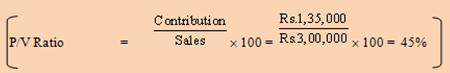All India Management Association (AIMA) 2008 M.B.A Marketing Management Accounting_for_ision_Making IIober_ - Question Paper
Question Paper
Accounting for Decision Making -
II (MB2D2): October
2008
|
Answer all 72 questions. Marks are indicated against each question. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Total Marks : 100 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Consider the following particulars of Shalet Ltd.:
The break even sales of the company are
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fixed cost is the product of
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Basu Ltd., presents the following estimates pertaining to its Department A:
The value of sales to be increased by the company to reach the break even sales is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Vaishali Ltd. has furnished the following data pertaining to its business: Variable cost Rs.38 per unit Fixed overhead Rs. 8 per unit Normal production 15,000 units Actual production 12,000 units Sales 10,000 units Sale price Rs.60 per unit The value of ending inventory using Absorption costing is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sakshi Technologies Ltd. furnishes the following information pertaining to its product for last two years:
If the company wants to earn a profit of Rs.55,000, desired sales would be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bakshi Ltd. has furnished the following data for the month of September 2008:
The Margin of safety of the company is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Vinayaka Ltd. furnishes the following information for a period, pertaining to its product T:
The profit per unit of the product was
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Vijay Ltd. has furnished the following cost data for 600 units (which is its 50% capacity) of its product:
The total cost for 950 units is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following is true with respect to target costing?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following factors is to be multiplied with contribution margin ratio to calculate profit?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The current sales price of product of Teddy Ltd. is Rs.180 per unit. Variable costs are expected to increase from Rs.140 to Rs.150 per unit. Fixed costs of Rs.6,00,000 will not change. The number of additional sales units required in order to maintain the existing operating income of Rs.7,20,000 is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The operating results of M/s. Swastik Steels Ltd. for the year 2007-08 were as follows:
Total sales value of all the products was Rs.550 lakh and fixed costs amounted to Rs.18 lakh. The composite Profit-Volume ratio of the company was
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Khullar Appliances Ltd. has provided the following information for its product for a period:
The prime cost of the product was
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
If the activity level is increased from 70% to 78%, the fixed cost
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Banta Ltd. manufactures product KDM for last ten years. The company maintains a margin of safety of 36% with an overall contribution to sales ratio of 35%. If fixed cost is Rs.8.4 lakh, the profit of the company is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The following is an excerpt from the income statement of Sai Ltd. for a period:
Value added by manufacturing is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following statements is false in respect of full cost pricing and contribution margin pricing?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bill James Ltd. manufactures 1,200 units of product PC during the year 2007-08. The variable cost per unit and fixed costs per annum are Rs.35 and Rs.45,000 respectively. If the company expects an annual profit of Rs.30,000, the mark-up percentage on variable cost is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Hansley Ltd. has furnished the following data for the month of September 2008:
The Profit-Volume ratio of the company is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
If the sales of Precious Ltd. for two consecutive years were Rs.64,000 and Rs.72,000 respectively and profits for the same years were Rs.8,000 and Rs.11,200 respectively, the fixed cost of the company was
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Under Subtractive Approach, which of the following items is not deducted from the sales revenue for computation of value added?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
If a company desires to earn a profit of 25% on selling price, the profit mark-up on cost should be
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Richies Ltd. currently operates at 60% capacity level. The normal capacity is 3,00,000 units. The variable cost per unit is Rs.33 and the total fixed costs are Rs.18,60,000. If the company desires to earn a profit of Rs.3,00,000, the sale price of the product per unit is
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cute Toys Ltd. produces and sells 50,000 toys at Rs.20 each with a profit of Rs.5 each. The company has furnished the following cost structure per unit for its product for the year 2008-09:
The direct material & labor costs are likely to increase by 35% during the next financial year. There will not be any change in the selling price and other costs. The company receives an offer to supply additional 20,000 toys. The contribution for additional 20,000 toys will be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A profit making firm can increase its return on investment by
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following statements is false?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Notional rent charged on business premises owned by the proprietor is an example of
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following statements is false with regard to value added?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
In a decision analysis situation, which of the following costs is generally not relevant?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
While computing the profits of a business, which of the following measures considers the cost of debt as well as the cost of equity?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following is a period cost?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Saurav Ltd. has furnished the following data for the month of September 2008:
The number of units to be sold by the company at break-even point was
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
All of the following are major considerations in fixing a selling price except
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The term relevant cost applies to all the following decisional situations, except
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following costs is a semi variable cost?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Target costing is based on the following premises, except
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following items would be treated as an indirect cost in manufacture of a chair?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
During the year 2006-07, Metro Ltd., produced 14,500 units with the total cost of Rs.2,68,100. In the year 2007-08 it increased its production to 16,000 units. The total cost of production has been increased by Rs.19,200 from the total cost of 2006-07. The variable cost per unit during the year 2007-08 was
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following statements is true?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Mirind Ltd. has furnished the following information pertaining to its production:
If the profit under Absorption costing method is Rs.88,200, the profit under Marginal costing method would be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following costs is not considered as a product cost under Absorption costing as well as Direct costing?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full-cost price is defined as
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The opportunity cost of making a component in a factory with no excess capacity is the
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following is false with regard to Economic Value Added (EVA)?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following is true if the decision for establishment of branch sales office is chosen in comparison with employing selling agents?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Market Value Added is the difference between
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Varoon Ltd. has received an order for the supply of 2,00,000 units of its product Y. There is enough capacity available but additional balancing equipment have to be purchased for Rs.80,000. The total costs of manufacturing the product will be Rs.5,47,940. Working capital required will be 50% of the sales value. If the company expects a return of 20% on the additional capital requirement for the order, the price of the order should be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Maniyar Ltd. has furnished the following data relating to its product for the year 2007-08:
The variable cost per unit was
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Consider the following data of Surabhi Ltd. for the year 2007-08:
The mark-up on total cost was
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GMV Ltd. has furnished the following data pertaining to its product for the year 2007-08:
The Cost of Goods Sold for the year was
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sathya Ltd. has furnished the following data :
If sales are 20% above break even point, the contribution per unit is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Morey Ltd. has estimated the following data pertaining to its product CMC for a period:
Margin of Safety as a percentage to total sales would be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
If the production of a company is equal to break even point, profit will increase by the
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The following information is provided by Mawai Ltd. for the year 2007-08:
It is estimated that variable costs will increase by 15% and fixed costs are expected to increase by 8% in 2008-09. If the company wants to maintain the same Profit-Volume ratio as in 2007-08, the selling price per unit would be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The following information is furnished by Nowin Ltd.:
If the desired rate of return is 35% of the capital employed, the number of units to be produced and sold are
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Swami Ltd. has furnished the following details:
The net profit of the company is
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following items is not included in preparation of a cost sheet?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following is a limitation of the absorption costing?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following statements is true?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A cost that can be substantially influenced by a manager is often referred to as which of the following?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A companys approach to make or buy decision
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The term variable cost refers to
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cost-volume-profit analysis is most important for the determination of
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
For product A of Shilpa Ltd., the prime cost is Rs.20 per unit, factory overheads are 20% of prime cost and administration overheads are 25% of Works cost. If the company desires to earn a profit of 25% on selling price, the selling price per unit of product A would be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following is not an example of finance module of application of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following statements is true?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The following are the advantages of Enterprise Resource Planning except
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Which of the following methods is used for Brand Valuation of a company?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The accountant of Katrina Ltd. is reviewing the profitability of the companys two products Q and R. The following is an excerpt from the income statement of the two products:
If product R is discontinued, the income will be
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Preksha Ltd. has furnished the following information relating to the manufacture of its product B:
The works cost of product B is
|
( |
2 |
marks) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The following factors influence the Brand Strength of a company except
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Under which of the following cases the margin of safety decreases?
|
( |
1 |
mark) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Suggested Answers
Accounting for Decision Making -
II (MB2D2): October
2008
|
|
Answer |
Reason |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Margin of safety = 20% of sales = Rs.15,000 Sales = Rs. 15,000 100 20 = Rs. 75,000. Break even sales = Sales Margin of safety = Rs.75,000 Rs. 15,000 = Rs.60,000. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Break-even point = \Fixed cost = Profit-volume ratio Break-even sales Hence, (d) is true. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
P/V Ratio = B E P Sales (in value) = Sales to be increased to reach the Break even = BEP sales Actual sales = Rs.8,75,000 Rs.7,00,000 = Rs.1,75,000. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
B |
Total fixed overhead = 15,000 units Rs.8 = Rs.1,20,000. Fixed overhead per unit = Rs.1,20,000 actual overhead 12,000 units actual production = Rs.10. Total cost per unit = Variable cost Rs.38 + Fixed overhead Rs.10 = Rs.48 Cost of ending inventory = Rs.48 2,000 units (12,000 units produced 10,000 units sold) = Rs.96,000. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
Sales required to earn a profit of Rs.55,000: P /V Ratio =
Contribution = Sales P /V Ratio = Rs. 1,20,000 0.20 = Rs. 24,000 Fixed cost = Contribution Profit = Rs.24,000 Rs.13,000 = Rs.11,000 Desired sales = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Contribution = Sales (Direct Materials + Direct Labour + Direct Expenses) = Rs.3,00,000 (Rs.95,000 + Rs.35,000 + Rs.35,000) = Rs.3,00,000 Rs.1,65,000 = Rs.1,35,000. Margin of safety = Sales Break-even sales Break-even sales =
Margin of safety = Rs.3,00,000 Rs.2,00,000 = Rs.1,00,000. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Variable overhead costs = Add: Fixed overhead cost = Rs.5,00,000 Total cost of 950 units = Rs.9,75,000 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
Target cost = Sale price (for the target market share) Desired profit. In competitive industries, a unit sale price would be established independent of the initial product cost. Management decides that the cost of a product should be based on marketing factors rather than manufacturing. Hence (e) is true. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
B |
Profit = Margin of safety Contribution margin ratio. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Projected unit sales = (Fixed costs + Target operating income) Unit contribution Projected unit sales = (Rs.6,00,000 + Rs.7,20,000) Rs.30. = 44,000 units. Current sales units = (Rs.6,00,000 + Rs.7,20,000) Rs.40 = 33,000 units. Increase in units: 44,000 33,000 = 11,000 units. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
P/V Ratio = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Prime Cost = Direct materials + Direct wages + Direct expenses Therefore prime cost = Rs.65,200 + Rs.53,300 + Rs.56,500 = Rs.1,75,000. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
If the activity level is increased from 70% to 78%, the total fixed costs remain fixed. Hence, the fixed cost per unit will reduce but not in the same proportion of 8%. Fixed cost per unit or in total does not increase with an increase in the activity level. Therefore (e) is correct. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Break-even sales = Rs.8.4 lakh 35% = Rs.24 lakh; Break-even sales = Total sales Margin of safety = 100% - 36% = 64% Total sales = Rs.24 lakh 64% = Rs.37.5 lakh Profit of the company = 36% of Rs.37.5 lakh 35% = Rs.13.5 lakh 0.35 = Rs.4.725 lakh. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
c |
Value added = Sales Operating expenses Excise duty Interest on bank overdraft = Rs.1,00,000 Rs.60,000 Rs.5,000 Rs.2,000 = Rs.33,000 Provision for taxation does not come under value added statement. Hence, it is to be ignored. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
When we look into the relationship between full cost pricing and contribution margin pricing we can conclude that although the full cost pricing and contribution margin based approach for pricing are considered distinctively different approaches, by and large, they represent to a certain degree, cost plus pricing. Hence statement (e) is true. They are considered complementary to each other but not competing. Hence statement (a) is true. In both the pricing models fixed costs are considered important. Hence option (c) is true. In both the methods, the selling prices proposed must be only tentative and they are always subjective. Hence statement (b) is also true. However, Full cost pricing makes a normal mark up on total costs and it does not take volume of production into consideration. On the other hand contribution margin approach to pricing is concerned about cost volume and profit. Hence statement (d) which states that contribution margin method also makes a normal markup on total costs is false. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
B |
Mark-up percentage = Now sales = 1,200 units Rs.35 + Rs.45,000 + Rs.30,000 = Rs.42,000 + Rs.45,000 + Rs.30,000 = Rs 1,17,000 Variable cost = Rs.35 1,200 = Rs.42,000 \ Mark-up
percentage = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Contribution = Sales (Direct Materials + Direct Labour + Direct Expenses) = Rs.2,75,000 (Rs.97,600 + Rs.79,450 + Rs.14,075) = Rs.2,75,000 Rs.1,91,125 = Rs.83,875. P/V Ratio = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Contribution to sales ratio = Change of profit Change of sales = Rs.3,200 Rs.8,000 = 0.40 = 40% Break-even point: Sales x contribution to sales ratio = Fixed cost + Profit Rs.64,000 40% = Fixed cost + Rs.8,000 Fixed cost = Rs.25,600 Rs.8,000 = Rs.17,600. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
All the items mentioned in (a), (b), (d) and (e), come under the subtractive approach for computation for value added except wages and salaries. This item comes under additive approach. Hence (c) is the correct answer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
B |
If the sale price is Rs.100, the profit is 25% i.e. Rs.25. Therefore, the cost is Rs.75. So, the profit mark-up on cost is Rs.25 Rs.75 i.e. 33.33%. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Total fixed cost = Rs.18,60,000 Expected profit = Rs.3,00,000 Variable cost at 60% level (60% 3,00,000 units Rs.33) = Rs.59,40,000 Total price = Rs.18,60,000 + Rs.3,00,000 + Rs.59,40,000 = Rs.81,00,000 Sale per unit price at 60% level = Rs.81,00,000/ (3,00,000 60%) = Rs.45. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
Contribution for additional 20,000 toys will be Rs.6.20 20,000 toys = Rs.1,24,000. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Return on investment (ROI) equals to income divided by invested capital. If a firm is already profitable, increasing sales and expenses by the same percentage will increase the ROI. Other options given in (a), (b), (c) and (e) are not correct. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
Under full cost pricing, the normal mark-up is not based on sales value. It is generally based on total cost or variable cost to recover profit and/or fixed cost. Under full cost pricing, sellers do not take advantage of the buyers when demand for the goods is very high, pricing decision may be influenced by internal factors and contribution margin approach to pricing is concerned with the cost, volume and profit. Therefore (a) is correct answer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
The costs which are not incurred but appeared in cost accounts only are called imputed costs. e.g. the notional rent charged on business premises owned by the proprietor is imputed cost. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
Net value added is derived by deducting depreciation from the gross value added and not vice versa. Thus statement in alternative (a) is false. The value added is the most relevant concept and the statement forms part of social responsibility reporting (b). Value added statements reflect the broader view of the companys objectives and responsibilities (c). It measures the value of increase in resources (d). The approaches adopted are additive approach and subtractive approach in computing value added (e). Thus, the alternatives (b), (c), (d) and (e) are true statements. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
Management decision analysis is based on the concept of relevant costs. Relevant costs differ among decision choices. Thus, incremental (differential or avoidable) costs are always relevant. Replacement cost is also relevant. Historical costs occurred in the past, are sunk costs and not relevant to most management decision analysis. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Economic value added measure considers the cost of debt as well as the cost of equity while computing profit of a business. Gross Value added (a) is arrived at by deducting from sales revenue and any other direct income and investment income, the cost of all materials and services and other extraordinary expenses and thus it includes other expenses in addition to the cost of debt and equity. And is not the correct answer. Net value added (b) is derived by deducting depreciation from the gross value added. Market value added (d) is the difference between the market value of the invested capital and book value of invested capital. It is a measure of shareholders value. And is not the correct answer. Brand Value Added (e) is a tool that quantifies the economic value of a brand. And is not the correct answer. Thus, (c) is the correct answer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
All research, administrative and selling costs are treated as period costs. i. Direct labor costs and Direct material costs are product or inventorial costs. ii. Indirect materials costs are treated as manufacturing overhead costs. iii. Power costs and repair costs are treated as product costs. The correct answer is (a). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
Variable cost per unit = Rs.12 + Rs.4 = Rs.16 Contribution per unit = Rs.24 Rs.16 = Rs.8 Fixed costs = Rs.6,48,000 + Rs.3,02,400 = Rs.9,50,400 Break even point in units = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
In fixing selling price - competitors price, unique product feature, price of the substitutes and capturing market share are considered. Product costs sets a floor to the price. Product costs, which set a ceiling to the price, are not correct. Therefore, (d) is the answer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
Relevant costs are those expected future costs that vary with the action taken. All other costs are assumed to be constant and thus have no effect on the decision. It is considered in the analysis of decisions to make or buy a product, accept a special order, replace capital equipment or delete a product line. It applies to many special decisions but not in determining a product price. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
d |
Depreciation on a machinery and factory rent are fixed costs. Suppliers and other indirect materials are variable costs and advertising is a discretionary fixed cost. Maintenance of machinery is a semi-variable costs consisting of planned maintenance that is undertaken whatever the level of the activity and a variable component that is directly related to the level of activity. So (d) is correct. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
Target costing is based on the premises of (i) Orienting products to customer affordability, (ii) Orienting products to market driven pricing, (iii) Treating product cost as an independent variable during the definition of a products requirements and (iv) Proactively working to achieve target cost during product and process development. It is not based on the premise of treating product cost as an dependent variable during the definition of a products requirements. Therefore, (e) is correct option. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
d |
Wood, Metal, Fabric and Leather used in the chair would be treated as direct cost but the staples used to fix the fabric will be treated as indirect cost. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Variable cost per unit = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Under marginal costing technique, products are valued at variable cost. Fixed costs are not considered for valuation of product. Therefore, this statement is correct. Other statements given in (a), (b), (d) and (e) are not correct. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
b |
Fixed overhead cost per unit = Rs.9,60,000 80,000 units = Rs.12. Profit under absorption costing = Rs.88,200 Fixed manufacturing overhead costs of increased inventory = 3,650 units Rs.12 = Rs.43,800 Profit under marginal costing = Rs.88,200 Rs.43,800 = Rs.44,400. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
e |
Under absorption costing, all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable are treated as product costs. Under direct costing, only variable cost of manufacturing is inventoried as product costs. Fixed manufacturing costs are expensed as period costs. Packaging and shipping costs are not product costs under either method because they are incurred after the goods have been manufactured. Instead they are included in selling and administrative expenses for the period. Other options (a), (b), (c) and (d) are as product cost under respective costing method. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
The correct answer is (a). Full-cost price is the price usually set based on absorption costing calculation and includes materials, labor and a full allocation of production overhead. (b) is not correct because it is variable cost. (c) is not correct because the market price is the price in the open market. (d) is not correct because it is the outlay cost plus opportunity cost. (e) is not correct because it is the variable cost plus pricing. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Opportunity cost is the maximum possible alternative earning that might have been earned if the productive capacity had been put to some alternative use. Hence, it can also be defined as the benefit foregone on choosing a particular course of action. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
b |
EVA can be improved by downsizing non-profitable operations, units or by selling off sub-standard assets. Hence, (b) is false. The computation of EVA involves a complex procedure. Stern and Stewart suggested 175 different assumptions and adjustments on the basic measure. EVA is a residual income measure that subtracts the cost of capital from the operating profit generated by a business. In other words, EVA measures whether the operating profit is enough competed to the total cost of capital. EVA is simply after-tax operating profit minus the total annual cost of capital. EVA is one variation if residual income with adjustments in the method of calculation. Unlike the traditional measure of accounting profit where only part of the cost of capital (cost of debt) is deducted, EVA requires deduction of full cost of capital (Cost of debt as well as cost of equity). EVA can be used for making day-to-day decisions as well as for strategic planning. For this purpose, EVA points have to be identified. An EVA point is one which has revenue, expenditure and capital issue attached to it. EVA destroyers for each EVA point are identified and steps are taken to improve them. EVA analysis is made for each and every EVA point for decision-making. Thus (a), (c), (d) and (e) are true. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
If establishment of branch sales office is chosen, fixed cost is more and the level of variable cost is less. If selling agents are employed, then the level of variable cost is more and fixed cost is less. Hence, option (d) is true. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
e |
Market Value Added is the difference between the market value of invested capital and book value of invested capital. MVA is a measure of shareholders' value. MVA measures how the executives managing the company have fared with regard to the optimal utilization of capital under their control. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
c |
Capital employed = Fixed assets + Working capital Working capital = 50% of Sales (given) Capital employed = Rs.80,000 + 50% (sales) : let sales be X X = Total Cost + 20% of capital employed X = Rs.5,47,940 + 0.20(Rs.80,000 + 0.5 X) X = Rs.5,63,940 + 0.1 X X = Rs.5,63,940 / 0.9 X = Rs.6,26,600 The price to be quoted is Rs.6,26,600. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
c |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
d |
Mark-up % on total cost = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
b |
Cost of good sold = Opening stock + (Purchases Purchase returns) Closing stock + Freight in = Rs.19,200 + (Rs.6,20,250 Rs.23,700) Rs.16,350 + Rs.9,300 = Rs.6,08,700. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
e |
Let selling price be Rs.100 Variable cost is 60% of selling price Rs.60 Contribution Rs.40 P/V ratio is contribution/sales = 40% Break even sales = 7,500 units Selling price per unit = Rs.1,12,500 Selling price per unit = Therefore, variable cost per unit is Rs.15 60% = Rs.9 Contribution per unit = Rs.6. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
Break even sales (Rs.) = Margin of safety = Total sales Break even sales = Rs.45,00,000 Rs.25,00,000 = Rs.20,00,000 Margin of safety as a percentage to total sales = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
At the breakeven point, total revenue equals the fixed cost plus the variable cost. Beyond the BEP each unit sale will increase operating income by the unit contribution margin because fixed costs have been recovered already. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
P/V ratio for the year 2007-08: = For the year 2008-09: Variable cost per unit = Rs.70 + 15% of Rs.70 = Rs.80.50 Fixed cost = Rs.3,50,000 + 8% of Rs.3,50,000 = Rs.3,78,000 P/V ratio in 2007-08 = 65% Variable cost percentage to sales = 35% Selling price required to maintain same P/V ratio as in
2007-08 = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
d |
Desired profit = Rs.10,00,000 35% = Rs.3,50,000 Number of units to be sold in order to earn a profit of Rs.3,50,000 = |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a |
Margin of safety is 65% of sales Margin of safety = Rs.37,50,000 x 65% = Rs.24,37,500 Margin of safety = Rs.24,37,500 = Net Profit = Rs.24,37,500 50% = Rs.12,18,750. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Interest paid is not included while preparing a cost sheet and all other items mentioned in options (a), (b), (c) and (e) are included in the cost sheet. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
The merits of absorption costing are (a) Price based on absorption costing ensures that all costs are covered, (b) It confirms accrual and matching concepts which require matching costs with revenue for a particular period, (c) Efficient or inefficient utilization of production resources is disclosed by indicating under or over absorption of factory overheads and (e) Computation of gross profit and net profit separately is possible in income statement. (d) Closing stocks are valued at cost of production (i.e., fixed cost and variable cost), which means a portion of fixed cost is carried forward to the next period is the limitation of absorption costing. Hence, the answer is (d) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
Management accounting is not mandatory. The applications of management accounting can be extended beyond the traditional accounting system. It focuses more on the parts/segments of a company and less on the company as a whole. It is not governed by GAAP. It prepares reports to fulfill the needs of management. Therefore, correct answer is (e), because management accounting focuses on providing information for internal users. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
A sunk cost is a cost that has been incurred in the past and cannot be altered by any current or future decision. A direct cost is a cost that can be directly traced to a particular department. A cost that is not direct cost is called indirect cost. An opportunity cost is a potential benefit given up when the choice of one action precludes selection of a different action. A cost that can be substantially influenced by a manger is called a controllable cost. Hence, the correct answer is (d). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
In a make or buy decision, the company analyses the costs that can be avoided in a particular situation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
Variable costs refer to all costs which fluctuate in total in response to small change in the rate of utilization of capacity. Other statements given in (a), (b), (c) and (d) are not correct in respect of meaning of variable cost. Therefore, (e) is correct. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Cost-volume-profit analysis is important for the determination of relationship between revenues and costs at various level of operation. Other options (a), (b), (c) and (e) are not correct in respect of cost-volume-profit analysis. Therefore, (d) is correct. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
*Thus if selling price = Rs.100, Profit = Rs.25; Cost =
Rs.100 Rs.25 = Rs.75. if cost is Rs.75, Profit is Rs.25. If Cost = Rs.30
then Profit = Hence Selling Price = Cost + Profit = Rs.30 + Rs.10 = Rs.40. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
C |
Examples of Finance Modules of ERP applications are: i. Accounts receivable Tracks payments from its customers to a company. ii. Accounts payable Schedules payments to suppliers and distributors. iii. Treasury management Analyzes and monitors financial deals, investment risk, and cash holdings. iv. General ledger Manages centralized charts of accounts and corporate financial balances. v. Fixed assets Handles costs related with tangible assets, including depreciation. vi. Cost control Handles corporate costs related to overhead, products, and manufacturing orders. Production planning is a part of Manufacturing and Logistics module of ERP. Therefore, option (c) is correct answer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
E |
An item of cost that is direct for one business may be indirect for another is a true statement. Other statements are not correct. Therefore, (e) is correct. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
Commitment to a single vendor is one of the limitations associated with ERP but not advantage. Alternatives (a), (b), (c) and (e) are the advantages of ERP. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
Brand valuation is a tool that quantifies the economic value of a brand. Earnings valuation method is the correct answer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
A |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
B |
Computation of works cost:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
D |
The brand strength of a company is based on its positioning, customer loyalty, the markets in which it operates, competition, stability, statutory protection, brand management by the company and long-term trends but not on short term trends. Therefore, option (d) is correct answer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
B |
The margin of safety decreases with increase in the variable cost. All the other options (a) Reduction in fixed cost, (c) Increase in the level of production or selling price or both, (d) Change in the sales mix in order to increase the contribution and (e) Substitute the existing unprofitable product with the profitable ones increase the margin of safety. Hence, the answer is (b). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Earning: Approval pending. |