Tamil Nadu Open University (TNOU) 2009-2nd Year M.Sc Mathematics Tamilnadu open university Maths Operation research 2006 - 07 batch - Question Paper
M.Sc. DEGREE exam —
JUNE, 2009.
(AY 2006–07 batch onwards)
Second Year
Mathematics
OPERATIONS RESEARCH
Time : three hours Maximum marks : 75
part A — (5 x five = 25 marks)
ans any 5 of the subsequent.
1.Obtain the dual of the subsequent linear programming issue
Maximize
subject to the constraints and .
2.Explain the linear goal programming.
3.Explain the concept of dynamic programming and the relation ranging from linear programming and dynamic programming approach.
4.Two players A and B match coins. If the coins match, then A wins 2 units of value, if the coins do not match, then B wins two units of value. Determine the optimum strategies for the players and the value of the game.
5.If the 2 person, zero-sum game
Player B
Player A
Strictly determinable and fair? Justify.
6.Explain the queuing model.
7.State the sufficient conditions in Lagrange’s multiple method.
8.Show that the issue is separable.
part B — (5 x 10 = 50 marks)
ans any 5 of the subsequent.
9.Use simplex method to maximize
subject to the constraints :
10.Carry out 3 iterations of Karmarkar’s algorithm for the subsequent issue :
Maximize
subject to
11.Solve the network by cyclic algorithm
12.Solve the subsequent linear programming issue by dynamic programming
Maximize
subject to the constraints
13.Use Branch and Bound method to solve the subsequent their programming issue
Maximize
subject to and
14.In a shop there is only 1 salesman at the counter. nine customers arrive on an avg. every
5 minutes, while the salesman can serve 10 customers in five minutes. Assuming Poisson distribution for arrivals and exponential distribution for service rate.
obtain (a) avg. number of customers in the system,
(b) avg. number of customers in the
queue, (c) avg. time a customer spends in the system, and (d) avg. time a customer spends in the queue.
15.Obtain the necessary conditions for the optimum solution of the subsequent issue
Minimize
Subject to the constraint .
16.Solve the subsequent geometric programming issue
Minimize .
——–––––––––
M.Sc. DEGREE EXAMINATION
JUNE, 2009.
(AY 200607 batch onwards)
Second Year
Mathematics
OPERATIONS RESEARCH
Time : 3 hours Maximum marks : 75
SECTION A (5 5 = 25 marks)
Answer any FIVE of the following.
1. Obtain the dual of the following linear programming problem
Maximize ![]()
subject to the constraints
![]()
and ![]() .
.
2. Explain the linear goal programming.
3. Explain the concept of dynamic programming and the relation between linear programming and dynamic programming approach.
4. Two players A and B match coins. If the coins match, then A wins two units of value, if the coins do not match, then B wins 2 units of value. Determine the optimum strategies for the players and the value of the game.
5. If the two person, zero-sum game
Player B
Player A ![]()
Strictly determinable and fair? Justify.
6.
Explain the ![]() queuing model.
queuing model.
7. State the sufficient conditions in Lagranges multiple method.
8.
Show that the problem ![]() is
separable.
is
separable.
SECTION B (5 10 = 50 marks)
Answer any FIVE of the following.
9.
Use simplex method to maximize ![]()
subject to the constraints :
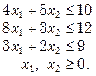
10. Carry out three iterations of Karmarkars algorithm for the following problem :
Maximize ![]()
subject to
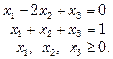
11. Solve the network by cyclic algorithm

12. Solve the following linear programming problem by dynamic programming
Maximize ![]()
subject to the constraints
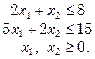
13. Use Branch and Bound method to solve the following their programming problem
Maximize ![]()
subject to
![]()
and ![]()
14. In
a shop there is only one salesman at the counter. 9 customers arrive on an
average every
5 minutes, while the salesman can serve 10 customers in 5 minutes. Assuming
Poisson distribution for arrivals and exponential distribution for service
rate.
Find (a) average number of customers in the system,
(b) average number of customers in the
queue, (c) average time a customer spends
in the system, and (d) average time a customer spends in the queue.
15. Obtain the necessary conditions for the optimum solution of the following problem
Minimize ![]()
Subject to the constraint
![]() .
.
16. Solve the following geometric programming problem
Minimize ![]() .
.
| Earning: Approval pending. |
