Andhra University 2007 B.E - Question Paper
CIVIL PAPERS
I Year B.E/B.Tech

(Effective from 2GG5 admitted batch)
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION ANDHRA UNIVERSITY VISAKHAPATNAM - 530 003
Year : 2GG7
Printed at : SRIRAM PRINTERS, Visakhapatnam - 530 027.
|
Paper No. |
Subject |
Page No. |
|
101 |
Mathematics - I |
04 |
|
102 |
Mathematics-II |
07 |
|
103 |
Physics |
10 |
|
104 |
Chemistry |
12 |
|
105 |
Computer Programming & Numerical Techniques |
14 |
|
106 |
Engineering Mechanics |
17 |
|
107 |
Strength ofMaterials & Theory of Structures-I |
21 |
I Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examinations MATHEMATICS - I
(Common to All Branches)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry marks
b) Obtain Taylors expansion of Tan 1(y/ x) about (1,1) upto and including the second degree terms.
a six / a
3. a) Evaluate J J (X + y2) dx dy by changing the order of
0 x/ a
integration.
b) Determine the M.I. about the X-axis of the area of a triangle with the vertices A(1,1), B(2,1) and C(3,3).
4. a) Find the equations to the line that intersects the lines
x + y+ z = 1, 2x- y- z = 2, x- y- z = 3,
2 x + 4y- z = 4 and passes through the point (1,1,1)
b) Find the equation of the sphere having its center on the plane
4x - 5y - z = 3 and passing through the circle
x2 + y2 + z2 -2x-3y + 4z+ 8 = 0, x- 2y+ z = 8
5. a) Show that if a series un is convergent than
Lt un = 0
n
b) Test the convergence of the following series
V2-V1 V3-V2 V4->/3
- +-+-+..........
1 2 3
6. a) Show that the harmonic series of order p,
n
converges for p > 1 and diverges for 0 < p < 1.
sin 2x sin 3x sin 4x sin x--j=I--j=---j=+............
2V2 3V3 W4
7. Express f(x) = | x|,-p<x<p as a Fourier series. Hence
p2 1 1 obtain = 1 + 32 + 52+.................
8. Obtain the half range sine and cosine series for the function f(x) = (x +1)2,0 < x< 1.
I Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examinations MATHEMATICS - II
(Common to All Branches)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8
1. a) State Culey Hamilton theorem
1 2 3 4
b) Product of the eigen values of A
is ?
c) Solve dy + 2x2y = 0
dx
d) Find the complementary function of(D2 + 3d + 4) Y = 0
e) Find the laplace transform of t Sin t.
5 6 7 8
6 7 8 9
2. a) Find the rank of
11 12 13 14 16 17 18 19
b) For what values of k the equations
x+ y+ z = 1, 2x+ y+ 4z = k,4x+ y+10z = k2 have a solution and solve them completely in each case
1 1 3
1 3 -3 -2 -4 -4
b) Reduce the quadratic form 2xy + 2yz + 2 zxinto canonical form.
4. a) Using Gauss elimination method.
Solve 2x1 + 4x2 + x3 = 3, 3x1 + 2x2 - 2x3 = -2 x1 - x2 + x3 = 6
b) Using iteration method find the largest eigen value and eigen
vector of the matrix A
1 2
3 4
5. a) Solve (2x+ y-3) dx = (x + 2y-3)dy
b) Solve (x3dx- y3 dy) = 3xy (ydx- xdy)
c) Solve x p2 + p - y = 0
6. a)
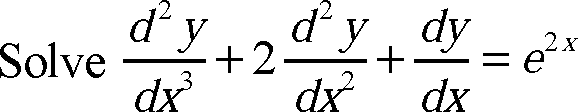
+ JL = e2 x + sin 2 x
dx dy
b) Solve = 5 x + y = y- 4 x
dt dt
i) log
ii)
v 5 y
7. a) Find the Laplace transform of f(t) given
i) f(t) = t e sin t
ii) f(t) = sin t 0< t<p
= 0 t >p b) Find the inverse transform of
'\ + sA
8. a) Using convolution theorem find the inverse transform of
1
(5 - 1)(5 - 9 )2
b) Using transform method solve y + 4 y + 3 y + e
PHYSICS
(Common to All Branches)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry equal marks
6. a) What is Piezo electric effect? Describe how this effect can
be used to produce ultrasonic waves.
b) Mention applications of ultrasonic waves.
7. a) Derive Schrodinger time independent wave equation and
obtain energy Eigen value and Eigen functions of a particle moving in one dimensional box using Schrodinger wave equation.
b) State and explain Heisenbergs uncertainty principle.
8. a) Distinguish between metals, semiconductors and insulators
based on band theory of solids.
b) Define Super conductivity, Meisner effect and write applications of Super conductors.
I Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examinations CHEMISTRY
(Common to Mechanical, Civil, EEE, ECE Branches)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8
1. a. Explain hardness of water?
b. What are galvanic cells? Give example?
c) Define HCV and LCV?
d) What are polymers? Classify
e) What are semi conductors?
2. a) What are boiler troubles? Explain. b) Explain Green house effect
3. Write short notes on
a) Break point chlorination
b) Desalination
c) BOD and COD
4. a) What are defects in solids? Explain b) Explain about organic semiconductors
5. a) What are primary and secondary cells?
b) Write the working of lead acid battery?
6. a) Differentiate between termo plastics and thermosetting
plastics.
b) Write the synthesis, properties and uses of polyethylene and PVC
7. a) How does the percentage of C,H,N,O,S calculated in a fuel? b) What is knocking? Explain.
8. Write short note on
a) setting and hardening of cement.
b) Lubricants
c) Paints and Varnishes.
COMPUTER PROGRAMMING AND NUMERICAL TECHNIQUES
(Common to All Branches)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry marks
b) Calculate the values of /(x + y) with x = 0.4845
and y = 0.4800, using normalized floating point airthematic.
Compare the value with (x- y). Determine relative error of the former.
5. a) Find the root of the following equations correct upto 2 deci
mal places using false position method.
b) Find the root of the following equation correct upto 2 decimal places using Newton - Raphson method.
sin x = 1 - x
6. a) From the following table find the value of f (x) when
x = 0.21.
| ||||||||||||||
|
b) From the following table find the value of f (x)when x = 4. |
|
x |
-1 |
0 |
3 |
6 |
7 |
|
f (x) |
3 |
-6 |
39 |
822 |
1611 |
7. a) Calculate the value of1 = J sin x dx by Simpson rule with
0
8 intervals.
b) Solve the following system by Gauss - Elimination method
5 x - 2 y + z = 4
7 x + y - 5 z = 8 3x + 7 y + 4 z = 10
8. a) Use Eulers method to find y (0.1)y = x + y withy (0 ) = 0
with h = 0.01.
b) Use Runge - Kutta method to find
y (0.2) in steps of 0.1 = x + y with y(0 ) = 1.
ENGINEERING MECHANICS
(Common to Mechanical, Civil branches)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry equal marks
a) What is the .law of superposition?
b) What is cone of static friction?
c) Two parallel forces of magnitude 3N and 7N are acting on a body. Then what could be thje magnitude of the resultant force in Newtons
i) 3 or 7 ii) 2 or 8 iii) 4 or 10 iv) 11 or 12
d) State the D Alemberts principle with an example.
e) Defferentiate circular frequency from natural frequency.
a) State and prove the theorem of Varignon for two concurrent forces.
b) Determine by applying the Pappus theorem (i) the surface area and (ii) volume of a hemisphere of radius a.
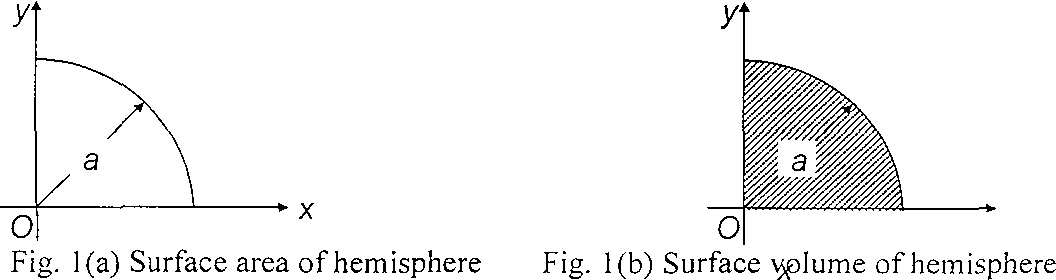
3. a) Discuss in detail about trusses and explain method of
joints of trusses with an example.
b) IN the plane of a figure OX and OY are one set of orthogonal axes. OX and OY are another set of orthogonal axes and OZ an axis perpendicular to the plane. If moments of inertia are Ix = 10, Iy = 15 and Ix1 = 8 units. Find out Iy1 and Iz.
c) State the principle of virtual work.
4. a) For a general case of forces in a plane show that the
equilibrium can be established by three moment equation.
b) State and prove parallel axis theorem and perpendicular axis theorem for moment of inertia of a plane lamina with an example.
5. a) A train moves with a uniform speed of 60 KMPH along
a straight level track. At a certain instant the engineer moves the throttle soas to increase thetraction by 20 per cent. What distance x will the train cover before acquiring a speed of 70 KMPH if the resistance to motion is constant and equal to 1/200 of the weight of the train?
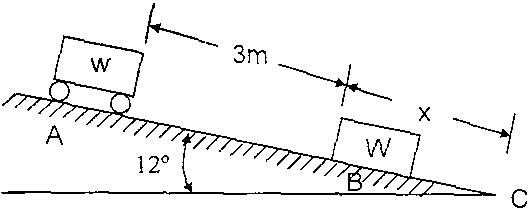
b) In Fig.2, a small car of weight w starts from rest at A and rolls without friction along an inclined plane to B where it strikes a block also of weight W and initially at rest. Assuming a plastic impact at B, the car and block will move from B to C as one particle. If the coefficient of friction between the block and plane is m = /, calculate the distance x to point C where the bodies come to rest.
a) Two adjacent guns having the same muzzle velocity of 400 m/sec fire simultaneously at angles of elevation for the same target at range 5000 m. Compute the time difference between the two hits.
b) Compute the circumferential tension produced in a uniformly rotating thin circular ring of uniform crosssectional area of10 cm2 and mean radius 5 cm if the peripheral velocityof the ring is 3 m/sec.
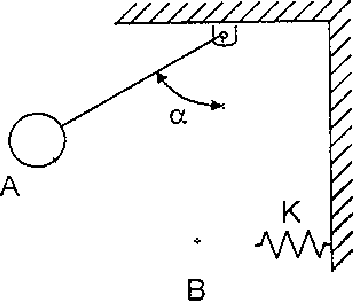
a) A simple pendulum ofweight w and length as shown in Fig.3 is released from rest at A( = 600), swings downward underthe influence of gravity and strikes a spring of stiffness K at B. Neglecting the mass of the spring, determine the compression that it will suffer.
b) The two step pulley in Fig.4 has weight W = 2 KN and radius of gyration K0 = 18cm. Develop a formula for the downward acceleration of the falling weight P on the right if P = 250 N, r1 = 25 cm and r2 = 40 cm.
 |
|
Fig : 3 |

US QD Fig : 4
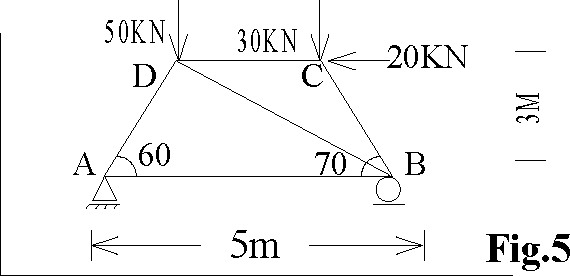
a) Find the period for small amplitudes of rotation of the horizontal bar AB in Fig.5 about the vertical axis through its mid-point C. Neglect the thickness of the bar.
b) A homogeneous square plate of wight W and having dimensions a hangs in a vertical plane by two pins A and B as shown in Fig.6. Calculate the horizontal and vertical components of the reaction at A an instant after the pin at B is removed.
////////////////////////
|
A B C |
 |
90 cm
30 crn 30 err 30 cryi
B
Fig : 6
Fig : 5
I Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examinations STRENGTH OF MATERIALS & THEORY STRUCTURES-I
(Civil Engineering)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry equal marks Assume any data if necessary
1. a) For a material the values of E = 2.1 x 105 N/mm2 and m = 0.25 are given. Find the values of other Elastic constants G and K.
b) Find the maximum normal stress in a beam having a span of 10m and cross section 300 x 800mm is subjected to a central concentrated load of 40 KN. Beam is simply supported.
c) The stress at a point in a material are = 150 N/mm2; = 110 N/mm2; = 50 N/mm2. Find the maximum normal stress at the point and their inclinations with respect to the plane on which the above stress are acting.
d) A cantilever having a span of 8m is subjected to a concentrated load of 30KN acting at 5m from fixed end. Determine the slope and deflection at free end in terms of EI.
e) Using castigrianos theirem 1 determine the displacem under the central concentrated load of W, acting on a simply. Supported beam having a span of l and modules of regidity E.I.
a) Determine the change in0 length of the bar shown in Eg.1 due to the loads. E = 2.1 x 104 N/mm2. The diameters of the portions AB, BC, CD are 30, 25, 40mm.
3KN
P<
4KN
6KN
le- 2 1.5 He1M>1 Fig.1
b) A rectangular block 300 x 50 x 20mm is acted on by the following axial forces i) 30 KN teusile along lenght,
ii) 300 KN compressive along width and iii) 250k tensil along the direction of thickness.Findthe change in volume. E = 2.1 x 105 N/mm2; = 0.25
a) Derive the equations for the stresses in composite bars having the same length and subjected to axial force.
b) A load of 2500 N is applied axially, on a composite copper. Steel imposite bar of length 4m and diameters the stress in each.
a) Draw the BMD and SFD stetches for a beam loaded as shown in Fig.2
15KN
"30KN/M
,C D
2
A
he 4m >|<
4m
B
Fig.2
A
300
-5mm
5mm
Describe Mohrs circle representation for finding stresses on inclined planes in a stressed body subjected to principal stresses.
5. a) b)
6. a) b)
7. a) b)
Aaxial load of 60 KN. The mean radius of the spring 100mm. Find the maximum shear stress and deflection. G = 0.8 x 105 N/mm2.
Derive the formulate for stress and angle of twist in torsion of a bar and write down the assumptions made there in
A shaft of diameter 25mm and length 1.5 m is subjected to a twisting moment 100 KNM. If G = 0.8 x 105 Find the maximum angle of twist and shear stress.
Determine the maximum displacement in a cantilever beam load as shown in terms of EI (Fig.4)
 |
|
N- 6m ->1 _ Fig.4 |
Detemine the forces in a truss loaded as shown in Fig.5 using Tension coefficient method.
8. a) Determine the strain energy stored in a beam loaded as shwon in Fig.6 in terms of EI.
-30KN/M
A W 3m0
N- 6m ->1
Fig.6
b) Using castiglianos theoren I, determine the displacement under the central concentrated load of 4.0 KN acting on a simply supported beam with a span of 8m interms of EI.
24
a) State and explain first law of thermodynamics.
b) Describe various operations of Cannots cycle and derive an expression for its efficiency.
a) Write a flow chart to find biggest of three numbers.
b) Write a program in FORTRAN to find the roots of a given quadtric equation.
a) Write a flow chart to find HCF a given two integers.
b) Write a program in C to test whether the given integer is prime or not.
b) Sketch the shear stress distribution in an I section (Fig.3) subjected to flexural shear force of 50KN.
II Year B.E/B.Tech

(Effective from 2GG5 admitted batch)
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION ANDHRA UNIVERSITY VISAKHAPATNAM - 530 003
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination MATHEMATICS - III
(Common to Civil, Mechanical, EEE & ECE Branches)
Maximum : 75 Marks
Time : Three hours
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry marks
1. a) Define scalar and vector point functions.
b) Write down the physical interpretation of curl.
c) Explain briefly the wave equation with reference to transverse vibration of a string.
d) Define Fourier transforms of the derivatives of a function.
e) State Parsevals identity for F - transforms.
2. a) What is the directional derivative of 0 = + yz5 at the
point (2, -1, 1) in the direction of the normal to the surface x log z - y2 = - 4 at (-1, 2, 1)?
b) Verify Stokes theorem for the vector field f = (2x-y) i -
yz2 j -y2z k over the upper half surface of x2 + y2+z2=1 bounded by its projection on the xy plane.
3. a) If r and R have their usual meaning and A is a constant

vector prove that Vx
b) Prove that the spherical polar coordinate system is orthogo-
nal.
Printed by : SRIRAM PRINTERS, Vsp-27. Copies : 1000, Year : 2007
x2 dx
~\2 -\2
dx2 +dy2
i
b) Evaluate (x2 +!) ( + 4)
5. a) Find the Fourier transform ofg-x2/2
Jl, O < x < a 1
b) Find the Fourier sine transform of f(x) = x>
d 2u _du
6. a) Find a solution of the equaion = y + in the form
u = f (x) g (y). Solve the equation subject to the conditions
a2 3
u = 0 and _1 + e y when x = 0 for all values of y. ax
b) A tightly stretched flexible string has its ends fixed at x = 0 and x = l. At time t = 0 the string is given a shape given by f (x) = m x (l x) where mis a constant and then released. Find the displacement of any point x of the string at any time t > 0.
7. a) A continuous distribution of a variable x in the range ( -3, 3)
is defined as
f(x)_ (3 + x)2, -3<x< 1.
16 ' =(2-6x)2 , -1 <x<1.
16
= (3 - x)2, 1 < x < 3.
16
Verify that the area under the curve is unity. Show that the mean is zero.
b) Fit a Poisson distribution to the following.
x : 0 12 3 4 f : 46 38 22 9 1
8. a) Find the correlation coefficient from the following data :
x : 1 2 3 4 5 y : 2 5 3 8 7
b) The following results were obtained in Applied Mechanics and Engineering Mathematics in an examiniation. Given r=0.95, Find both the regression equations.
Applied Mech. Engg. Maths
(x) (y)
Mean 47.5 10.5
Standard deviation 16.8 10.8
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination STRENGTH OF MATERIALS AND THEORY OF STRUCTURES - II
(Civil Engineering)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry equal marks
b) Draw the B.M.D and SFD for a continuous beam loaded as shown in Fig. 1.
|
10KN/m 1 A 4m I -- B |
40KN 2.5m4m2 5m - c D |
3. a) Derive the equation for Rankines crippling load for a col
umn.
b) A steel stanction is made of an I section 250 x 150 mm with
I x = 92 x 106 mm4 ; I y = 415 x 104 mm 4 ; A = 6500 mm2 and two symmetrical flange plates of 210 x 20 mm size. Both ends of the stanction are fixed and its length is 15m.
Find the Rankines crippling load s4 = 250 N/ mm2 and
a = 1/7500.
4. a) Derive an equation for failure load for a long column sub
jected to eccentric load.
b) The corss section of a long column 5.0m long is shown in Fig.2 One end of the column is fixed and the other end is hinged. Determine Eulers critical load.
E = 2.1 x 105 N/ mm2
k 150
5. a) Explain Rankines theory of failure for specimen subjected
to sx ,sy ,txy
b) Determinie the stress at failure according to principal strain theory for a rod subjected to
20mm
T
140mm
20mm Fig.2
sx = 260; oy = 100; Ty = 60N/mm
6. a) Dervice the criterion for maximum bending moment to occur under a wheel load when two rolling load Wp W2 are moving on a beam with Wj leading an seperated by a from W2
b) A train of moving loads as shown in Fig. 3 is mover on a beam of span 20m. Find the position ofloads when the B.M. is maximum at 9M. from left end.
50KN
fig. 3
m
2|3|1.5
I70 X80 X 200 X
7. a) Determine the condition required for B.M. at a sec to become maximum when a set of loads is rolling the beam.
b) Draw the influence lines for the forces in members a and c of the warren truss shown in Fig 4.
 |
B |
|
30 - | |
20 cm
0.6cm
8. a) Give the procedure for calculating the maximum stress in a beam subjected to unsymmetrical bending.
b) Determine the shear centre for a channel section shown in Fig5.
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination FLUID MECHANICS - I
(Civil Engineering)
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8.
All questions carry equal marks
1. Answer the following briefly, Each bit carries 3 marks.
(a) What are the basic differences between the energy and momentum equations ?
(b) The pressure under the nappie of a contracted sharp crested weir will be hydrostatic Justify or contradict the statement through proper reasoning.
(c) Obtain the friction factor for laminar flow through a pipe in terms of Reynolds number.
(d) A geometrically similar model is kinematically similar too. Justify or contradict this statement with proper reason.
(e) It is not possible to simultaneously satisfy both Reynolds law and Froude law Justify or contradict the statement through proper reasoning.
2. (a) Plot the variation of deformation in terms of the velocity
gradient for various types of fluids as a function of the shear stress. Clearly identify the types of fluids giving the type of equation for each category of fluid. (5 marks)
(b) A circular disc of radius R rotates at an angular velocity (!), maintaining a small distance h above a fixed bed under the support of a fluid layer of viscosity is m . Obtain the expression for the torque on the disc. (6 marks)
(c) Distinguish between Surface forces and body forces
(4 marks)
3. (a) Arrive at the condition for irrotationality of an ideal fluid in
terms of the velocity gradients. (5 Marks)
(b) What is the significance of energy correction factor in Bernoullis equation? Arrive at the expression for the same.
(6 Marks)
(c) Explain the importance of flow net in engineering applications. (4 Marks)
4. (a) An oil of sp. gr. 0.90 flows through a vertical pipe of diam
eter 20cm. The flow is measured by a 20cmx10cm venturimeter. The throat is 10cm above the inlet. A differential U-tube mercury manometer is connected to the Venturimeter. If Cd = 0.99, what is (a) the flow for a manometer reading of 9 cm and (b) the manometer reading for a flow of 50 lps ? (8 Marks)
(b) Derive the expression for emptying a hemispherical tank of radius R through an orifice of area a whose coefficient of discharge is Cd.
5. (a) State the laws offiiction for turbulent flow in a pipe. (4Marks)
(b) A concrete pipe 90 cm in diameter and 20 m long is used as a culvert. The pipe is laid on a slope of1 in 60 and has square entrance. During a heavy flow of1.50m 3/s, ifthe culvert is submerged and the depth offlow over the invert at the downstream end is 1.25 m, estimate the depth ofwater above the pipe invert at the upstream end. [Assume Z=0.025] (7 Marks)
(c) Derive the expression for loss of head due to sudden contraction in a pipe. (4 Marks)
6. (a) Water from a reservoir flows through a pipe line of length L
and diameter d and discharges though a nozzle of diameter dn. If the loss of head in the nozzle is K [V2n / 2g] where K= constant and Vn = velocity in the nozzle. Show that for maximum power transmission through the pipeline is
X
(1 + k )d 2 fL
dn
d
where /is the friction coefficient for the pipe.
(b) Water is discharged from a reservoir into the atmosphere through a pipe 39 m long. There is a sharp entrance to the pipe and the diameter is 50 mm for 15 m from the entrance. The pipe then enlarges suddenly to 75 mm in diameter for the reminder of its length. Taking into account the loss of head at entry, enlargement, calculate the difference of level between the water surface of the resevoir and the pipe exit which will maintain a flow of 2.8 Its/sec. Take /= 0.02 for 50 mm pipe and 0.025 for 75 mm pipe. Draw also HGL and total energy gradient lines.
7. (a) Explain the Weber law ofsimilarity. (4 Marks)
(b) Show that the total resistance Rof a floating ship is given by
Ci
CF
-1
r + rf
where l is the
the expression
scale ratio, r is the total resistance on the model, rf is the frictional resistance on the model and C, and C, are the
fs fm
frictional coefficients for the ship and its model respectively. It may be assumed that the ship and the model are towed in the same water. (6 Marks)
(c) A spillway model is to be built to a geometrically similar scale of 1/50 across a flume of 60 cm width.The prototype
is 15 m high and the maximum head on it is expected to be 1.5m. (i) What height of model and what head off the model should be used? (ii) If the flow over the model at a particular head is 12 lps, what flow per meter width of the prototype is expected ? (iii) If the negative pressure in the model is 20 cm, what is the negative pressure in the prototype ? Is it practical ? (5 Marks)
8. Write short notes on any Three (3x5 = 15 Marks)
(a) Flow net (b) Pipes in parallel (c) Syphon
(d) Reynolds experiment (e) Distorted models (f) Lock gates
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination BUILDING PLANNING AND DESIGN
(Civil Engineering)
Time : Four hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Part - A
1. a) Give the sizes of plots for the different income groups in
India 5 x 3 = 15
b) What is the significance of the principle of flexbibility in a building ?
c) What comfortable conditions are to be created in a building of humid tropics ?
d) Explain Anthropometrics with two sketches.
e) Draw Conventional Symbols for the following i) Plaster ii) Glass iii) Stone
2. a) Explain the factors to be considered in the selection of site
for a Residential Building. (8)
b) Distinguish between detached and semi detached houses.(7)
3. a) Define Orientation. What are the important points for good
orientation of the buildings in a tropical climate ? (8)
b) Define Ventilation ? What are the types of Ventilation ? (7)
4. Write a brief note on
i) Aspect ii) Grouping iii) Cirulation in buildings. (15)
5. a) Howare buildings classified according to building bye-
laws ? (8)
b) Explain with neat sketches the purpose and requirements of the following rooms i) Kitchen ii) Dining (7)
6. Design a house for a moderate family. Site particulars : Size 20 x 25 (interior plot). Road parallel to width of site and facing North, Location : Kakinada. Wind direction : S, SW - W; climate Zone : Hot and humid : Space requirements :
a) Front Verndah ; b) Living room, c) Dining room for six persons d) Kitchen and suitable utility verandah; e) Master bedroom with attached W.C f) Guest bed room; g) Separate bathroom with WC with in the building with an easy access to guest bed room and other users ; h) Staircase room leading to terrace.
The plinth area should be between 200 to 240sqm. Front open space 6m. Minimum side open space 2m on either side, rear open space 3m minimum.
Marks distribution for Question No. 6
Design and draw plan 10 marks
Section 5 marks
Elevation 5 marks
Site plan 5 marks
Schedule of doors and windows 5 marks
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination REINFORCED CONCRETE STRUCTURES - I
Civil Engineering
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
1. a) What is the advantage of limit state design over working
stress method ?
b) Under what conditions doubly reinforced beams are adopted?
c) Reinforced concrete slabs are generally safe in shear. Comment ?
d) List the functions of transverse reinforcement in a reinforced concrete beam.
e) What do you understand by development lenght ?
2. A reinforced concrete beam of rectangular section has to carry a uniformly distributed load of 8 kN/m over an effective span of10 m. Design the section using M20 and Fe415 grade steel, when i) there is no restriction on the size beam section ii) the size of the section is restricted to 250 m x 500 effective. Use working stress method.
3. Determine the area oftensile reinforcement required for singly reinforced beam section of size 300 x 550 mm effective to carry a factored moment of 180 kNm. The concrete is M20 and steel is Fe415 grade.
4. A series of beams placed at 2.5 m centres are supported on masonry walls and the effective span of the beam is 5m. the slab thickness is 100mm and ribs below the slab are 200mm wide and 250 deep. If the slab and beams are so cast to act together, determine the reinforcement at mid span for the T beam to carry an imposed load of 5 kN/m2 of the slab. Use concrete M20 and steel Fe415 grade.
5. A reinforced concrete rectangular beam section of230mm width and 450 mm overall depth is reinforced with 4 bars of16 mm of Feb415 grade, placed at an effective cover of 228 mm. Design he shear reinforcement if the beam is subject to a uniformly distributed load of 50 kN/m over a simply supported clear span of 6 m. Concrete is M20.
6. Design a reinforced concrete slab 4.5x 3.2 simply supported on all four sides. It has to carry a characteristic live load of 4 kn/m1 in addition to its dead weight. Asume M20 and Fe415 steel. Also assume that exposure condition is mild.
7. A reinforced concrete column of unsupported length 3 m is to be designed for a factored load of1200 kN. Determine the cross sectional dimensions of the column and the reinforcement required for the two cases.
i) There is no restriction on the column size.
ii) One side of the column is restriced to 230 mm.
The grade of concrete is M20 and steel is Fe415.
8. A solid footing has to transfer a total load of 800 kN. Assuming Fe 415 and fck = 20 MPa, and safe bearing capacity to be 200 kN/m2, design the footing.
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination STEEL STRUCTURES - I
Civil Engineering
Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8 All questions carry equal marks

7. A plate girder is composed of the following elements :
(i) Web plate : 900mm depth x 10mm thickness
(ii) Two angles : ISA 200 mm x 100mm x 12.0mm @ 27.2 kg/m, in each flange
(iii) Two flange plates : 500 mm x 16 mm in each flange.
The girder is simply supported over an effective span of15m. The diameter of rivets used for connecting flange angles to the web and flange plates to flange angles is 20 mm.
Determine the safe uniformly distributed load which the girder can carry, inclusive of its own weight. Assume that the compression flange is not restrained against lateral bending, but the ends are restrained against torsion. Take f = 250 N/ mm2.
8. A column section I.S.H.B. 350 @ 674 N/m carries an axial load of1100 kN. Design a suitable gusset base. Allowable bearing pressure on concrete is 4000 kN/m2.
plate at a distance of 100mm from the flange of the column section and a = 250mm and d = 250 mm.
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination SOIL MECHANICS
Civil Engineering Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8.
All questions carry equal marks
b) In a falling head permeability test on a sample 12.2cm high and 44.4Cm3 in cross sectional area, the water level in a standpipe of6.25mm internal diameter dropped from a height of 75cm to 25cm in 20 minutes. Find the coefficient of permeability. (8)
State the assumptions made in Boussinesqs theory of stress distribution in soils. (5)
5. a)
b) Derive Terzaghis differential equation of one dimensional consolidation theory. Explain various assumptions made in the theory. (10)
a) Discuss Merits and Demerits of Direct Shear Test. (6)
6.
|
b) The results of Triaxial test (UU) performed on a clay sample are as follows. | ||||||||
| ||||||||
|
Plot failure envelope and determine the shear parameters (9) |
II Year B.E./B.Tech Degree Examination ENGINEERING GEOLOGY
Civil Engineering Time : Three hours Maximum : 75 Marks
Question 1 is compulsory Answer any four from Questions 2 to 8.
All questions carry equal marks
21
(a) Discuss in detail the advantages and disadvantages of steel
as a structural material.
(b) What are the different Rolled Steel Sections ? How are they designated ?
a) Establish relationship between Bul Density, Dry Density
and Water Content. (5)
b) In a liquid limit test, specimens of certain sample of clay at water contents of 31.9, 27.6, 25.5 & 23.3% required 5, 16, 23 and 42 blows respectively to close the standard groove. The plastic limit of the clay is 13%. Find the liquid limit, plasticity Index, Flow Index & Toughness Index. (10)
Define land form ? Explain the land forms given below.
a. Sand dunes b. Ventifacts c. Spits and Bars d. Sea Cliff
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
