Gujarat Technological University 2010-3rd Sem B.Tech Biotechnology Thermodynamics - university paper
Seat No. Enrolment No.
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
B.E. Sem-III Remedial Examination March 2010 Subject code: 130405 Subject Name: THERMODYNAMICS
Date: 11 /03 /2010 Time: 03.00 pm - 05.30 pm
Total Marks: 70
Instructions:
1. Attempt all questions.
Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
Figures to the right indicate full marks.
All the Notations bear their conventional meanings.
With special reference to mathematical statement of the second law of thermodynamics, justify that All isentropic processes are adiabatic, but all adiabatic processes are not isentropic.
A system consisting of a gas confined in a cylinder is undergoing the following series of processes before it is brought back to the initial conditions:
Step 1: A constant pressure process when it receives 50 J of work and gives up 25 J of heat.
Step 2: A constant volume process when it receives 75 J of heat.
Step 3: An adiabatic process.
Determine the change in internal energy during each step and the work done during the adiabatic process.
Handbook values for the latent heat of vapourization in J/g are given in the table
2.
3.
4.
(a)
Q.1
07
(b)
07
Q.2 (a)
07
|
for the pure liquids at 25 C and at Tn, the normal soiling point. | |||||||||||||||
|
For these substances, calculate the value of the latent heat at Tn by Watson method, given the value at 25oC and find out the percentage difference from those listed in the table.
Methane gas at 550 K and 5 bar undergoes a reversible adiabatic expansion to 1 bar. Assuming that methane behaves as an ideal gas at these conditions, what is its final temperature? The heat capacity equation for methane is:
(b)
07
= 1.702 + 9.081x10-3Tlm - 2.164x10-6TamTlm
R
OR
Liquid/Vapour saturation pressure Psat temperature by an equation of the form:
is often represented as a function of 07
(b)
b
logio Psa (torr) = a -
t(oC) + c
Here, parameters a, b and c are substance-specific constants. Suppose it is required to represent Psat by the equivalent equation:
sat * B
ln Psat (kPa) = A -
T(K) + C
Show how the parameters in the two equations are related.
If the heat capacity of a substance is correctly represented by an equation of the form, Cp = A + BT + DT-2, show that the error resulting when <Cp>H is assumed equal to Cp evaluated at the arithmetic mean of the initial and final temperatures
05
V
T - T t2 T1
D
is
TT T1 t2
T
V T2
+ T
(b) The turbines in a hydroelectric plant are fed by water falling from a 50 m height. 05 Assuming 91% efficiency for conversion of potential to electrical energy, and 8% loss of the resulting power in transmission, what is the mass flow rate of water required to power a 200 W light bulb?
(c) Calculate the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of methane from 04 260 oC to 600 oC in a flow process at a pressure sufficiently low that methane may be considered an ideal gas.
Data: Cpig/R = 4.021 + 7.899 x 10-3 t - 2.164 x 10-6 t2, t is in oC
OR
Q.3 (a) A steel casting weighing 2 kg has an initial temperature of 500 oC; 40 kg of 07 water initially at 25 oC is contained in a perfectly insulated steel tank weighing 5 kg. The casting is immersed in the water and the system is allowed to come to equilibrium. What is its final temperature? Ignore any effect of expansion or contraction, and assume constant specific heats of 4.18 kJ/kg K for water and
0.50 kJ/kg K for steel.
(b) VLE in Benzene (1)/ Toluene (2) system is well represented by Raoults Law at 07 low to moderate pressures. Using the following data prepare a table of T-x-y for P = 101.3 kPa._
|
T (oC) |
P:sat (kPa) |
P2sat (kPa) |
|
80.1 |
101.3 |
38.9 |
|
88 |
128.5 |
50.8 |
|
94 |
154.6 |
61.6 |
|
100 |
180.1 |
74.2 |
|
110.6 |
237.8 |
101.3 |
Explain cubic equations of state and derive expressions of constants a and b of Vanderwaals equations of state in terms of critical properties of a substance. Given that the vapor pressure of methyl chloride at 60 oC is 13.76 bar. Use Vanderwaals equation to calculate the molar volumes of saturated vapour and saturated liquid at these conditions. Critical temperature and Critical pressure for methyl chloride are 416.3 K and 66.8 bar respectively.
Q.4 (a) (b)
07
07
OR
With the help of neat sketch, explain criteria of chemical reaction equilibrium in details.
Q.4 (a)
(b) Q.5 (a) (b)
(c)
08
06
06
04
04
Explain the factors affecting the choice of a refrigerant with examples.
State and prove Carnot theorem for heat engines.
Starting from basic principles, obtain different forms of virial equations. Also, explain the physical significance of virial co-efficients.
Derive the following thermodynamic relationship:
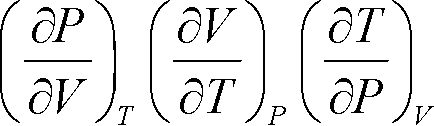 |
= -1 |
OR
Q.5 (a)
05
(b)
(c)
05
04
The reading on a mercury manometer at 25 oC (open to the atmosphere at one end) is 56.38 cm. The local acceleration of gravity is 9.832 m/s2. Atmospheric pressure is 101.78 kPa. What is the absolute pressure in kPa being measured? The density of mercury at 25 oC is 13.534 g/cm3.
Distinguish between reversible and irreversible processes.
Write a short note on thermodynamic diagrams.
*************
2
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
