Cochin University of Science and Techology (CUST) 2005-6th Sem B.Tech Mechanical Engineering ,, Dynamics Of Machinery - Question Paper
BTS(C) -VI - (S) - 05 - 072 (H)
B. Tech. Degree VI Semester (Supplementary) Examination, November 2005
ME 601 DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY
( 2002 Admissions )
Time: 3 Hours
I a)
b)

o*C
C a
II
a)
b)
(15)
III
a)
b)
(5)
(15)
(5)
IV
a)
b)
V
b)

Explain the terms shaking forces and shaking moments.
A horizontal steam engine running at 240 rpm has a bore of 20 cm and stroke of 36 cm. The piston rod is 2 cm in diameter and connecting rod length is 90 m. The mass of the reciprocating parts is 7 kg. and the frictional resistance is equivalent to a force of 500N. Determine the following when the crank is at 120 from the inner dead centre, the mean pressure being 50x10 N/m2 on the cover side and 1 x 102 on crank si i) thrust on the connecting rod ii) thrust on the cylinder walls iii) Load on the bearings iv) turning moment on the crank shaft
Define the terms : i) Coefficient of fluctuation of energy
ii) Coefficient of fluctuation of speed Turning moment curve for one revolution of a multicylinder engine above and below line of mean resisting torque are given by -0.32, +4.06, -2.71, +3.29, -3.16, +2.32,
-3.74, +2.71, and -2.45 sq.cm. The vertical and horizontal scales are 1 cm=60000 Kg.cm and 1cm = 24 respectively. The fluctuation of speed is limited to 1.5% of mean speed which 250 rpm. The hoop stress in rim material is limited to 56Kg/cm2. Neglecting the effect of boss and arms, determine suitable diameter and cross section of flywheel rim. Density of rim material is 0.0072Kg/cm\ Assume width of rim equal to four times its thickness.
OR
Obtain the expression for the gyroscopic couple.
A racing car weighs 20KN. It has a wheel base of 2m, track width 1 m and height of c.g 0.3m above the ground level and lies midway between the front and rear axle.
The engine flywheel rotates at 3000 rpm clockwise when viewed from the front.
The moment of inertia of the flywheel is 4 kg.m2. and moment of inertia of each wheel is 3Kg.m2. Find the reactions between the wheels and the ground when the car takes a curve of 15m radius towards right at 30km/hr, taking into consideration the gyroscopic and centrifugal effects. Each wheel radius is 0.4m.
Explain the term static balancing and dynamic balancing.
Three masses which rotate in planes 1,2 and 3 are to be balanced by the
addition of two rotating masses in planes A and B at a radius of 250mm each. Given that m\ = 4kg, m2 = 6.4kg and m} = 2kg. The location of c.g of masses 1,1112 and m3 are 150mm, 100mm and 225 mm respectively, from the rotor axis. Angular location of masses mi, m2,m3 are 30, 300 and 135 respectively. If the planes of mi, m2,m3 and B from the plane of A are 75mm, 200mm, 500mm, 625mm respectively. Determine the balancing masses at A & B and their angular positions for complete balance. (15)
Explain the principle of superposition.
The figure shows a four bar linkage with external forces applied at points B and C. Draw free body diagrams of each link and show all the forces acting on each. Find the torque that must be applied to link 2 to maintain equilibrium.
s 75T wio AC * 300 row*
O n t AOO rnir>
A 6-= 300 mm 150 w>'
Maximum Marks: 100
(15)
(5)
OR
(5)
(15)
(5)
Explain the balancing of two cylinder inline engine. (5)
A four crank engine has the two outer cranks set at 120 to each other, and their reciprocating masses are each 400kg. The distance between the planes of rotation of adjacent cranks are 45,75 and 60 cm. if the engine is to be in complete primary balance, find the reciprocating mass and the relative angular position for each of the inner cranks.
VI a) b)
If the length of each crank be 30cm, the length of each connecting rod is 10cm, and the speed of rotation 240 rpm, what is the maximum secondary unbalanced force? (15)
VII a) b)
VIII a) b)
What is meant by logarithmic decrement? Obtain the expression for the logarithmic decrement in terms of the damping factor. , (5)
A racing car is modeled as a single degree of freedom damped system vibrating in the vertical direction. The elevation of the road is assumed to vary sinusoidally. The distance from peak to trough is 0.2m and the distance between the peaks is 70m.
The natural frequency of the system is 2Hz and the damping ratio is 0.15. Determine the amplitude of vibration of the car at a speed of 120 km/hr. Also determine the most unfavourable speed of the car (the speed at which the amplitude reaches the maximum). (15)
OR
Explain the working of a seismometer. (5)
An electric motor of mass 68 kg is mounted on an isolator block of mass 1200 kg and the natural frequency of the total assembly is 160 cycles/minute with a damping factor =0.1 of there is an unbalance in the motor the results in a harmonic force of F=100 Sin 31.4t, determine the amplitude of vibration of the block and the force transmitted to the floor.
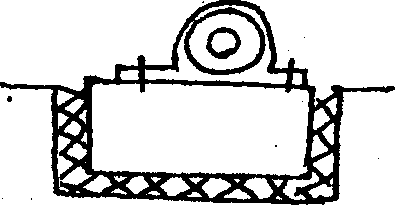
(15)
A machine having a mass of m=1500 kg and a mass moment of inertia of J0 - 400kgm2 is supported on elastic supports as shown. If the stiffnesses of the supports are KOOON/mm, and K2=2000 N/mm determine the natural frequencies of vibration of the machine tool and the mode shaper.
IX
(20)
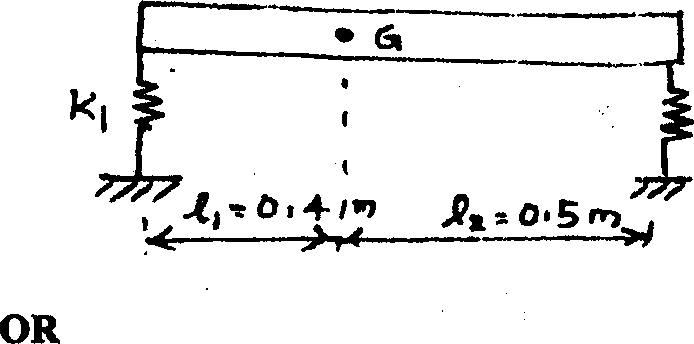
The arrangement of the compressor -turbine-generator in a thermal power plant is shown. Find the natural frequencies and mode shapes of the system.
6MNm/rad 3MN m/rad 18kgm2 14kgm2 9kgm2
Stiffness
K,
K2
Ic
I,
uwiiw
Turlin
***
(20)
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
