University of Hyderabad (UoH) 2010 Entrance Exams Other Entrance Exams Ph.D Programme Entrance - Statistics - Question Paper
Ph.D Programme Entrance examination - Statistics
University of Hyderabad, Entrance Examination, 2010 Ph.D. (Statistics-OR)
Hall Ticket No.
|
|
21 |
a |
b |
c |
d |
|
22 |
a |
b |
c |
d |
|
23 |
a |
b |
c |
d |
|
24 |
a |
b |
c |
d |
|
25 |
a |
b |
c |
d |
PART A
Find the correct answer and mark it on the answer sheet on the top page.
A right answer gets 1 mark and a wrong answer gets -0.33 mark.
1. Xi,...,Xn are i.i.d random variables with absolutely continuous distribution
n
function F(x;9), then sjlogF{Xi\6) has
i=1
(a) Normal distribution.
(b) Beta distribution. '
(c) Gamma distribution.
(d) Weibull distribution.
2. Let x be an observation from Bernoulli random variable taking values 0 and 1 with probabilities 9 and 1 9 respectively. If 9 e [|, |], the ML estimate of 9 is
(b) x + 2.
(d) 23.
3. Let X\,..., Xn be a random sample from the Bernoulli distribution as described in Question 2, an unbiased estimator for 91 is
X-nX2 2(n1)
(a)
X-nX2
(b) n1
(d)
n1 *
4. Let T be Binomial random variable with parameters n and 9, E () for each r = 0,1,..., n are equal to
(a) n(n l)9r(I 9)n~r, r = 0, l,...,n.
(b) n9r(l 9)n~r, r = 0,1,
(c) (yr(l-9)n-r, r = 0,1,
(d) a(i -9)n~r, r = 0,1, ...,n.
5. Let X\,X2 be a random sample from the N(8,1) population, define <f>(X 1) E[X\Xi], then V(<f>(Xi) is
(a) I-
(b)
(c) I-
(d) 3
3
6. Let Xi,...,Xn be a random sample from a distribution whose parameter 9 is greater than 1 and pdf
(1 + 0)xe 0
0 < x < 1 otherwise
Then MLE of 6 is (a)
E-iVi
(c) 1 - "
sr=i i9xi
(d) n(log n"=i i)_1 + 1
7. Let X be a non-negative continuous random variable with finite mean /j. Let h(.) be the hazard rate of X, then
(a) E(h(X)) = i.
(b) E(h(X))=fi.
(c) E(h(X)) > J.
(d) E{h{X)) < J.
8. {N(t),t > 0} is Poisson process with parameter | and let Yk be time till the kth arrival, P(Yk > 2) is equal to
|
(a) | |
|
(b) | |
|
(c) |
e_1. |
|
(d) |
e-2. |
9. Consider the function f(xi,x2) = x\ + 2x\ 2x\x2 2x2 + 2x\, x\, x2 6 K, let H(Xi,X2) denotes its Hessian, which of the following is correct?
(a) H(xi,x2) positive definite and hence f(xi,x2) is convex.
(b) H(xi,x2) positive definite but nothing can be said about the convexity of the function.
(c) H{xi,x2) indefinite.
(d) H(xi,x2) negative definite.
10. X ~ Poisson(2) , Y ~ Poisson(3) and are independent. If X + Y = 10, the variance of X is
(a) f.
(b) f-
(c)
(d) I-
11. X and Y are two random variables where P(X > Y) = 1, then which of the following is correct?
(a) E(X) > E(Y).
(b) E(X) > E(Y). .
(c) E(X) < E(Y).
(d) Nothing definite can be said.
12. For a random variable X with parameter 8, if the functions L(.) and U(.) satisfy Pg (L(X) < 9) = 1 a\ and Pg {L(X) < 9 < U(X)) = 1 cti a2 and L(x) < U{x) for all x then Pg (U(X) >9) is
(a) 1 a2.
(b) a2.
(c)
(d)
13. In a randomized block design of 4 treatments and 3 blocks the degrees of freedom of the residual sum of squares( Error sum of squares) is
|
(a) |
3. |
|
(b) |
4. |
|
(c) |
5. |
|
(d) |
6. |
14. A population of 30 units is divided into three strata with 6, 12,12 units each. The number of different ways in which a stratified random sample of 5 units can be drawn in accordance to proportional allocation is
(a) 63 x ll2.
(b) 5 x 63 x 11.
(c) 20 x 122.
(d) 25 x 11 x 12.
15. For any Gauss Markov model (Ynxi, X/?pxl, cr2I), with rank of X equal to p 1 and n > p, which of the following is correct?
(a) Every component of (3pxi is certainly estimable.
(b) Certainly no component of /?pxi is estimable.
(c) Every component of /?pxi may be non estimable.
(d) Exactly one component of (3pxi is estimable.
16. In a hypothesis testing problem, the pvalue was 0.06, which of the following is a correct decision?
(a) The null hypothesis should be rejected at 0.05 level of significance.
(b) The null hypothesis should be accepted at 0.05 level of significance.
(c) The null hypothesis should be accepted at 0.07 level of significance.
(d) None of the above.
17. Customers arrive in a super market in accordance with a homogeneous Poisson process, if the expected number of arrivals in one hour is 20, the expected length of time between the arrival times of the 6th and 7th customer is
(a) 3 minutes.
(b) 10 minutes.
(c) 5 minutes.
(d) 30 minutes.
18. X ~ N20 (0, S) where X* = (Xt,X2,...,X2o), the diagonal elements of are
20 20
1 and the off diagonal elements are |, then Y\ = Xt and Y2 are
i=1 i=1
independently distributed if 20
(a) ai = -20. i=1
20
(b) ai = 0. i=1
20
(c) y di i.
i=1 .
(d) such a Y2 cannot be determined.
19. X is a random variable with probability distribution
P(X = +1) = P(X = -l) = \
its characteristic function is
(a) .
(b) eu.
(c) sint.
(d) cost.
20. Which of the following is always correct for any 5x5 real, skew-symmetric matrix A? -
(a) det A > 0.
(b) det A > 0.
(c) A is singular.
(d) A is definite.
21. Xi ~ C/(1, +l),i = 1,2,... and are independent. LirrinP t Xi>oj
(a) is 0.
(b) is
(c) is 1.
(d) does not exist.
22. Xi, i 1,2,3,... are independently distributed with the following distributions
P(Xi = -1) = P(Xi = 0) = P(Xi = +1) = i for i = 1, 3, 5,...
P(Xi = -1) = P(Xi = +1) = \ for i = 2,4,6,...
n
Let rn = J2xl- Then i=1
(a) Y > 1 almost surely.
(b) Yn > 0 almost surely.
(c) Yn > 0 in probability but not almost surely.
(d) Yn 1 in probability but not almost surely.
23. A fair die is rolled and then a fair coin is tossed as many times as the number that shows up on the die, the expected number of heads is
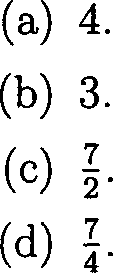
24. The transition probability matrix of a Markov chain with state space S =
L>-sr
{0,1,2} is
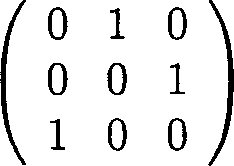
Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) This Markov chain is irreducible.
(b) This Markov chain has a stationary distribution.
(c) This Markov chain is recurrent.
(d) This Markov chain is aperiodic.
25. The multiple correlation coefficient between Y and Xlt X2, is 0.98, and between Y and Xi,X% is 0.91. The partial correlation coefficient between Y and X3 after removing the effects of X\ and X2 is in the interval
(a) (0.3,0.4],
(b) (0.5,0.7].
(c) (0.7,0.8],
(d) (0.8,0.9].
PART B
There are 15 questions in this part. Answer as many as you can.
The maximum you can score is 50. Marks are indicated against each question.
The answers should be written in the separate answer script provided to you.
1. An urn contains 10 balls of which X are red and the rest are white, where X takes values 0,1,2,3 with probabilities \ each. 3 balls were drawn without replacement of which 2 were white and 1 was red, determine the probabilities that 0,1,2,3 balls in the urn are red. [5 marks]
2. The conditional density function of X given Y = y is
(1 4- y)xv 0 < x < 1
f(x\y) i q otherwise
and the marginal distribution of Y is U(1,1), determine E(X). [4 marks]
3. Candidates are allowed to appear for the civil service exams at most 4 times with the condition that he cannot write the exam if he has cleared in any of the earlier attempts. . For Ashok the probabilities of the clearing the exam in the first attempt is 0.3, in the second it is 0.5, in the third it is 0.6 and in the fourth it is 0.8.
(a) Determine the probability of failing in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd and the 4th attempts.
(b) Expected number of attempts. [6 marks]
4. Let X and Y be independent standard normal random variables and let R and 0 be the polar coordinates of the vector (X,Y). Show R2 and 0 are independent with R2 being exponential with mean 2 and 0 being uniformly distributed over (0,27r). [5 marks]
5. A random variable Y is said to have Weibull distribution with parameter
a, (3 > 0 if its distribution function is given by
y < 0
Define X ()3, what is the distribution of X? [4 marks]
6. Suppose that X\,..., Xn is a random sample from a distribution with pdf
ft . n\ _ / xe 6x x > 0 \ 0 otherwise
where 9 > 0. Find the UMVUE of 9. using Rao-Blackwell-Lehmann-Scheffe theorem. [4 marks]
7. {JsTn}i is a sequence of independent random variable with following distribution
P(Xn = -1) = P(Xn = +1) = 1
n2 + 1
and
1
n
P(Xn = 0)
n2 + 1
Show that p( < z'j $(2) as n * 00, where S. = X\ + ... + Xn and cr2 V{X\ + ... + Xn). [6 marks]
8. Let Xi, ...,Xn be a random sample from the N(0,6), 9 > 0 population. Give an example of a Pivotal Quantity and use it to obtain a (1 a)100% confidence interval of 9. [5 marks]
9. Show that the Fisher information contained in a sample of size 4 from a Cauchy distribution with location parameter 9 is 2. [3 marks]
10. X = (Xi1X2,X3,Xi) and X ~ N(0, |(/ + J)), where J is a 4 x 4 matrix in which every element is 1.
(a) Compute E ((J) |() - (2)) and D (()| () = ("2)) [5 marks]
(b) Show that \{X2 + Xi - XxX2) ~ x2(l) [4 marks]
11. A population consists of N units Ui,...,Un- X and Y are two variables of interest. Obtain an unbiased estimator for population covariance
N
i1
based on a srswor of size n. (Xi, Yi) are values of (X, Y) respectively for Ui, z = 1,2,..., [5 marks]
12. The starting and current simplex tableaus of a given linear programming prob-lem( minimization problem) are given below. Find the values of unknowns
a,b,..., 1 [6 marks]
|
Starting Tableaux | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
Current Tableaux | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
13. Consider the problem
n
minimize subject to
3 = 1
n
IJX3 = 1 j=l
(a) What are the KKT conditions for the problem?
(b) Using the KKT conditions, find an optimal solution to the problem.
[5 marks]
14. Let Xn be the size of a group that enters a restaurant at time n, n = 1,2,..., further X'ns are i.i.d random variables taking values 1,2,... ,d with probabilities 2 each. Now define a random variable Yn to be the size of the largest group that entered the restaurant till time n.
(a) Show that the {Yn,n = 1,2,...} is a Markov chain and write down its transition probability matrix.
(b) Classify the states into communicating classes and identify the recurrent and transient classes.
(c) For each transient state j and for each recurrent state k compute fjk-
[10 marks]
15. A sample of n units is selected from a population of N units without replacement in the following way. The first selection is made with unequal probabilities while the remaining n 1 units are selected with equal probabilities. Let the first draw selection probabilities be Pi, P2,..., Pn for the population units U\, U2, , Un respectively. Define
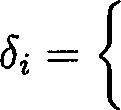
1 if Ui is included in the sample
0 otherwise
Find Ilj( Probability that Ut is in the sample) and Ily (Probability that Ui and Uj are in the sample) for each i, j = 1,2,..., iV. [6 marks]
9
Part A carries 25 marks. Each correct answer carries 1 mark and each wrong answer carries 0.33 mark. If you want to change any answer, cross out the old one and circle the new one. Over written answers will be ignored.
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
