet for our children.
(A) uphold (B) restrain (C) cherish (D) conserve
58. The question below consists of a pair of related words followed by four pairs of words. Select the pair that best expresses the relation in the original pair. Unemployed: Worker
(A) fallow: land (B) unaware: sleeper (C) wit: jester (D) renovated: house
59. Which of the following options is the closest in meaning to the word below: Circuitous
(A) cyclic (B) indirect (C) confusing (D) crooked
60. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to the complete the following sentence:
His rather casual remarks on politics_his lack of seriousness
about the subject.
(A) masked (B) belied (C) betrayed (D)suppressed
Q. No. 61 - 65 Carry Two Marks Each
61. Hari (H), Gita (G), Irfan (I) and Saira (S) are siblings (i.e. brothers and sisters). All were born on 1st January. The age difference between any two successive siblings (that is born one after another) is less than 3 years. Given the following facts:
i. Hari's age + Gita's age > Irfan's age + Saira's age
ii. The age difference between Gita and Saira is 1 year. However, Gita is not the oldest and Saira is not the youngest.
iii. There are no twins.
In what order were they born (oldest first)?
(A) HSIG (B) SGHI (C) IGSH (D) IHSG

62. 5 skilled workers can build a wall in 20days; 8 semi-skilled workers can build a wall in 25 days; 10 unskilled workers can build a wall in 30days. If a team has 2 skilled, 6 semi-skilled and 5 unskilled workers, how long will it take to build the wall?
(A) 20 days (B) 18 days (C) 16 days (D) 15 days
63. Modern warfare has changed from large scale clashes of armies to suppression of civilian populations. Chemical agents that do their work silently appear to be suited to such warfare; and regretfully, there exist people in military establishments who think that chemical agents are useful tools for their cause.
Which of the following statements best sums up the meaning of the above passage:
(A) Modern warfare has resulted in civil strife.
(B) Chemical agents are useful in modern warfare.
(C) Use of chemical agents in warfare would be undesirable
(D) People in military establishments like to use chemical agents in war.
64. Given digits 2,2,3,3,4,4,4,4 how many distinct 4 digit numbers greater than 3000 can be formed?
(A) 50 _ (B) 51 (C) 52 (D) 54
65. If 137+276=435 how much is 731 + 672?
(A) 534 _ (B) 1403 (C) 1623 (D) 1513
All rights reserved by Gateforum Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. No part of this document may be reproduced or utilized in any form without the
written permission. Discuss GATE 2010 question paper at www.gatementor.com. 12
I Engineering Success ME | GATE Paper 2009
III 1
www. gateforum. com
Q. No. 1 - 20 Carry One Mark Each
1. For a matrix [M] =
3 4 5 5 3
x 5.
, the transpose of the matrix is equal to the inverse of the matrix [M]t = [M]"1. The value of x is given by
(D) 4
2. The divergence of the vector field 3xzi + 2xyj - yz2k at a point (1,1,1 ) is equal to
(A) 7 (B) 4 (C) 3 (D) 0
1
3. The inverse Laplace transform of
is
(A) 1 + et
(B) 1 - et
(D) 1 + e-
(C) 1 - e-t
4. If three coins are tossed simultaneously, the probability of getting at least one head
(A) 1/8
(C) 1/2
(D) 7/8
(B) 3/8
5. If a closed system is undergoing an irreversible process, the entropy of the system
(A) Must increase
(B) Always remains constant
(C) Must decrease
(D) Can increase, decrease or remain constant
6. A coolant fluid at 30C flows over a heated flat plate maintained at a constant temperature of 100C. The boundary layer temperature distribution at a given location on the plate may be approximated as T = 30 + 70 exp (-y) where y (in m)
is the distance normal to the plate and T is in C. If thermal conductivity of the fluid is 1.0W/mK, the local convective heat transfer coefficient (in W/m2K) at that location will be
(A) 0.2 (B) 1 (C) 5 (D) 10
7. A frictionless piston-cylinder device contains a gas initially at 0.8MPa and 0.015 m3. It expands quasi-statically at constant temperature to a final volume of 0.030 m3. The work output (in kJ) during this process will be
(A) 8.32 (B) 12.00 (C) 554.67 (D) 8320.00
8. In an ideal vapour compression refrigeration cycle, the specific enthalpy of refrigerant (in kJ/kg) at the following states is given as:
Inlet of condenser: 283
Exit of condenser: 116
Exit of evaporator: 232
The COP of this cycle is
(A) 2.27 (B) 2.75 (C) 3.27 (D) 3.75
9. A compressor undergoes a reversible, steady flow process. The gas at inlet and outlet of the compressor is designated as state 1 and state 2 respectively. Potential and kinetic energy changes are to be ignored. The following notations are used:
v= specific volume and P=pressure of the gas.
The specific work required to be supplied to the compressor for this gas compression process is 2 2 (A) JPdv (B) JvdP (C) vj (P2 - Pj) (D) -P2 (vj - v2)
1 1
10. A block weighing 981N is resting on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block and the horizontal surface is = 0.2A vertical cable attached to the block provides partial support as shown. A man can pull horizontally with a force of 100N. What will be the tension, T (in N) in the cable if the man is just able to move the block to the right?

(A) 176.2 (B) 196.0 (C) 481.0 (D) 981.0
11. If the principal stresses in a plane stress problem, are a1 = 100MPa, a2 = 40MPa, the magnitude of the maximum shear stress (in MPa) will be
(A) 60 (B) 50 (C) 30 (D) 20
12. A simple quick return mechanism is shown in the figure. The forward to return ratio of the quick return mechanism is 2:1. If the radius of the crank O1P is 125 mm, then the distance 'd' (in mm) between the crank centre to lever pivot centre point should be

(D) 250.0
(A) 144.3
13. The rotor shaft of a large electric motor supported between short bearings at both deflection of 1.8mm in the middle of the rotor. Assuming the rotor to be perfectly balanced and supported at knife edges at both the ends, the likely critical speed (in rpm) of the shaft is
(A) 350 (B) 705 (C) 2810 (D) 4430
14. A solid circular shaft of diameter d is subjected to a combined bending moment M and torque, T. The material property to be used for designing the shaft using the
relation -Wm2 + T2 is nd3
|
(A) ultimate tensile strength (Su) (C) torsional yield strength (Ssy) |
(B) tensile yield strength (Sy) (D) endurance strength (Se) |
15. The effective number of lattice points in the unit cell of simple cubic, body centered cubic, and face centered cubic space lattices, respectively, are
(A) 1,2,2 (B) 1,2,4 (C) 2,3,4 (D) 2,4,4
16. Friction at the tool-chip interface can be reduced by
(A) decreasing the rake angle (B) increasing the depth of cut
(C) decreasing the cutting speed (D) increasing the cutting speed
17. Two streams of liquid metal, which are not hot enough to fuse properly, result into a casting defect known as
(A) cold shut (B) swell (C) sand wash (D) scab
18. The expected time (te) of a PERT activity in terms of optimistic time (t0), pessimistic time (tp) and most likely time (tl) is given by
to + 4t + tp to + 4tp +1,
(A) te = p (B) te
6 ' ' e 6
(C) te = to + 4tl + tp (D) te = to + 4t' +tj
19. Which of the following is the correct data structure for solid models?
(A) solid part faces edges vertices
(B) solid part edges faces vertices
(C) vertices edges faces solid parts
(D) vertices faces edges solid parts
20. Which of the following forecasting methods takes a fraction of forecast error into account for the next period forecast?
(A) simple average method (B) moving average method
(C) weighted moving average method (D) exponential smoothening method
Q. No. 21 - 56 Carry Two Marks Each
21. An analytic function of a complex variable z = x + iy is expressed as f (z) = u(x,y) + iv(x, y) where i = >/_! . If u = xy, the expression for v should be
2
2
2
2
x
y
y
(B)
+ k
(C)
+ k
2
2
(D) + k
22. The solution of x + y = x4 with the condition y (1) = 6 is
dx yv ; 5
x4 1 4x4 4 x4 x5
(A) y = x. +1 (B) y = + -4 (C) y = X +1 (D) y = x. +1
5 x 5 5x 5 5
23. A path AB in the form of one quarter of a circle of unit radius is shown in the figure. Integration of (x + y )2 on path AB traversed in a counter-clockwise sense is y

(A) n_ 1
(D) 1
X
24. The distance between the origin and the point nearest to it on the surface z2 = 1 + xy is
(C) 73
(A) 1
(D) 2
25. The area enclosed between the curves y2 = 4x and x2 = 4y is
(A) (B) 8 (C) (D) 16
26. The standard deviation of a uniformly distributed random variable between 0 and
1 is
1
5
7
(A)
(C)
(D)
V12
V12
V12
(b)T!
27. Consider steady, incompressible and irrotational flow through a reducer in a horizontal pipe where the diameter is reduced from 20cm to 10cm. The pressure in the 20cm pipe just upstream of the reducer is 150kPa. The fluid has a vapour pressure of 50kPa and a specific weight of 5 kN/m3. Neglecting frictional effects, the maximum discharge (in m3/s) that can pass through the reducer without causing cavitation is
(A) 0.05 (8) 0.16 (C) 0.27 (D) 0.38
28. In a parallel flow heat exchanger operating under steady state, the heat capacity rates (product of specific heat at constant pressure and mass flow rate) of the hot and cold fluid are equal. The hot fluid, flowing at 1kg/s with Cp = 4kJ/kgK, enters the heat exchanger at 102C while the cold fluid has an inlet temperature of 15C. The overall heat transfer coefficient for the heat exchanger is estimated to be 1kW/m2K and the corresponding heat transfer surface area is 5m2. Neglect heat transfer between the heat exchanger and the ambient. The heat exchanger is characterized by the following relation:
2e = 1 - exp (-2NTU).
The exit temperature (in C) for the cold fluid is
(A) 45 (B)55 (C) 65 (D) 75
29. In an air-standard Otto cycle, the compression ratio is 10. The condition at the beginning of the compression process is 100kPa and 27C. Heat added at constant volume is 1500kJ/kg, while 700kJ/kg of heat is rejected during the other constant volume process in the cycle. Specific gas constant for air=0.287 kJ/kgK. The mean effective pressure (in kPa) of the cycle is
(A) 103 (B) 310 (C) 515 (D) 1032
30. An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50kW. The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17C and 75C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is
(A) 50 (B) 250 (C) 300 (D) 360
31. You are asked to evaluate assorted fluid flows for their suitability in a given laboratory application. The following three flow choices, expressed in terms of the two-dimensional velocity fields in the xy-plane, are made available.
P. u = 2y, v = -3x
Q. u = 3xy, v = 0
R. u = -2x, v = 2y
Which flow(s) should be recommended when the application requires the flow to be incompressible and irrotational?
(A) P and R (B) Q (C) Q and R (D) R
32. Water at 25C is flowing through a 1.0km long G.I pipe of 200mm diameter at the rate of 0.07m3/s. If value of Darcy friction factor for this pipe is 0.02 and density of water is 1000kg/m3, the pumping power (in kW) required to maintain the flow is
(A) 1.8
(C) 20.5
(D) 41.0
(B) 17.4
33. Consider steady-state heat conduction across the thickness in a plane composite wall (as shown in the figure) exposed to convection conditions on both sides.
|
iii | |
|
l|| |
pr |
|
iii |
III |
|
L1 . |
L2 |
h,,T
h0, T~,0
Given:
h = 20W /m2K; h0 = 50W /m2K; = 200C; =-20C; k = 20W/mK; k2 = 50W/mK;
L1 = 0.30m and L2 = 0.15m.
Assuming negligible contact resistance between the wall surfaces, the interface temperature, T (in C), of the two walls will be
(A) -0.50 (B) 2.75 (C) 3.75 (D) 4.50
34. The velocity profile of a fully developed laminar flow in a straight circular pipe, as
/
R2
shown in the figure, is given by the expression u (r ) = -
is a constant. The average velocity of fluid in the pipe is dx
2
dp
dx y
where

(A) - R-1dp 8-
(B) - dp
4-
(C) - f dp
2-
(D) - - [
- I dX y
dX y
dX y
dX y
35. A solid shaft of diameter, d and length L is fixed at both the ends. A torque, T0 is applied at a distance, L/4 from the left end as shown in the figure given below

(C) 8,0
nd3
4T
(D)
nd3
(B)
nd3
The maximum shear stress in the shaft is
12T
(A)
nd3
36. An epicyclic gear train is shown schematically in the adjacent figure
The sun gear 2 on the input shaft is a 20 teeth external gear. The planet gear 3 is a 40 teeth external gear. The ring gear 5 is a 100 teeth internal gear. The ring gear 5 is fixed and the gear 2 is rotating at 50 rpm ccw (ccw=counter-clockwise and cw=clockwise)
The arm 4 attached to the output shaft will rotate at

(A) 10 rpm ccw
(D) 12 rpm ccw
37. A forged steel link with uniform diameter of 30mm at the centre is subjected to an axial force that varies from 40kN in compression to 160kN in tension. The tensile (Su), yield (Sy) and corrected endurance (Se) strengths of the steel material are 600MPa, 420MPa and 240MPa respectively. The factor of safety against fatigue endurance as per Soderberg's criterion is
(A) 1.26 (B) 1.37 (C) 1.45 (D) 2.00
38. An automotive engine weighing 240kg is supported on four springs with linear characteristics. Each of the front two springs have a stiffness of 16MN/m while the stiffness of each rear spring is 32MN/m. The engine speed (in rpm), at which resonance is likely to occur, is
(A) 6040 (B) 3020 (C) 1424 (D) 955
39. A vehicle suspension system consists of a spring and a damper. The stiffness of the spring is 3.6kN/m and the damping constant of the damper is 400Ns/m. If the mass is 50kg, then the damping factor (d) and damped natural frequency (fn), respectively, are
(A) 0.471 and 1.19Hz (B) 0.471 and 7.48Hz
(C) 0.666 and 1.35Hz (D) 0.666 and 8.50Hz
40. A frame of two arms of equal length L is shown in the adjacent figure. The flexural rigidity of each arm of the frame is EI. The vertical deflection at the point of application of load P is
a
PL3
(A) 3EI
2PL3
3EI
L
(B)
P
PL3 (C) V ' EI
-a
4PL3
3EI
(D)
L
41. A uniform rigid rod of mass M and length L is hinged at one end as shown in the adjacent figure. A force P is applied at a distance of 2L/3 from the hinge so that the rod swings to the right. The reaction at the hinge is

(A) -P
(B) 0
(C) P/3
(D) 2P/3

|
42. Match the approaches given below to perform stated kinematics / dynamics analysis of machine. | ||||||||||
|
(A)
P-1,Q-2,R-3,S-4 (B) P-3,Q-4,R-2,S-1
P-2,Q-3,R-4,S-1 (D) P-4,Q-2,R-1,S-3
(C)
43. A company uses 2555 units of an item annually. Delivery lead time is 8 days. The recorder point (in number of units) to achieve optimum inventory is
(A) 7 (B) 8 (C) 56 (D) 60
44. Consider the following Linear Programming Problem (LPP):
Maximize z = 3xj + 2x2
Subject to xj < 4
x2 < 6 3xj + 2x2 < 18 x! > 0, x2 > 0
(A) The LPP has a unique optimal solution
(B) The LPP is infeasible
(C) The LPP is unbounded
(D) The LPP has multiple optimal solutions
45. Six jobs arrived in a sequence as given below:
|
Jobs |
Processing Time (days) |
|
I |
4 |
|
II |
9 |
|
III |
5 |
|
IV |
10 |
|
V |
6 |
|
VI |
8 |
Average flow time (in days) for the above jobs using Shortest Processing Time rule is
(A) 20.83 (B) 23.16 (C) 125.00 (D) 139.00
46. Minimum shear strain in orthogonal turning with a cutting tool of zero rake angle is
(A) 0.0 (B) 0.5 (C) 1.0 (D) 2.0
47. Electrochemical machining is performed to remove material from an iron surface of 20mmx20mm under the following conditions:
Inter electrode gap = 0.2mm
Supply voltage (DC) = 12V
Specific resistance of electrolyte = 2Hcm
Atomic weight of Iron = 55.85
Valency of Iron = 2
Faraday's constant = 96540 Coulombs
The material removal rate (in g/s) is
(A) 0.3471 (B) 3.471 (C) 34.71 (D) 347.1
48. Match the following
|
NC Code |
Definition |
|
P. M05 |
1. Absolute coordinate system |
|
Q. G01 |
2. Dwell |
|
R. G04 |
3. Spindle stop |
|
S. G90 |
4. Linear interpolation |
(A) P-2,Q-3,R-4,S-1 (B) P-3,Q-4,R-1,S-2
(C) P-3,Q-4,R-2,S-1 (D) P-4,Q-3,R-2,S-1
49. What are the upper and lower limits of the shaft represented by 60 f8?
Use the following data:
Diameter 60 lies in the diameter step of 50-80mm
Fundamental tolerance unit, i, in m=0.45D1/3+0.001D, where D is the representative size in mm;
Tolerance value for IT8=25i. Fundamental deviation for 'f' shaft = -5.5D041
(A) Lower limit = 59.924mm, Upper Limit = 59.970mm
(B) Lower limit = 59.954mm, Upper Limit = 60.000mm
(C) Lower limit = 59.970mm, Upper Limit = 60.016mm
(D) Lower limit = 60.000mm, Upper Limit = 60.046mm
50. Match the items in Column I and Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
P. Metallic Chills |
1. Support for the core |
|
Q. Metallic Chaplets |
2. Reservoir of the molten metal |
|
R. Riser |
3. Control cooling of critical sections |
|
S. Exothermic Padding |
4. Progressive solidification |
(A) P-1,Q-3,R-2,S-4 (C) P-3,Q-4,R-2,S-1
(B) P-1,Q-4,R-2,S-3 (D) P-4,Q-1,R-2,S-3
Common Data Questions: 51 & 52
The inlet and the outlet conditions of stream for an adiabatic steam turbine are as indicated in the notations are as usually followed
hi
figure.
V
1
3200kJ/kg = 160m/s
Z1 = 10m P1 = 3MPa
h2 = 2600kJ/kg V2 = 100m /s Z2 = 6m P2 = 70kPa
51. If mass flow rate of steam through the turbine is 20kg/s, the power output of the turbine (in MW) is
(A) 12.157 (B) 12.941 (C) 168.001 (D) 168.785
52. Assume the above turbine to be part of a simple Rankine cycle. The density of water at the inlet to the pump is 1000kg/m3. Ignoring kinetic and potential energy effects, the specific work (in kJ/kg) supplied to the pump is
(A) 0.293 (B) 0.351 (C) 2.930 (D) 3.510
Common Data Questions: 53 & 54
Radiative heat transfer is intended between the inner surfaces of two very large isothermal parallel metal plates. While the upper plate (designated as plate 1) is a black surface and is the warmer one being maintained at 727C, the lower plate (plate 2) is a diffuse and gray surface with an emissivity of 0.7 and is kept at 227C. Assume that the surfaces are sufficiently large to form a two-surface enclosure and steady state conditions to exist. Stefan Boltzmann constant is given as 5.67x10-8W/m2K4
53. The irradiation (in kW/m2) for the upper plate (plate 1) is
(A) 2.5 (B) 3.6 (C) 17.0 (D) 19.5
54. If plate 1 is also a diffuse and gray surface with an emissivity value of 0.8, the net radiation heat exchange (in kW/m2) between plate 1 and plate 2 is
(A) 17.0 (B) 19.0 (C) 23.0 (D) 31.7
Common Data Questions: 55 & 56
Consider the following PERT network:

|
The optimistic time, most likely time and pessimistic time of all the activities are given in the table below | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
55. The critical path duration of the network (in days) is
(A) 11 (B) 14 (C) 17 (D) 18
56. The standard deviation of the critical path is
(A) 0.33 (B) 0.55 (C) 0.77 (D) 1.66
Linked Answer Questions: Q.57 to Q.60 Carry Two Marks Each Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 57 & 58
|
In a machining experiment, tool life was found to vary with the cutting speed in the following manner: | ||||||
|
57. The exponent (n) and constant (k) of the Taylor's tool life equation are (A) n = 0.5 and k = 540 (B) n = 1 and k = 4860
(C) n = -1 and k = 0.74 (D) n = -0.5 and k = 1.155
58. What is the percentage increase in tool life when the cutting speed is halved? (A) 50% (B) 200% (C) 300% (D) 400%
Statement for Linked Answer Questions: 59 & 60
A 20 full depth involute spur pinion of 4mm module and 21 teeth is to transmit 15kW at 960rpm. Its face width is 25mm.
The tangential force transmitted (in N) is
59.
(A) 3552 (B) 2611 (C) 1776 (D) 1305
60. Given that the tooth geometry factor is 0.32 and the combined effect of dynamic load and allied factors intensifying the stress is 1.5; the minimum allowable stress (in MPa) for the gear material is
(A) 242.0 (B) 166.5 (C) 121.0 (D) 74.0
All rights reserved by GATE Forum Educational Services Pvt. Ltd. No part of this booklet may be reproduced or utilized in any form without the
written permission. Discuss this questions paper at www.aateforum.com. Page 13 of 13
THE GATE ACADEMY
A Forum of IISc/IIT Graduates
<o
|
GATE CS & IT-2010 Solutions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Page 1
Correspondence Course * Classroom Coaching * All India Mock Test Series * Postal Test Series * Video Lectures * Online Tests/Classes* Crash Course Head Office : #74, Keshava Krupa (Third Floor), 30th Cross, 10th Main, Jayanagar 4th Block, Bangalore- 11, Ph : 080-22445535, Mob: +91 9663376248,
Copyright reserved. Log on to www.thegateacademy.com for details, updates, free online test, analysis, downloads, discussions etc.
|
GATE ECE-2010 Solutions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
<s> | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GATE ME-2010 Solutions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A Forum of IISc/IIT Graduates
iv iv iv. theaateacadem v. com
|
GATE EE-2010 Solutions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GATE IN-2010 Solutions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

Note: For detailed and descriptive solutions of the GATE papers, Please log in to
""Correspondence Course * Classroom Coaching * All India Mock Test Series * Postal Test Series * Video Lectures * Online Tests/Classes* Crash Course Head Office : #74, Keshava Krupa (Third Floor), 30th Cross, 10th Main, Jayanagar 4th Block, Bangalore- 11, Ph : 080-22445535, Mob: +91 9663376248,
Copyright reserved. Log on to www.thegateacademv.com for details, updates, free online test, analysis, downloads, discussions etc.
Page 2
$*n tOWi . ~w* Bntinoerini Scrvioc *
DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO
|
T.B.C : O-FTF-J-NFA Serial No.  |
Test Booklet Series  |
f mt i Maximum Marks : 200
Time Allowed : Two Hours
INSTRUCTIONS
1. IMMEDIATELY AFTER THE COMMENCEMENT OF THE EXAMINATION, YOU SHOULD CHECK THAT THIS TEST BOOKLET DOES NOT HAVE ANY UNPRINTED OR TORN OR MISSING PAGES OR ITEMS, ETC. IF SO, GET IT REPLACED BY A COMPLETE TEST BOOKLET.
2. ENCODE CLEARLY THE TEST BOOKLET SERIES A, B, C OR D AS THE CASE MAY BE IN THE APPROPRIATE PLACE IN THE ANSWER SHEET.

3. You have to enter your Roll Number on the Test Booklet in the Box provided alongside, DO NOT write anything else on the Test Booklet.
4. This Test Booklet contains 120 items (questions). Each item comprises four responses (answers). You will select the response which you want to mark on the Answer Sheet. In case you feel that there is more than one correct response, mark the response which you consider the best. In any case, choose ONLY ONE response for each item.
5. You have to mark all your responses ONLY on the separate Answer Sheet provided. See directions in the Answer Sheet.
6. All items carry equal marks.
7. Before you proceed to mark in the Answer Sheet the response to various items in the Test Booklet, you have to fill in some particulars in the Answer Sheet as per instructions sent to you with your Admission Certificate.
8. After you have completed filling in all your responses on the Answer Sheet and the examination has concluded, you should hand over to the Invigilator only the Answer Sheet. You are permitted to take away with you the Test Booklet.
9. Sheets for rough work are appended in the Test Booklet at the end.
10. Penalty for wrong answers ;
THERE WILL BE PENALTY FOR WRONG ANSWERS MARKED BY A CANDIDATE IN THE OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION PAPERS.
(i) There are four alternatives for the answer to every question. For each question for which a wrong answer has been given by the candidate, one-third (0*33) of the marks assigned to that question will be deducted as penalty.
(ii) If a candidate gives more than one answer, it will be treated as a wrong answer even if one of the given answers happens to be correct and there will be same penalty as above to that question.
(iii) If a question is left blank, i.e., no answer is given by the candidate, there will be no penalty for that question.
( DO NOT OPEN THIS TEST BOOKLET UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO )
|
1. Ice kept in a well insulated thermo flask is an example of which system ? (a) Closed system (b) Isolated system (c) Open system (d) Non-flow adiabatic system 2. The relation ds = "!p > where s represents entropy, Q represents heat and T represents temperature (absolute), holds good in which one of the following processes ? (a) Reversible processes only (b) Irreversible processes only (c) Both reversible and irreversible processes (d) All real processes 3. Consider the following properties of vapour : 1. Pressure 2. Temperature 3. Dryness fraction 4. Specific volume Which of these two properties alone are not sufficient to specify the condition of a vapour ? (a) 1 and 2 (b) 1 and 3 (c) 2 and 3 (d) 3 and 4 |
4. In a reversible isothermal expansion process, the fluid expands from 10 bar and 2 m3 to 2 bar and 10 m3, during the process the heat supplied is lOO.kW. What is the work done during the process ? (a) 33-3 kW (b) 100 kW (c) 80 kW (d) 20 kW 5. Measurement of temperature is based on which law of thermodynamics ? (a) Zeroth law of thermodynamics (b) First law of thermodynamics (c) Second law of thermodynamics (d) Third law of thermodynamics 6. 85 kJ of heat is supplied to a closed system at constant volume. During the next process, the system rejects 90 kJ of heat at constant pressure while 20 kJ of work is done on it. The system is brought to the original state by an adiabatic process. The initial internal energy is 100 kJ. Then what is the quantity of work transfer during the process ? (a) 30 kJ (b) 25 kJ (c) 20 kJ (d) 15 kJ |
|
7. An inventor says that his new concept of an engine, while working between temperature limits of 27C and 327C rejects 45% of heat absorbed from the source. His engine is then equivalent to which one of the following engines ? (a) Carnot engine (b) Diesel engine (c) An impossible engine (d) Ericsson engine 8. Three engines A, B and C operating on Carnot cycle use working substances as Argon, Oxygen and Air respectively. Which engine will have higher efficiency ? (a) Engine A (b) Engine B (c) Engine C (d) All engines have same efficiency 9. A series combination of two Carnots engines operate between the temperatures of 180C and 20C. If the engines produce equal amount of work, then what is the intermediate temperature ?
|
10. An engine working on Camot cycle rejects 40% of absorbed heat from the source* while the sink temperature is maintained at 27C, then what is the source temperature ? (a) 750C (b) 477C (c) 203C (d) 67*5C 11. A thermal electric power plant produces 1000 MW of power. If the coal releases 900 x 107 kJ/h of energy, then what is the rate at which heat is rejected from the power plant ? (a) 500 MW (b) 1000 MW (c) 1500 MW (d) 2000 MW 12. A heat engine is supplied with 250 kJ/s of heat at a constant fixed temperature of 227C; the heat is rejected at 27C, the cycle is reversible, then what amount of
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
13. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists : List-I List-II A. Isolated system 1. Energy is always constant B. Nozzle 2, Increase in velocity at the expense of its pressure drop C. Throttling device 3. Appreciable drop in pressure without any change in energy D. Centrifugal compressor 4. Enthalpy of the fluid increases by the amount of work input |
15. In a throttling process, which one of the following parameters remains constant ? (a) temperature (b) pressure (c) enthalpy (d) entropy 16. For a given value of TH (Source temperature) for a reversed Carnot cycle, the variation of TL (Sink temperature) for different values of COP is represented by which one of the following graphs ? '(a)  |
|
Code : A |
B |
C |
D |
|
(a) 4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
|
(b) 1 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
|
(c) 4 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
|
(d) 1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
14. 0-70 kg/s of air enters with a specific enthalpy of 290 kJ and leaves it with 450 kJ of specific enthalpy. Velocities at inlet and exit are 6 m/s and 2 m/s respectively. Assuming adiabatic process, what is power input to the compressor ?
(b)

(c)

(d)

(a) 120 kW
(b) 118 kW
(c) 115 kW
(d) 112 kW
|
17. Which cycle consists of two reversible isotherms and two reversible isobars ? (a) Carnot cycle (b) Stirling cycle (c) Ericsson cycle (d) Brayton cycle 18. Which one of the following parameters is significant to ascertain chemical equilibrium of a system ? (a) Clapeyron relation (b) Maxwell relation (c) Gibbs function (d) Helmholtz function 19. Consider the following : 1. Air 2. Gaseous combustion products 3. Steam Which of these are pure substances, assuming there is no phase change ? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1 and 3 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1,2 and 3 |
20. Consider the following properties : 1. Temperature 2. Viscosity 3. Specific entropy 4. Thermal conductivity Which of the above properties of a system is/are intensive ? (a) 1 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 2, 3 and 4 only (d) 1, 2, 3 and 4 21. Consider the following properties : 1. Entropy 2. Viscosity 3. Temperature 4. Specific heat at constant volume Which of the above properties of a system is/are extensive ? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 2, 3 and 4 <d) 1, 2 and 4 22. A reversible heat engine rejects 50 percent of the heat supplied during a cycle of operation. If this engine is reversed and operates as a heat pump, then what is its coefficient of performance ? (a) 1*0 (b) 1-5 (c) 2 0 ' (d) 2-5 |
|
23. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists : List-I List-II (Gas Cycles) (Thermodynamic coordinates) A. Camot cycle 1. Pressure-Entropy B. Brayton cycle 2. Pressure-Tempe- rature C. Ericsson cycle 3. Temperature- Volume D. Stirling cycle 4. Temper ature- Entropy Code ; A B C D (a) 4 2 1 3 (b) 3 2 1 4 (c) 4 1 2 3 (d) 3 1 2 4 24. The bore and stroke of the cylinder of a 6-cylinder engine working on an Otto-cycle are 17 cm and 30 cm respectively, total clearance volume is 9225 cm3, then what is the compression ratio ? (a) 7-8 (b) 6*2 (c) 15 8 (d) 5-4 |
25. Which of the following performance advantages does a rocket engine have as compared to a turbojet engine ? 1. No altitude limitation 2. Higher efficiency 3. Longer flight duration 4. No ram drag Select the correct answer from the code given below: (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1 and 4 only (c) 1,2 and 3 (d) 2, 3 and'4 26. Which of the following symptoms shows that the combustion is necessarily complete ? (a) Presence of free carbon in exhaust (b) Presence of CO in exhaust (c) Presence of oxygen in exhaust (d) Presence of nitrogen in exhaust 27. What is the purpose of supercharging an engine ? (a) To increase the power output of engine (b) To reduce specific fuel consumption (c) To reduce the noise of the engine (d) To improve cooling of cylinders |
|
28. With natural uranium, which of the following is used as moderator ? (a) Heavy water (b) Graphite (c) Beryllium (d) All the above 29. Which one of the following statements is correct ? The nuclear radiators produced in a reactor, which must be shielded, are : (a) Electrons only (b) Alpha, Beta and Gamma rays (c) Neutrons and Gamma rays (d) Electrons and Gamma rays 30. In MLT0 system (0 being time and T temperature), what is the dimension of thermal conductivity ? (a) ML_1T'l0-3 (b) MLT-e-1 (c) MLB-'T-3 (d) MLe-'T-2 31. A steel plate of thermal conductivity 50 W/m-K and thickness 10 cm passes a heat flux by conduction of 25 kW/m2. If the temperature of the hot surface of the plate is 100C, then what is the temperature of the cooler side of the plate ? (a) 30C (b) 40C (c) 50C (d) 60C |
32. A composite slab has two layers of different materials having internal conductivities k, and kj. If each layer has the same thickness, then what is the equivalent thermal conductivity of the slab ? 2k, 2k, k, 33. A composite wall of a furnace has 3 layers of equal thickness having thermal conductivities in the ratio of 1 : 2 : 4. What will be the temperature drop ratio across the three respective layers ? (a) 1:2:4 (b) 4:2:1 <c) 1:1 : 1 (d) log4 : log2 : logl 34. What is the heat lost per hour across a wall 4 m high, 10 m long and 115 mm thick, if the inside wall temperature is 30C and outside ambient temperature is 10C ? Conductivity of brick wall is 115 W/mK, heat transfer coefficient for inside wall is 2-5 W/m2K and that for outside wall is 4 W/m2K. (a) 3635 kJ (b) 3750 kJ (c) 3840 kJ (d) 3920 kJ |
|
35. When a liquid flows through a tube with sub-cooled or saturated boiling, what is the process known ? (a) Pool boiling (b) Bulk boiling (c) Convection boiling (d) Forced convection boiling 36. In a balanced counter flow heat exchanger with mhch =mccc, the NTU is equal to 10. What is the effectiveness of the heat exchanger ? (a) 0*5 (b) 1-5 (c) 0-33 (d) 0-2 37. A large concrete slab 1 m thick has one dimensional temperature distribution : T = 4 lOx + 20x2 + 10x3, where T is temperature and x is distance from one face towards other face of wall. If the slab material has thermal diffusivity of 2 x 10-3 m2/hr, what is the rate of change of temperature at the other face of the
|
38. Air at 20C blows over a hot plate of 50 x 60 cm made of carbon steel maintained at 220C. The convective heat transfer co-efficient is 25 W/m2K* What will be the heat loss from the plate ? (a) 1500 W (b) 2500 W (c) 3000 W (d) 4000 W 
What wilt be the view factor F21 for the geometry as shown in the figure above (sphere within a cube) ? (a) \ (b) J |
|
40. In vapour compression refrigeration system, at entrance to which component the working fluid is superheated vapour ? (a) Evaporator (b) Condenser (c) Compressor (d) Expansion valve 41. Which one of the following expansion processes takes place in a vapour compression cycle ? (a) Polytropic process with change in temperature (b) Adiabatic process with work transfer (c) Isentropic process with changc in enthalpy (d) Adiabatic process with constant enthalpy 42. Condenser  Compressor Evaporator Expansion valve ''WVNN -AAAAA-
Condenser Expansion valve Evaporator Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to the schematic diagram as shown above ? (a) Multi-evaporator vapour compression system of refrigeration (b) Two stage compression vapour compression refrigeration system (c) Cascade system of vapour compression refrigeration system (d) None of the above |
43. The thermal efficiency of a Carnot heat engine is 30%. If the engine is reversed in operation to work as a heat pump with operating conditions unchanged, then what will be the COP for heat pump ? (a) 0*30 (b) 2*33 (c) 3-33 (d) Cannot be calculated 44. In vapour absorption refrigeration system heating in generator is done at 177C, refrigeration in evaporator at 3C and cooling in condenser at 27C. Then what will be the maximum COP of the system ? (a) 1-5 (b) 20 (c) 30 (d) 4 0 45. In conventional refrigerants what is the element responsible for ozone depletion ? (a) Chlorine (b) Fluorine (c) Carbon (d) Hydrogen |
|
46. The refrigerating efficiency, that is, the ratio of actual COP to reversible COP of a refrigeration cycle is 0*8, the condenser and evaporator temperatures are 51C and 30C respectively. If cooling capacity of the plant is 2-4 kW then what is the work requirement ? (a) 100 kW (b) 1*33 kW (c) 1 -25 kW (d) 2 08 kW 47. The atmospheric air at 760 mm of Hg, dry bulb temperature 15C and wet bulb temperature 11C enters a heating coil whose temperature is 41C. If the by-pass factor of the heating coil is 0 5, then what will be the dry bulb temperature of the air leaving the coil ? (a) 28C (b) 29C (c) 30C (d) 26C 48. In a psychrometric chart, what does a vertical downward line represent ? (a) Sensible cooling process (b) Adiabatic saturation process (c) Humidification process (d) Dehumtdification process |
49. In a sample of moist air at standard atmospheric pressure of 101*325 kPa and 26C the partial pressure of water vapour is T344 kPa. If the saturation pressure of water vapour is 3-36 kPa at 26C, then what are the humidity ratio and relative humidity of moist air sample ? (a) 0 00836 and 1*32% <b) 0 00836 and 40% (c) 0*01344 and 1-32% (d) 0 01344 and 40% 
DBT A classroom is to be air-conditioned by obtaining the comfort conditions of 22C dbt and 55% RH from outdoor conditions of 32C dbt and 22C wbt. The weight of outside air supplied is 30 kg/m in. The comfort conditions required are achieved first by chemical dehumidification and then by cooling with a cooling coil as shown in the psychrometric chart above. What is the capacity of the dehumidification in kg/hr ? (a) 3-2 (b) 5-4 (c) 6-8 (d) 9-5 |
Which one of the following statements is correct for a cooling and humidification process 1 -2 as shown on the psychrometric chart above ? (a) Wbt decreases in the process (b) The total enthalpy increases in the * process (c) The total enthalpy remains constant in the process (d) It is an adiabatic saturation process 52. What is the saturation temperature at the partial pressure of water vapour in the air-water vapour mixture called ? (a) Dry bulb temperature (b) Web bulb temperature (c) Dew point temperature (d) Saturation temperature 53. The humidity ratio of atmospheric air at 28C dbt and 760 mm of Hg is 0*016 kN/m2. What is the partial pressure of water vapour ? (a) 2*242 kN/m2 (b) 2-535 kN/m2 (c) 3-535 kN/m2 (d) 4-242 kN/m2 |
54. Operating temperature of a cold storage is -2C. From the surrounding at ambient temperature of 40C heat leaked into the cold storage is 30 kW. If the actual COP of the plant is 1/10*h of the maximum possible COP, then what will be the power required to pump out the heat to maintain the cold storage temperature at -2C ? (a) 1-90 kW (b) 3-70 kW (c) 20-28 kW (d) 46-50 kW 55. Air enters a rectangular duct measuring 30 x 40 cm with a velocity of 8-5 m/s and a temperature of 40C. Kinematic viscosity of the air is 16-95 * 106m2/s. What will be the Reynolds number ? (a) 1*72 x 105 (b) 2*58 x 105 (c) 0-86 x io5 (d) 0-72 x 10s 56. What is the capillary rise in a narrow two-dimensional slit of width cw ? (a) Half of that in a capillary tube of diameter w (b) Two-third of that in a capillary tube of diameter w (c) One-third of that in a capillary tube of diameter w' (d) One-fourth of that in a capillary tube of diameter w |
|
57. What is the difference in pressure head, measured by a mercury-oil differential manometer for a 20 cm difference of mercury level ? (Sp. gravity of oil = 0-8) (a) 2*72 m of oil (a) (b) 2*52 m of oil (c) 3*40 m of oil (d) 2 00 m of oil 58. In order to increase sensitivity of U-tube manometer, one leg is usually inclined by an angle 0. What is the sensitivity of inclined tube compared to sensitivity of U-tube ? (a) sin 0 (b) sinO 1 (c) COS0 (d) tan 0 59. A tank has in its side a very small horizontal cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston. The head of liquid above the piston is h and the piston area a, the liquid having a specific weight y. What is the force that must be exerted on the piston to hold it in position against the hydrostatic pressure ? (a) 2yha (b) yha 2yha (c) 3 yha (d) |
60. What is the vertical distance of the centre of pressure below the centroid of the plane area ? A*h Ir, * sin 0 , x IG-sin2e Ah IG sin2 0 (d) 61. What are the forces that influence the problem of fluid statics ? (a) Gravity and viscous forces (b) Gravity and pressure forces (c) Viscous and surface tension forces (d) Gravity and surface tension forces 62* A body weighs 30 N and 15 N when weighed under submerged conditions in liquids of relative densities 0*8 and 1*2 respectively. What is the volume of the body ? (a) 12-50 I (b) 3-82 / (c) 18*70 / (d) 75 *50 / |
|
63. For floating bodies, how is the metacentric radius defined ? (a) The distance between centre of gravity and the metacentre. 1. 2. 3. 4. (b) Second moment of area of plane of flotation about centroidal axis perpendicular to plane of rotation/ immersed volume.
(c) The distance between centre of gravity and the centre of buoyancy. (d) Moment of inertia of the body about its axis of rotation/immersed volume. 64. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists : List-! List-II 66. A. Singing of tele- 1. Vortex flow phone wires B. Velocity profile 2. Drag in a pipe is initially parabolic and then flattens C. Formation of 3. Vortex shedding cyclones 67. D. Shape of rota- 4. Turbulence meter tube
|
du d\ j r dr(rVr)+dz(Vz) Which of the above equations are forms of continuity equations ? (Where u, v are velocities and V is volume) (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 (c) 2 and 3 (a) 3 and 4 A penstock pipe of 10 m diameter carries water under a pressure head of 100 m. If the wall thickness is 9 mm, what is the tensile stress in the pipe wall in MPa ? (a) 2725 (b) 545-0 (c) 272-5 (d) 1090 Which one of the statements is correct for a forced vortex ? (a) Turns in an opposite direction to a free vortex (b) Always occurs in conjunction with a free vortex (c) Has the linear velocity directly proportional to the radius (d) Has the linear velocity inversely proportional to the radius |
70. Three identical pipes of length I, diameter d and friction factor f are connected in parallel between two reservoirs. What is the size of a pipe of length / and of the same friction factor f equivalent to the above pipe ? (a) 1-55 d (b) 1-4 d (c) 3 d (d) 1-732 d 71. How does the head loss in turbulent flow in pipe vary ? (a) Directly as velocity (b) Inversely as square of velocity (c) Approximately as square of velocity (d) Inversely as velocity |
72. In a submerged orifice flow, the discharge is proportional to which one of the following parameters ? (a) Square root of the downstream head (b) Square root of the upstream head (c) Square of the upstream head (d) Square root of the difference between upstream and downstream heads 73. Which one of the following statements is correct for a fully developed pipe flow ? (a) Pressure gradient balances the wall shear stress only and has a constant value. (b) Pressure gradient is greater than the wall shear stress. (c) The velocity profile is changing continuously. (d) Inertia force balances the wall shear stress. 74. Which one of the following statements is appropriate for the free surface, the hydraulic gradient line and energy gradient line in an open channel flow ? (a) Parallel to each other but they are different lines (b) All coinciding (c) Such that only the first two coincide (d) Such that they are all inclined to each other 75. A sluice gate discharges water into a horizontal rectangular channel with a velocity of 12 m/s and depth of flow of 1 m. What is the depth of flow after the
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
76. What is the commonly used boundary layer 79. control method to prevent separation ? (a) Use of smooth boundaries (b) Using large divergence angle in the boundary (c) Suction of accelerating fluid within the boundary layer 80 (d) Suction of retarded fluid within the boundary layer 77. The time period of a simple pendulum depends on its effective length / and the local acceleration due to gravity g. What is the number of dimensionless parameter involved ? (a) Two (b) One (c) Three (d) Zero 81. 78. What is the correct dimensionless group formed with the variables pdensity, Nrotational speed, ddiameter and pcoefficient of viscosity ? pNd2 (a) (b) (c) (d) pNd 82. Nd PM Nd2 PM |
Which one of the following is proper for a normal shock wave ? (a) Reversible (b) Irreversible (c) Isentropic (d) Occurs in a converging tube Which one of the following statements relates to expression pvc ? (a) Pressure rise in a duct due to normal closure of valve in the duct (b) Pressure rise in a duct due to abrupt closure of valve in the duct (c) Pressure rise in a duct due to slow opening of valve in the duct (d) Pressure rise in a duct due to propagation of supersonic wave through the duct Which one of the following is correct for tangential component of velocities before and after an oblique shock ? (a) Unity (b) Equal (c) Unequal (d) None of the above A hydraulic reaction turbine working under a head of 16 m develops 640 kW of power. What is the unit power of the turbine ?
| ||||||||||||
|
83. A Francis turbine working at 400 rpm has a unit speed of 50 rpm and develops 500 kW of power. What is the effective head under which this turbine operates ? (a) 62-5 m (b) 64 0 m (c) 40 0 m (d) 100 m 84. A centrifugal pump with radial vane tips at the outlet has an impeller of 100 mm outer diameter. If the rotative speed is 3000 rpm and manometric efficiency 0-8 then what is the net head developed ? (a) 10 m (b) 20 m (c) 30 m (d) 40 m 85. The speed ratio of a Pelton wheel operating under a head of 900 m is 0*45. What is the peripheral velocity of the turbine wheel ? (a) 28 m/s (b) 96 m/s (c) 42 m/s (d) 60 m/s 86. A mixed flow pump is driven by a 8 kW motor running at 1000 rpm. It delivers water at the rate of 1000 liters/min against a total head of 25 m. What is the specific speed of the pump in meter-minutes ? (a) 90 (b) 50 (c) 45 (d) 75 |
87. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists : A. Pelton turbine 1. Specific speed from 300 to 1000 + axial flow with fixed runner vanes. B. Francis turbine 2, Specific speed from 10 to 50 + Tangential flow. C. Propeller turbine 3. Specific speed from 60 to 300 + mixed flow. D. Kaplan turbine 4. Specific speed from 300 to 1000 + axial flow with adjustable runner vanes. Code :
|
|
Which one of the following graphs represents the characteristics of a torque converter ? Where suffix r stands for turbine runner and P stands for pump impeller.
(b)
L, T C. D.
|
89. Which one of the following combination represents the power transmission systems ? (a) Pump, hydraulic accumulator, hydraulic intensifier and hydraulic coupling (b) Pump, turbine, hydraulic accumulator and hydraulic coupling (c) Turbine, accumulator, intensifier and hydraulic coupling (d) Accumulator, intensifier, hydraulic coupling and torque converter 90. Which one of the following is NOT an accessory for the boiler ? (a) Condenser (b) Economizer (c) Air preheater (d) Feed water pump 91. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists : List-I List-II (Type of boiler) (Features) A. Benson 1. Vertical fire tube B. Stirling 2. Horizontal fire tube Babcock-Wilcox 3. Bent water tube 4. Once through flow 5. Inclined water tube Cochran
|
|
92. Steam pressures at the inlet and exit of a nozzle are 16 bar and 5-2 bar respectively and discharge is 0-28 m3/s. Critical pressure ratio is 0-5475. If the exit pressure is reduced to 3*2 bar then what will be the flow rate in mVs ? (a) 0-280 (b) 0-328 (c) 0-356 (d) 0-455 93. Consider the following statements : Choked flow through a nozzle means : 1. Discharge is maximum 2. Discharge is zero 3. Velocity at throat is supersonic 4. Nozzle exit pressure is less than or equal to critical pressure. Which of the above statements is/are correct ? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 (c) 2 and 3 (d) 1 and 4 94. The index of expansion of dry saturated steam flowing through a nozzle is equal lo 1135, and then what is the critical pressure ratio for this flowing steam in the nozzle ? (a) 0-96 (b) 0*58 (c) 0-33 (d) 0*15 |
95. Water (Cp = 4 kJ/kgK) is fed to a boiler at 30C, the enthalpy of vaporization at atmospheric pressure in the boiler is 2400 kJ/kg; the steam coming from the boiler is 0-9 dry. What is the net heat supplied in the boiler ? (a) 2160 kJ/kg (b) 2400 kJ/kg (c) 2440 kJ/kg (d) 2280 kJ/kg 96. In a simple impulse turbine the nozzle angle at the entrance is 30. For maximum diagram efficiency what is the blade-speed ratio ? (Note : sin 30 = 0 5, cos 30 = 0-866, sin 15 = 0-259, cos 15 - 0-966) (a) 0-259 (b) 0-75 (c) 0-5 (d) 0-433 97. Consider the following statements pertaining to gas turbines : 1. The degree of reaction of a reaction turbine is the ratio of energy transfer in fixed blade to the overall energy transfer across a stage. 2. The overall pressure drop in a turbine is the product of pressure drop per stage and number of stages. 3. Gas turbine cycle (Brayton cycle) is not as efficient as Rankine cycle for steam. Which of the above statements is/are correct ? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 (d) 3 only |

The pressure and velocity diagram as shown in the figure above for a steam turbine refers to which one of the following ? (Where : Mmoving blade, Ffixed blade) (a) Impulse turbine-Velocity compounded (b) Impulse turbine-Pressure compounded (c) Impulse turbine-Pressure and Velocity compounded (d) Reaction turbine stages  99. If the enthalpy drop in the moving blades and fixed blades of a steam turbine is 10 kj/kg and 15 kJ/kg respectively then what is the degree of reaction ? (a) 67% (b) 60% (c) 40% (d) 33% 100. In a simple single stage gas turbine plant, if T is the minimum temperature and T3 is the maximum temperature then what is the work ratio in terms of r ?
 p 't* (a) 1-V M X (b) i--V  T (c) 1-r/-1 (d) 1-rJ |
101. Which one of the following statements is correct ? (a) Reciprocating compressors are used to supply large quantities of air at a lower pressure ratio. (b) Centrifugal compressors are used to supply large quantities of air at a lower pressure ratio. (c) Centrifugal compressors are used to supply small quantities of air at a lower pressure ratio. (d) Centrifugal compressors cannot be run at high speed because of impeller, diffuser and casing. 102. Which one of the following graphs shows the correct representation of the processes for a two stage air compressor with perfect intercooling and no pressure drop in the intercooler ? |
|
103. Consider the following statements pertaining to axial flow compressors : 1. Like centrifugal compressor, axial flow compressors are limited by surge at low mass flow rates. 2. Axial flow compressors experience choking at low flow rates. 3. The design point of axial flow compressors is close to the surge limit. 4. As mass flow diminishes the compressor blades stall causing flow separation.  Which of the above statements is/are correct ? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 1,2 and 3 (c) 1,3 and 4 (d) 3 and 4 only 104.
 
In the graph as shown above, for an axial flow compressor, surging is likely to occur in which one of the following.zones ? (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D |
105. Which one of the following diagrams depicts correctly the radial distribution of axial velocity over the blades in the last stage of multistage axial flow compressors ? tip root (d) |
|
106. Which one of the following statements is correct ? Increasing the number of reheating stages in a gas turbine to infinity, makes the expansion tending : (a) Reversible adiabatic (b) Isothermal (c) Isobaric (d) Adiabatic 107. Which one of the following statements is correct ? In a boiler, the air preheater is invariably located between : (a) Forced draft fan and chimney (b) Forced draft fan and furnace (c) Economizer and feed pump (d) Condenser and feed pump 
The above T-S diagram for a gas turbine plant is drawn for the case where : (a) Compression of air is done in two stages incorporating an intercooler between two. (b) Expansion of gases is done in two stages followed by regeneration. (c) Expansion of gases is done in two stages with a reheater between the two. (d) Expansion of gases is done in two stages with a reheater between the two followed by regeneration. |
Each of the next TWELVE (12) items consists of two statements, one labelled as the Assertion (A) and the other as Reason (R)\ You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the answers to these items using the codes given below : Codes : (a) Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A (b) Both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A (c) A is true but R is false (d) A is false but R is true 109. Assertion (A): An air-conditioner operating as a heat pump is superior to an electric resistance heater for winter heating. -Reason (R) : A heat pump rejects more heat than the heat equivalent of the heat absorbed. 110. Assertion (A) : After burning increases the thrust of a jet engine. Reason (R) : The air fuel ratio of jet engine is high. 111. Assertion (A) : Cork is a good insulator. Reason (R) : Good insulators are highly porous. |
|
Drop-wise condensation is associated with higher heat transfer rate as compared to the heat transfer rate in film condensation. In drop condensation there is free surface through which direct heat transfer takes place. 116. Assertion (A) : Reason (R) 117. Assertion (A) : Reason (R) 118. Assertion (A) : Reason (R) 119. Assertion (A) : Reason (R) 120. Assertion (A) : Reason (R) Reason (R) 113. Assertion (A) : For the similar conditions the values of convection heat transfer coefficients are more in forced convection than in free convection. In case of forced convection system the movement of fluid is by means of external agency. Reason (R) 114. Assertion (A) : Reason (R) 115. Assertion (A) : Reason (R) If a domestic refrigerator works inside an adiabatic room with its door open, the room temperature gradually decreases. Vapour compression refrigeration cycles have high COP compared to air refrigeration cycles. In a fluid, the rate of deformation is far more important than the total deformation itself. A fluid continues to deform so long as the external forces are applied. |
A narrow glass tube, when immersed into mercury causes capillary depression, and when immersed into water causes capillary rise. Mercury is denser than water. The local acceleration is zero in a steady motion. The convective component arises due to the fact that a fluid element experiences different velocities at different locations. The dimples on a golf ball are intentionally provided. A turbulent boundary layer, since it has more momentum than a laminar boundary layer, can better resist an adverse pressure gradient. Increase in static suction lift of centrifugal pump may cause cavitation. Available Net Positive Suction Head increases with increase in static suction lift. Multistaging compression is done only in reciprocating compressors. : Reciprocating compressors are used to compress a large pressure ratio and low discharge. |
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
SPACE FOR ROUGH WORK
1. Fluids Mechanics and Fluid Properties
What is fluid mechanics? As its name suggests it is the branch of applied mechanics concerned with the statics and dynamics of fluids - both liquids and gases. The analysis of the behaviour of fluids is based on the fundamental laws of mechanics which relate continuity of mass and energy with force and momentum together with the familiar solid mechanics properties.
1.1 Objectives of this section
Define the nature of a fluid.
Show where fluid mechanics concepts are common with those of solid mechanics and indicate some fundamental areas of difference.
Introduce viscosity and show what are Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids
Define the appropriate physical properties and show how these allow differentiation between solids and fluids as well as between liquids and gases.
There are two aspects of fluid mechanics which make it different to solid mechanics:
1. The nature of a fluid is much different to that of a solid
2. In fluids we usually deal with continuous streams of fluid without a beginning or end. In solids we only consider individual elements.
We normally recognise three states of matter: solid; liquid and gas. However, liquid and gas are both fluids: in contrast to solids they lack the ability to resist deformation. Because a fluid cannot resist the deformation force, it moves, it flows under the action of the force. Its shape will change continuously as long as the force is applied. A solid can resist a deformation force while at rest, this force may cause some displacement but the solid does not continue to move indefinitely.
The deformation is caused by shearing forces which act tangentially to a surface. Referring to the figure below, we see the force F acting tangentially on a rectangular (solid lined) element ABDC. This is a shearing force and produces the (dashed lined) rhombus element ABDC.
 |
|
Shearing force, F, acting on a fluid element. |
We can then say:
A Fluid is a substance which deforms continuously, or flows, when subjected to shearing forces.
and conversely this definition implies the very important point that:
If a fluid is at rest there are no shearing forces acting.
All forces must be perpendicular to the planes which the are acting.
When a fluid is in motion shear stresses are developed if the particles of the fluid move relative to one another. When this happens adjacent particles have different velocities. If fluid velocity is the same at every point then there is no shear stress produced: the particles have zero relative velocity.
Consider the flow in a pipe in which water is flowing. At the pipe wall the velocity of the water will be zero. The velocity will increase as we move toward the centre of the pipe. This change in velocity across the direction of flow is known as velocity profile and shown graphically in the figure below:
 |
|
Velocity profile in a pipe. |
Because particles of fluid next to each other are moving with different velocities there are shear forces in the moving fluid i.e. shear forces are normally present in a moving fluid. On the other hand, if a fluid is a long way from the boundary and all the particles are travelling with the same velocity, the velocity profile would look something like this:

Velocity profile in uniform flow
and there will be no shear forces present as all particles have zero relative velocity. In practice we are concerned with flow past solid boundaries; aeroplanes, cars, pipe walls, river channels etc. and shear forces will be present.
1.2.1 Newtons Law of Viscosity
How can we make use of these observations? We can start by considering a 3d rectangular element of fluid, like that in the figure below.
Fluid element under a shear force
The shearing force F acts on the area on the top of the element. This area is given by A = ds xdx. We can thus calculate the shear stress which is equal to force per unit area i.e.
F
shear stress, t =
A
The deformation which this shear stress causes is measured by the size of the angle f and is know as shear strain.
In a solid shear strain, f, is constant for a fixed shear stress t. In a fluid f increases for as long as t is applied - the fluid flows.
It has been found experimentally that the rate of shear stress (shear stress per unit time, t/time) is directly proportional to the shear stress.
If the particle at point E (in the above figure) moves under the shear stress to point E and it takes time t to get there, it has moved the distance x. For small deformations we can write
x
shear strain f =
y
f
rate of shear strain = t
x x 1 = ty ~ t y u
y
x
where = u is the velocity of the particle at E.
Using the experimental result that shear stress is proportional to rate of shear strain then
u
t= Constant x
y
u
The term is the change in velocity with y, or the velocity gradient, and may be written in the du
differential form The constant of proportionality is known as the dynamic viscosity, m , of the fluid, giving

In the above we have discussed the differences between the behaviour of solids and fluids under an applied force. Summarising, we have;
1. For a solid the strain is a function of the applied stress (providing that the elastic limit has not been reached). For a fluid, the rate of strain is proportional to the applied stress.
2. The strain in a solid is independent of the time over which the force is applied and (if the elastic limit is not reached) the deformation disappears when the force is removed. A fluid continues to flow for as long as the force is applied and will not recover its original form when the force is removed.
It is usually quite simple to classify substances as either solid or liquid. Some substances, however, (e.g. pitch or glass) appear solid under their own weight. Pitch will, although appearing solid at room temperature, deform and spread out over days - rather than the fraction of a second it would take water.
As you will have seen when looking at properties of solids, when the elastic limit is reached they seem to flow. They become plastic. They still do not meet the definition of true fluids as they will only flow after a certain minimum shear stress is attained.
1.2.3 Newtonian / Non-Newtonian Fluids
Even among fluids which are accepted as fluids there can be wide differences in behaviour under stress. Fluids obeying Newtons law where the value of m is constant are known as Newtonian fluids. If m is constant the shear stress is linearly dependent on velocity gradient. This is true for most common fluids.
Fluids in which the value of m is not constant are known as non-Newtonian fluids. There are several categories of these, and they are outlined briefly below.
These categories are based on the relationship between shear stress and the velocity gradient (rate of shear strain) in the fluid. These relationships can be seen in the graph below for several categories
 |
|
Rate oF shear, 8u/8y Shear stress vs. Rate of shear strain 8u/8y Each of these lines can be represented by the equation |
/ e \n ou
t= A + B
\Yj
where A, B and n are constants. For Newtonian fluids A = 0, B = m and n = 1.
Below are brief description of the physical properties of the several categories:
Plastic: Shear stress must reach a certain minimum before flow commences.
Bingham plastic: As with the plastic above a minimum shear stress must be achieved. With this classification n = 1. An example is sewage sludge.
Pseudo-plastic: No minimum shear stress necessary and the viscosity decreases with rate of shear, e.g. colloidial substances like clay, milk and cement.
Dilatant substances; Viscosity increases with rate of shear e.g. quicksand.
Thixotropic substances: Viscosity decreases with length of time shear force is applied e.g. thixotropic jelly paints.
Rheopectic substances: Viscosity increases with length of time shear force is applied
Viscoelastic materials: Similar to Newtonian but if there is a sudden large change in shear they behave like plastic.
There is also one more - which is not real, it does not exist - known as the ideal fluid. This is a fluid which is assumed to have no viscosity. This is a useful concept when theoretical solutions are being considered - it does help achieve some practically useful solutions.
Although liquids and gasses behave in much the same way and share many similar characteristics, they also possess distinct characteristics of their own. Specifically
A liquid is difficult to compress and often regarded as being incompressible.
A gas is easily to compress and usually treated as such - it changes volume with pressure.
A given mass of liquid occupies a given volume and will occupy the container it is in and form a free surface (if the container is of a larger volume).
A gas has no fixed volume, it changes volume to expand to fill the containing vessel. It will completely fill the vessel so no free surface is formed.
1.3 Causes of Viscosity in Fluids
The molecules of gasses are only weakly kept in position by molecular cohesion (as they are so far apart). As adjacent layers move by each other there is a continuous exchange of molecules. Molecules of a slower layer move to faster layers causing a drag, while molecules moving the other way exert an acceleration force. Mathematical considerations of this momentum exchange can lead to Newton law of viscosity.
If temperature of a gas increases the momentum exchange between layers will increase thus increasing viscosity.
Viscosity will also change with pressure - but under normal conditions this change is negligible in gasses.
There is some molecular interchange between adjacent layers in liquids - but as the molecules are so much closer than in gasses the cohesive forces hold the molecules in place much more rigidly. This cohesion plays an important roll in the viscosity of liquids.
Increasing the temperature of a fluid reduces the cohesive forces and increases the molecular interchange. Reducing cohesive forces reduces shear stress, while increasing molecular interchange increases shear stress. Because of this complex interrelation the effect of temperature on viscosity has something of the form:
where /lT is the viscosity at temperature TC, and m0 is the viscosity at temperature 0C. A and B are constants for a particular fluid.
High pressure can also change the viscosity of a liquid. As pressure increases the relative movement of molecules requires more energy hence viscosity increases.
The properties outlines below are general properties of fluids which are of interest in engineering. The symbol usually used to represent the property is specified together with some typical values in SI units for common fluids. Values under specific conditions (temperature, pressure etc.) can be readily found in many reference books. The dimensions of each unit is also give in the MLT system (see later in the section on dimensional analysis for more details about dimensions.)
The density of a substance is the quantity of matter contained in a unit volume of the substance. It can be expressed in three different ways.
Mass Density, p, is defined as the mass of substance per unit volume.
Units: Kilograms per cubic metre, kg/ m3 (or kgm-3)
Dimensions: ML-Typical values:
Water = 1000 kgm- , Mercury = 13546 kgm- Air = 1.23 kgm- , Paraffin Oil = 800 kgm- .
(at pressure =1.013 x 10-5 Nm~2 and Temperature = 288.15 K.)
Specific Weight w, (sometimes g, and sometimes known as specific gravity) is defined as the weight per unit volume.
or
The force exerted by gravity, g, upon a unit volume of the substance.
The Relationship between g and w can be determined by Newtons 2nd Law, since
weight per unit volume = mass per unit volume x g w = pg
Units: Newtons per cubic metre, N/ m3 (or Nm-)
Dimensions: ML~2 T-2.
Typical values:
Water =9814 Nm-, Mercury = 132943 Nm-, Air =12.07 Nm-, Paraffin Oil =7851 Nm-
For solids and liquids this standard mass density is the maximum mass density for water (which occurs at 4c) at atmospheric pressure.
Ssubs tan ce SH2O( at 4" c)
s =
Units: None, since a ratio is a pure number.
Dimensions: 1.
Typical values: Water = 1, Mercury = 13.5, Paraffin Oil =0.8.
Viscosity, m, is the property of a fluid, due to cohesion and interaction between molecules, which offers resistance to sheer deformation. Different fluids deform at different rates under the same shear stress. Fluid with a high viscosity such as syrup, deforms more slowly than fluid with a low viscosity such as water.
All fluids are viscous, Newtonian Fluids obey the linear relationship
du
given by Newtons law of viscosity. t = I~, which we saw earlier.
where t is the shear stress,
Units Nm-; kg m- s-
Dimensions MU1 T-2. du
is the velocity gradient or rate of shear strain, and has
dy
Units: radians s,
Dimensions t-
/I is the coefficient of dynamic viscosity - see below.
1.4.2.1 Coefficient of Dynamic Viscosity
The Coefficient of Dynamic Viscosity, I, is defined as the shear force, per unit area, (or shear stress t), required to drag one layer of fluid with unit velocity past another layer a unit distance away.
I du Force / Velocity Force x Time Mass
1 I dy Area / Distance Area Length xArea
Units: Newton seconds per square metre, N sm- or Kilograms per meter per second, kgm- s-. (Although note that I is often expressed in Poise, P, where 10 P = 1 kgm- s_1.)
Typical values:
Water =1.14 x 10-3 kgm- s_1, Air =1.78 x 10-5 kgm- s_1, Mercury =1.552 kgm- s_1,
Paraffin Oil =1.9 kgm- s_1.
p
Units: square metres per second, m2 s-1
(Although note that n is often expressed in Stokes, St, where 104 St = 1 m2 s_1.) Dimensions: L T-1.
Typical values:
Water =1.14 x 10-6 m2 s_1, Air =1.46 x 10-5 m2 s_1, Mercury =1.145 x 10-4 m2 s_1, Paraffin Oil =2.375 x 10-3 m2 s_1.
CIVE 1400: Fluid Mechanics Fluid Mechanics and Properties of Fluids 18
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |









