University of Hyderabad (UoH) 2010 Entrance Exams Other Entrance Exams Ph.D Programme Entrance - Plant Sciences - Question Paper
Ph.D Programme Entrance examination - Plant Sciences
U-60
ENTRANCE EXAMINATION, 2010 Ph.D. Plant Sciences Date: 01-06-2010
Time: 2 hours Maximum Marks: 75
HALL TICKET NO.
Please read carefully before answering the questions
1. Answers are to be marked on the OMR answer sheet following the instructions provided there upon.
2. Hand over both the question paper booklet and OMR answer sheet at the end of the examination.
3. The question paper contains 75 questions (Part -A Q. Nos. 1-25; Part -B: Q. Nos. 26-75) of multiple-choice type printed in 15 pages. including this page and the OMR answer sheet provided separately. Please check.
4. The marks obtained in Part-A will be used for resolving the tie cases.
5. Each question carries one mark.
6. There is negative marking for wrong answers, in PARTS-A and B. For each wrong answer, 0.33 marks will be deducted.
7. Calculators and mobile phones are not allowed
1) In population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 75% of the individuals have a dominant allele for a particular gene (p = 0.75) and 25% have a recessive allele (q = 0.25). The proportion of homozygous recessive individuals in the FI generation will be
A. 2.5%
B. 6.25%
C. 18.75%
D. 25%
2) Following antimicrobial drug inhibits formation of peptide bonds and thereby protein synthesis in bacteria
A. Chloramphenicol
B. Sulfonamide
C. Tetracycline
D. Erythromycin
3) The lateral diffusion rate of lipid molecules can be quantitatively determined by
A. Immuno fluorescence
B. Fluorescence photo-bleaching recovery technique
C. Transverse diffusion test
D. Calculating the ratio between saturated to unsaturated fatty acids
4) Which of the following is a site specific nuclease in T-DNA transfer
A. VirG
B. VirA
C. VirDl
D. VirE2
5) Trypsin specifically cleaves peptide bonds
A. Between any negatively charged residue and proline
B. After positively charged residues, if the next residue is not proline
C. Between Lysine and proline
D. Non-polar amino acids
6) Which of the following is a mobile electron carrier protein in the photosynthetic electron transport
A. Plastoquinone
B. Plastocyanin
C. Phycocyanin
D. D1 protein
7) Gene that code for functional [3-galactosidase is a part of
A. pUC18
B. pBR322
C. pSF2124
D. pBR327
8) Mutation of a gene that codes for a negative regulator of genes X, Y and Z leads to
A. Inhibition of X,Y and Z transcription
B. Constitutive expression of X, Y and Z genes
C. Rapid degradation of X,Y and Z mRNA
D. Disappearance of X, Y and Z proteins
9) Based on the time dependent changes in the fatty acid composition of a bacterial membrane as shown in the following figure, identify the abiotic stress treatment given to the bacterial culture
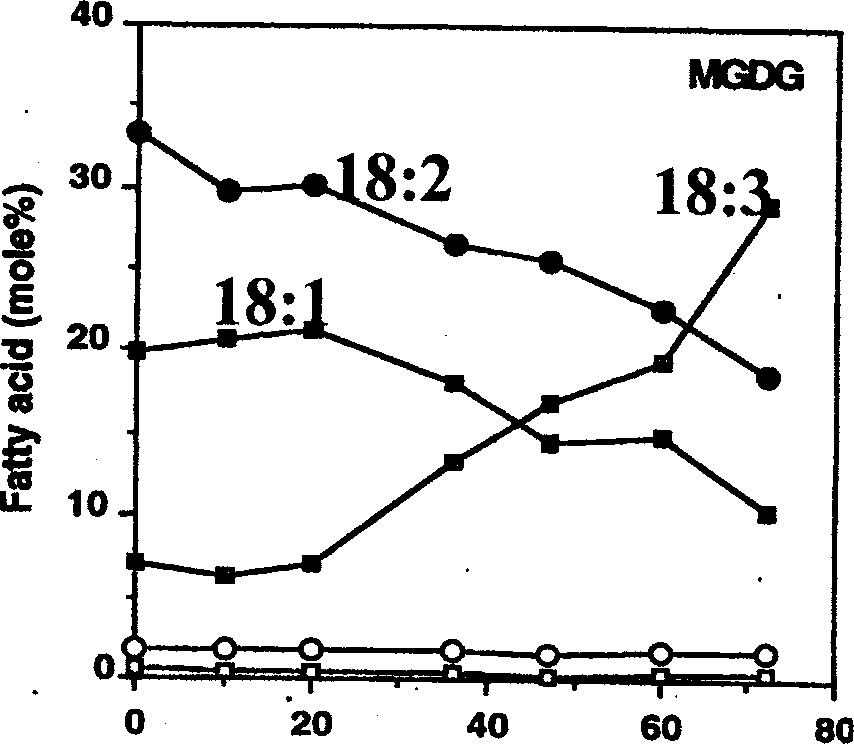 |
|
Time (hours) |
A. Heat stress
B. Salt stress
C. Cold stress
D. Oxidative stress
10) The activity of one of the following enzymes is not regulated by protein phosphorylation-dephosphorylation
A. Sucrose-phosphate synthase
B. Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
C. Dinitrogenase reductase .
D. Nitrate reductase
11) In competitive inhibition
A. Vmax unchanged and Km increases
B. Vmax decreases and Km unchanged
C. Both Vmax and Km decrease
D. Both Vmax and Km increase
12)cDNA from control and treated E.coli cultures were labeled with Cy3 and Cy5 respectively and using these labeled cDNAs a DNA microarray experiment was performed. Cy5 / Cy3 ratio of genes A and B were 10 and 0.1 respectively. It means
A. Gene A is repressed and gene B is upregulated due to treatment
B. mRNA levels of Gene A is relatively higher than Gene B in the control E.coli cells
C. Gene A is upregulated and gene B is down regulated due to treatment
D. mRNA levels of Gene B is relatively higher than Gene A in the control E.coli cells
13) An example of antagonistic role of auxins and gibberellins is
A. Sequential senescence
B. Fruit growth
C. Root initiation in stem cuttings
D. Stem elongation
14) Which one of the following E. coli sigma subunit is required for transcription of heat inducible genes
A. ct 70
B. a 32
C. a 54
D. a 28
15) The source of visible radiation in UV-Visible spectrophotometer is
A. Tungsten filament lamp
B. Hydrogen lamp
C. Deuterium lamp
D. Nemst glower
16) Based upon the features of F factor Shizuya et al in 1992 developed a high capacity insert vector, which is very much in use for preparing genomic library of higher organisms. What is the name of the vector?
A. BAC vector
B. PAC vector
C. YAC vector
D. Fosmid vector
17) When DNA solution is heated, the OD260
A. Remains unchanged
B. Increases
C. Decreases
D. First decreases and then increases
18) In isoelectricfocssing the following substances are used to give a pH gradient
A. Veronal
B. Tris
C. Polyamino polycarboxylic acids
D. Phosphate buffer
19) Give an example of cationic detergent
A. Sodium dodecyl sulphate
B. Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB)
C. P-mercaptoethanol
D. Urea
20) The fixative used for fats in electron microscopy is
A. Osmium tetroxide
B. Glutaraldehyde
C. Bromophenol blue
D. Glycerol
21) In an FT-IR spectrum, methyl group bending is seen at a frequency of (cm'1)
A. 1460
B. 1365
C. 2720
D. 2870
22) Physical relationship between two organisms with complementary physiological properties (each thrive for the other) are called:
A. Consortium
B. Parasitism
C. Amensalism
D. Symbiotic
23) Which of the following is incorrect about sex-linked dominance
A. No generations are skipped
B. Affected males must come from affected mothers
C. All the daughters, but none of the sons, of an affected father are affected
D. If both parents affected, all children will be affected
24) Tm of a DNA molecule is high, when ..
A. Its G+C content is low
B. Its A+T content is high
C. The salt concentration in the DNA solution is high
D. It is in circular form
25) Genomospecies are
A. Strains with approximately 97% or greater DNA-DNA relatedness at optimal conditions and with 5 C or less ATm
B. Strains with approximately 70% or greater DNA-DNA relatedness at optimal
conditions and with 10 C or less ATm
C. Strains with approximately 70% or greater DNA-DNA relatedness at optimal
conditions and with 5 C or less ATm
D. Strains with approximately 97% or greater DNA-DNA relatedness at optimal
conditions and with 10 C or less ATm
26) The pilus between the plant and Agrobacterial cells for T-DNA transfer is formed by
A. VirA-VirG complex
B. VirD2-VirF complex
C. VirEl-VirE2 complex
D. VirB-VirD4 complex
27) One of following is an antiviral drug
A. Acyclovir
B. Flucytosine
C. Chloroquine ,
D. Erythromyicin
28) Ribosomes stalled on secondary structured mRNA are rescued by
A. Translation release factor
B. EF-Tu
C. tmRNA
D. tRNA
29) Polynucleotide ligase joins two DNA molecules together by forming a covalent bond between
A. Two OH groups of adjacent strands
B. A 3'OH group and a 5' PO4 group
C. A3'PO4 group and a 5'OH group
D. Two carbon atoms of adjacent nucleotides on the same strand
30) The presence of horns in the Dorset breed of sheep is due to sex-influenced locus with horns dominant in males and recessive in females. Polled (hornless) males are mated to horned females. The fraction of F2 expected to be polled is
A. 1/2
B. 3/4
C. 1/4
D. 3/8
31) Alkalophiles are those species which grows best at pH range
A. 7-8
B. 8-9
C. 8.5-11.5
D. 7.5-8.5
32) The most commonly used trait for counter-selection when genes are mapped by interrupted conjugation is
A. Lactose fermentation
B. Antibiotic resistance
C. Phage resistance
D. Vitamin synthesis
33) Asporogenic species are those
A. Which contain the majority of sporulation specific genes but the cells do not sporulate
B. Which contain the majority of sporulation specific genes and thus the cells sporulate
C. Which do not contain majority of sporulation specific genes but still the cells sporulate
D. Which contain all the sporulation specific genes and sporulate
34) The most widely used detector in GC is
A. Photocells
B. Photomultiplier
C. Thermocouple
D. Flame ionization detector
35) For any color to be developed in the aleurone layer of com kernels, the dominant alleles at two loci plus the recessive condition at the third locus (A-R-ii) must be present. Any other genotypes will produce colorless aleufone. What phenotypic ratio of colored: colorless would be expected in the progeny from matings between parental plants of genotype AaRrli?
A. 8 colored : 56 colorless
B. 9 colored : 55 colorless
C. 58 colored: 6 colorless
D. 52 colored : 12 colorless
36) Given the DNA codon of antisense strand as 3'TAC 5,' the anticodon that pairs with the corresponding mRNA codon could be
A. 3'CAT 5'
B. 3' UAC 5'
C. 5'AUG 3'
D. 3' CAU 5'
37) Genome annotation means
A. Removal of vector sequence from the clone and also removal of redundant overlapping sequences from the assembled sequence to make a final draft of pure genome sequence
B. The confirmation of genome sequence by an alternative method using some reliable molecular biology tools
C. Fingerprinting of all clones which was used in sequencing with different restriction enzymes
D. Obtaining biological information such as gene, promoter and other important sequence elements from unprocessed sequenced data
A. Eukaryotic, unicellular absorptive heterotroph
B. Eukaryotic, multicellular absorptive heterotroph
C. Eukaryotic, multicellular photosynthetic autotroph
D. Prokaryotic, unicellular
39) Which of the following pairs is incorrectly matched?
A. Azadirachta indica - Meliaceae
B. Ricinus communis -Euphorbiaceae
C. Jatropha curcus- Fabaceae
D. Tamarindus indica - Caesalpiniaceae
40) The membrane-bound organelle which detoxifies molecules such as hydrogen peroxide in the cell is the
A. Glyoxysome
B. Peroxisome
C. Liposome
D. Chromosome
41) Mutations that destroy true homeotic genes often result in
A. Formation of unrecognizable masses
B. Deletion of half an organism
C. Conversion of non-homologous segments into homologous segments
D. Conversion of homologous segments into non-homologous segments
42) A plant hormone derived from cell wall fragments is called as
A. Oligosaccharins
B. Extensin
C. Polyamine
D. Pectin
43) Many of the genes in lambda phage are clustered based on functional similarity. Which of these clusters could most likely be deleted and replaced with foreign DNA, making the recombinant phage a useful cloning vector?
A. Nucleases to destroy host DNA
B. Head capsomeres
C. Phage-specific RNA polymerase
D. Establishment and maintenance of lysogeny
44) Fruit ripening of mango is enhanced by application of
A. Jasmonic acid
B. Ethylene
C. Salicyclic acid
D. Abscisicacid
45) An enzyme introducing a carbon-carbon double bond into a fatty acid in a specific position is known as
A. Hydrolase
B. Catalase
C. Desaturase
D. Polymerase
46) In which form water is available to the plants?
A. Hygroscopic water
B. Gravitational water
C. Capillary water
D. Mineral water
47) Technique to identify possible interaction between two proteins
A. Western blotting
B. Gel mobility shift assay
C. DNA foot printing
D. Yeast-two hybrid system
48) Process in which plants are exploited to prevent migration of environmental contaminants to sites where they may pose a danger to human health.
A. Phytostabilisation
B. Phytovolatilization
C. Phytomobilization
D. Phytoinnoculation
49) The plant hormone derived from degradation of carotenoid is
A. Auxin
B. Kinetin
C. Abscisic acid
D. Salicylic acid
 |
|
from the mating between hairless and normal dogs? A. 2 normal 4 hairless and 2 sparingly hairy |
B. 4 hairless and 4 normal
C. 6 normal and 2 hairless
D. 2 normal and 6 hairless
51) Exploitation of microorganisms within the root zone of plants to
remove
A. Rhizoremediation
B. Bioremediation
C. Phytoremediation
D. Phycoremediation
52) All of the following statements are correct regarding the Calvin cvcle of photosynthesis EXCEPT
A. Elucidating the biochemical reactions of this cycle earned Dr. Melvin Calvin a Nobel Prize
B. The energy source utilized is the ATP and NADPH obtained through the light reactio L. 1 hese reactions begin soon after sundown and end before sunrise
D. The 5-carbon sugar RuBP is constantly being regenerated
53) A natural or synthetic chemical that promotes the wetting, solubilization, and emulsification of various types of organic chemicals is known as *
A. Surfactant
B. Biocatalyst
C. Siderophore
D. Allelochemical
54) A pair of codominant sex-linked alleles in a mammal produce red pigment when
homozygous or hemizygous for A , colorless when homozygous or hemizygous for
A and pink when heterozygous. If a pink female is crossed to a white male we expect among the progeny 5
A. 50% females are white
B. 50% of all the progeny are pink
C. 50% of males are pink
D. 25% of all progeny are white
55) Protein fluorescence arises primarily from which residue?
A. Arginine
B. Tryptophan
C. Tyrosine
D. Cysteine
56) Grana refers to
A. Glycolysis of glucose
B. A constant in quantum equation
C. A product of photosynthesis
D. Stacks of thylakoids in plastids of higher plants
57) Functional elucidation of a gene by mutation and subsequent phenotype characterization is known as
A. Forward genetics
B. Reverse genetics
C. Behavioral genetics
D. Genetic polymorphism
58) Which of the following is not a macronutrient?
A. That which is radioactive and can be traced by a Geiger counter
B. That which is required in a very minute amount
C. That which was discovered in the protoplasm
D. That which draws other elements out of protoplasm
59) The number of genotypes that would be obtained by crossing AaBbCcDd X AaBbCcDd (assuming dominance) is
A. 9
B. 18
C. 27
D. 81
60) Round-up is
A. A chemical that inhibits the synthesis of aromatic amino acids and when sprayed on plants makes them smell better
B. A chemical that rounds up pollinating insects and thus increases the number of seeds formed on sprayed plants
C. A chemical that rounds up and kills plant-eating insects and thus improves plant growth
D. A chemical that kills plants by inhibiting the synthesis of aromatic amino acids
61) Series of experiments involving, 1) restriction digestion of the genomic DNA from a plant material 2) ligation of an adapter to the digested DNA fragments 3) preamplification with unlabelled adapter primers 4) selective amplification using labeled primers with 2-3 extended selective nucleotides 5) analysis of the final finger print and visualization by autoradiography, are collectively called as
A. RAPD (Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA)
B. RFLP (Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism)
C. AFLP (Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism)
D. SPAR (Single Primer Amplification Reaction)
62) LYS2 is a selectable marker for
A: Baeterionhase X
B. E.coli
C. Yeast
D. Protozoa
63) In an animal with X-0 method of sex determination, which of the following could be the normal number of chromosomes in its somatic cells
A. 26 in males
B. 17 in females
C. 33 in females
D. 13 in males
64) For separation of protein molecule Polyacrylamide gels are commonly used. During preparation of gels APS and TEMED is used. What are APS and TEMED?
A. Ammonium persulphate and trichloroethelenemonoethyldiamine
B. Ammonium persulphate and tetramethylethylenediamine
C. Amino acid with pure sulphur and tetramethylethylenediamine
D. Ammonium persulphate and TEMED is not an abbreviated term, rather it itself is a name of a compound.
65) A deep-rooted plant that obtains water from the deep water table is called as
A. Phreatophyte
B. Hydrophyte
C. Xerophytes
D. Psammophyte
66) An overlapping series of clones or sequence reads that correspond to a contiguous segment of the source genome is known as
A. Sequence coverage
B. Repeated sequence
C. Contig
D. Segmental duplication
67) During isolation of DNA from plant cell, a particular ratio of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol is used. How do they work?
A DVi Qrinl /A An nfi 4-_ .1 _ 1__1. -1.1. J 1 *1 T t
1 * vuui UWUC41U1V piuiui aiiu isomnyi mvunui ueinuure piasmia jjina
B. Phenol denature protein and isoamyl alcohol prevent loss of DNA and frothing
C. Phenol denature cell wall and isoamyl alcohol denature plasma membrane
D. This ratio helps in the final stage of DNA isolation for precipitation of DNA.
68) Which one of the compound does not exhibit UV absorption
A. n-hexane
B. Aniline
C. n-hexeadiene
D. Benzaldehyde
69) India participated in the International collaborative projects of highthrouput genome sequencing of
A. Long arm of chromosome 11 of rice and long arm of chromosome 11 of tomato
B. Long arm of chromosome 5 of rice and long arm of chromosome 5 of tomato
C. Short arm of chromosome 11 of rice and long arm of chromosome 11 of tomato
D. Long arm of chromosome 11 of rice and euchromatin regions of chromosome 5 of tomato
70) A plant population that reproduces by self pollination is an extreme example of
A. The bottleneck effect
B. The founder effect
C. Rapid gene flow
D. Assortative mating
71) Which of the following online software is used for gene prediction?
A. NCBI and EMBL
B. ClustalW and SMART
C. SWISS-PROT and Pfam
D. FGENESH and GENSCAN
72) PCR primers, Primer-F and Primer-R were supplied with the following specifications from Sigma Inc.,
Specifications Primer F Primer R
|ig/OD 30.3 35.6
Hg 262 337
(alforl00(iM 421 565
Each primer was first dissolved in 1000 |il of TE buffer and then lOx times diluted. 2\l\ of each primer was then added to a PCR reaction mix (Total reaction volume = 251). What is the final concentration of primer F and R in the PCR reaction mix?
A. 52.4 and 67.4 ng
TJ O d an A f\l 4 no
X-t f V I
C. 26.2 and 33.7 ng
D. 52.4 and 67.4 pg
73) A member of a group that does not contain all the descendents of a common ancestor is known as
A. Monophyletic
B. Polyphyletic
C. Paraphyletic
D. Symplastic
74) Which of the following antibiotics resistance gene is present in BAC vector?
A. Ampicillin
B. Kanamycin
C. Chloramphenicol
D. Tetracycline
75)DNA molecule in E.coli is heavy (fully labelled with N15) and is allowed to replicate in a medium containing N14, after one generation of replication the two daughter molecules
A. Will be similar in density, but will differ from that of parent DNA
B. Will differ in density from one another and also from that of the parent DNA
C. Will have the same density as that of the parent DNA
D. Will differ in density from one another but will resemble the parent molecules
*************
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
