University of Hyderabad (UoH) 2011 M.Sc Mathematics Entrance for - Question Paper
V-o 7
Entrance Examination : M.Sc. Mathematics, 2011
Hall Ticket Number
Time : 2 hours Part A : 25 marks
Max. Marks. 75 Part. B : 50 marks
Instructions
1. Write your Booklet Code and Hall Ticket Number on the OMR Answer Sheet given to you. Also write the Hall Ticket Number in the space provided above.
2. There is negative marking. In pai t A a right answer gets 1 mark and a wrong answer gets - 0.33 mark. In part B a right answer gets 2 marks and a wrong answer gets 0.66 mark.
3. Answers are to be marked on the OMR answer sheet following the instructions provided there upon.
4. Hand over the question paper booklet and the OMR answer sheet at. the end of the examination.
5. No additional sheets will be provided. Rough work can be done in the question paper itself/space provided at the end of the booklet.
6. Calculators are not allowed.
7. There are a total of 50 questions in Part, A and Part B together.
8. The appropriate answer should be coloured in either a blue or black ball point or sketch pen. DO NOT USE A PENCIL.
1. Statement: All mathematicians are intellectuals. Conclusions:
(1) Raju is not a mathematician so he is not an intellectual
(2) All intellectuals are mathematicians
A. Only (1) is correct
B. Only (2) is correct
C. Both (1) and (2) are correct
D. Neither (1) nor (2) is correct
2. For any natural number r>, the sum, J -i-2 ( 0 J +3 ( 0 J H-----hn
A. n2"
B. n2n_1
C. n2"+1
D. none of the above
3. Let / : R {0} > R be defined as f(x) = |x| then
A. / is continuous and differentiable
B. / is continuous but not differentiable
C. / differentiable but discontinuous
D. / is discontinuous
4. I.t (an),(b) be two convergent sequences converging to l,m respec-
.. i jr , c I -n + m if n is odd, .
tively. If we define c < . , , then
1 * + / if n is even,
A. (r-n) Ls a Cauchy sequence which is not convergent
B. (Cn) is bounded but not convergent
C. (cn) is a convergent sequence converging to I + m
D. (Cn) has only two convergent subsequences
5. Let G be a group and a. b e G. If a17 = 617 and a = 630 then
A. a = 6
B. ab = 6a and o(a) / o(b)
C. a = b~l and o(a) o(b)
D. o(a) = o(b) and a = h
6. Let /, <t> be vector valued and scalar valued functions on R3 respectively, then
A. curl (grad 4>) = 0
B. curl(curl /) = 0
C. grad(div /) = 0
D. div(grad (j>) 0
7. The number of points in the plane equidist ant from P = ( 1,0), Q = (1,0), (0,1) is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. infinite
8. The number of subgroups of Zm is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
9. The number of nontrivial homomorphisms from the cyclic, group to a group of order 7 is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 6
10. Let X = {0,1}, Y {2,7}, Z = {0,2,4}. Which of them admit group structure
A. only X
B. only X, Z
C. all of them
D. none of them
11. Two coins whose probabilities of heads showing up arc p\, p? are tossed, the probability that, at least one tail shows up is
A. 2 - pi - p2
B. pip?
C. pi(l -p2)
D. 1 -p\p2
12. 2 ones. 2 twos. 1 three and 1 five are to bo arranged to get a 6 digit number. The number of different numbers that can be obtained this way is
A. 6 !
13. Let an > 0, Vn N then consider the statements:
51) If 2 an converges then Yi an also converges iS'2) If 52 an converges then <in also converges
A. Both Si and S2 are t rue
B. Si is true but S2 is false
C. S2 is true but S\ is false
D. Both Si and S2 are false
14. Let x R, [x] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to x, then consider the statements:
52) !*2| = M2
A. Both S\ and S2 are true
B. Si is true but S2 is false
C. S2 is true but Si is false
D. Both S\ and S2 are false
15. Let iGR - {0} then the correct statement is:
A. If x2 G Q, then x3 6 Q
B. If x3 Q, then x2 e Q
C. If x2 Q and x4 G Q then x3 Q
D. If x2 Q and x6 Q then x Q
16. The number of solutions of X* = 1 (mod 163) in is
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
17. Let / : E -> R be a polynomial such that /(0) > 0 and /(/(x)) = 4x + 1 Vx R, then /(0) is
A. 1/4
B. 1/3
C. 1/2
D. 1
18. Let J : R -> R be a polynomial and let. (xn) be a sequence of real numbers converging to 2. Then the sequence (/(x)) converges to
A. /(2)
b. m
D. /(16)
19. Let V be the vector space of continuous functions on [-1,1] over R. Let U1,U2,U3,W4 V defined as i(x) = x, Ua(x) =. |x|, 113(1) = x2, 1x4(3:) = x|x| then
A. {u!,u2} is linearly dependent.
B. {iti, U3, 1/4} is linearly dependent
C. {111,1x2,1x4} is linearly dependent
D. none of the above
|
1 |
2 |
1 |
-1 |
|
-1 |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
1 |
5 |
4 |
-1 |
|
-1 |
4 |
5 |
1 |
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
21. If p(x) is a polynomial of degree 102011 then lim p{x)c.
A. is 0
B. is 1
C. is oo
D. docs not exist, p = J y/l x dx, q = / vl x2 dx and r
= f y/l x2 dx and r = f Vl + x Jo J o
+ x dx.
22. Let-Then
A. p < q < r < 1
B. p<g<l<r
C. q < p < 1 < r
D. 1 < p < q < r
23. Let A be a 4 x 4 real matrix. Which of the following 4 conditions is not equivalent to the other 3?
A. The matrix .4 is invertible.
B. The system of equations At 0 has only trivial solution.
C. Any two distinct rows u and v of A are linearly independent.
D. The system of equat ions Ax = b has a unique solution V6 R4.
z\2 is
24. The set of complex numbers satisfying the equation z =|
A. an empty set
B. a finite set.
C. an infinite set.
D. a line.
25. Let A be a subset of real numbers containing all the rational numbers. Which of the following statement s is true?
A. A is countable.
B. If A is uncountable, then A = R.
C. If A is open, then A = R.
D. None of the above st atement is true.
Part B
26. Let X be the set of all nonempty finite subsets of N. Which one of the following is not an equivalence relation on X:
A. A ~ B if and only if min A = min B
B. A~ B if and only if 4, B have same number of elements
C. A ~ B if and only if A = B
D. A ~ B if and only if A n B 0
27. Which of the following statements is not true:
A. Every bounded sequence ol real numbers has a convergent subsequence
B. If subsequences (xtn) and (3n) of a sequence (xn) converges respectively to x and y then r = y
C. A monotone sequence of xeal numbers is convergent if and only if it is bounded
D. A sequence (xn) of real numbers is convergent if and only if the sequence (|in|) is convergent
28. The absolute maximum value of J(x) = ,1 r, on R is
1 + |x| 1 + \x - 1|
attained at
A. x = 0 only
B. x = 1 only
C. x = 0 and x = 1 only
D. no point of R
29. Which of the following functions is uniformly continuous
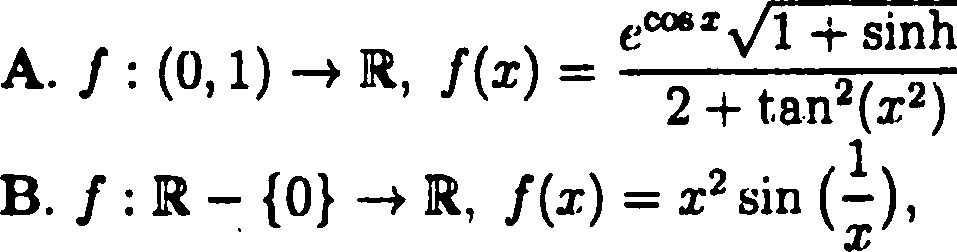
C. / : R {0} > R, f(x) = cos ()
x
D. none of the above
30. If / : R > R then pick up a true statement from the following:
A. If / is continuous then |/| is continuous
B. If / is differentiable then |/| is differentiable
C. If / is integrable then f{\/\x\) is integrable
D. If / is discontinuous then |/| is discontinuous
31. Let / = (l,h(x,y, z),fz(x,y,z)) be solenoidal where /2,/s are scalar valued functions. Let S be the unit sphere in Ra and n be unit outward
normal. Then J xf.hdS =
A. 0
B. 7T
C. 4tt/3
D. 4rr
32. Let M3(R) be the space of all 3 x 3 real matrices. Let V C Ms(R) be the space of symmetric matrices with trace 0. Then dimension of the * * A/3(R) .
quotient space
is
A. 6
B. 5
C. 4
D. 3
33. Let V be the vector space of continuous functions on [-1,1] over R. Which one of the following is a subspace of V
A. {/ 6 V/f vanishes at some point in [-1,1]}
b. </ v/m=o}
C. {/ e v/f{x) f o1
{/e VV/(x)0V*[-l,l]}
34. Let Afa(R) be the space of all 2 x 2 real matrices, / be the identity matrix in Ma(R). Pick up the correct statement
A. 3 two different matrices A, B A/2(K) such that -t- = /
B. 3 two different matrices A, B MiiR) such that /45 BA = I
C. 3 a singular matrix A 6 .(R) such that A2 + / = 0
D. 3A 6 A/2(R) such that A3 0 but. A4 = 0
35. Let G = {1, 1, *, i} be the group under multiplicat ion. Which of the following statements is true
A. identity map is the only homomorphism from G to G
B. the map z - z is a homomorphism from G to G
C. the map z -* z2 is not a homomorphism from G to G
D. none of the above
36. Each element of a 2 x 2 matrix A is selected randomly from the set {-1,1} with equa] probability. The probability that A is singular is
A. 1/8
B. 2/8
C. 3/8
D. 4/8
d*y
37. General solution of + y = 0 is
A. Cie1 - Ci~x + C3cosj: - C4 sinx
B. C\ex + C2xe~x + C3 cosx + C 4 sin x
C. Cie* Cze'* + C3 cosh x - sinh x
D. Cixe* - C2e~x + C3 cos x - C\ sin x
38. Let An and Z?n, n N be non empty subsets of R such that Ai D A-i D
A3 2 ... and Iii C B2 C B3 C____ Let the cardinality of An be cin
and the cardinality of Bn be bn. Then the cardinality of
OO
A. Pi An is lim On
1 n->oo
n=l
OO
B. P| An is min On
n=l
oo
C. I I Bn is lim 6
n-*oo
n= 1 oo
D. IjB r is max b
n= 1
39. The area bounded on the right by x + y = 2, on the left by y = x2 and below by x-axis is
A. 23/6
B. 5/6
C. 17/20
D. 0
40. The distance of the point (3, 4,5) from the plane 2x + Ay + Gz + 6 = 0 measured along a line with direction ratios 2,1,3 is
A. y/14
B. n/24
C. v/iio
D. y/94
1
0
is similar to a diagonal
1
41. Consider the statements:
5i) In the set of 2 x 2 real matrices
matrix
S2) If M is a 2 x 2 real matrix and Mn = I for some n N then M I
A. Both S\ and S2 are true
B. Si is true but is false
C. S2 is true but Si is false
D. Both i and S% arc false
42. Let f(x) = (x 2)(x 4)(x 6) + 2 then / has
A. all real roots are between 0 and 6
B. a real root between 0 and 1
C. a real root between 6 and 7
D. exactly two roots between 0 and 6
43. For a fixed y [0, 1], the value of / [;) y]dx is (where for a real
number t, [] is the greatest integer less than or equal to t)
|
A. 0 |
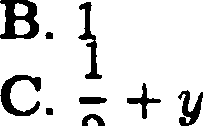 |
|
' 2 D. y |
44. Let V be the vector space of all 2 x 3 real matrices and W be vector space of all 2 x 2 real matrices. Then
A. there is a one-one linear transformation from V > W.
B. kernel of any linear transformation from V > W is nontrivial.
C. there is an onto linear transformation from W V.
D. there is an isomorphism from V W.
45. Let A be a 2 x 2 real matrix. Which of the following statements is t rue?
A. All the entries of A2 are non-negative.
B. The determinant of A2 is non-negative.
C. the trace of A2 is non-negative.
D. all the eigenvalues of A2 are non-negative.
46. Let /, g : R R be two differentiable functions. Suppose that f{x) > g'(x) > 0 for x > 0. Then
A. f(x) > g(x) for all x > 0
B. f(x) < g(x) for all x > 0
C. f (x) /(0) > g(x) <7(0) for all x > 0
D. f(x) f(0) > g(x) - <7(0) for all x.
47. Let / : R -> R be given by f(x) = |x| sin(x). Then
A. / is differentiable at 0 and /'(0) = 0.
B. / is differentiable at 0 and /'(0) = 1.
C. / is continuous at 0, but not differentiable at 0.
D. / is not continuous at 0, but differentiable at 0.
48. Consider the group Zp x Zp under addition. The number of cyclic subgroups of order p is
A. 1
B. p 1
C. p +1
D. p2 - 1
49. Let R be a ring with unity. Then
A. The set of r11 nonzero elements in R forms a group under multiplication
B. The set of all nonzero invert ible elements in R forms a group under multiplication
C. The set of all non zero divisors in R forms a group under multiplication
D. none of the above
50. Let At B C R and C {a + 6/a G A, b G B}. Then the false statement in the following is:
A. If A, B arc bounded sets, then C is a bounded set
B. If C is a bounded set. then A, B arc bounded sots
C. If R A, R B are bounded sets, then R C is a bounded set
D. If R C is a bounded set, then R A, R B arc bounded sets
12
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
