University of Mumbai 2009 Post Graduate Diploma Operations Management (PGDOM) in Operations Research Management - Question Paper
Post Graduate Diploma in Operations Research Management
I slhulf-TO-nSiDC-l 19
Pope* ZZ5 - Advance. Opemiotn Lesea&tft ~x
rrxxf szaocj BB-8766 to 8768
[Total Marks : 100
Con. 2305&(a-b)-09.
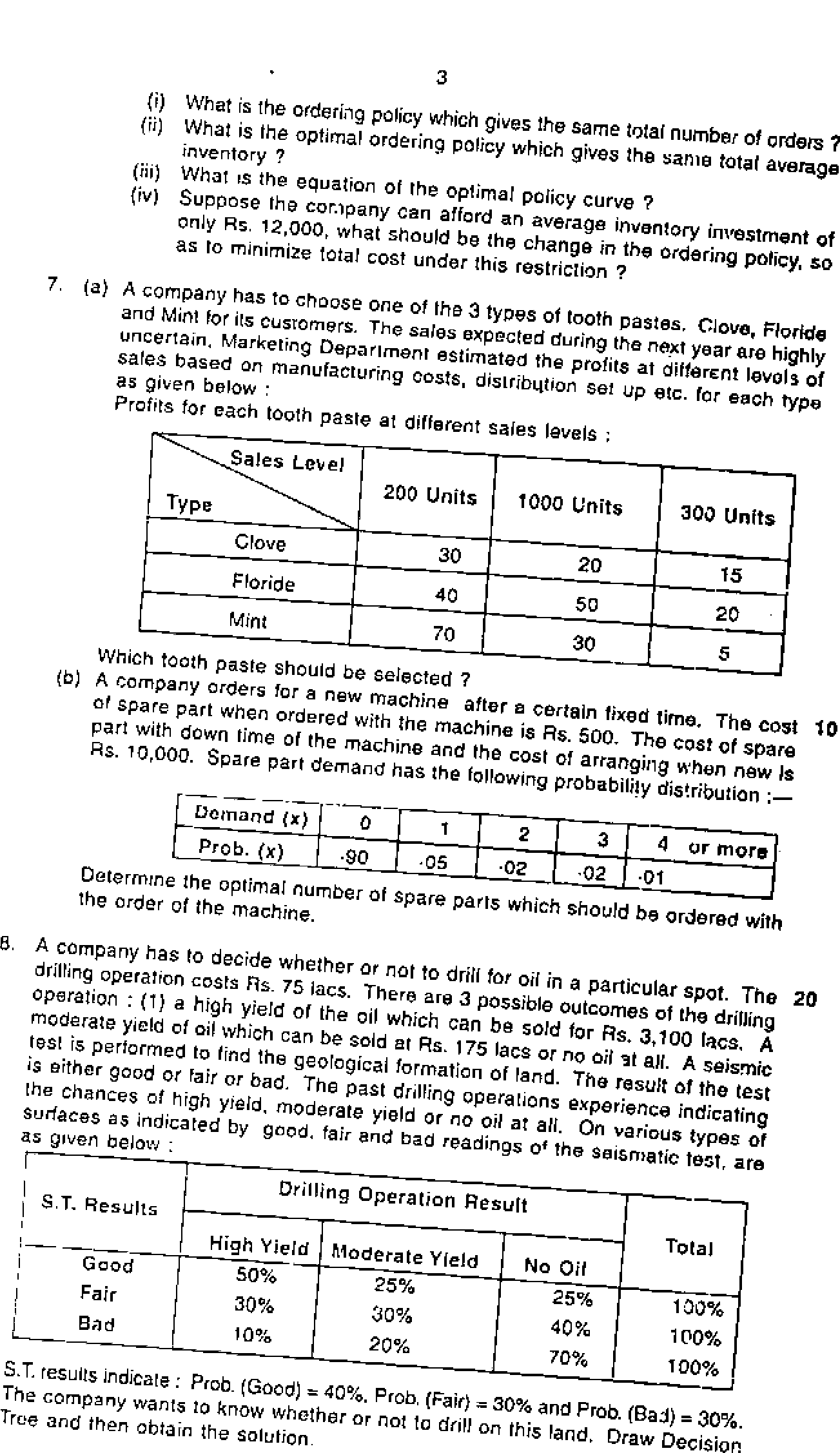
(3 Hours)
N.B,: (1J Attempt any five questions.
(2) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
(3) Use of statistical tables and non-programmable calculator is permitted.
(4) Answers must be brief and to the point.
(5) Intermediate explanations and calculations must be given.
(6) Assumptions wherever necessary must be given.
1, (a) Solve the following LPP using Graphical method.
10
Z = 5x, + 3x2
Minimize Subject to
2x,
5x2 > 480
8x, + 5x. > 720,
Write down the Dual praoblem of the following LPP. Maximize Z =
Subject to
10
(b)
2x1 - 3xa + 5x3 c, + 2x2 > 40
+ 3x2 = 60
x,>0 and x2 unrestricted.
Solve the following LPP using Gomery's cutting plane method : Maximize Z = 7x, + 4x2 Subject to x1 + 3x2 < 6
2. (a)
10
7x.
+ x2 < 35
|
xv Xj >0 and integer. Optimum non-integer solution of the above LPP is- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
What are the artificial variables and why we need them ? How do they differ 10 from slack/surplus variables ? |
(b)
|
3. Optimal simplex table for a LPP is given below : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
10
Write down the mising figures (-) in the above table.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
(vii)
Obtain the original LPP.
What is the optimal solution ? Interpret it,
Determine the range for C, so that the variables in the Basis wilt not change. If a constraint 3x, + 5Xj < 25 is added, what will be the optimal solution ? Determine the range for b, so that the basic variables will not change.
When will x2 enter the basis ?
J sitail f-09-nkDC-120 \
|
4. (a) A manufacturer produce 4 products A, B, C and D by using 2 types of machines 10 M1 and The times required on the 2 machines to manufacture one unit of each product, the profit per unit of the product and the total time available on the 2 types of machines M, and M2, are given below : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Find the number of units to be manufactured of each product per day for maximize the profit.
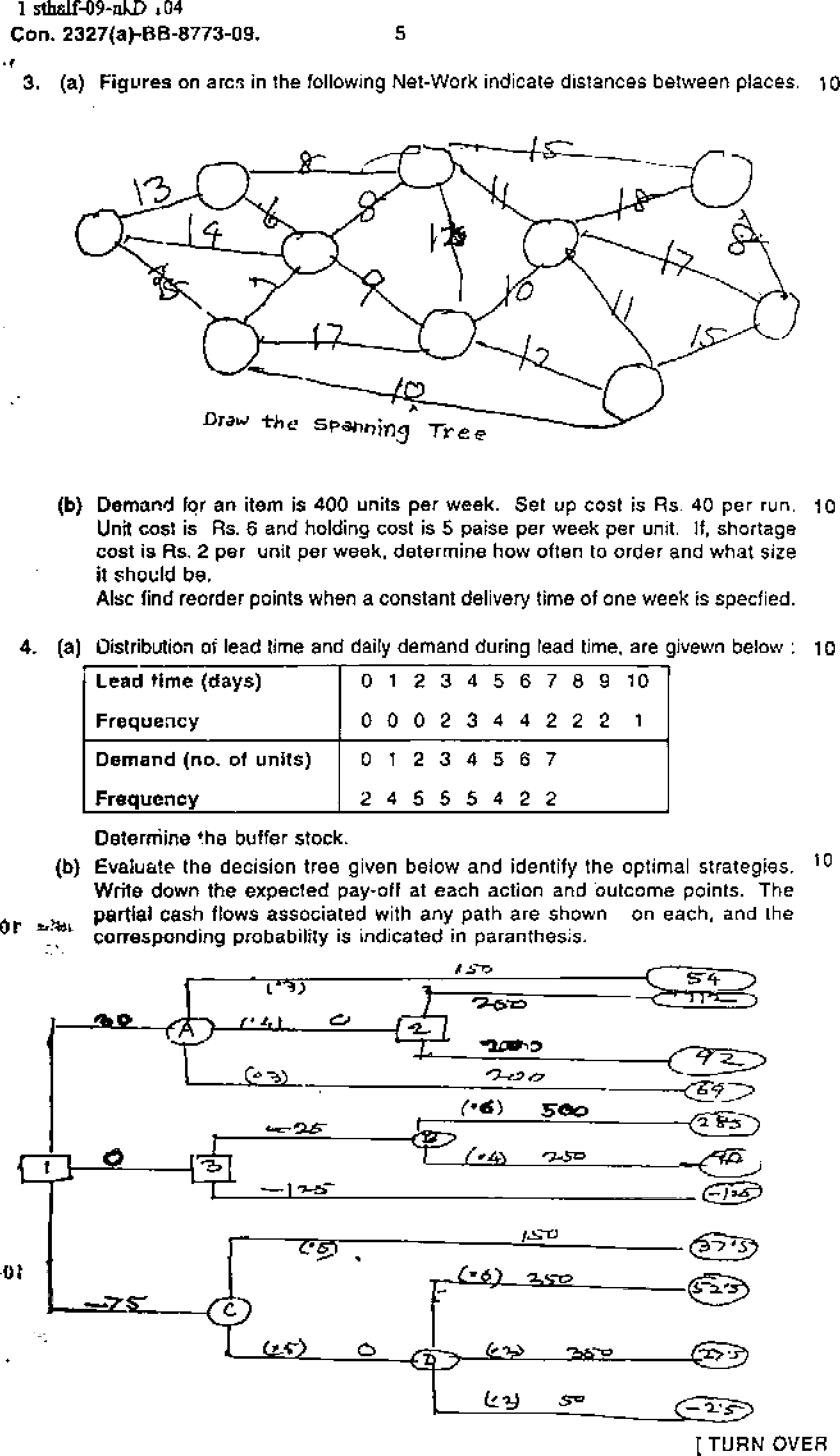
(b) Sole the following spanning tree problem. 10
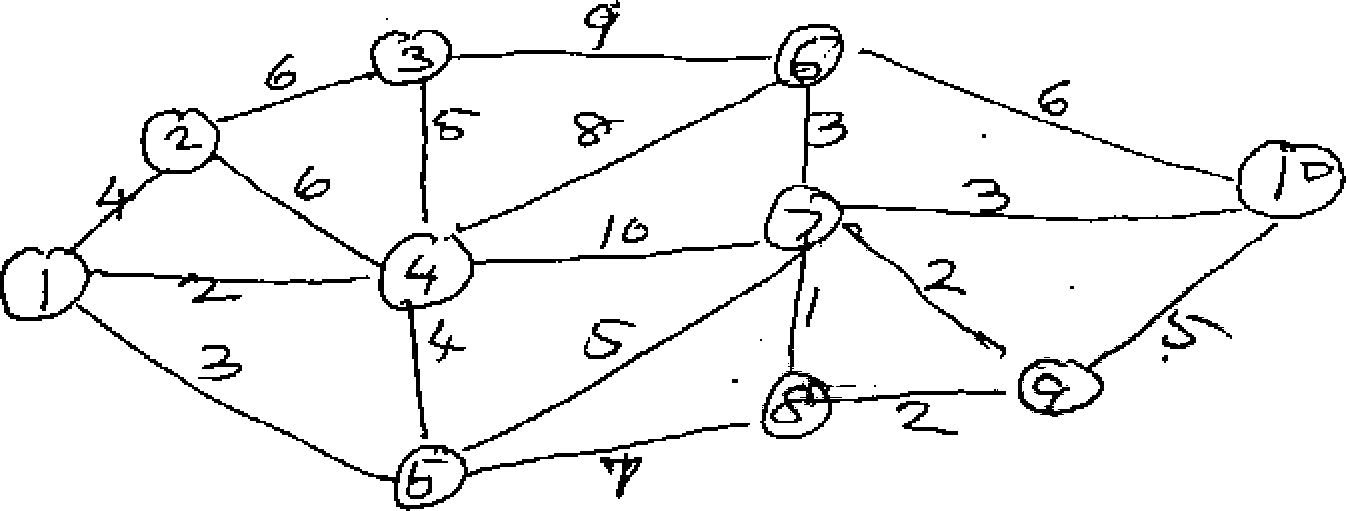
Figures on arcs are distances between the nodes.
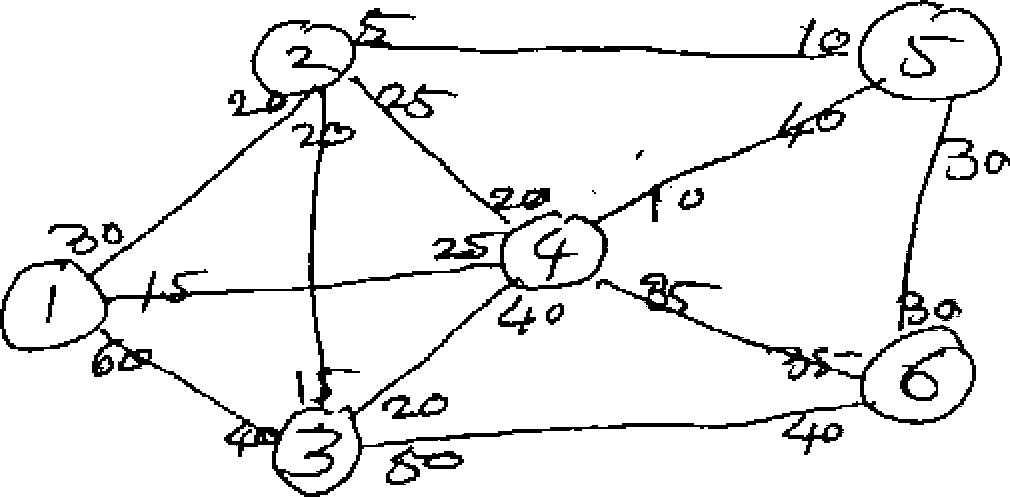
5. Consider the pipe net-work below, showing the flow capacities between various 20 pairs of locations.
Find the maximal flow from Node (1) (source) to Node (6) (sink)
BB-8767 [Total Marks : 100
Con. 2305 & (a)-09.
(3 Hours)
N.B.: (1) Attempt any five questions.
(2) All questions carry equal marks.
(3) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
(4) Necessary explanations at intermediate stages.
{5) Use of ordinary non-programmable calculate and statistical table is allowed.
10
x2 > 0
10
1. (a) Solve the following LPP
Maximize Z = x, + x3 Subject to 3x( + 4x? < 15 2x, + x? >_ 5 3x, + 5x2 =16, X,
(b) Write down the Dual of the following LPP.
Minimize Z = 20x, + 16xP
Subject to x, > 2.5, x2 > 6, 2x, + x2 > 13 2x,+x2>17
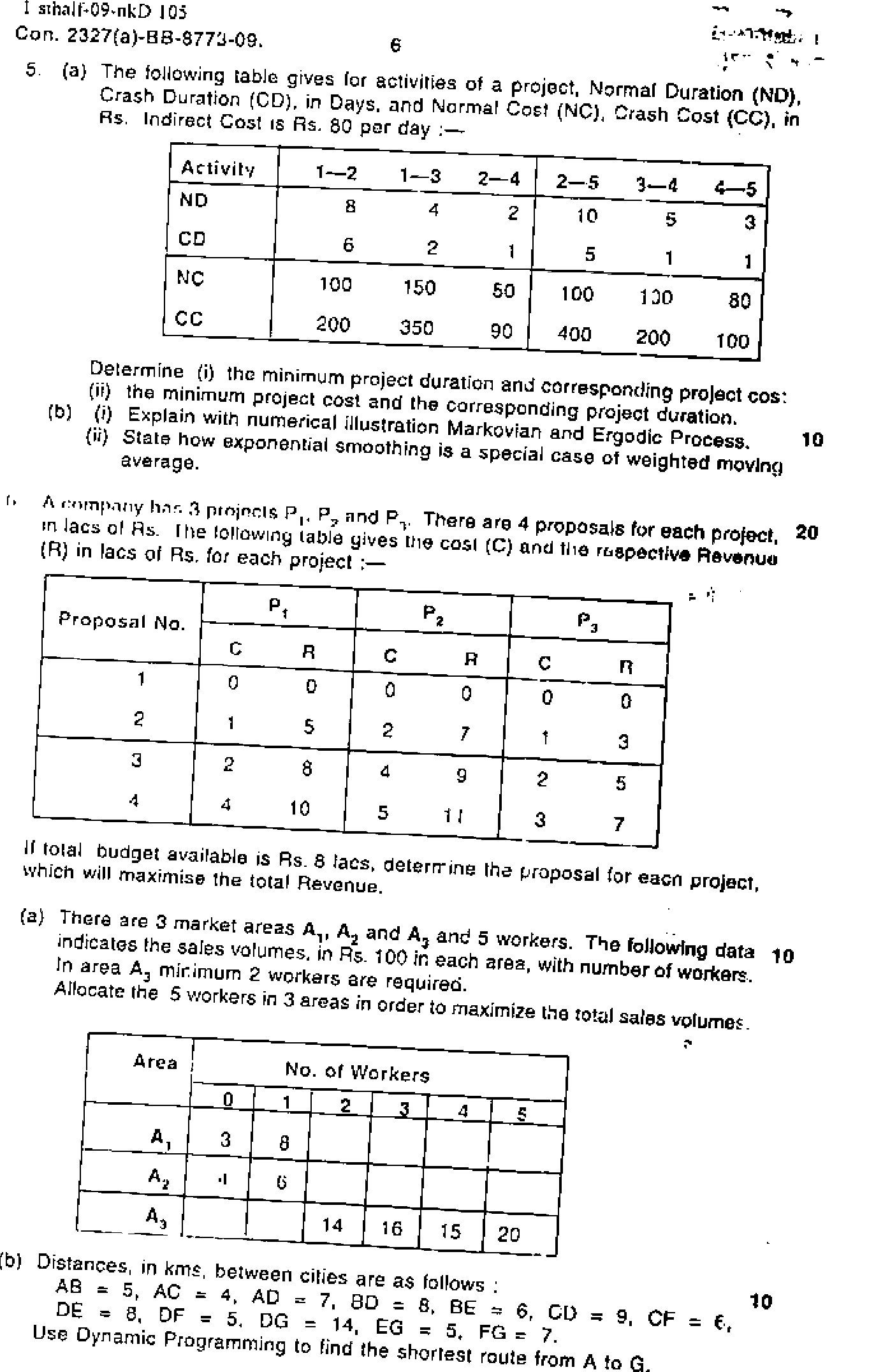
2, (a) A progressive university has decided to keep the Library open round the clock 10 and gathered ttiat the following number of attendants are to reshelve the books.
|
Time of day hours |
04 |
4fl |
812 |
1216 |
1620 |
2024 |
|
Maximum number of attendent required |
4 |
8 |
10 |
9 |
14 |
3 |
If each attendant works 8 consecutive hours, per day, and starts the duty at the beginning of any one of the above stated period formulate the problem as a LPP to meet the necessary requirement at each period.
(b) A worker must carry 3 spare parts if he is to perform the job efficients. The spare parts to be carried have the volumes of 1, 2 and 3 cubic meters respectively. Only 10 cubic meters of storage space is available to the spare parts. Past experience suggests that the demand for the spare parts follow the Poisson distribution with means 4, 2 and 1 repectively.
10
It has also been estimated the costs of running out spare parts (i.e. stock out costs) are Rs. 800, 600 ad 1300 respectively.
Determine the number of spare parts that should be carried if the stock out costs are to be minimized.
3. (a)
Solve the Minimize
following Linear Integer Programming Problem.
Z = 5x, + 4x21 subject to x., + 3x2 > 2, 4x1 + x2 > 5,
10
2
>>~l 0
2x, + 3x
x, x2 > 0 and integers.
(b)
Solve the following LPP by Revised Simplex method. Maximi2ie Z = 2xt Subject to
10
+ 3x2 - 6xa
'1
+ 2x
- x(
4x. + x < 4.
x > 0
4. (a) Solve the following integer programming problem by Branch and Bound Technique. 1D
Maximize Z = 7x, + 6x2, subject to 2x, + x2 <8, 5x, + 3x2 < 30. x, x2 > , 0 and integer.
(b) Six cities A, B, C, D, E and F are to be connected through ST bus routes. Distances, in Kms, are give below :
AB = 4, AC = 10, AD = 3, BC = 7, BE = 4 BE = 5, BF = 6, CD = 12, CE = 8,
DE = 10 DF = 8, EF = 9. Determine the optimal routs connecting all cities.
|
5. A flight is scheduled to leave Bombay for Nagpur every day at 8 a.m. Past experience 20 shows that the patient of delay in departure is a sfollows : | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
Flight time between Bombay ard Nagpur varies as follows t | ||||||||||||||||
|
If scheduled arrival at Nagpur is 9 a.m. Use Monteo Carlo method of simulation to determines what percentage of flights will arrive late at Nagpur.
Carry out 15 iterations. Use the following random minutes.
3102 8963 4830 9172 0983 8352 0012 3542 9173 6384 0132 6834
|
6. (a) Probability distribution of demand for cakes on every day is given below 10 | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
|
Preparation cost is Rs. 3 per unit and price is Rs. 4 per unit, Unsold cakes are waste. |
Determine the number of cakes ordering which will maximise the daily profit.
(b) A maintenance project consists of the job shown below. Normal Duration (ND) 10 and crash. Duration (CD), in days, and Normat cost (NC) and Crash cost (CC) in Rs. for each activity are given below :
|
Activity |
NO |
CO |
NC |
CC |
|
12 |
5 |
2 |
100 |
200 |
|
13 |
2 |
1 |
50 |
80 |
|
14 |
2 |
1 |
150 |
180 |
|
1 CM |
5 |
3 |
20 |
40 |
|
34 |
3 |
1 |
60 |
ao |
|
45 |
3 |
1 |
200 |
240 |
The indirect cost per day, is Rs. 40
Find the EST, LFT and Total Float for each activity.
Determine the total project cost when duration is minimum, and the project duration when the total cost is minimum,
7. (a) Times of completion for each activity of a project are uncertain. However, past experience gives, in the table below optimistic (A) Most likely (M) and Pessimistic (B) estimates of their durations, in weeks.
|
Activity |
1-2 |
13 |
14 |
to 1 kn |
35 |
46 |
56 |
|
A |
1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
M |
1 |
4 |
2 |
1 |
5 |
5 |
6 |
|
B |
7 |
7 |
8 |
1 |
14 |
8 |
15 |
Find the expected duration and variance for each activity. What is the expected project completion time ? Calculate the S.D. of the project duration. What is the probability that the project will be completed in 4 weeks later then the expected project duration ?
(b) Duration, indays, and number of men required for each activity of the project are as given below : _
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Find the number of men on each day required for the project. Level out the number of men without increasing the project duration. |
8. (a) Two firms, F, and F2 are competing for higher share of the market. Each firm has 3 courses of action in the following table. The expected outcome (in terms of changes in market shares) of these actions is given in the following pay-off matrix to Fv
|
Advertising |
Cutting price |
Selling on terms | |
|
Advertising |
5 |
1 |
0 |
|
Cutting price |
3 |
4 |
2 |
|
Selling on terms |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
Figures on areas are capacities. |
[Total Marks : 100
(3 Hours)
N.B.: [1) Attempt any five questions.
(2) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
(3) Use of statistical table and non-programmable calculator is permitted.
(4) Explanations at intermediate stages much be given.
(5) Make suitable assumptions wherever necessary.
(6) Answer should be brief and to the points.
10
10
1. (a) Solve the following LPP by Dual Simplex Method.
Minimize Z = 3x, + 6xa Subject to x, + 6x > 9
3x, + 2x2 > 10 x,, xz > 0 ,
(b) Write down Dual problem of the following LPP>
Maximize 2 = 3*, + 4x2
2x, + x, = 5
Subject to
> 3
10
2. (a)
10
(b)
4x, + x2 < 4, x, is intertiated x2 > 0.
Solve the following LPP by Revised Simplex method. Maximize Z = 2x, + 5xa Subject to 3x, + 7xa < 400 2x, + 6x2 < 420 4x, + x2 < 450, x,,xa>0 From the following table, find
(i) the project duration with minimum, project cost.
f- ___ . .1 nrniort Hliratifin
5x, - x,
|
Activity |
12 |
13 |
24 |
34 |
45 |
|
Normal Duration, Days |
6 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
|
Crash Duration, Days |
5 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
Normal Cost, Hs. (100) |
25 |
15 |
16 |
15 |
14 |
|
Crash Cost, Rs. (100) |
30 |
33 |
25 |
35 |
18 |
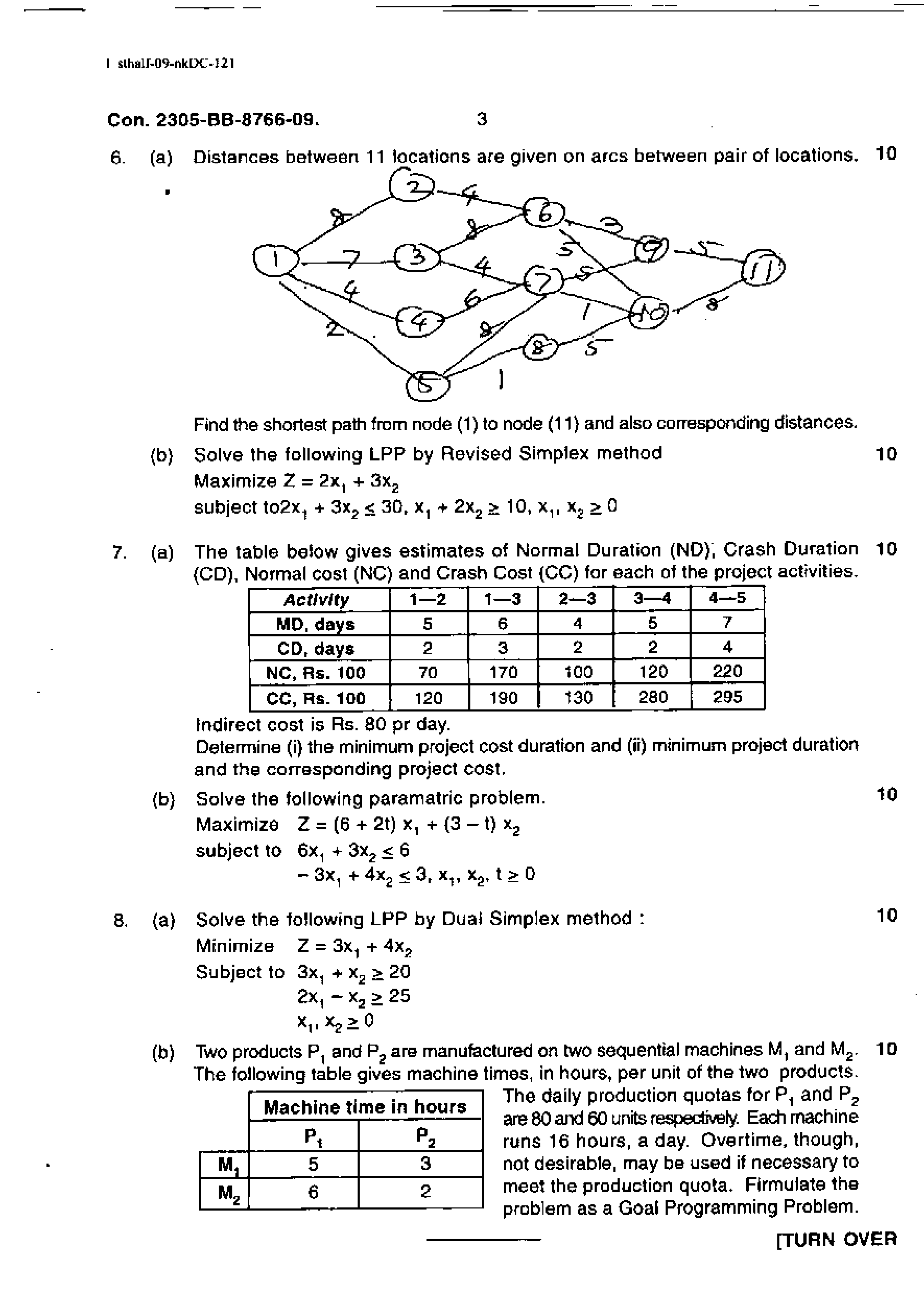
3. (a) Find the maximum flow (units) of a commodity that can be transported through 10 a network with the paths listed below from source 1 to sink 4. The paths and capaciteis are listed below.
10
|
Paths |
12 |
13 |
24 |
14 |
34 |
|
Capacities |
10 |
15 |
5 |
12 |
9 |
(b) Solve the following LPP Maximize Z = 3x, + xa Subject to 4x, - 3x2 < 2 x, - 3xa < 5 x,, x, > 0 and integers.
The following table gives estimates of Normal Duration (ND), Crash 10 Duration{CD),in days, NOrmal Cost (NC) and Crash Cost (CC), in Rs. for each activity. Indirect Cost is Rs, 100 per day.
|
Activity |
12 |
1-3 |
24 |
34 |
45 |
|
ND |
5 |
6 |
8 |
5 |
4 |
|
CD |
2 |
3 |
5 |
2 |
2 |
|
NC |
10 |
22 |
30 |
35 |
40 |
|
CC |
25 |
37 |
45 |
56 |
60 |
Find
4. (a)
(i) the minimum project cost and the corresponding project duration.
(ii) The minimum project duration and the corresponding project cost, Explain the following terms with illustrations. to
(b)
(i) Degenercy in LPP.
(ii) Gomrrys Cutting plane algorithm for integer LPP.
(iii) Dynamic Programming.
Solve the following parametric Programming Problem.
i
5. (a)
10
Maximize 2 = 3x, + 2xa
Subject to x1 + 2x < 10-50, 4x, - x2 < 3 - 4t.
The following table gives activities, duration, in days and manpower requirements 10 for a certain pro ect.
(b)
| ||||||||||||||||||
|
Level out and the resources withour increasing the porject duration. |
6. A company panuractures 2 products P, and P2. The following table give, the
10
|
Product |
Technical service hours |
Labour in hours |
Units Project in Rs. |
|
3 |
2 |
7 | |
|
2 |
2 |
5 |
Demand for Pz < 7, 9 hours of capacity, in Technical service hours represents requalr time hours and it is possible to work overtime in each department. Regular time in labour hoours is 8 hours. Total overtime, in both the departments together, iin excess of 15 hours, should be minimum.
Formulate the problem as a Goal Programming Problem and obtain the optimum solution.
|
in hours for each activity of a project. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(i) Find the mean and variance of each activity duration.
(ii) Waht is the probability that the project will be completed, in 4 days more thanexpected duration of the project ?
(b) A company produces 2 products A and B on two machines and M?. The 10 processing time of P, on M2 per unit, 5 hours end on M? 4 hours. The processing time of Pj on M, is 10 hours and on U2 is 4 hours per unit. The maximum number of hours available per week on M, and M2 are 60 and 40 hours respectively. Also profit per unit selling P, and P2 are Rs. 600 and Rs. 800 respectively.
Formualte a LPP to determine the production volume of each of ihe proeucts such that the total profit is maximized.
|
8. The optimal solutin is given below with some missing figures. 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Find the missing figures and then obtain the original LPP. |
[ Total Marks : 100
( 3 Hours )
'2 6) o M BB-877S
N.B.: (1) Attempt any five questions.
(2) All questions carry equal marks. (20 each)
1. Discuss various input and output devices,
2. Discuss the types of computers and its evolution in the past.
3. Using examples in business, explain the E-R diagrams,
4. What are database management systems ? Discuss its limitations with respect to RDBMS,
5. What are high level and low level programming languages ? Give examples of the both. Discuss the current computer programming scenario
6. Discuss the stages in software development.
7. What do you understand by simulation ? Where do you find its applications ? Discuss one of the applications of simulation mentioning the type of simulation.
8. What role computer plays in data analysis ? How Operations Research Models can be solved using computers ? What softwares are available for this purpose ? Explain one of
them.
9. What is Management Information System ? How is it beneficial for decision making in business ? Discuss the stages in MIS development.
-Second or pcHDOlPJ'f. f4- m<X/ pQpp* Jx. Tviejrrvkd Approach 'Zexxj Ao opemtfon 'R-rJfnic BB-8782
(3 Hours) [Total Marks : 100
Con, 2529-09,
N.B. : (1) Answer question No. 1 which is compulsory and any four from the rest.
(2) Res! life examples will receive more weightage.
(3) Answers must be brief and to the point.
(4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
1. The new paradigm for an organization is now focusing on TRIPLE BOTTOM LINE - Financial profitability, Environmental sustainability and social responsibility.
20
Highlight applications of suitable OR techniques towards increased effectiveness in each of the above three dimensions or an organisation's long torn success OR
Write contribution of OR techniques to achieve breakthrough improvements in Health Care Services (eg. Hospitals) or Educational Institutions or any other service industry you are familiar with.
20
Itemise at least three OR techniques which are applicable in Deterministic, Probabilistic io and uncertain situations.
2. (a) (b)
3. (a) (b)
4. (a)
In each of the above cases provide at least one example each from Industry, Business, 10 Administration and Marketing.
Explain the application of OR in Environmental, Scanning and Resource Planning with examples in each case. Your explanation must Include brief description of methodology and technique to be used.
Briefly describe phases of Planning and Execution of a Management Information System (MIS), You must highlight linkages between its elements and steps for its implementation.
10
10
Discuss the relationship between theory and practice in different stages of a typical OR 10 study. Illustrate with examples.
(b)
Compare old and new approaches and corresponding application of or techniques to 8 decision making processes tor programmed (repetitive) and non-programmed (one-shot) problems.
As you are aware the popular Linear Programming (LP) model has five basic limitations. 5 Itemise them with your logic.
5. (a)
(b)
(c)
In tackling each of them, at least one or technique was developed. Highlight one specific 10 OR technique developed to tackle each limitation.
What problems do you anticipated during implementing solution of LP problems brought 5 out by computer packages.
(a) Explain concept of Decision Support Systems and the role of OR in their development. 10
6.
(b) Highlight synergies between decision support systems and information systems towards 10 overall improvement of bottom line of an organization.
7. Write briefly on any four of the following :-
(a) Satisficing, optimising and Adaptising
(b) Critical factors for slow progress of OR as a discipline in India.
(c) Roie of OR in the midst of Computer Revolution.
(d) Application of OR in Advertising Budget Decision.
(e) Integration of OR with Lean six sigma
(f) Strategic, Tacticaf and Operational decisions.
|
1 sthalf-09-nfcD 100 Con. 2327 & (a - b}-09. |
BB-8772 to 8774 |
N.B,:[1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
t- (a)
to
(*>)
(a)
10
(3 Hours}
Attempt any five questions.
Figures to (he right ndicate full marks
Assumptions required in the question wherever necessary must be exotamart Necessary explanations and calculations at intermediate stages must to given!
batch3' peranVr an "em iS 400 units P0' <** ordering cost is RS 20 Mr batch. Production cost par item Is Rs. 15. Unit cost is Rs fi nr
inventory cost is per units. 10% of unit cost per year Discount to 5*
De term me the breakdown order quantity. * 15 5%- .
Discuss the following terms with illustrations
(] Bayesian Approach in Decision Making 10
(it) Advantages of Decision Trees in Decision Waking.
There are 3 products P P anrt p ti______. ,
below 2 d P=' The nec0SSar/ information is given
K = Production Rate, in 100 units par day, " '
r = Demand Rate, in 1000 units per day
C, = Inventory cost per unit per year Rs
C3 = Set up cost, in Rs. '
[ Total Marks : 100
-r
Product
c,
010
35
50
10
10
015
12
020 I 20
20
r vfaw j CU
(j) Determine Ihe optimum no. of runs per year (II) Find the optimum runs length for each products.
(b)
| ||||||||
|
il may be Slocked oMatf 'h* end *,h9 " month. The cost ol prc-duclion is RS 1000 oe bitch nn 1 item p9r |
(a)
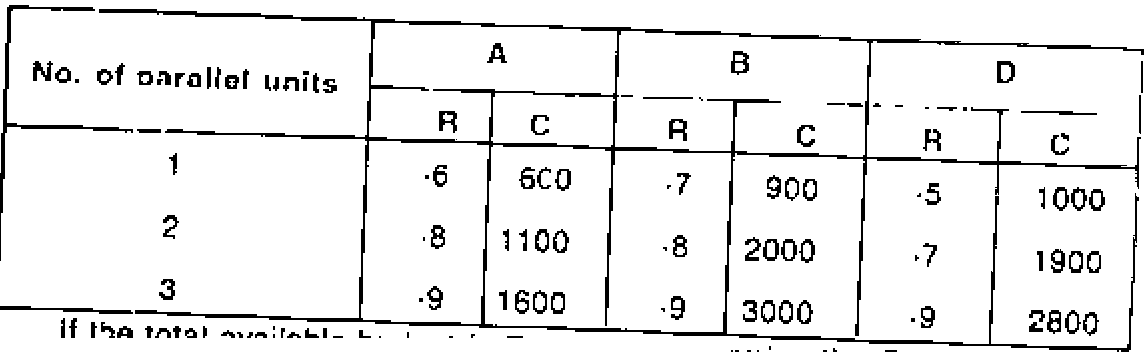
R = Reliability, C = Cost, in Rs. 1.000.
Component 1
Component 2
Component a
No. ol parallel units
3
e
8
2
4
5
6
7
8
5
7
3
L___
w mira ms
3
4
I ithalf-09-akD 103
Con. 2327(a )-09. 4
BB-0773 [Total Marks ; 100
(3 Hours)
Attempt any five questions.
(2) Figures to the right indicate full marks
be given.
"h!rever reuired must be explained.
(6) Answers should be brief and to ihe points.
1 beta!!1*'59 dSmand duri'19 January-May 2008 ol
a particular item is given io
Month
February
March
April
May
J35
195
f?! rrSt demanCt f0r June' 2000 bv lakmg = .Z ,6 an
in each Deri',aIicn <MAD> a"<* Mean Squared Error (MSEI
/h\ t. a comment on selection ol u
(b) A company has 5 salesmen for allocation in 3 areasA A ann a e ,
Ss' in in -* - nUmbwiZatrA;S# 10
Actual Demand 200
175
and o
January
310
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SET" P,ima' a"ocalion in order t the tool sales | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 states S, and S3, 10 s (ii) Steady slale. | ||||||||
|
(bl Damand distribution of Banana's was as follows ; | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
|
Purchase price is Rs, 12 par dozen. |
Sailing price is Rs, 15 per dozen for fresh bananas. One day oJd * Rs. 10 por dozen.
in
* Determine the optimum stock.
t sthalf-09-nkD ! 06 Con. 2327(a)-BB-8773-09.
8. (a)
an (NO), 10 (CC}. in
t=L
ein-reliability {probability of not failure) of th h 9 01 the devicQ- The
ore or YZs *"
follow,no aata gives Reliability rm 3n jV component, in parallel The units. ' 9 Heflability (Rj and Cost (C) for each components parallel
uuuge, ,s Hs good, dete, Explain the following terms with Illustrations
|
30 | ||
|
o Q | ||
|
ect cost | ||
|
Dn. | ||
|
ess. |
10 | |
|
moving | ||
|
project. |
20 | |
|
evenue | ||
(I) EMV. EPPI and EVPI
10
(II) Prior analysis (ill) Posterior analysis (rv) Preposterior analysis.
Con. 2327(b)-Q9.
BB-8774 { Total Marks : 100
(3 Hours)
Attempt any five questions (2) Figures to the right indicate full marks
(5) Assumptions wherever necessary must be explained
(6) Answers should be brief and to the points.
' . , ........
foject,
9 data 10 Jrkers.
lumas.
January February
200
March ] April
May
Actual Demand
136
195
310
175
W o'ae,0rJune'1998 by ,akin9 e*ponemia'
W 2T!,Urf Ab5WS DeWa,i0n and Mean Square Error in each case and comment on selection of a,
2. (a)
|
The data represents monthly sales, in number of units . | ||||||||||||
|
10
10
with a single ingS 7 0 ,n3
P = 0-3 -o forecast h mo'n.h Ub' Sm,hi"9 factr
----- .v, vlM MlUHlfl.
22Z!s~ *" *" won
(b)
to
I slhalf-OO-nkl) 10S
Con, 2327(b)-BB-8774-09. 9
6. (a) Find out the steady state probabilities for ihe following transition matrix for 10
2 states S, and Sj.
|
Also determine the transition probability matrix for the third period. | |||||||||
| |||||||||
|
(b) Explain Markovian Decision Process and its application to determine steady 10 state probabililtes. |
7. (a) 6 jobs are processed on three machines M M, and M, with machine *0 order Mr lor each job,
|
Job No. |
1 |
2 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
ie in mi 6 |
|
M, |
9 |
13 |
6 |
12 |
S |
5 |
|
Mj |
5 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
3 |
4 |
|
4 j 2 |
5 |
5 |
3 |
1 | ||
Doturmmo iho opi,mum suquonco lor ihe Jobs which wiil complete them In shortest possibel timo. Represent this optimum sequence by Gnatt chart
(b)
moa nM mrnu er ib has an exponential distribution with
10
Th? ul! T repa',rS T V' S0,S ln lhe ord6r in whictl !hpy come ir>.
The number of arriving sets lor repairing follows a Poisson distribution with an average rate ol 10 per 8-hour day.
(i) Find the expected idei time ol Ihe repairman each day. (ii) How marw fobs are ahead of the average set just brought in ?
(a)
fb)
A super market has 3 girls at the sales couriers. Service time for each counter 10
lashfonaMh* ,,bUtn,h moan 4 'nutes, Customers arrival at Poisson fashion at the counter ai (he rate of 10 per hour
(I) What is the probability of having to wait for service ? (ii) Find the percents of .die time for each girl (iii) What is ,he expected time of a oustX wftt
IheyrLi1
10
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
