Karnatak University 2002 Entrance Exams Gate Entrance Exam GATE- CIVIL ENGINEERING - Question Paper
GATE 2002
COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING
Section A
(75 Marks)
CS 1. This question" consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-questions, 1.1 to 1.25, of ONE mark each. For each of the sub-questions, four alternatives, A, B, C, and D are provided. Choose the most appropriate alternative and darken its bubble on the OBJECTIVE RESPONSE SHEET (ORS) against the corresponding sub-question number using a soft HB pencil. Do not darken more than one bubble for any sub-question. Do not use the ORS for any rough work. You may use the Answer Book (last few pages) for any rough work.
- The rank of the matrix
![]()
is
- 4
- 2
- 1
- O
1.2 The trapezoidal rule for integration gives exact result when the integrand is a polynomial of degree
- 0 but not 1,
- 1 but not 0
- 0 or 1
- 2
1.3 The solution to the recurrence equation T(2 k ) = 3 T(2 k-l) + 1, T(1) = 1 is:
- 2k
- (3 k+1 - 1)/2
- 3 log 2 k
- 2 log 3 k
1.4 The minimum number of colours required to colour the vertices of a cycle with n nodes in such a way that no two adjacent nodes have the same colour is:
- 2
- 3
- 4
- n 2 n/2 + 2
1.5 In the worst case, the number of comparisons needed to search a singly linked list
of length n for a given element is
- log 2 n
- n/2
- log 2 n 1
- n
1.6 Which of the following is true?
- The set of all rational negative numbers forms a group under multiplication.
- The set of all non-singular matrices forms a group under multiplication.
- The set of all matrices forms a group under multiplication.
- Both B and C are true.
1.7 The language accepted by a Pushdown Automaton in which the stack is limited to 10 items is best described as
- Context Free
- Regular
- Deterministic Context Free
- Recursive
1.8 If X then Y unless Z" is represented by which of the following formulas in
propositional logic ? (" " is negation, " " is conjunction, and " " is implication)
- (X Z) Y
- (X Y) Z
- X (Y Z)
- (X Y) Z
1.9 A device employing INTR line for device interrupt puts the CALL instruction on the data bus while
- INTA is active
- HOLD is active
- READY is active
- None of the above
1.10 In 8085 which of the following modifies the program counter?
- Only PCHL instruction
- Only ADD instructions
- Only JMP and CALL instructions
- All instructions
1.11 In serial data transmission, every byte of data is padded with a '0' in the beginning
and one, or two 1's at the end of byte because
- Receiver is to be synchronized for byte reception
- Receiver recovers lost '0's and '1's from these padded bits
- Padded bits are useful in parity computation
- None of the above.
1.12 . Minimum sum of product expression for f(w,x,y,z) shown in Karnaugh-map below is
|
wx |
|
|
|
|
|
yz |
00 |
01 |
11 |
10 |
|
00 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
01 |
X |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
11 |
X |
0 |
0 |
I |
|
10 |
0 |
I |
1 |
x |
A. xz +y'z
B. xz' + zx'
C. x'y + zx'
D. None of the above
1.13 Which of the following is not a form of memory?
- instruction cache
- instruction register
- instruction opcode
- translation look aside buffer
1.14 The decimal value 0.25
- is equivalent to the binary value 0.1
- is equivalent to the binary value 0.01
- is equivalent to the binary value 0.00111
- cannot be represented precisely in binary
1.15. The 2's complement representation of the decimal value -15 is
- 1111
- 11111
- 111111
- 10001
1.16. Sign extension is a step in
- floating point multiplication
- signed 16 bit integer addition
- arithmetic left shift
- converting a signed integer from one size to another
- In the C language
- At most one activation record exists between the current activation record and the activation record for the main
- The number of activation records between the current activation record and the activation record for the main depends on the actual function calling sequence.
- The visibility of global variables depends on the actual function calling sequence.
- Recursion requires the activation record for the recursive function to be saved on a different stack before the recursive function can be called.
1.18 The- results returned by functions under value-result and reference parameter passing conventions
- Do not differ
- Differ in the presence of loops
- Differ in all cases
- May differ in the presence of exceptions
- Relation R with an associated set of functional dependencies, F, is, decomposed into BCNF. The redundancy (arising out of functional dependencies) in the resulting set of relations is
- Zero
- More than zero but less than that of an equivalent 3NF decomposition
- Proportional to the size of P+
- Indeterminate
1.20 With regard to the expressive power of the formal relational query languages, which of the following statements is true?
- Relational algebra is more powerful than relational calculus
- Relational algebra has the same power as relational calculus
- Relational algebra has the same power as Safe relational calculus
- None of the above
1.21 In 2's complement addition, overflow
- is flagged whenever there is carry from sign bit addition
- cannot occur when a positive value is added to a negative value
- is flagged when the carries from sign bit and previous bit match
- None of the above
1.22 Which of the following scheduling algorithms is non-preemptive?
- Round Robin
- First-In First-Out
- Multilevel Queue Scheduling
- Multilevel Queue Scheduling with Feedback
1.23 The optimal page replacement algorithm will select the page that
- Has not been used for the longest time in the past.
- Will not be used for the longest time in the future .
- Has been used least number of times.
- Has been used most number of times.
1.24 In the absolute addressing mode
- the operand is inside the instruction
- the address of the operand is inside the instruction
- the register containing the address of the operand is specified inside the instruction
- the location of the operand is implicit
1.25 Maximum number of edges in a n - node undirected graph without self loops is
- n 2
- n (n-1)/2
- n-1
- (n+1)(n)/2
CS2. This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-questions, 2.1 to 2.25, of TWO marks each. For each of the sub-questions, four alternatives, A, B, C, and D are provided. Choose the most appropriate alternative and darken its bubble on the OBJECTIVE RESPONSE SHEET (ORS) against the corresponding sub-question number using a soft HB pencil. Do not darken more than one bubble for any sub-question. Do not use the ORS for any rough work. You may use the Answer Book (last few pages) for any rough work.
2.1 Consider the following logic circuit whose inputs are functions f 1, f 2, f 3 and output is f.
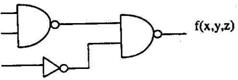
f 1(x,y,z)
f 2(x,y,z)
f3 (x,y,z)= ?
Given that
f 1(X,Y,Z) = (0,1,3,5),
f 2(X,Y,Z) = (6,7), and
f(x,y,z) = (I,4,5),
f3 is
A. (1,4,5)
B. (6,7)
C. (0,1,3,5)
D. None of the above
2.2 Consider the following multiplexor where I0, I1, I2, I3 are four data input lines
selected by two address line combinations AIAO =00,01,10,11 respectively and f is
the output of the multiplexor. EN is the Enable input.
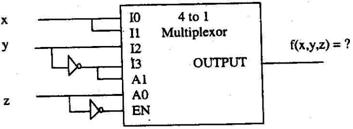
The function f (x, y ,z) implemented by the above circuit is
- xyz
- xy+z
- x+y
- None of the above
2.3. Let f(A,B} = A' +B . Simplified expression for function f (f(x+y.y),z) is
- x' +z
- xyz'
- xy' + z
- None of the above.
2.4. What are the states of the Auxiliary Carry (AC) and Carry Flag (CY) after executing the following 8085 program?
MVI H, 5DH
MVI L , 6BH
MOV A, H
ADD L
- AC= 0 and CY =0
- AC= 1 and CY= 1
- AC= 1 and CY=O
- AC = 0 and CY = 0
2.5 The Finite state machine described by the following state diagram with A as
starting state, where an arc label is x/y and x stands for I-bit input and y stands for
2-bit output
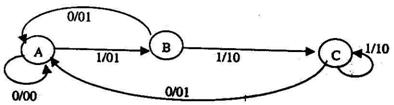
- Outputs the sum of the present and the previous bits of the input.
- Outputs 01 whenever the input sequence contains 11
- Outputs 00 whenever the input sequence contains 10
- None of the above
2.6 The performance of a pipelined processor suffers if
- the pipeline stages have different delays
- consecutive instructions are dependent on each other
- the pipeline stages share hardware resources
- all of the above
2.7 Horizontal microprogramming
- does not require use of signal decoders
- results in larger sized microinstructions than vertical microprogramming
- uses one bit for each control signal
- all of the above.
2.8 Consider the following declaration of a 'two-dimensional array in C:
char a[100][100];
Assuming that the main memory is byte-addressable and that the array is stored starting from memory address 0, the address of a[40][50] is
- 4040
- 4050
- 5040
- 5050
2.9. The number of leaf nodes in a rooted tree of n nodes, with each node having 0 or 3 children is:
- n/2
- (n-1)/3
- (n-1)/2
- (2n+1)/3
2.10. Consider the following algorithm for searching for a given number x in an unsorted - array A[1..n] having n distinct values:
- Choose an i uniformly at random from 1..n;
- If A[i] = x then Stop else Goto 1;
Assuming that x is present in A, what is the expected number of comparisons made by the algorithm before it terminates?
- n
- n-l
- 2n
- n/2
2.11. The running time of the following algorithm
Procedure A(n)
If n <= 2 return(1) else return (A ( n ));
is best described by
- O(n)
- O(log n)
- O(1og log n)
- O(1)
2.12. A weight-balanced tree is a binary tree in which for each node. The number of nodes
in the left sub tree is at least half and at most twice the number of nodes in the right
sub tree. The maximum possible height (number of nodes on the path from the root to the farthest leaf) of such a tree on n nodes is best described by which of the following?
- log 2 n
- log 4/3 n
- log 3 n
- log 3/2 n
2.13. The smallest finite automaton which accepts the language
{x | length of x is divisible by 3} has .
A. 2 states
B. 3 states
C. 4 states
D. 5 states
2.14. Which of the following is true?
- The complement of a recursive language is recursive.
- The complement of a recursively enumerable language is recursively enumerable.
- The complement of a recursive language is either recursive or recursively enumerable.
- The complement of a context-free language is context-free.
- The Newton-Raphson iteration X n+l == (X n/2) + 3/(2X n)
can be used to solve the equation
- X 2 =3
- X 3=3
- X 2=2
- X 3=2
2.16 Four fair coins are tossed simultaneously. The probability that at least one head and one tail turn up is
- 1/16
- 1/8
- 7/8
- 15/16
2.17 The binary relation S = f (empty set) on set A = { 1,2,3} is
- Neither reflexive nor symmetric
- Symmetric and reflexive
- Transitive and reflexive.
- Transitive and symmetric
2.18 The C language is.
- A context free language
- A context sensitive language
- A regular language
- Parsable fully only by a Turing machine
2.19. To evaluate an expression without any embedded function calls
- One stack is enough
- Two stacks are needed
- As many stacks as the height of the expression tree are needed
- A Turing machine is needed in the general case
2.20 Dynamic linking can cause security concerns because
- Security is dynamic
- The path for searching dynamic libraries is not known till runtime
- Linking is insecure
- Cryptographic procedures are not available for dynamic linking
- Which combination of the following features will suffice to characterize an OS as a multi programmed OS?
- More than one program may be loaded into main memory at the same time for execution.
- If a program waits for certain events such as I/O. another program is immediately scheduled for execution.
- If the execution of a pr ogram terminates, another program is immediately scheduled for execution.
- a
- a and b
- a and c
- a, b, and c
2.22 In the index allocation scheme of blocks to a file, the maximum possible size of the file
depends on .
- the size of the blocks, and the size of the address of the blocks.
- the number of blocks used for the index, and the size of the blocks.
- the size of the blocks, the number of blocks used for the index, and the size of the
address of the blocks.
d. None of the above
2.23 A B + -tree index is to be built on the Name attribute of the relation STUDENT. Assume that all student names are of length 8 bytes, disk blocks are of size 512 bytes, and index pointers are of size 4 bytes. Given this scenario, what would be the best choice
of the degree (i.e. the number of pointers per node) of the B+ -tree? .
- 16
- 42
- 43
- 44
2.24 Relation R is decomposed using a set functional dependencies, F, and relation S is decomposed using another set of functional dependencies, G. One decomposition is definitely BCNF, the other is definitely 3NF, but it is not known which is which. To make a guaranteed identification, which one of the following tests should be used on the decompositions? (Assume that the closures of F and G are available).
- Dependency-preservation
- Loss less-join
- BCNF definition
- 3NF definition
2.25 From the following instance of a relation schema R (A,B,C), we can conclude that:
|
A |
B |
C |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
0 |
|
2 |
3 |
2 |
|
2 |
3 |
2 |
- A functionally determines B and B functionally determines C
- A functionally determines B and B does not functionally determine C
- B does not functionally determine C
- A does not functionally determine B and B does not functionally determine C
| Earning: Approval pending. |
