University of Pune 2009-1st Sem B.E Instrumentation and Control Engineering T.E.(Instrumentation) s - Question Paper
Illllllllllllllllllllll [3563] - 160
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Semester - II) Examination, 2009
INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT
(2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions : I) Answer three questions from Section I and three questions from Section - II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Define strategic planning. Explain Mergers and Take-overs as a strategic
alternatives with its importance to current business scenario. 12
b) State and explain the concept of Mind - Mapping. 4
OR
2. a) Describe various functions of management. Explain the role of managers to
manage a business enterprise in a competitive market. 10
b) What is Business Process Re-engineering ? Explain its importance to business. 6
3. a) Explain the following quality standards : 8
i) ISO - 9000
ii) ISO - 14,000
b) Define quality. State and explain the concept of statistical process control. 8 OR
4. a) Explain the following concepts : 10
i) Patent management
ii) Business expansion and diversion strategy.
b) Critically explain the WTO agreement and its impact on export and import of India. 6
5. a) A Co. uses a particular component and the annual uses is 36000 based on its
production forecast. The ordering cost is Rs. 200/- per order and inventory carrying cost is estimated at 20% of average annual investment. The cost per one unit of the component is Rs. 10 and safety stock is 3000 units. Assuming 300 working days in a year, determine :
i) Economic order quantity.
ii) No. of orders per year
iii) Inventory cycle.
iv) Total inventory cost and
v) If price increases from Rs. 10/- to Rs. 15/- What would be the EOQ ? 12
b) What is EOQ ? Derive the formula of EOQ. Is it a cost reduction technique ? Explain. 6
OR
6. a) State and explain the objectives, importance of production planning. Do you
consider outsourcing is a part of production planning ? Explain. 10
b) Explain the concept of supply chain management. How it influence the profit of a business enterprise ? 8
7. a) Define Man Power Planning. Explain the functions and process of man power
planning. 8
b) Do you consider Down sizing is a potential measure to reduce cost and increase operational efficiency of business ? Give reasons. 8
OR
8. a) Critically evaluate Maslows need hierarchy theory of motivation. 8 b) State and explain various methods of training. How it influence productivity ? 8
9. a) Explain project costing. What are the various project costs and also explain
how the project report is prepared ? 10
b) Explain the following concepts : 8
i) Net-present value
ii) Pay-back period
iii) Earning per share
iv) Return on Investment.
OR
10. a) What is letter of credit (LOC) ? How it is created ? and explain the procedures
of LOC. 8
b) State and explain how Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Account evaluate the
performance of a company. 10
11. Explain the following Acts with their salient features : 16
i) Company Act - 1956
ii) Factory Act - 1948
OR
12. Explain the following : 16
i) Value Added Tax
ii) Excise duties
iii) Service Tax
iv) Market Participant Identification Number.
B/I/09/870
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
N.B. x IA Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books. 2A Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3A Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4A Your answers will be valued as a whole.
5A Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. A) Why it is necessary to refer packaging standard while designing an instrument,
explain DIM standard. 8
B) Explain Bureau of Indian Standard and NEMA Standard. 8
OR
2. A) Is it true that, quality and reliability has inter-related to design of an instrument ?
Justify it. 8
B) Explain the selection of IP third number which protect against mechanical impacts, also explain IP 64. 8
3. A) Explain electrostatic discharge with the reference to Human Body Model. 6
B) Why burst noise is also called as Popcorn noise, where it was first discovered ? 4
C) Compare contact noise with thermal noise. 6
OR
4. A) Prove that thermal noise is a universal function and independent of the
composition of resistance. 8
B) Grounds fall into which two categories, explain multipoint ground system. 8
5. A) With the help of diagram, explain the method of offset (zero) and span
adjustment in XTR - 110, precision voltage to current converter. 8
B) I) Find servo gain (K1), when forward current IF a 10 mA and servo photo
current Ip1 a 70 ju A at temperature 25C. 4
OR
6. A) 1) What is the output voltage of AD 595 when 200C temperature is applied to
pin no. 1 and 14 through Chromel Alumel thermocouple, while output voltage of this thermocouple is observed to be 8.137 mV ? 6
2) What caution should take while testing AD 595 or AD 594 ? 4
B) 1) What are the advantages of AD 620 over conventional 3-Op-Amp
instrumentation amplifier ? 2
2) Draw and explain simplified schematic ofAD 620. 6
SECTION - II
7. Explain test circuit diagram and timing diagram of ICM 7217 A with following functions. 18
|
1) |
SCAN |
2) |
|
3) |
EQUAL |
4) |
|
5) |
BCD I/O |
6) |
OR
8. 1) How many phase comparators are used in CD 4046 B, explain function of
phase comparator - II (edge-controlled) ? 9
2) Explain any one application of CD 4046 B. 9
9. I) How digital PCBs problems can help to overcome by proper value of wave
impedance zero ? 8
2) Explain BERGERON reflection chart for reflections. 8 OR
10. I) Explain general considerations of layout check. 4
2) What are the types of soldering fluxes, according to the nature of their residues ? 4
3) Explain wave soldering. 8
11. 1) Explain catastrophic failures using failure rate curve. 8
OR
12. 1) Explain manufacturing costs against reliability. 8
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Sem. - II) Examination, 2009 PROCESS LOOP COMPONENTS (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
Instructions : I) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
P) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Draw the standard symbols for following :
10
i) Pneumatic signal line
ii) Temperature indicator and controller
iii) Level transmitter
iv) Pneumatically operated control valve
v) Level Alarm High/Low.
b) List various components of typical process control loop located in field area and control from area. Indentify different standard transmission signals.
8
OR
2. a) Design signal conditioning for following application sensor used : J type T/C.
Input temperature range : Ambient to 500oC
Output : 0 to 5 V DC.
Reference junction temp. : 0oC
12
|
Temperature (Hot junction) |
mV |
|
0 C |
0 |
|
Ambient |
1.5 |
|
500 C |
27.39 |
b) Give the advantages of current transmission over voltage transmission. What is need for standard signal ? 6
3. a) Explain following w.r.t. I/P convertor :
i) Need/Application
ii) Construction
iii) Calibration
Draw suitable diagram.
b) Draw and explain block diagram of SMART transmitter and state its advantages.
c) Explain various lags involved in process.
OR
4. a) Explain difference betn transmitter and converters. Give application of P-I
converter.
b) Explain zero elevation and zero suppression with respect to DPT for level measurement.
c) Give the specification of pressure transmitter.
5. a) Explain with neat sketch rate before reset action.
b) Explain effects of process reaction rate and dead time on On-off control action and on P-control action.
OR
6. a) Explain block diagram of digital controler. Explain front facia of digital controller.
b) What is mean by tunning of controller ? List various methods of controller tunning. Explain any one in detail.
SECTION - II
7. a) List and explain 3 typical modes of operation of PLC.
b) A pump is to be used to fill 2 storage tanks. The pump is manually started by the operator from a START/STOP station. When the first tank is full, the control logic must stop flow to first tank and direct flow to the second tank with the help of solenoid valve. When second tank is full, the pump must shut down automatically. Indicator lamps are to be included to signal when each tank is full. Draw sketch of the process. Prepare a typical relay ladder diagram for the same. OR
8. a) With the help of neat block diagram, list 4 tasks performed by an input module.
Also list important specifications of input module. 8
b) Develop PLC ladder diagram for the following when START button is pushed, a single acting pneumatic cylinder starts reciprocating automatically and continuously until stop push button is pressed. Comment on inerfacing of PLC to pneumatics. 10
9. a) List different selection criteria for control valve. 8
b) A control valve operates from a 3 to 15 psi control signal to have a 40 gal/min flow rate, express the signal in both psi and in % of range if :
i) It is a linear valve from 0 to 90 gal/min.
ii) It is a equal percentage with R a 6 Q . a 15 gal/min. 8
OR
10. a) Comment of the following statement Valve positioner enhance the performance
of control value. 8
b) Suppose a pressure of 90 KPa is applied to the diaphragm of the control valve
to open it. The area of the diaphragm is 30 cm2. Find the force generated. 4
c) Define the term Cv. State its significance. 4
11. a) Explain significance of square root extractor with reference to DPT. 8
b) Explain the front panel controls of Alarm Annunciator. Also give the standard ISA sequences for Alarm Annunciator. 8
OR
12. Write short notes on (any two) : 16
i) Flow totaliser
ii) Dampers
iii) High/low selector.
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Semester - II) Examination, 2009 PROCESS PLANT OPERATION (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions x I) Answer any three questions from each Section.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. Explain different types of Unit Operations involved in sugar industries with flow sheet symbols.
OR
2. Explain in detail about the following :
a) Dryer and its types
b) Distillation. 16
3. Explain the types of reactions in detail. Compare different types of reactors. 16
OR
4. Explain the laws of thermodynamics in detail. Explain the role of kinetics in chemical industries. 16
5. Derive the material and energy balance equation of boiler and heat exchanger. 18
OR
6. Explain the following terms :
1) Cooling tower
2) Evaporators
3) Refrigeration. 18
SECTION - II
7. What is size separation and screening ? Explain different types of separators in detail. 16
OR
8. What is froth floatation ? Explain it in detail. Also explain hydrocyclone. 16
9. Explain corrosion and its protection techniques in detail. 16
OR
10. a) What are the aspects to be consider while selecting metals and alloys in
construction of field instruments ? 8
b) Explain any two types of hardness testing method. 8
11. Explain with flow sheet diagram about manufacturing of Urea from Ammonium Carbonate. 18
OR
12. Define pulp and its production methods. Explain with flow sheet diagram about the making of paper from pulp using sulphate. 18
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control Engg.) (Semester - II) Examination, 2009 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions : 1) Answer 3 questions from Section - I and 3 questions from Section - II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Compare Digital Signal processing with analog signal processing in details. 8 b) Determine the output response of the relaxed system characterized by the impulse
(1Y
response h(n)= u(n) to the input signal x(n) = 2n u(n).Also find magnitude
V 2 )
and phase response of the system. 8
OR
2. a) Determine and sketch magnitude and phase response of
y(n) = 1 [x(n) + x (n - 2)]. 8
2
b) Obtain cascade form and parallel form realization following system. 8
y(n) = - 0.1 y(n - 1) + 0.2 y(n - 2) + 3 x(n) + 3.6 x (n - 1) + 0.6 x (n - 2).
3. a) Explain following properties of Discrete Fourier Transform 8
i) periodicity
ii) Linearity
iii) Symmetry
iv) Multiplication of two DFTS.
xi(n) = j21 2,1 j x2(n) = j 1 2, 3, 4 j . Use Basic formula of circular
convolution. 8
OR
4. a) Find fast fourier transform of following input sequence using decimation in
Frequency algorithm. 8
x (n) = 2n ; 0 < n 7 = 0 ; otherwise
b) Explain the Goertzel Algorithm in details. 8
5. a) Give advantages and disadvantages of digital filters. 4
b) Compare Finite Impulse Response Filters with Infinite Impulse Response Filters. 4
c) Determine the FIR Filter coefficient for M = 7 for Following desired response specifications : 10
Use Blackmanns window. Find frequency response of designed filter.
OR
6. a) Explain Gibbs phenomenon in details.
6
b) Design a Bandpass Filter which approximates the ideal Filter with cut off frequencies at 0.2 rad/sec and 0.3 rad/sec. The filter order is M = 7. Use the Hanning window Function. Also find Magnitude and phase of designed
IMI56IMIMI56I -3- [3563] - 156
SECTION - II
7. a) Why physically realizable and stable IIR Filters cannot have linear phase ? Explain
in details. 6
b) How mapping from s - plane to z - plane is done in Bilinear Transformation IIR Filter design method ? Derive the expression using Trapezoidal Formula for
b 2 I1 - z 1)
analog filter given by H(s) =-which should map with s = --
s + a T / -i
1 + z
into digital domain. 12
OR
8. a) Convert the analog Bandpass Filter with system Function Ha(S) =-12-
(S + 0.1) + 9
into digital IIR Filter by use of backward difference for the derivative.Also Find the poles of digital Filter. 6
b) Design Butterworth Filter for specifications given below : 12
0.8< H(eJ")|< 1; 0<<0.2n
< 0.2 ; 0.6n< < n
H(e )
Use impulse invariant transformation method.
9. a) Compare Fixed point and floating point DSP Processors. 8
b) Explain features of TMS320C67XX DSP Processor. 8
OR
10. a) Explain Architecture of TMS320C6XX DSP with neat block diagram. b) Explain SPORT in details w.r.t. TMS320C67XX.
8
11. a) Write Assembly language program for FIR Filter (Low pass) using TMS 320C67XX
Instructions. 8
b) Explain commonly used assembler directives : 8
i) .Short
ii) . int
iii) .Float
iv) .double
OR
12. Explain following assembly instructions w.r.t. TMS320C67XX DSP processor. 16
i) STW . D2 A1, *+A4 [20]
ii) MVKL .S1 x, A4
iii) LDH . D2 *B2++, B7
iv) B .S2 Loopname.
Max. Marks : 100
Time : 3 Hours
Instructions : 1) Answer any 3 questions from each Section.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Your answers will be valued as a whole.
6) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
7) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Explain Q. meter with respect to
i) Principle of working with circuit diagram.
6
4
ii) Two applications.
b) i) Find true r.m.s. value of sine wave with peak to peak voltage 8 volts
super imposed on d.c. voltage of 4 volts.
4
ii) Find true r.m.s value of pulse waveform with Vp = 15 volts, Ton = 1 ms and
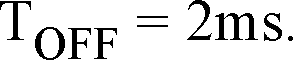
4
OR
2. a) Explain working principle and constructional detail of True RMS meter.
8
10
b) With the help of neat block diagram explain working ofAutomatic Test Equipment
(ATE).
3. a) What is Frequency synthesis ? Explain direct and indirect Frequency synthesis. 12
b) List two differences between function generator and frequency synthesizer. 4 OR P.T.O.
[3563] - 155 -2- 1*35131551*
4. a) With the help of neat block diagram, explain working of function generator. 8
b) Explain working of pulse generator with block diagram. 8
5. a) Explain various sweep modes in cathode ray oscilloscope. 6
b) With neat block diagram explain Digital Storage Oscilloscope. 10
OR
6. a) Explain in detail the Alternate and chop mode used in dual Trace oscilloscope. 6
b) Explain following modes in Digital Storage Oscilloscope. 10
i) Post Trigger Mode
ii) Roll mode
iii) Pre Trigger Mode
SECTION - II
7. Write short notes on any three : 18
i) Specifications of ADC
ii) Dual slope integration type ADC
iii) Sample and hold circuit and its characteristics
iv) Delta pulse modulation type ADC
v) Specifications of DAC.
OR
8. a) Determine resolution and accuracy of 3 bit DAC with IV full scale voltage and
accuracy 0.2 %.
6
12
8
b) Explain variable Frequency typeADC in detail with block schematic and timing diagram.
9. a) With the help of neat block diagram explain Universal Counter.
b) Explain with the help of neat diagram, the autozeroing technique in digital instrument.
OR
10. a) Explain following errors in a conventional counter. 12
i) 1 count error
ii) Time Base error
iii) Trigger error
iv) Systematic error.
b) List any four specifications of electronic counter. 4
11. a) Explain working of Fundamental suppression type distortion meter with block
schematic. 8
b) Write short note on Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM). 8
OR
12. a) What is virtual instrumentation ? Explain any one application of virtual
instrumentation in detail. 8
b) Short note on logic Analyzer. 8
Total Marks: 100
Instructions x I) Answer 3 questions from Section I and 3 questions from
Time: 3 Hours
Section II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of Logarithmic Tables, Slide Rule, Mollier Charts, Electronic Pocket Calculator and Steam Tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. A) Differentiate between the classical methods and instrumental methods for
chemical analysis on the basis of their advantages and disadvantages. Give suitable examples. 8
B) Explain the principle of 8
i) voltametry
ii) coulometry
Also draw the experiment setup of polarography.
OR
2. A) Explain the principle of potentiometry. Also explain zero current potentiometry
and constant current potentiometry. 8
B) Draw a block diagram of typical absorption instrument and explain the function of all components. 8
3. A) State and explain Beer and Lambert law (Derivation is expected).
B) With the help of neat diagram explain ratio recording UV-visible absorption spectrophotometer.
OR
4. A) Explain the principle ofAAS with the help of its spectra at different points of the
instrument. Also draw the block diagram ofAAS.
B) For each individual plane reflection grating, find the missing information in the following table assuming normal incidence and order of grating m =1
Grating Grooves/mm wavelength (nm) Reflection angle (r)
A - 600 26.4
B 1300 300 -
5. A) With the help of neat diagrams explain the fourier transform Infrared
spectrophotometer.
B) With the help of neat diagram explain the direct current plasma.
OR
6. A) Explain the principle, construction and working of flame photometer with the
help of neat diagram.
B) List various sources used in Atomic Emission spectroscopy. Explain AC arc and DC arc excitation sources.
SECTION - II
7. A) With the help of neat block diagram explain the functioning of single beam filter
fluorimeter.
B) With the help of neat diagram explain COp analyser.
OR
8 A) With the help of neat diagram explain NMR spectrometer.
B) With the help of neat block diagram explain Raman spectrophotometer.
9. Explain the principle, construction and working of Gas chromatography. List the detectors used in GC. Explain any one detector. 18
OR
10. Explain the principle of mass spectrometry. List various mass analysers. Explain time of flight mass analyser in detail. 18
11. Write short notes on : 16
a) Differential refractometer
b) Geiger Muller counter.
OR
12. Write short notes on :
a) X-ray diffractometer
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions x I) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
2) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Explain in brief basic principle of producing rotating magnetic field. 4
b) Explain in brief Back EMF and how it regulates the flow of armature current. 4
c) With proper justification explain any two industrial applications of DC series
and compound motor. 8
OR
2. a) What is the difficulty in starting a three phase IM without a starter ? Also, state
the functions of a starter. 4
b) A 6 pole, 50 Hz, Squirrel cage IM runs on load at a shaft speed of 975 rpm. Calculate :
i) The percentage slip
ii) The frequency of induced current in the rotor
iii) The frequency of the rotor currents at standstill
iv) The speed at which the magnetic field of the stator is rotating. 8
c) Explain any four salient features of synchronous motor. 4
3. a) Explain with neat sketch interfacing of a stepper motor with 8051 Microcontroller.
8
b) Explain with neat sketch AC position control system using servomotor. 10
OR
4. a) What is the advantage of a revolving fieldAC generator over that of a stationary
field type ? 4
b) An equal percentage control valve moves from closed to open with five turns of a shaft. The shaft is driven through a 5:1 reducer from a stepping motor of 3.6 degrees per step. If the maximum i/p pulse rate to the motor is 200 steps per second. Find the fastest time for the valve to move from closed to open position.
6
c) State and explain the various losses which takes place in a d.c. generator. 8
5. a) Draw the symbol and state any one application of :
i) Temperature switch
ii) Flow switch
iii) Pressure switch
iv) Level switch. 8 b) Compare relays with contactor and write specifications of Industrial contactors. 8
OR
6. a) Write two specifications and two applications of :
i) Rotary switch
ii) Thumbwheel switch. 8
b) Explain with neat sketch the working of Solid State Relay and give any two
applications. 8
7. a) Explain the following w.r.t MCC
i) Advantages ii) Layout and front panel controls
iii) Power distribution iv) Interlocking 8
b) Draw using standard symbols, EWD for material handing system. Two conveyor belts transfer material from feed hopper to an output wagon. The start sequence is 2-1 and stop sequence is 1-2. Also draw the process diagram. 10
OR
8. a) Explain the following terms :
i) Jogging/Inching ii) Reverse current braking. 8
b) Draw using standard symbols, EWD for the following :
i) DOL starter
ii) Star delta starter. 10
9. a) List different types of special pneumatic cylinders. State application or need of
such cylinders. 6
b) Embossed name plates are to be produced from a thin metal sheet press with a stamping die. The double acting cylinder should extend when both the valves
S1 and S2 are activated simultaneously. The return stroke is to occur automatically only after the forward end position and preset time have been reached to get the consistent quality. The cylinder should immediately retract if emergency push button SQ is pressed. 10
OR
10. a) Draw symbols and explain the basic function of the following pneumatic components :
i) Flow control valve
ii) Check valve
iii) 3/2 Direction control valve
iv) Shuttle valve. 8
b) Draw pneumatic circuits for implementing the following equation
Y a AB + BC + AC A, B and C are manual PB(push buttons)
Output Y is given to single acting cylinder. 8
11. a) Justify the following :
i) Hydraulic systems are not suitable for food application
ii) Pressure relief valve is used in hydraulic power pack
iii) Hydraulic systems are not suitable for long distance transmission
iv) Oil cooler is needed in a hydraulic supply. 8 b) Draw hydraulic circuits for following :
I) Meter in 2) Bleed off. 8
OR
12. a) State advantages of hydraulic system over pneumatic system. 6
b) With the help of neat sketch explain the construction and working of pressure relief valve. Draw hydraulic circuit showing the use of pressure relief valve. 10
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Semester - I) Examination, 2009 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions :1) Answer 3 questions from Section I and 3 questions from Section II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Explain properties of linear convolution. 9 b) Which of the following impulse responses corresponds to stable LTI systems ?
i) hi (t) a e-t cos (2t) u(t)
ii) h2 (n)=ncosnju(n)
iii) hQ@t) a e-(1-2J)t u(t)
iv) h4(n) a 3nu(-n + 10) 8
OR
2. a) Determine and sketch the convolution y(t) a x(t)*h(t) of
x(t) a e-at u(t), a > 0
and h(t) a u(t) 8
b) Determine whether the following signals are periodic. If the signal is periodic determine its fundamental period.
i) x1(t) a jei10t
ii)
b) Identify the ROCs associated with z-transforms of the following
u(-n) + 3 u(n)
i)
u(n) + 7 - u(n)
ii)
v
Find the z-transforms and plot signals as well as ROCs. OR
8
4. a) Determine the inverse Laplace Transform of
2(s + 2)
X(s) =
e{s} > - 3
s + 7s +12
Given that e_at u(t) < L >
e(s) > Re {-a}
8
s + a
b) Determine for each of the following z-transform whether the corresponding signal has an approximately low pass, band pass or high pass characteristic. Also sketch the pole-zero plots
i)
9
5. a) Find the Fourier transform of the system output, if the input and system impulse
responses are
i) x(t) a 4e-t u(t), h(t) a 3e-2t u(t)
ii) x(t) a g(t), h(t) = -e_t/2u(t) 8
b) Determine the Fourier series representation of a square wave of unit amplitude and period T. (Assume even symmetry of square wave). 8
OR
6. a) Prove the following properties of DTFT if
x(n) = < DTFT > X(ej)
i) -jnx(n)< DTFT >-j-X(eJW)
dro
ii) 8
' k=
b) State any four properties of DTFT. 8
SECTION - II
7. a) Define and explain
i) Power spectral density
ii) Auto correlation function 8
b) Determine the autocorrelation of the sequence x(n) a {I, 2, 3, 4, 7}, Use the
graphical method. 9
OR
8. a) Determine the autocorrelation function of
x(t) a e-5t u(t)
Also find its energy spectral density. 9
b) Determine the cross-correlation of
i) x(n) a {I, 2, I, I}, y (n) a {3, 2, I, I}
ii) x(n) a {I, I, 3, 2}, y (n) a {4, 2, I, I} 8
9. a) Define
i) Random variables
ii) Distribution function
iii) Probability density function. 9
b) What are the properties of following ?
i) Distribution function
OR
10. a) Define
i) Mean
ii) Moment
iii) Variance
iv) Standard deviation. 8
b) Let X be a continuous random variable with pdf
fkx, 0 < x <1
[0, otherwise
where k is contant
i) Determine the value of k and sketch fx(x)
ii) Find and sketch the corresponding cdf Fx(x)
-<X< 2 4
iii) Find
11. a) Compare FDM and TDM. 8
b) Explain the Sinusoidal Amplitude in detail with the help of neat diagram. 8
OR
12. a) Compare narrow band frequency modulation and wide band frequency
modulation. 8
b) Explain PAM in detail. 8
T.E. (Instru. and Control) (Semester - I) Examination, 2009 MICROCONTROLLER TECHNIQUES (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
SECTION - I
1. a) Draw and explain power on reset circuit of 8051. What is an external access ? 8
b) Assume internal RAM memory locations 63-69H contains the daily temperature as shown below. Search to see if any of the value equals 33. If the value doesnot exist in the table give its location to R4. Otherwise make R4 a 00.
63H a (25), 64H a (29), 65H a (39), 66H a (34), 67 H a (31), 68H (35), 69H a (33). 8 OR
2. a) Assume that P3 is an input port connected to a sensor. Write a program to read
the sensor output and test it for the value 45. From the test results, place the sensor output value into the registers indicated by the following : if sensor o/p a 45 then place into A a 45 if sensor o/p < 45 then place into R6
if sensor o/p > 45 then place into R7. 8
b) Enlist salient features of 8051 microcontroller. 8
3. a) Explain interrupt structures of 8051. Enlist steps in execution in an interrupt. 8
b) Describe various modes of 8051 timers. 8
OR
4. a) Assuming the clock pulses are fed into pin T write a program for counter 1 in
mode 2 to count the pulses and display the state of the TL1 count on Pp. 8
b) Write a program to transfer the message CONTROL serially at 9600 baud,
8 bit data, 1 stop bit. (Assume FXtal a 11.0592 MHz). 8
5. a) Draw typical interfacing scheme of 4x4 keypad to 8051. Draw the flowchart for
scanning and identifying the pressed key. 10
b) Write assembly language program for detection of keys. 8
OR
Draw the interfacing scheme of DAC @0808). Write a program to generate triangular wave. 10
Draw the interfacing scheme of stepper motor and write a program to rotate it anticlockwise. 8
6. a) b)
7. a) b)
8. a)
b)
9. a) b)
10. a) b)
11. a) b)
12. a) b)
SECTION - II
Draw interfacing scheme of serial ADC to 89C51. Explain how to send control byte and read data byte from serial ADC. 10
Draw and explain interfacing of RTC to 89C51. 8
OR
Design a digital pressure meter for a sensor output 5m%pa for the range of 0 - 50 kPa.
i) Draw the interfacing scheme. 8
ii) Write program for pressure indication. 6 Explain RS232 standards. 4
Draw and explain architecture of PIC 16C6X/7X. 8
Write a program to add two 16 bit no. for PIC microcontroller. 8
OR
Explain Register file structure of PIC 16C6X/7X. 8
Explain following instructions with examples : 8
i) goto label
ii) rrff, F(w)
iii) btfss f, b
iv) xorwf f, F(w).
Explain interrupt structure of PIC 16F8XX. 8
Explain compare mode operation of 16F8XX. 8
OR
Draw the connections used in SPI mode (Single Master/Single Slave Implementation). Describe SSPCON register. 8
Compare SPI and I2 C with suitable applications. 8
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Sem. - II) Examination, 2009 OPTOELECTRONICS INSTRUMENTATION (Old) (1997 Course)
Time : 3 Hours
Marks: 100
Instructions : I) Answer any 3 questions from each Section.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written to separate books.
SECTION - I
1. A) State whether the following statements are true or false and justify :
1) Portable devices uses LCD as display.
2) PLCs I/P, O/P are optoisolated.
3) LED can work as photodetector.
4) Rerated life of incandenscent lamp increases if it is operated below the design voltage.
5) PMT works on UV, Visible and JR region.
B) Define : 6
1) Inrush current.
2) Rerated life.
3) Rerated MSCP.
2. A) Differentiate between : 8
1) LED and LASER Diode.
2) Radiometry and photometry.
B) What is population inversion ? Explain working of He-Ne LASER.
3. A) Explain operation of photomultiplier tube.
8
B) Explain properties of LASER.
8
4. A) Explain working of LED. Draw graphs of LED characteristics. 8 B) Explain solar cell and draw its equivalent ckt. 8
5. Write short notes (any three) : 18
A) Light sources.
B) Photodetectors.
C) Light properties.
D) LCD and LED.
SECTION - II
6. A) Define and derive expression for Numerical Aperture of optical fiber. 8 B) Describe light propagation principle through fiber optic cable. 8
7. A) Compare fiber optic cable transmission and Cu cable transmission. 8 B) Explain analog and digital data transmission using fiber optic cable. 8
8. A) Explain optical measurement techniques for temperature measurement. 8 B) Describe optical power budget in fiber optic communication. 8
9. A) What is dispersion ? State its effects on fiber optic communication. 8
B) Give specifications of Opto-Isolators. State applications of Opto-Isolators. 8
10. Write short notes (any 3) : 18
1) O.T.D.R.
2) Optical power meter.
3) Holography.
4) Spectrum analysers.
B/I/09/50
, , 8
1+z"1 Z 81
Illllllllllllllllllllll [3563] - 160
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Semester - II) Examination, 2009
INDUSTRIAL MANAGEMENT
(2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions x I) Answer three questions from Section I and three questions from Section - II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Define strategic planning. Explain Mergers and Take-overs as a strategic
alternatives with its importance to current business scenario. 12
b) State and explain the concept of Mind - Mapping. 4
OR
2. a) Describe various functions of management. Explain the role of managers to
manage a business enterprise in a competitive market. 10
b) What is Business Process Re-engineering ? Explain its importance to business. 6
3. a) Explain the following quality standards : 8
i) ISO - 9000
ii) ISO - 14,000
b) Define quality. State and explain the concept of statistical process control. 8 OR
4. a) Explain the following concepts : 10
i) Patent management
ii) Business expansion and diversion strategy.
b) Critically explain the WTO agreement and its impact on export and import of India. 6
5. a) A Co. uses a particular component and the annual uses is 36000 based on its
production forecast. The ordering cost is Rs. 200/- per order and inventory carrying cost is estimated at 20% of average annual investment. The cost per one unit of the component is Rs. 10 and safety stock is 3000 units. Assuming 300 working days in a year, determine :
i) Economic order quantity.
ii) No. of orders per year
iii) Inventory cycle.
iv) Total inventory cost and
v) If price increases from Rs. 10/- to Rs. 15/- What would be the EOQ ? 12
b) What is EOQ ? Derive the formula of EOQ. Is it a cost reduction technique ? Explain. 6
OR
6. a) State and explain the objectives, importance of production planning. Do you
consider outsourcing is a part of production planning ? Explain. 10
b) Explain the concept of supply chain management. How it influence the profit of a business enterprise ? 8
7. a) Define Man Power Planning. Explain the functions and process of man power
planning. 8
b) Do you consider Down sizing is a potential measure to reduce cost and increase operational efficiency of business ? Give reasons. 8
OR
8. a) Critically evaluate Maslows need hierarchy theory of motivation. 8
b) State and explain various methods of training. How it influence productivity ? 8
9. a) Explain project costing. What are the various project costs and also explain
how the project report is prepared ? 10
b) Explain the following concepts : 8
i) Net-present value
ii) Pay-back period
iii) Earning per share
iv) Return on Investment.
OR
10. a) What is letter of credit (LOC) ? How it is created ? and explain the procedures
of LOC. 8
b) State and explain how Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss Account evaluate the
performance of a company. 10
11. Explain the following Acts with their salient features : 16
i) Company Act - 1956
ii) Factory Act - 1948
OR
12. Explain the following : 16
i) Value Added Tax
ii) Excise duties
iii) Service Tax
iv) Market Participant Identification Number.
B/I/09/870
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
N.B. : IA Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books. 2A Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3A Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4A Your answers will be valued as a whole.
5A Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. A) Why it is necessary to refer packaging standard while designing an instrument,
explain DIM standard. 8
B) Explain Bureau of Indian Standard and NEMA Standard. 8
OR
2. A) Is it true that, quality and reliability has inter-related to design of an instrument ?
Justify it. 8
B) Explain the selection of IP third number which protect against mechanical impacts, also explain IP 64. 8
3. A) Explain electrostatic discharge with the reference to Human Body Model. 6
B) Why burst noise is also called as Popcorn noise, where it was first discovered ? 4
C) Compare contact noise with thermal noise. 6
OR
4. A) Prove that thermal noise is a universal function and independent of the
composition of resistance. 8
B) Grounds fall into which two categories, explain multipoint ground system. 8
5. A) With the help of diagram, explain the method of offset (zero) and span
adjustment in XTR - 110, precision voltage to current converter. 8
B) I) Find servo gain (K1), when forward current IF a 10 mA and servo photo
current Ip1 a 70 ju A at temperature 25C. 4
OR
6. A) 1) What is the output voltage of AD 595 when 200C temperature is applied to
pin no. 1 and 14 through Chromel Alumel thermocouple, while output voltage of this thermocouple is observed to be 8.137 mV ? 6
2) What caution should take while testing AD 595 or AD 594 ? 4
B) 1) What are the advantages of AD 620 over conventional 3-Op-Amp
instrumentation amplifier ? 2
2) Draw and explain simplified schematic ofAD 620. 6
SECTION - II
7. Explain test circuit diagram and timing diagram of ICM 7217 A with following functions. 18
|
1) |
SCAN |
2) |
|
3) |
EQUAL |
4) |
|
5) |
BCD I/O |
6) |
OR
8. 1) How many phase comparators are used in CD 4046 B, explain function of
phase comparator - II (edge-controlled) ? 9
2) Explain any one application of CD 4046 B. 9
9. 1) How digital PCBs problems can help to overcome by proper value of wave
impedance zero ? 8
2) Explain BERGERON reflection chart for reflections. 8 OR
10. 1) Explain general considerations of layout check. 4
2) What are the types of soldering fluxes, according to the nature of their residues ? 4
3) Explain wave soldering. 8
11. 1) Explain catastrophic failures using failure rate curve. 8
OR
12. 1) Explain manufacturing costs against reliability. 8
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Sem. - II) Examination, 2009 PROCESS LOOP COMPONENTS (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80
Instructions : I) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
P) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Draw the standard symbols for following :
10
i) Pneumatic signal line
ii) Temperature indicator and controller
iii) Level transmitter
iv) Pneumatically operated control valve
v) Level Alarm High/Low.
b) List various components of typical process control loop located in field area and control from area. Indentify different standard transmission signals.
8
OR
2. a) Design signal conditioning for following application sensor used : J type T/C.
Input temperature range : Ambient to 500oC
Output : 0 to 5 V DC.
Reference junction temp. : 0oC
12
|
Temperature (Hot junction) |
mV |
|
0 C |
0 |
|
Ambient |
1.5 |
|
500 C |
27.39 |
b) Give the advantages of current transmission over voltage transmission. What is need for standard signal ? 6
3. a) Explain following w.r.t. I/P convertor :
i) Need/Application
ii) Construction
iii) Calibration
Draw suitable diagram.
b) Draw and explain block diagram of SMART transmitter and state its advantages.
c) Explain various lags involved in process.
OR
4. a) Explain difference betn transmitter and converters. Give application of P-I
converter.
b) Explain zero elevation and zero suppression with respect to DPT for level measurement.
c) Give the specification of pressure transmitter.
5. a) Explain with neat sketch rate before reset action.
b) Explain effects of process reaction rate and dead time on On-off control action and on P-control action.
OR
6. a) Explain block diagram of digital controler. Explain front facia of digital controller.
b) What is mean by tunning of controller ? List various methods of controller tunning. Explain any one in detail.
SECTION - II
7. a) List and explain 3 typical modes of operation of PLC.
b) A pump is to be used to fill 2 storage tanks. The pump is manually started by the operator from a START/STOP station. When the first tank is full, the control logic must stop flow to first tank and direct flow to the second tank with the help of solenoid valve. When second tank is full, the pump must shut down automatically. Indicator lamps are to be included to signal when each tank is full. Draw sketch of the process. Prepare a typical relay ladder diagram for the same. OR
8. a) With the help of neat block diagram, list 4 tasks performed by an input module.
Also list important specifications of input module. 8
b) Develop PLC ladder diagram for the following when START button is pushed, a single acting pneumatic cylinder starts reciprocating automatically and continuously until stop push button is pressed. Comment on inerfacing of PLC to pneumatics. 10
9. a) List different selection criteria for control valve. 8
b) A control valve operates from a 3 to 15 psi control signal to have a 40 gal/min flow rate, express the signal in both psi and in % of range if :
i) It is a linear valve from 0 to 90 gal/min.
ii) It is a equal percentage with R a 6 Q . a 15 gal/min. 8
OR
10. a) Comment of the following statement Valve positioner enhance the performance
of control value. 8
b) Suppose a pressure of 90 KPa is applied to the diaphragm of the control valve
to open it. The area of the diaphragm is 30 cm2. Find the force generated. 4
c) Define the term Cv. State its significance. 4
11. a) Explain significance of square root extractor with reference to DPT. 8
b) Explain the front panel controls of Alarm Annunciator. Also give the standard ISA sequences for Alarm Annunciator. 8
OR
12. Write short notes on (any two) : 16
i) Flow totaliser
ii) Dampers
iii) High/low selector.
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions : I) Answer any three questions from each Section.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. Explain different types of Unit Operations involved in sugar industries with flow sheet symbols.
OR
2. Explain in detail about the following :
a) Dryer and its types
b) Distillation. 16
3. Explain the types of reactions in detail. Compare different types of reactors. 16
OR
4. Explain the laws of thermodynamics in detail. Explain the role of kinetics in chemical industries. 16
5. Derive the material and energy balance equation of boiler and heat exchanger. 18
OR
6. Explain the following terms :
1) Cooling tower
2) Evaporators
3) Refrigeration. 18
SECTION - II
7. What is size separation and screening ? Explain different types of separators in detail. 16
OR
8. What is froth floatation ? Explain it in detail. Also explain hydrocyclone. 16
9. Explain corrosion and its protection techniques in detail. 16
OR
10. a) What are the aspects to be consider while selecting metals and alloys in
construction of field instruments ? 8
b) Explain any two types of hardness testing method. 8
11. Explain with flow sheet diagram about manufacturing of Urea from Ammonium Carbonate. 18
OR
12. Define pulp and its production methods. Explain with flow sheet diagram about the making of paper from pulp using sulphate. 18
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control Engg.) (Semester - II) Examination, 2009 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions : 1) Answer 3 questions from Section - I and 3 questions from Section - II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Compare Digital Signal processing with analog signal processing in details. 8 b) Determine the output response of the relaxed system characterized by the impulse
(1Y
response h(n)= u(n) to the input signal x(n) = 2n u(n).Also find magnitude
V 2 )
and phase response of the system. 8
OR
2. a) Determine and sketch magnitude and phase response of
y(n) = 1 [x(n) + x (n - 2)]. 8
2
b) Obtain cascade form and parallel form realization following system. 8
y(n) = - 0.1 y(n - 1) + 0.2 y(n - 2) + 3 x(n) + 3.6 x (n - 1) + 0.6 x (n - 2).
3. a) Explain following properties of Discrete Fourier Transform 8
i) periodicity
ii) Linearity
iii) Symmetry
iv) Multiplication of two DFTS.
xi(n) = j 1 j x2(n) = j 4 j. Use Basic formula of circular
convolution. 8
OR
4. a) Find fast fourier transform of following input sequence using decimation in
Frequency algorithm. 8
x (n) = 2n ; 0 < n 7 = 0 ; otherwise
b) Explain the Goertzel Algorithm in details. 8
5. a) Give advantages and disadvantages of digital filters. 4
b) Compare Finite Impulse Response Filters with Infinite Impulse Response Filters. 4
c) Determine the FIR Filter coefficient for M = 7 for Following desired response specifications : 10
Use Blackmanns window. Find frequency response of designed filter.
OR
6. a) Explain Gibbs phenomenon in details.
6
b) Design a Bandpass Filter which approximates the ideal Filter with cut off frequencies at 0.2 rad/sec and 0.3 rad/sec. The filter order is M = 7. Use the Hanning window Function. Also find Magnitude and phase of designed
II351315HI -3- [3563] - 156
SECTION - II
7. a) Why physically realizable and stable IIR Filters cannot have linear phase ? Explain
in details. 6
b) How mapping from s - plane to z - plane is done in Bilinear Transformation IIR Filter design method ? Derive the expression using Trapezoidal Formula for
b 2 (1 - z 1)
analog filter given by H(s) =-which should map with s = --
s + a T -1
1 + z
into digital domain. 12
OR
8. a) Convert the analog Bandpass Filter with system Function Ha(S) =--
(S + 0.1) + 9
into digital IIR Filter by use of backward difference for the derivative.Also Find the poles of digital Filter. 6
b) Design Butterworth Filter for specifications given below : 12
0.8< H(eJ")|< 1; 0<<0.2n
<0.2 ; 0.6n< < n
H(e )
Use impulse invariant transformation method.
9. a) Compare Fixed point and floating point DSP Processors. 8
b) Explain features of TMS320C67XX DSP Processor. 8
OR
10. a) Explain Architecture of TMS320C6XX DSP with neat block diagram. b) Explain SPORT in details w.r.t. TMS320C67XX.
8
11. a) Write Assembly language program for FIR Filter (Low pass) using TMS 320C67XX
Instructions. 8
b) Explain commonly used assembler directives : 8
i) .Short
ii) . int
iii) .Float
iv) .double
OR
12. Explain following assembly instructions w.r.t. TMS320C67XX DSP processor. 16
i) STW . D2 A1, *+A4 [20]
ii) MVKL .S1 x, A4
iii) LDH . D2 *B2++, B7
iv) B .S2 Loopname.
Max. Marks : 100
Time : 3 Hours
Instructions : 1) Answer any 3 questions from each Section.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Your answers will be valued as a whole.
6) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
7) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Explain Q. meter with respect to
i) Principle of working with circuit diagram.
6
4
ii) Two applications.
b) i) Find true r.m.s. value of sine wave with peak to peak voltage 8 volts
super imposed on d.c. voltage of 4 volts.
4
ii) Find true r.m.s value of pulse waveform with Vp = 15 volts, Ton = 1 ms and

OR
2. a) Explain working principle and constructional detail of True RMS meter.
8
10
b) With the help of neat block diagram explain working ofAutomatic Test Equipment
(ATE).
3. a) What is Frequency synthesis ? Explain direct and indirect Frequency synthesis. 12
b) List two differences between function generator and frequency synthesizer. 4 OR P.T.O.
4. a) With the help of neat block diagram, explain working of function generator. 8 b) Explain working of pulse generator with block diagram. 8
5. a) Explain various sweep modes in cathode ray oscilloscope. 6
b) With neat block diagram explain Digital Storage Oscilloscope. 10
OR
6. a) Explain in detail the Alternate and chop mode used in dual Trace oscilloscope. 6
b) Explain following modes in Digital Storage Oscilloscope. 10
i) Post Trigger Mode
ii) Roll mode
iii) Pre Trigger Mode
SECTION - II
7. Write short notes on any three : 18
i) Specifications of ADC
ii) Dual slope integration type ADC
iii) Sample and hold circuit and its characteristics
iv) Delta pulse modulation type ADC
v) Specifications of DAC.
OR
8. a) Determine resolution and accuracy of 3 bit DAC with IV full scale voltage and
accuracy 0.2 %.
6
12
8
b) Explain variable Frequency typeADC in detail with block schematic and timing diagram.
9. a) With the help of neat block diagram explain Universal Counter.
b) Explain with the help of neat diagram, the autozeroing technique in digital instrument.
OR
10. a) Explain following errors in a conventional counter. 12
i) 1 count error
ii) Time Base error
iii) Trigger error
iv) Systematic error.
b) List any four specifications of electronic counter. 4
11. a) Explain working of Fundamental suppression type distortion meter with block
schematic. 8
b) Write short note on Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM). 8
OR
12. a) What is virtual instrumentation ? Explain any one application of virtual
instrumentation in detail. 8
b) Short note on logic Analyzer. 8
Total Marks: 100
Instructions x I) Answer 3 questions from Section I and 3 questions from
Time: 3 Hours
Section II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of Logarithmic Tables, Slide Rule, Mollier Charts, Electronic Pocket Calculator and Steam Tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. A) Differentiate between the classical methods and instrumental methods for
chemical analysis on the basis of their advantages and disadvantages. Give suitable examples. 8
B) Explain the principle of 8
i) voltametry
ii) coulometry
Also draw the experiment setup of polarography.
OR
2. A) Explain the principle of potentiometry. Also explain zero current potentiometry
and constant current potentiometry. 8
B) Draw a block diagram of typical absorption instrument and explain the function of all components. 8
3. A) State and explain Beer and Lambert law (Derivation is expected).
B) With the help of neat diagram explain ratio recording UV-visible absorption spectrophotometer.
OR
4. A) Explain the principle ofAAS with the help of its spectra at different points of the
instrument. Also draw the block diagram ofAAS.
B) For each individual plane reflection grating, find the missing information in the following table assuming normal incidence and order of grating m =1
Grating Grooves/mm wavelength (nm) Reflection angle (r)
A - 600 26.4
B 1300 300 -
5. A) With the help of neat diagrams explain the fourier transform Infrared
spectrophotometer.
B) With the help of neat diagram explain the direct current plasma.
OR
6. A) Explain the principle, construction and working of flame photometer with the
help of neat diagram.
B) List various sources used in Atomic Emission spectroscopy. Explain AC arc and DC arc excitation sources.
SECTION - II
7. A) With the help of neat block diagram explain the functioning of single beam filter
fluorimeter.
B) With the help of neat diagram explain COp analyser.
OR
8 A) With the help of neat diagram explain NMR spectrometer.
B) With the help of neat block diagram explain Raman spectrophotometer.
9. Explain the principle, construction and working of Gas chromatography. List the detectors used in GC. Explain any one detector. 18
OR
10. Explain the principle of mass spectrometry. List various mass analysers. Explain time of flight mass analyser in detail. 18
11. Write short notes on : 16
a) Differential refractometer
b) Geiger Muller counter.
OR
12. Write short notes on :
a) X-ray diffractometer
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions x I) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
2) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3) Black figures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Explain in brief basic principle of producing rotating magnetic field. 4
b) Explain in brief Back EMF and how it regulates the flow of armature current. 4
c) With proper justification explain any two industrial applications of DC series
and compound motor. 8
OR
2. a) What is the difficulty in starting a three phase IM without a starter ? Also, state
the functions of a starter. 4
b) A 6 pole, 50 Hz, Squirrel cage IM runs on load at a shaft speed of 975 rpm. Calculate :
i) The percentage slip
ii) The frequency of induced current in the rotor
iii) The frequency of the rotor currents at standstill
iv) The speed at which the magnetic field of the stator is rotating. 8
c) Explain any four salient features of synchronous motor. 4
3. a) Explain with neat sketch interfacing of a stepper motor with 8051 Microcontroller.
8
b) Explain with neat sketch AC position control system using servomotor. 10
OR
4. a) What is the advantage of a revolving fieldAC generator over that of a stationary
field type ? 4
b) An equal percentage control valve moves from closed to open with five turns of a shaft. The shaft is driven through a 5:1 reducer from a stepping motor of 3.6 degrees per step. If the maximum i/p pulse rate to the motor is 200 steps per second. Find the fastest time for the valve to move from closed to open position.
6
c) State and explain the various losses which takes place in a d.c. generator. 8
5. a) Draw the symbol and state any one application of :
i) Temperature switch
ii) Flow switch
iii) Pressure switch
iv) Level switch. 8 b) Compare relays with contactor and write specifications of Industrial contactors. 8
OR
6. a) Write two specifications and two applications of :
i) Rotary switch
ii) Thumbwheel switch. 8
b) Explain with neat sketch the working of Solid State Relay and give any two
applications. 8
7. a) Explain the following w.r.t MCC
i) Advantages ii) Layout and front panel controls
iii) Power distribution iv) Interlocking 8
b) Draw using standard symbols, EWD for material handing system. Two conveyor belts transfer material from feed hopper to an output wagon. The start sequence is 2-1 and stop sequence is 1-2. Also draw the process diagram. 10
OR
8. a) Explain the following terms :
i) Jogging/Inching ii) Reverse current braking. 8
b) Draw using standard symbols, EWD for the following :
i) DOL starter
ii) Star delta starter. 10
9. a) List different types of special pneumatic cylinders. State application or need of
such cylinders. 6
b) Embossed name plates are to be produced from a thin metal sheet press with a stamping die. The double acting cylinder should extend when both the valves S1 and S2 are activated simultaneously. The return stroke is to occur automatically only after the forward end position and preset time have been reached to get the consistent quality. The cylinder should immediately retract if emergency push button SQ is pressed. 10
OR
10. a) Draw symbols and explain the basic function of the following pneumatic components :
i) Flow control valve
ii) Check valve
iii) 3/2 Direction control valve
iv) Shuttle valve. 8
b) Draw pneumatic circuits for implementing the following equation
Y a AB + BC + AC A, B and C are manual PB(push buttons)
Output Y is given to single acting cylinder. 8
11. a) Justify the following :
i) Hydraulic systems are not suitable for food application
ii) Pressure relief valve is used in hydraulic power pack
iii) Hydraulic systems are not suitable for long distance transmission
iv) Oil cooler is needed in a hydraulic supply. 8 b) Draw hydraulic circuits for following :
I) Meter in 2) Bleed off. 8
OR
12. a) State advantages of hydraulic system over pneumatic system. 6
b) With the help of neat sketch explain the construction and working of pressure relief valve. Draw hydraulic circuit showing the use of pressure relief valve. 10
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Semester - I) Examination, 2009 SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
Instructions :1) Answer 3 questions from Section I and 3 questions from Section II.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
1. a) Explain properties of linear convolution. 9 b) Which of the following impulse responses corresponds to stable LTI systems ?
i) hi (t) a e-t cos (2t) u(t)
ii) h2 (n)=ncosnju(n)
iii) hQ@t) a e-(1-2J)t u(t)
iv) h4(n) a 3nu(-n + 10) 8
OR
2. a) Determine and sketch the convolution y(t) a x(t)*h(t) of
x(t) a e-at u(t), a > 0
and h(t) a u(t) 8
b) Determine whether the following signals are periodic. If the signal is periodic determine its fundamental period.
i) x1(t) a jei10t
ii)
b) Identify the ROCs associated with z-transforms of the following
u(-n) + 3 u(n)
i)
/'jY*
u(n) + 7 - u(n)
ii)
v
Find the z-transforms and plot signals as well as ROCs. OR
8
4. a) Determine the inverse Laplace Transform of
2(s + 2)
X(s) =
e{s} > - 3
s + 7s +12
Given that e_at u(t) < L >
e(s) > Re {-a}
8
s + a
b) Determine for each of the following z-transform whether the corresponding signal has an approximately low pass, band pass or high pass characteristic. Also sketch the pole-zero plots
i)
9
5. a) Find the Fourier transform of the system output, if the input and system impulse
responses are
i) x(t) a 4e-t u(t), h(t) a 3e-2t u(t)
ii) x(t) a g(t), h(t) = -e_t/2u(t) 8
b) Determine the Fourier series representation of a square wave of unit amplitude and period T. (Assume even symmetry of square wave). 8
OR
6. a) Prove the following properties of DTFT if
x(n) = < DTFT > X(ej)
i) -jnx(n)< DTFT >-j-X(eJW)
dro
ii) 8
' k=
b) State any four properties of DTFT. 8
SECTION - II
7. a) Define and explain
i) Power spectral density
ii) Auto correlation function 8
b) Determine the autocorrelation of the sequence x(n) a {1, 2, 3, 4, 7}, Use the
graphical method. 9
OR
8. a) Determine the autocorrelation function of
x(t) a e-5t u(t)
Also find its energy spectral density. 9
b) Determine the cross-correlation of
i) x(n) a {1, 2, 1, 1}, y (n) a {3, 2, 1, 1}
ii) x(n) a {1, 1, 3, 2}, y (n) a {4, 2, 1, 1} 8
9. a) Define
i) Random variables
ii) Distribution function
iii) Probability density function. 9
b) What are the properties of following ?
i) Distribution function
OR
10. a) Define
i) Mean
ii) Moment
iii) Variance
iv) Standard deviation. 8
b) Let X be a continuous random variable with pdf
fkx, 0 < x <1
[0, otherwise
where k is contant
i) Determine the value of k and sketch fx(x)
ii) Find and sketch the corresponding cdf Fx(x)
-<X< 2 4
iii) Find
11. a) Compare FDM and TDM. 8
b) Explain the Sinusoidal Amplitude in detail with the help of neat diagram. 8
OR
12. a) Compare narrow band frequency modulation and wide band frequency
modulation. 8
b) Explain PAM in detail. 8
T.E. (Instru. and Control) (Semester - I) Examination, 2009 MICROCONTROLLER TECHNIQUES (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 100
SECTION - I
1. a) Draw and explain power on reset circuit of 8051. What is an external access ? 8
b) Assume internal RAM memory locations 63-69H contains the daily temperature as shown below. Search to see if any of the value equals 33. If the value doesnot exist in the table give its location to R4. Otherwise make R4 a 00.
63H a (25), 64H a (29), 65H a (39), 66H a (34), 67 H a (31), 68H (35), 69H a (33). 8 OR
2. a) Assume that P3 is an input port connected to a sensor. Write a program to read
the sensor output and test it for the value 45. From the test results, place the sensor output value into the registers indicated by the following : if sensor o/p a 45 then place into A a 45 if sensor o/p < 45 then place into R6
if sensor o/p > 45 then place into R7. 8
b) Enlist salient features of 8051 microcontroller. 8
3. a) Explain interrupt structures of 8051. Enlist steps in execution in an interrupt. 8 b) Describe various modes of 8051 timers. 8
OR
4. a) Assuming the clock pulses are fed into pin T write a program for counter 1 in
mode 2 to count the pulses and display the state of the TL1 count on Pp. 8
b) Write a program to transfer the message CONTROL serially at 9600 baud,
8 bit data, 1 stop bit. (Assume FXtal a 11.0592 MHz). 8
5. a) Draw typical interfacing scheme of 4x4 keypad to 8051. Draw the flowchart for
scanning and identifying the pressed key. 10
b) Write assembly language program for detection of keys. 8
OR
Draw the interfacing scheme of DAC (0808). Write a program to generate triangular wave. 10
Draw the interfacing scheme of stepper motor and write a program to rotate it anticlockwise. 8
6. a) b)
7. a) b)
8. a)
b)
9. a) b)
10. a) b)
11. a) b)
12. a) b)
SECTION - II
Draw interfacing scheme of serial ADC to 89C51. Explain how to send control byte and read data byte from serial ADC. 10
Draw and explain interfacing of RTC to 89C51. 8
OR
Design a digital pressure meter for a sensor output 5m%pa for the range of 0 - 50 kPa.
i) Draw the interfacing scheme. 8
ii) Write program for pressure indication. 6 Explain RS232 standards. 4
Draw and explain architecture of PIC 16C6X/7X. 8
Write a program to add two 16 bit no. for PIC microcontroller. 8
OR
Explain Register file structure of PIC 16C6X/7X. 8
Explain following instructions with examples : 8
i) goto label
ii) rrff, F(w)
iii) btfss f, b
iv) xorwf f, F(w).
Explain interrupt structure of PIC 16F8XX. 8
Explain compare mode operation of 16F8XX. 8
OR
Draw the connections used in SPI mode (Single Master/Single Slave Implementation). Describe SSPCON register. 8
Compare SPI and I2 C with suitable applications. 8
T.E. (Instrumentation and Control) (Sem. - II) Examination, 2009 OPTOELECTRONICS INSTRUMENTATION (Old) (1997 Course)
Time : 3 Hours
Marks : 100
Instructions : I) Answer any 3 questions from each Section.
2) Answers to the two Sections should be written to separate books.
SECTION - I
1. A) State whether the following statements are true or false and justify :
1) Portable devices uses LCD as display.
2) PLCs I/P, O/P are optoisolated.
3) LED can work as photodetector.
4) Rerated life of incandenscent lamp increases if it is operated below the design voltage.
5) PMT works on UV, Visible and JR region.
B) Define : 6
1) Inrush current.
2) Rerated life.
3) Rerated MSCP.
2. A) Differentiate between : 8
1) LED and LASER Diode.
2) Radiometry and photometry.
B) What is population inversion ? Explain working of He-Ne LASER.
3. A) Explain operation of photomultiplier tube.
8
B) Explain properties of LASER.
8
4. A) Explain working of LED. Draw graphs of LED characteristics. 8 B) Explain solar cell and draw its equivalent ckt. 8
5. Write short notes (any three) : 18
A) Light sources.
B) Photodetectors.
C) Light properties.
D) LCD and LED.
SECTION - II
6. A) Define and derive expression for Numerical Aperture of optical fiber. 8 B) Describe light propagation principle through fiber optic cable. 8
7. A) Compare fiber optic cable transmission and Cu cable transmission. 8 B) Explain analog and digital data transmission using fiber optic cable. 8
8. A) Explain optical measurement techniques for temperature measurement. 8 B) Describe optical power budget in fiber optic communication. 8
9. A) What is dispersion ? State its effects on fiber optic communication. 8
B) Give specifications of Opto-Isolators. State applications of Opto-Isolators. 8
10. Write short notes (any 3) : 18
1) O.T.D.R.
2) Optical power meter.
3) Holography.
4) Spectrum analysers.
B/I/09/50
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
