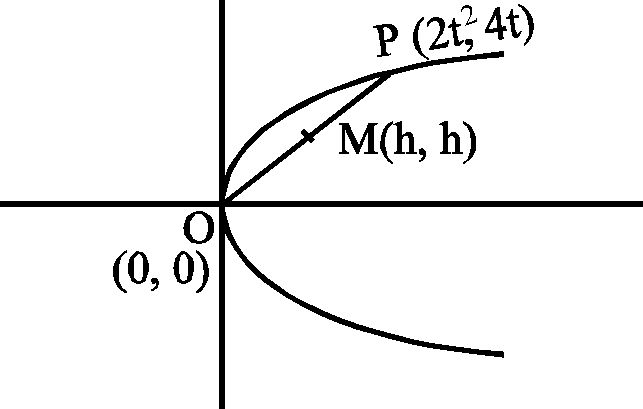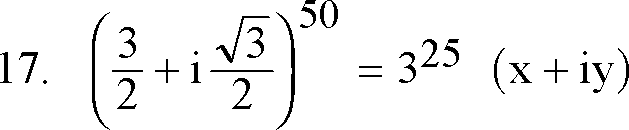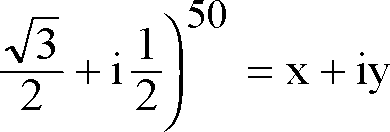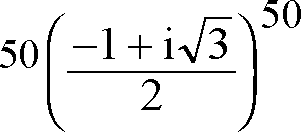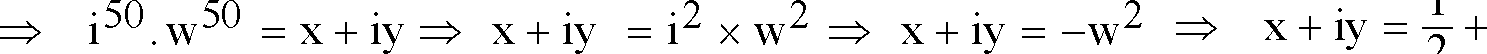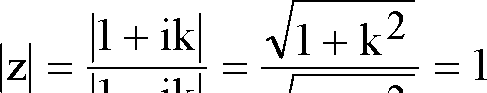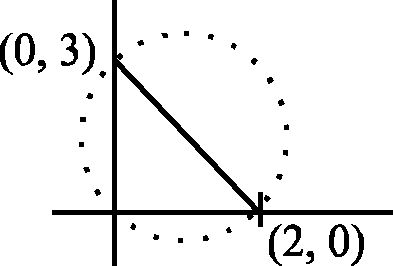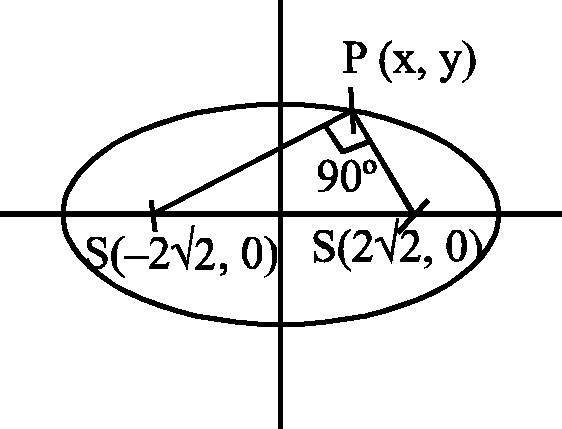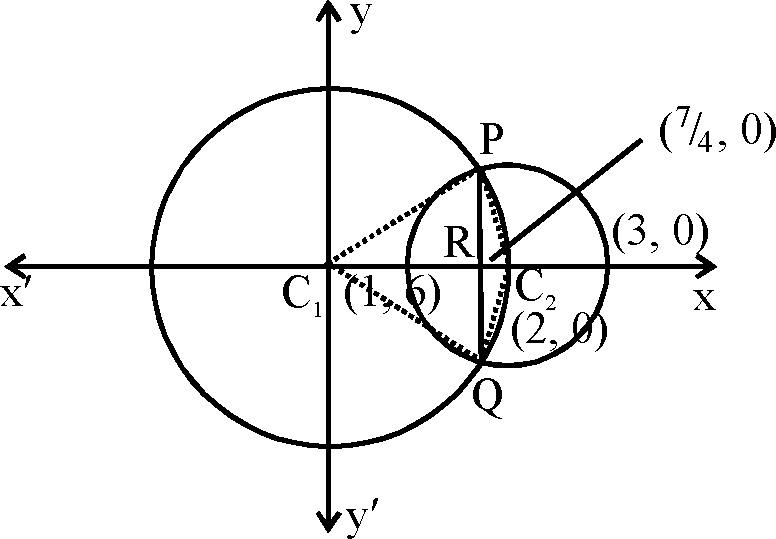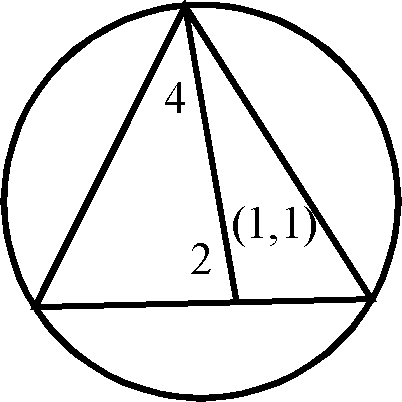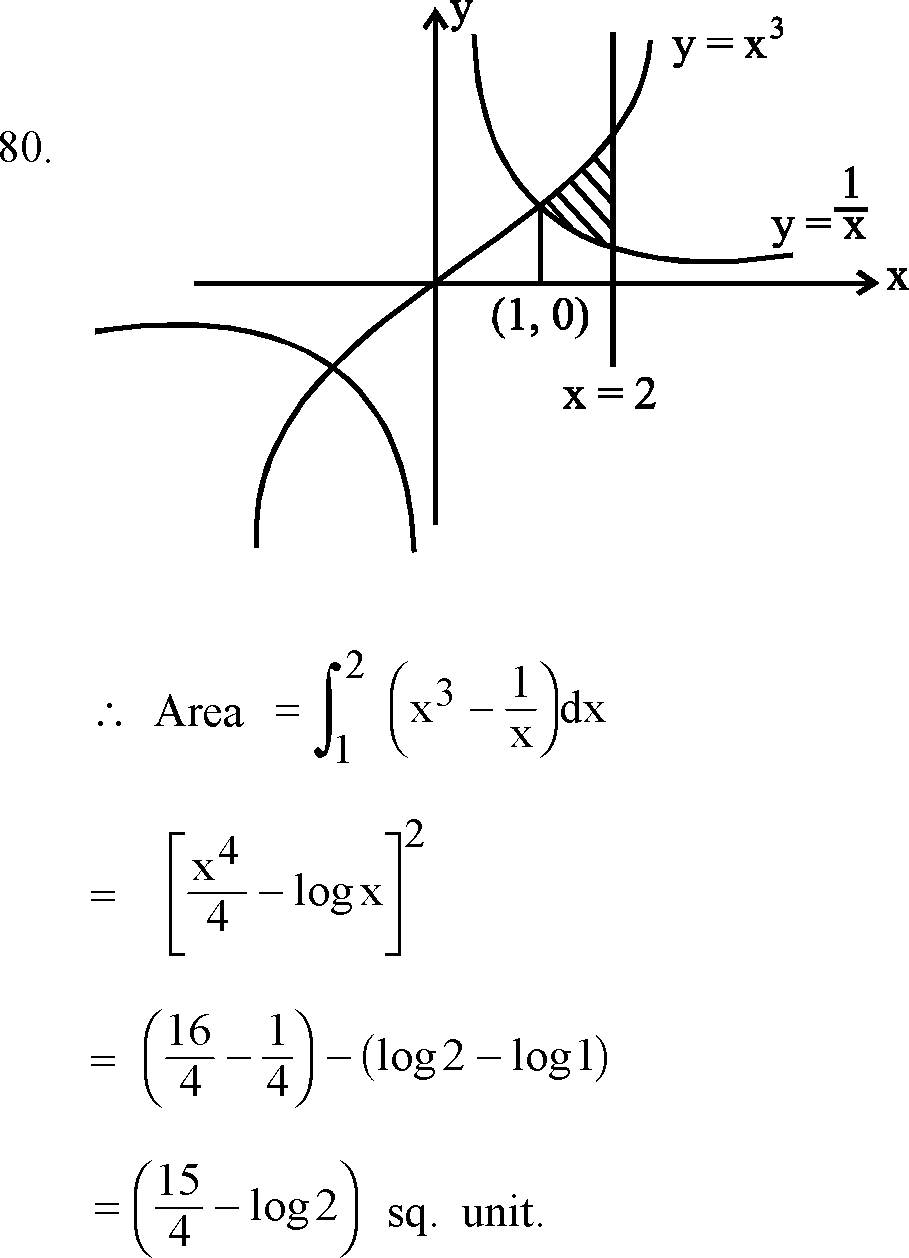West Bengal Institute of Technology (WBIT) 2012-2nd Year B.Tech Wbjee Mathematics year- - Question Paper
Wednesday, 17 July 2013 11:55Web
Page 1 of 2
See attachment.
M 2012
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS
[ Q. 1 to 60 carry one mark each ]
. -1 . -1 . -1 3 n 9 + 9 + 9__1
1. If sin x + sin y + sin z = , then the value ofx y 999 is equal to
2 x y z
A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3
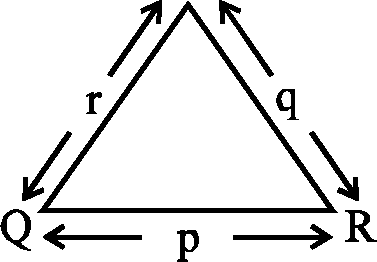
2. Let p, q, r be the sides opposite to the angles P, Q, R respectively in a triangle PQR. If r2 sin P sin Q = pq, then the triangle is
A. equilateral B. acute angled but not equilateral
C. obtuse angled D. right angled
3. Let p, q, r be the sides opposite to the angles P, Q, R respectively in a triangle PQR. Then
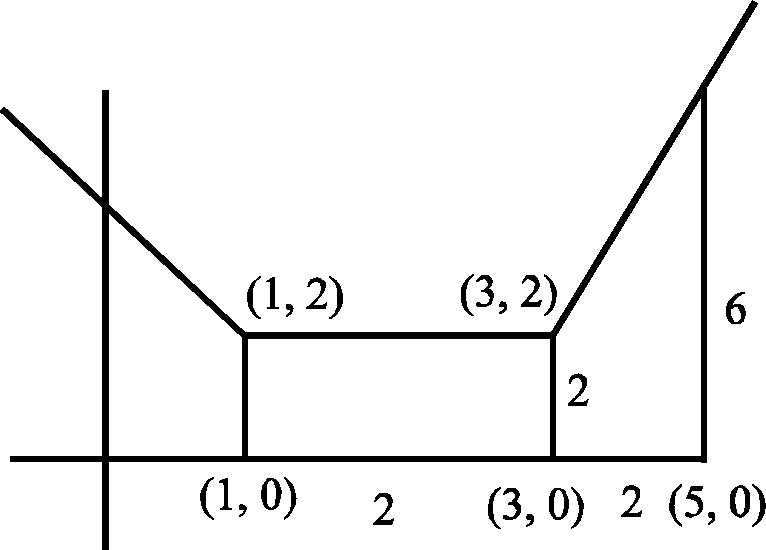
F P - Q + RI 2prsin|--- equals
2
A. p2 +q2 + r2 B. p2 + r2 - q2 C. q2 + r2 - p2 D. p2 + q2 - r2
4. Let P (2, -3), Q (-2, 1) be the vertices of the triangle PQR. If the centroid of APQR lies on the line 2x + 3y = 1, then the locus of R is
A. 2x + 3y = 9 B. 2x - 3y = 9 C. 3x + 2y = 5 D. 3x - 2y = 5
5. lim
A. does not exist B. equals loge (n2 j C. equals 1
D. lies between 10 and 11
6. If f is a real-valued differentiable function such that f(x)f' (x) < 0 for all real x, then
A. f (x) must be an increasing function
B. f (x) must be a decreasing function
C. |f (x)| must be an increasing function
D. |f (x)| must be a decreasing function
7. Rolles theorem is applicable in the interval [-2, 2] for the function A. f (x) = x3 B. f (x) = 4x4 C. f (x) = 2x3 + 3
2 1
8. The solution of 25y - 10 + y = 0, y(0) = 1, y(1) = 2e5 is
2 dx
dx
x
9. Let P be the midpoint of a chord joining the vertex of the parabola y2 = 8x to another point on it. Then the locus of P is
2
x
10 .The line x = 2y intersects the ellipse + y = 1 at the points P and Q. The equation of the circle with
PQ as diameter is
2 + 2 1 A. x +y = -
2 2 x y
11. The eccentric angle in the first quadrant of a point on the ellipse -+-= 1at a distance 3 units from
the centre of the ellipse is
12. The transverse axis of a hyperbola is along the x-axis and its length is 2a. The vertex of the hyperbola bisects the line segment joining the centre and the focus. The equation of the hyperbola is
A. 6x2 - y2 = 3a2 B. x2 -3y2 = 3a2 C. x2 - 6y2 = 3a2 D. 3x2 - y2 = 3a2
13. A point moves in such a way that the difference of its distance from two points (8,0) and (-8,0) always remains 4. Then the locus of the point is
A. a circle B. a parabola C. an ellipse D. a hyperbola
14. The number of integer values of m, for which the x-coordinate of the point of intersection of the lines 3x + 4y = 9 and y = mx + 1 is also an integer, is
A. 0 B. 2 C. 4 D. 1
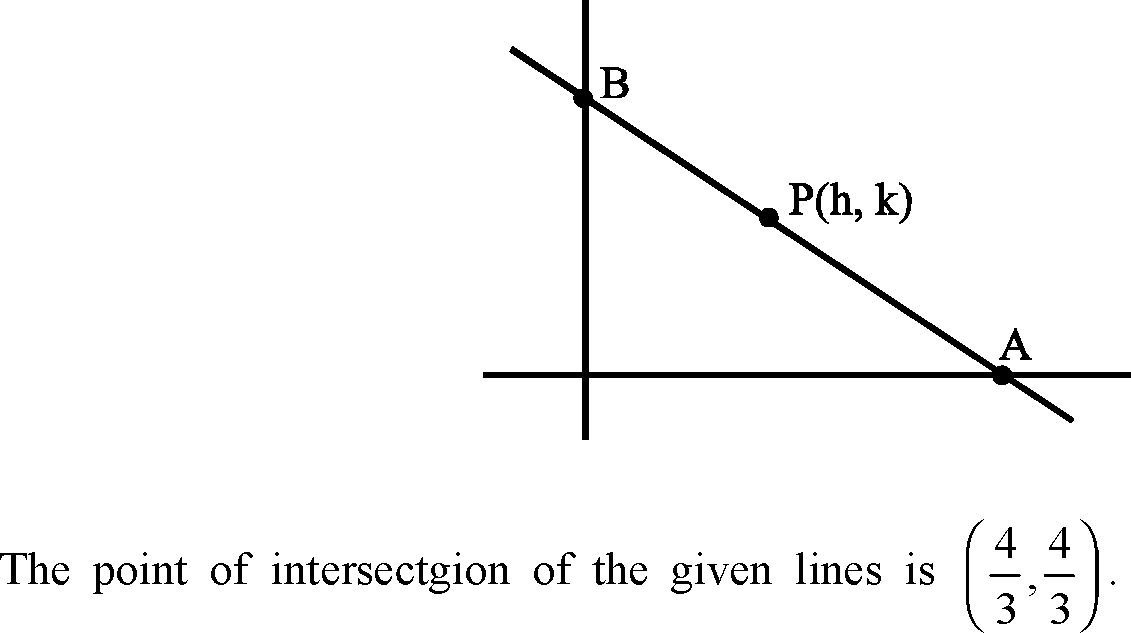
15. If a straight line passes through the point (a,P) and the portion of the line intercepted between the axes is
divided equally at that point, then
A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 4
16. The maximum value of |z| when the complex number z satisfies the condition
A. 3 B. 3 +/2 C. 3 +1 D. 3 _ 1
25
C. (0, -3)
z 1
18. If-is purely imaginary, then
z +1
A. |z| = 1 B. |z| = 1 C. |z| = 2 D. |z| = 3
19. There are 100 students in a class. In an examination, 50 of them failed in Mathematics, 45 failed in Physics, 40 failed in Biology and 32 failed in exactly two of the three subjects. Only one student passed in all the subjects. Then the number of students failing in all the three subjects.
A. is 12 B. is 4
C. is 2 D. cannot be determined from the given information
20. A vehicle registration number consists of 2 letters of English alphabet followed by 4 digits, where the first digit is not zero. Then the total number of vehicles with distinct registration numbers is
A. 262 x 104 B. 26 p2 x10 P4 C. 26 P2 x 9 x10 P3 D. 262 x 9 x 103
21. The number of words that can be written using all the letters of the word 'IRRATIONAL' is
10! 10! 10!
A. (2!)3 B. (2!)2 C2l" D. 10!
22. Four speakers will address a meeting where speaker Q will always speak after speaker P. Then the number of ways in which the order of speakers can be prepared is
A. 256 B. 128 C. 24 D. 12
23. The number of diagonals in a regular polygon of 100 sides is
A. 4950 B. 4850 C. 4750 D. 4650
24. Let the coefficients of powers of x in the 2nd, 3rd and 4th terms in the expansion of (1 + x)n, where n is a positive integer, be in arithmetic progression. Then the sum of the coefficients of odd powers of x in the expansion is
A. 32 B. 64 C. 128 D. 256
25. Let f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, g(x) = px2 + qx + r such that f(1) = g(1), f(2) = g(2) and f(3) g(3) = 2. Then f(4) g(4) is
A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7
26. The sum 1 *1! + 2 * 2! + ... + 50 x 50! equals
A. 51! B. 51! - 1 C. 51! + 1 D. 2 * 51!
27. Six numbers are in A.P. such that their sum is 3. The first term is 4 times the third term. Then the fifth term is
A. -15 B. -3 C. 9 D. -4
1 1 1.3 1.3.5 1.3.5.7
28. The sum of the infinite series 1 is equal to
3 3.6 3.6.9 3.6.9.12
A. V2 B. V3 C. D.
29. The equations x2 + x + a = 0 and x2 + ax + 1 = 0 have a common real root
A. for no value of a B. for exactly one value of a
C. for exactly two values of a D. for exactly three values of a
30. If 64, 27, 36 are the Pth, Qth and Rth terms of a G.P., then P + 2Q is equal to A. R B. 2R C. 3R D. 4R
31. The equation y2 + 4x + 4y + k = 0 represents a parabola whose latus rectum is A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
32. If the circles x2 + y2 + 2x + 2ky + 6 = 0 and x2 + y2 + 2ky + k = 0 intersect orthogonally, then k is equal to
3 3 3 3
A. 2 or - B. -2 or - C. 2 or D. -2 or
2 2 2 2
33. If four distinct points (2k, 3k), (2, 0), (0, 3), (0, 0) lie on a circle, then
A. k< 0 B. 0 < k < 1 C. k = 1 D. k> 1
34. The line joining A(b cos a, b sin a) and B(a cos P, a sin P), where ab, is produced to the point M(x, y)
a+P . a+P
so that AM : MB = b : a. Then xcos + ysm
2 2
A. 0 B. 1 C. -1 D. a2 + b2
x2
35. Let the foci of the ellipse + y2 = 1 subtend a right angle at a point P. Then the locus of P is
A. x2 + y2=1 B. x2 + y2 = 2 C. x2 + y2 = 4 D. x2 + y2 = 8
_ dy x + y + 1
36. The general solution of the differential equation = 2x + 2y + 1 is
A. loge |3x + 3y + 2|+3x + 6y = c B. loge |3x + 3y + 2|-3x + 6y = c
C. loge |3x + 3y + 2|-3x - 6y = c D. loge |3x + 3y + 2|+3x - 6y = c
p/2 F1 + sin2x + cos2x J A
37. The value of the integral : dx is equal to
Jn/6 V sinx + cosx J
A. 16 B. 8 C. 4 D. 1
ft 1 4
38. The value of the integral J 1 + 01 is equal to
ft ft ft
A. 1 B. - C. D 4
dy
39. The integrating factor of the differential equation 3xlogex + y = 21ogex is given by
dx
B. loge(logex)
40. Number of solutions of the equation tanx + secx = 2cosx,x e[0, n]is A. 0 B. 1 C. 2
41. The value of the integral
n
4
|* sin x + cos x ,
J 3 + sin2x dx is equal to
sinx + loge (2 + x), x > -1. Then at x = 0, equals
42. Let y =
A. 1 B. 0 C. -1
x 2
43. Maximum value of the function f(x) = + x on the interval [1, 6] is A. 1
the value of {tan 1 , cosx } is equal to dx L 1 + sinxj
sinx
(1 + sin x)
45. The value of the integral J(1 + 2sinx)elxl dx is equal to
-2
A. 0 B. e2 -1 C. 2(e2 - j
46. If (a + /p j and ( a - Jfi j are the roots of the equation x2 + px + q = 0 where a, p, p and q are real, then the roots of the equation (p2 - 4qj(p2x2 + 4pxj - 16q = 0 are
D. 1
|
\ |
/ \ 1 1 |
|
G __+1 j |
|
|
|
and
J |
H -# K |
B. |
vVa P y |
and |
vVa |
|
p |
|
\
f \ 11
d. (ya+ypj and |
47. The number of solutions of the equation log2(x2 + 2x -lj = 1 is
1 n 1n 1 n
48. The sum of the series 1 + - Ci + - C-> + .... +--T C is equal to
2132 n + 1n
T
Q = PP , then the value of the determinant of Q is equal to
A. 2 B. -2 C. 1
51. The remainder obtained when 1! + 2! + ... + 95! is divided by 15 is A. 14 B. 3 C. 1
-1 cosR cosQ cosR -1 cosP cos Q cos P -1
52. If P, Q, R are angles of triangle PQR, then the value of
A. -1 B. 0 C. 2
53. The number of real values of a for which the system of equations
x + 3y + 5z = ax 5x + y + 3z = ay 3x + 5y + z = az
has infinite number of solutions is
A. 1 B. 2 C. 4 D. 6
54. The total number of injections (one-one into mappings) from ja1, a2, a3, a4} to {b1, b2 , b3 , b4 , b5 , b6 , b7 } is
A. 400 B. 420 C. 800 D. 840
7 5 3
10 . , 7 r p
55. Let (1 + x)10 = crxr and + x = 2~idrx If P = 2~i2r and Q = 2~id2r+1, then q is equal to
r=0 r=0 r=0 Q
r=0
A. 4 B. 8 C. 16 D. 32
56. Two decks of playing cards are well shuffled and 26 cards are randomly distributed to a player. Then the probability that the player gets all distinct cards is
A. 52C26 / 104C26 B. 2 x 52C26 / 104C26
C. 213 x 52C26 / 104C26 D. 226 x 52C26 / 104C26
57. An urn contains 8 red and 5 white balls. Three balls are drawn at random. Then the probability that balls of both colours are drawn is
A _40 B .70 C 3 D 10
A. 143 B. 143 C. 13 13
58. Two coins are available, one fair and the other two-headed. Choose a coin and toss it once ; assume that
3
the unbiased coin is chosen with probability 4. Given that the outcome is head, the probability that the twoheaded coin was chosen is
3 2 12
A. 5 B. 5 C. 5 D. 7
59. Let R be the set of real numbers and the functions f : R R and g : R R be defined f(x) = x2 + 2x - 3 and g(x) = x +1. Then the value of x for which f(g(x)) = g(f(x)) is
A. -1 B. 0 C. 1 D. 2
60. If a, b, c are in arithmetic progression, then the roots of the equation ax2 _ 2bx + c = 0 are
A. 1 and B. _ and -c C. -1 and _c D. -2 and -
a a a 2a
[ Q. 61 to 80 carry two marks each ]
dy y2
61. Let y be the solution of the differential equation x =- satisfying y(1) = 1. Then y satisfies
dx 1 - y log x
A y = xy 1 B. y = xy C. y = xy+1 D. y = xy+2
62. The area of the region, bounded by the curves y = sin-1 x + x(1 - x) and y = sin-1 x - x(1 - x) in the first quadrant, is
1 1 1 A. 1 B. - C. - D. -
2 3 4
63. The value of the integral J [|x - 3 +11 - xl]dx is equal to
A. 4 B. 8 C. 12 D. 16
64. If f(x) and g(x) are twice differentiable functions on (0, 3) satisfying f"(x) = g"(x), f(1) = 4, g'(1) = 6, f(2) = 3, g(2) = 9, then f(1) - g(1) is
A. 4 B. -4 C. 0 D. -2
65. Let [x] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then the value of the integral J (|x| - 2[x])dx
66. The points representing the complex number z for which arg
v z + 2 J
A. a circle B. a straight line C. an ellipse D. a parabola
67. Let a, b, c, p, q, r be positive real numbers such that a, b, c are in G.P. and ap = bq = cr. Then
A. p, q, r are in G.P. B. p, q, r are in A.P. C. p, q, r are in H.P. D. p2, q2, r2 are in A.P.
68. Let Sk be the sum of an infinite G.P. series whose first term is k and common ratio is
rc (-1) k
the value of - is equal to
2/3 \ 2
69. The quadratic equation 2x -1 a + 8a -11x + a - 4a = 0 possesses roots of opposite sign. Then
70. If loge ex2 - 16j < loge (4x - 11), then
71. The coefficient of x10 in the expansion of 1 + (1 + x)+...+(1 + x)20 is
,9 j. v.10
72. The system of linear equations
Xx + y + z = 3 x - y - 2z = 6 -x + y + z = has
A. Infinite number of solutions for X -1 and all
B. Infinite number of solutions for X = -1 and = 3
C. No solution for X -1
D. Unique solution for X = -1 and = 3
73. Let A and B be two events with P(AC) = 0.3, P(B) = 0.4 and P(A n BC) = 0.5. Then P(B\A u BC) is
74. Let p, q, r be the altitudes of a triangle with area S and perimeter 2t. Then the value of 1 +1 +1 is
P q r
2s
D.
t
I ..2 A 4- _
s
75. Let C1 and C2 denote the centres of the circles x2 + y2 = 4 and (x - 2)2 + y2 = 1 respectively and let P and Q be their points of intersection. Then the areas of triangles C1PQ and C2PQ are in the ratio A. 3 : 1 B. 5 : 1 C. 7 : 1 D. 9 : 1
76. A straight line through the point of intersection of the lines x + 2y = 4 and 2x + y = 4 meets the coordinates axes at A and B. The locus of the midpoint of AB is
A. 3(x + y) = 2xy B. 2(x + y) = 3xy C. 2(x + y) = xy D. x + y = 3xy
77. Let P and Q be the points on the parabola y2 = 4x so that the line segment PQ subtends right angle at the vertex. If PQ intersects the axis of the parabola at R, then the distance of the vertex from R is
A. 1 B. 2 C. 4 D. 6
78. The incentre of an equilateral triangle is (1, 1) and the equation of the one side is 3x + 4y + 3 = 0. Then the equation of the circumcircle of the triangle is
|
A. x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y - 2 = 0
C. x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y + 2 = 0 |
B. x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y - 14 = 0
D. x2 + y2 - 2x - 2y + 14 = 0 |
1
(n!)n
79. The value of lim -- is
n
Q 1
80. The area of the region bounded by the curves y = x3, y = , x = 2 is
x

68010
M 2012
SUBJECT : MATHEMATICS
KEY ANSWERS WITH EXPLANATIONS
1. Given sin 1 x + sin 1 y + sin 1 z = 3. 2
-1 -1 -1 2
: sin 1 x = sin 1 y = sin 1 z =
: x = y = z = 1
9 9 9 1
x + y + z
999 x .y .z
= 1 +1 +1 - j = 3 -1 = 2 Ans. C.
2. r2.sinP.sinQ = pq
2 p q r2 X 2R2R = pq
r2 = 4R2 r = 2R
side = 2 x circumradius = diameter So, triangle is right angled triangle. Ans. D.
3. Given P + Q + R = 180
: P + R = 180-Q
(180-2Q'
= sin(90-Q) = cosQ
Now 2pr cos Q
pz + rz - qz 2 2 2
= 2pr -2pr = p + - q
Ans. B.
4. Let R = (h, k)
'2 - 2 + h 1 - 3 + k
3
. 23+lij2 =1
f+k - 2 =1 2h + 3k = 9
Required locus 2x + 3y = 9 Ans. A.
% x -1
5. lim
+ x - 1
(%x - i)(vr+x+ij
= lim
x0
%x - 1
= lim
x Q x
= (log2 %) x 2 = log2 %2 Ans. B.
6. Given f(x).f '(x) < Q Vx e R and f(x) is differentiable
f(x) is continuous function and f(x) and f'(x) are opposite of sign either f(x) >0 or f(x) < 0 but It can not cut the x-axis
When f(x) > 0 then f '(x) < 0 . f(x) is decresing function When f(x) < 0 then f '(x) > 0 . f(x) is increasing function
We can say that |f(x)| is decreasing function.
Ans. D.
7. Check the options individually. Take option (b) f(x) = 4x4
Now, Rolles theorem is applicable. Ans. B.
8. Let y = emx
dy
mx
= me
dx
d2y dx2
25m2emx - 10memx + emx = 0 25m2 - 10m +1 = 0
(5m -1)2 = 0
1 1
m = 55
.'. General solution is y = (A + Bx)e 5 y (0) =1
1 = A .1 A = 1
1
y(1) = 2e 5
2e 5 = (A + B)e 5
2 = (1 + B)
B = 1
x
.. y = (1 + x)e5
Ans. C.
9. y2 = 8x y2 = 4ax 4a = 8 a = 2
, 2t2 + 0,2 +2 u
h = 2 = t2 or t2 = h
, 4t + 0 0+ + k
k = 2 = 2t or t =
. k2 h .. = h
. k2 = 4h y2 = 4x Ans. B.
10. x2 + y2 = 1
2
+ y2 = 1
4
2y2 = 1 2 = 1
y =
y = -
x =
P
equation of circle PQ as diameter is (x - 42 j(x + 42 j +
x2 - 2 + y2 - 2 = 0 2 2 5 x2 + y2 =
Ans. D.
11. Let the pt on the first quadrant T0cos 0, 48 sin 0 j distance from the centre = 3 10cos2 0 + 8sin2 0 = 9 8 + 2cos2 0 = 9
2 1 1 cos 0 = cos 0 = + [v pt lie on 1st quadrant]
2 v2
0 = *
4
Ans. B.
2 2
12. Let the hyperbola = 1
a2 b2
Length of the transverse axis = 2a vertex = (a, 0)
(f, 0) = (a, 0)
focus (ae, 0) centre = (0, 0)
ae
= a
e2 = 4
b
1 + -b2 = 4 b2 = 3a a2
x2 y2
Equation : ---= 1
a2 3a2
Ans. D.
13. The distance between (8, 0) and (-8, 0) = 16 > 4.
According to the defination of hyperbola the locus is a hyperbola. Ans. D.
f=+m: Hh19} 3x+4(mx+1f=9
(3 + 4m)x = 5
5
e I
3 + 4m
.. 3 + 4m = -5, - 1, 1, 5 when m e I . m can take only two values m = -1, - 2.
Ans. B.
x y
15. Let the equation of the line + t- = 1
a b
Its passes through (a, p)
|
(0,b) | 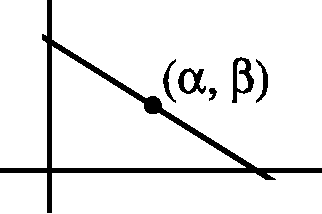 |
|
(a, 0)' |
a+p = 1
ab
(a, p) is the mid points of (a, 0) and (0, b)
a . n b
a = and p =
a = 2a, b = 2p
Equation of the line = 1 y = 2
n 2a 2p a p
Ans. C.
= 2
<|z| +R
2
|z|+|z| - 2
|z|2 -2|z| + 2 - 0
|z|2 -2|z| + 1 < 3
(|z|-1)2 < 3
-S < (|z|-1) <V3
1 -V3 < |z|< 1 + V3 1 -V3
v |z|- 0 Ans. C.
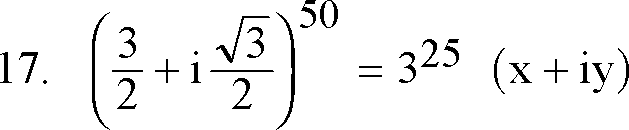
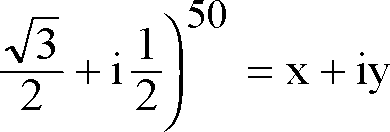
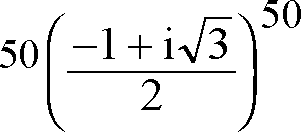 |
x + iy |
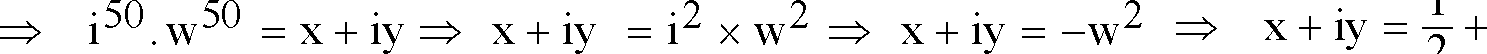
2 2
Ans. D.
z 1
--r = ik, k e R, k
z + 1
2z ik +1 . ..
2 = ik1; by comp.-div.
1 + ik
z = i-
|
1 - ik |
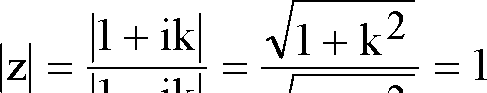 |
|
1 - ikl V1 + k2 |
Ans. B.
19. n(M) = 50 = No. of failed in maths. n(P) = 45 n (B) = 40
n(M0P) + n(M0B) + n(P 0B) - 3n(M0 P 0B) = 32
We have to find n(M 0 P 0 B)
Total no of student =100 n(M U P U B) = 99
n(M) + n(P) + n(B) - |n(M 0 P) + n(M 0 B) + n(P 0 B)} + n(M 0 P 0 B) = 99 50 + 45 + 40 - {32 + 3n(M 0 P 0 B)} + n(M 0 P 0 B) = 99 135 - 32 - 2n(M 0 P 0 B) = 99 2n(M 0 P 0 B) = 4
n(M 0 P 0 B) = 2 Ans. C.
20. 1 2 3 4 5 6
two alphabet we can choose 262 ways. and 1st number we can choose 9 ways. next 3 numbers we can choose 103 ways.
Ans. D.
21. I - 2 R - 2 A - 2 T - 1 N - 1
O - 1 L - 1
10!
Number of words -
(2!)3
Ans. A.
22. Required number of ways is which the order of speakers can be prepared
=n
= ~!
= 4
= 2
= 12 [Taking speakers P & Q as identical]
Ans. D.
23. No. of diagonals in a regular polygon = 100C2 -100
= 100x9 -100 2
= 50 x 99 - 100 = 4950 - 100 = 4850 Ans. B.
24. nC1, nC2, nC3 are in A.P.
_ n - 2) +
-2?-=--+ n
-2 6
n2 - 3n + 2
or, n - 1 =--+ 1
or, 6n - 6 = n1 - 3n + 2 + 6 or, n2 - 9n +14 = 0 n = 7, n = 2 not acceptable.
2n 27 sum = 2- = = 26 = 64
Ans. B.
25. f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, g(x) = px2 + qx + r
(a - b) + (b - q) + (c - r) = 0
Now f(1) = g(1) a + b + c = p + q + r
4 (a - b) + 2 (b - q) + (c - r) = 0
f(2) = g(2) 4a + 2b + c = 4p + 2q + r
3(a - b) + (b - q) = 0
[using (1)] f(3) - g(3) = 2
9(a - p) + 3(b - q) + (c - r) = 2 8(a - p) + 2(b - q) = 2 [using (1)]
4(a - p) + (b - q) =1 (a - p) =1 (using (2))
Now, f(4) - g(4) = 16(a - p) + 4(b - q) + (c - r)
= 15 (a - p) + 3(b - q) (using (1))
{v a - p = 1 } { b - q = -3j
= 15 - 9 = 6
Ans. C.
26. 1x1! + 2 x 2! + 3 x 3! + .... + n x n!
= (n + 1)! - 1
1 x 1! + 2 x 2! + ... + 50 x 50!
= 51! - 1
Ans. B.
27. Six numbers are in A.P.
a - 5d, a - 3d, a - d a + d, a + 3d, a + 5d 6a = 3
1
a =
2
- 5d = 4H - d
2 H 2
--5d = 2 - 4d 2
d = - -
2
Fifth term = a + 3d
1
comparing, nx =
3
nx (nx - x) 1 3
3 6
1
--x
'3 H 3
29. Let a be the common root
2
a + a + a = 0
2
a + aa + 1 = 0
(~)_
a(l a) + a 1 = 0
(l a)(a l) = 0
Either a = 1 or, a =1
Put a =1 in the 1st equation
1 + 1 + a = 0 a = - 2 Put a = 1
. 2 + x + 1 = 0 x2 + x + 1 = 0
They have no real common root.
Put a = -2
x2 + x - 2 = 0 &x2 -2x+ 1 = 0 they have a one real common root. Ans. B.
30. Let A be the 1st term & r be the c.r.
A . rp - 1 = 64 = 26 A . rq - 1 =27 = 33 A . rR - 1 = 36 = 22 . 32
1 p~1 Now, 2 = A 6 r 6
1 q~1
3 = A 3 r 3
1 R~1
2 3 = A 2 r 2
1 p~1 1 q~1 1 R ~1
A6 r6 A3 r3 = A2 r2
p~1+2q~2 3R ~3
r 6 6 = r 6
p 1 + 2q 2 3R 3 6 = 6 p + 2q = 3R Ans. C.
31. y + 4y = -4x - k
y + 4y + 4 =-4x + 4 - k
(y + 2)2 =-4x - (k - 4)
Y2 = -4 AX L.R. = 4A = 4 unit.
Ans. D.
32. Apply, 2(gig2 + f1f2 ) = C1 + C2
2 (1X 0 + k k) = 6 + k
2k2 = 6 + k
or, 2k2 - k - 6 = 0
or, 2k2 - 4k + 3k - 6 = 0 or, 2k(k - 2) + 3(k - 2) = 0
or, (k - 2)(2k + 3) = 0
3
k = 2, - j Ans. A.
33. Equation of circle is (x - 2)(x - 0) + (y - 0)(y - 3) = 0
x2 - 2x + y2 - 3y = 0 x2 + y2 - 2x - 3y = 0 4k2 + 9k2 - 4k - 9k = 0
13k2 = 13k .. k = 0, 1 k = 1 Ans. C.
ab cos P ab cos a b a
= uab = (cos p- cos af b - a v r '
ab
a+P . a+P
xcos:--+ y sin-= 0
2
Ans. A.
2 2
35. x_+z_ = 1
9 1
a = 3, b = 1
2
2
e2 = 1
2
a
242
e =
3
= 22
mps x mps' = 1
y 0 y 0
-X-
x + 2%/2 x 2/2
2
y
= 1
2
x 8
y2 = - x2 + 8
x2 + y2 = 8 Ans. D.
dy _ x + y + 1
36.
dx 2 (x + y) + 1
Let x + y = z
dy dz
1 + = dx dx
dy = dz 1 dx dx
dz z + 1 --1 =
dx 2z + 1
dz z +1
+1
dx 2z +1
_ z +1 + 2z +1
= 2z+1
3z + 2
2z +1
2z +1
or, -dz = dx
3z +1
2 f 3z + 2 or, -dz = I dx + c
2 j* 3z + 2 - \
or, -- dz = x + c
3J 3z + 2
f 3
or, z----:-1 = x + c
3 3 3 J 3z + 2
21
z--log 3z + 2 _ x + c
3 9 1
2(x + y) - -1log|3x + 3y + 2| = x + c
6x + 6y - log|3x + 3y + 2| = 9x + c'
or, 3x - 6y + log|3x + 3y + 2| = c Ans. D.
or,
%
2 (sinx + cosx)2 + (cosx + sinx)(cosx - sinx)
%
6
%
2
j[(cosx + sinx) + (cosx - sinx)]dx
%
6
%
= 2sinx 2
6
. % . %
sin--sin
2 6
= 2 1 -1
2,
= 2.1 = 1
2
Ans. D.
%
2
1
-dx
/ \101 sinx
0 1 +
cosx
101
( cos x)
I x101 / n101
sin x + cos x
a a
Apply j f (x)dx = j f (a - x)dx 0 0
%
2
= j