University of Pune 2009-1st Sem B.E Instrumentation and Control Engineering .(Instrumentation) s - Question Paper
Total No. of Questions : 12] [Total No. of Pages : 2
[35641 - 244 P1160 B.E. (Instru.) PROJECT ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT (1997 & 2003 Course)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks :100
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer three questions from section I and three questions from section II.
2) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
3) Pigures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QI) a) Explain the following standards. [8]
- ISA
- ANSI
- NEMA
- API
b) With an example explain the term Degree of Automation. [8]
OR
Q2) a) With an example explain the term Project Statement. [8]
b) Explain the following standards. [8]
- ISA
- ANSI
- NEMA
- API
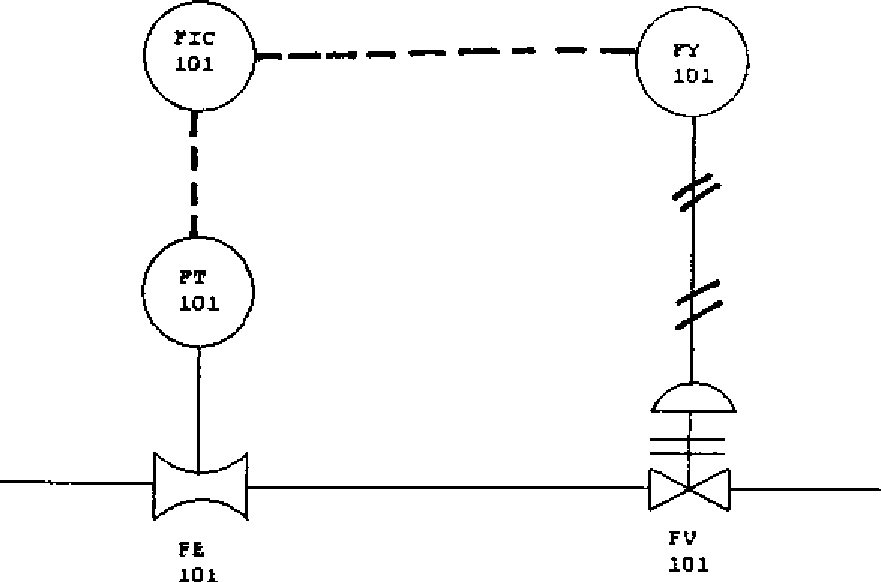
Q3) a) For the following figure I give the naming conventions as per ISA standard.
i) For loop ii) For instruments. [4]
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
sCfe sCfe sCfe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
P1159 t3564! - 243 B.E. (Instrumentation & Control) PROCESS INSTRUMENTATION -1 (2003 Course) (406261)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks :100
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer three questions from section I and three questions from section II.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Pigures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QI) a) Elaborate control valve selection criteria. [8]
b) With the help of necessary equations explain control valve actuator design.
[8]
OR
Q2) a) Explain the various sources of noise in a control valve and the methods to reduce them. [10]
b) Level is being controlled in a tank. The flow range is 100 to 1,000 gpm. The liquid is mineral oil and has a specific gravity of 0.88. Line pressure is 100 to 150 psi and the throttling pressure drop varies from 50 to 110 psi. The temperature may vary from 70 to 140 0F.
Size the control valve and select a characteristic type that will satisfy the process. [6]
Q3) a) With a suitable example explain why single capacity processes are easy to control. [8]
b) List various non-linear elements in a control loop and explain any two of them. [8]
OR
b) Derive the equation for the time constant of a process having single time constant. [8]
Q5) a) Compare feedback and feed forward control. [9]
b) With suitable example justify the use of selective control in process equipment protection. [9]
OR
Q6) a) What is Split Range Control? Explain with suitable application. [9] b) Explain the working and use of Ratio control. [9]
SECTION - II
Q7) a) Explain the functional blocks of SLPC in detail. [8]
b) Explain the features of MLPC. [8]
OR
Q8) What is the need of analyzing process control loops? Explain the procedure to test flow control loop. Derive necessary mathematical equations. [16]
Q9) a) Compare conventional and Intelligent controllers. [8]
b) What are the advantages, limitations and applications of a self tuning controller. [8]
OR
QI0) a) With the help of a suitable block diagram explain. What is MRAC? [8] b) What is predictive control? Explain its uses. [8]
QII) a) With the help of block schematic explain the working of FUZZY controller . [9]
b) Explain Dynamic matrix control with reference to its applicability. [9]
OR
Q12) a) Explain the role of ANN to enhance performance of process. [9]
b) List applications ofSPC. [9]
B.E. (Instrumentation) POWER PLANT INSTRUMENTATION (2003 Course)
Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 100
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer 3 questions from section-I and 3 questions from section-II.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QV What are various forms of energy? Explain it major sources in detail with respect to India. [16]
OR
Q2) What is the meaning of distance protection, Islanding? How it is achieved?
[16]
Q3) a) What are the various components used in steam generation? Draw neat sketch of steam generator. [10]
b) Enlist various auxiliaries associated with it. [6]
OR
Q4) Draw the neat sketches and explain in brief : [16]
a) Natural Circulation Boiler.
b) Forced Circulation Boiler.
c) Once Through Boiler.
d) Combined circulation Boiler.
Q5) a) Explain the Instrumentation system for controlling boiler drum level using three elements? Also enlist other elements to be incorporated to make it four and five element drum level control system. [12]
b) What is coal benefication? Explain with neat diagram of the same. [6]
OR
Why it is essential to measure thermal stress? How it is measured? [9] Explain with neat sketch the method to control the same. [9]
Explain working of Pressurized water rector (PWR) with neat sketch. [8]
Q7) a)
b)
Q8) a)
b)
c)
Q9) a)
b)
QIO) a)
b)
QII) a)
b)
Q12) a)
b)
A small generating plant of 100 kW capacity uses gas of calorific value 1000 kCal/m3. The overall efficiency of plant is 20% determine the volume of gas required per hour when plant is running at full load. [8]
OR
Draw a neat sketch of BWR? [4]
Explain Boiling water reactor power plant? [6]
State its advantages and disadvantages? [6]
Why efficiency of a Power Plant needs to be measured? How it is measured? What are various methods to improve the efficiency of the power plant? [8]
What are the most concerned pollutants from fossil fuel and Nuclear power plants? Explain their effect on environment and Human being. [8]
OR
What is the role of ESP? Explain its working with neat sketch. [8]
What is Energy Audit? Why it is required? What are various energy conservation measures? [8]
Draw and explain Solar Thermal Central Receiver System power plant.
[9]
Write advantages and disadvantages of wind power plant. [9]
OR
Explain with neat sketch Simple Single-Pool and Two-Pool Tidal system for power generation in brief. [9]
How energy can be stored? Enlist various methods of storage of energy? Discuss types battery storage in brief. [9]
[3564] - 72 B.E. (IE) SOFTWARE ENGINEERING (1997 Course)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks:100
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer any 3 questions from each section.
2) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QI) Explain S/W engg. myths. What is the reality? [16]
Q2) Explain water fall process model 8 compare it with others. [16]
Q3) Explain any one S/W estimation technique. [16]
Q4) What is the need of FTR (formal technical reviews)? What are guidelines for conducting FTR. [16]
Q5) Write notes on : [18]
a) S/W Architecture styles.
b) S/W risks.
SECTION - II
Q6) What is S/W risk? Explain RMMM. [16]
Q7) Why is testing necessary? In which stages of SDLC is the testing carried out? 8 why. [16]
Q8) Explain any one S/W testing technique. [16]
a) White box.
b) Black box.
c) System testing.
Q9) What is S/W quality? How is it measured. [16]
QI 0) Write notes on (any two): [18]
a) S/W CASE tools.
b) Forward engg.
c) Reverse engg.
d) Debugging 8 Antibugging.
[3564] - 68 B.E. (IE) COMPUTER TECHNIQUES (1997 Course)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. MarksxIOO
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer any 3 questions from each section.
2) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QV What are the advantages of parallel processing over sequential processing? State the applications in detail. [16]
Q2) Give three classification schemes of parallel processing with examples. merits and demerits. [16]
Q3) Compare TCP/IP with ISO-OSI model. by giving details of each. [16]
Q4) Explain array processors with block diagrams. case studies. [16]
Q5) Write notes on : [18]
a) Super computers.
b) Data flow computers.
Q6) Explain all the generations of mobile communication. (telephone system). [16]
Q7) Write shell program for menu driven file commands for. [16]
a) File Delete.
b) File Copy.
c) Compare.
Q9) Explain any one network security method. [16]
a) DES.
b) SSL.
c) PGP.
QI0) Write notes on (any two): [18]
a) Neural n/w computing.
b) Computerviruses.
c) Network topologies.
[3564] - 256 B.E. (Instrumentation) PROCESS MODELING & OPTIMIZATION (2003 Course)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks:100
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer 3 questions from Section I and 3 questions from Section II.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
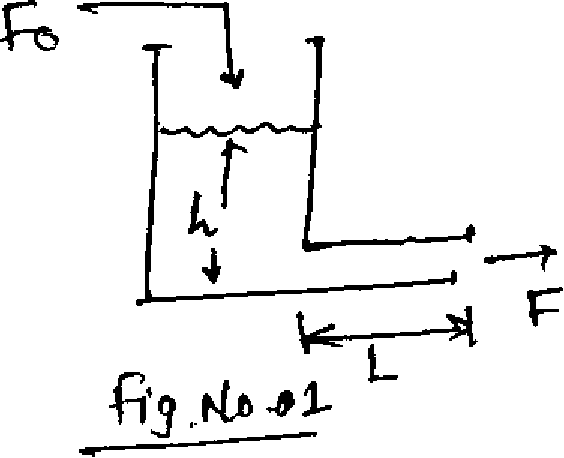
Find the model of liquid storage process as shown in Figure No. 01. Where,
QI) a)
L = Length of exit line A = Exit line cross-sectional area p
A = Tank cross-sectional area.
[8]
Fit the data to the model, y = aH + ax + a2x2 Data :
b)
|
x |
y |
|
1 |
9.80 |
|
3 |
13.0 |
|
6 |
9.10 |
|
8 |
0.60 |
By using Lagrange interpolation method.
[8]
OR
Q2) a) Find the mathematical model of field controlled D.C. Motor. [8] b) Consider the CSTR system shown in figure No. 02. [8]
Assume :
Perfectly mixed liquid.
Chemical reaction takes.
Place in liquid : A > B Find the model of given system.
a
J
<SL
T
Q3) a) Find the model of Vaporizer as sketched in fig. No. 03. [9]
Where,
Q = Rate of beat added
Wv = Liquid vaporising rate
F = Flow rate of gas coming out of drum.
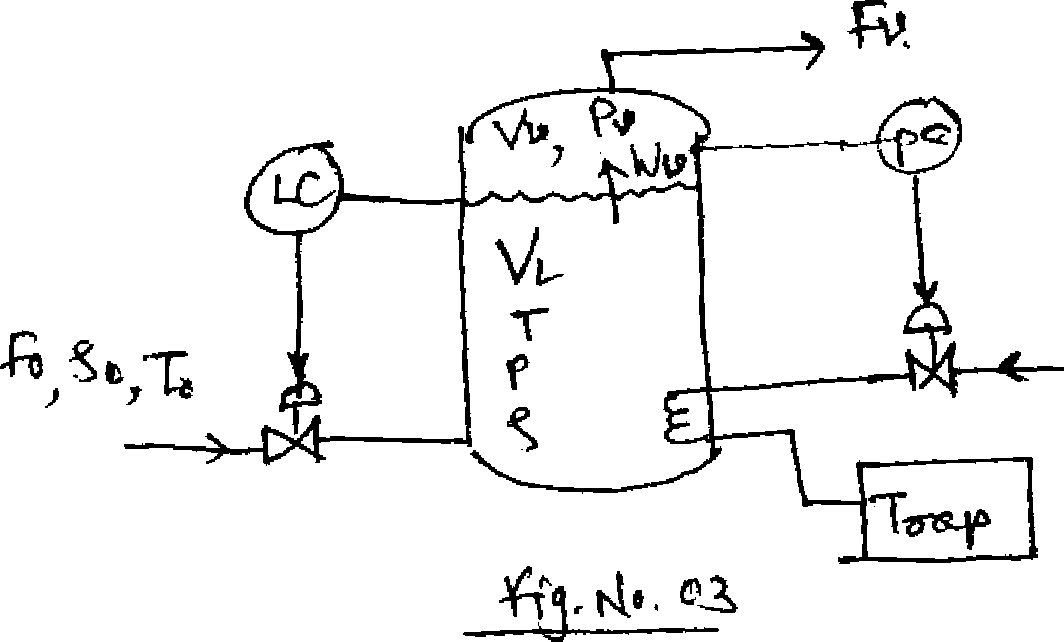
b) Consider a reactor sketched in fig .No. 04. A reactor is filled with reacting gasses. k [9]
A reversible reaction occures : A
B Where
h
Si
cs
ft
So-
6
Where,
FQ, Fj = Volumetric flow rates, p0, Pj = Densities YQ, Yj = Mole fraction of Reactant A, P = Pressure inside reactor T = Temp, is constant, V = Volume of reactor, Ph = Vessel press. Find model of given system.
OR
Derive the model of series of 3-CSTRs as shown in figure No. 05. [9] Assume :
i) Temperature, volumes are constant
ii) Reaction in 3-CSTRs is A B
L3
|
Ca-l |
|
b) Consider the liquid-level system shown in figure No. 06. In the system Qj and Q2 are steady-state in flow rates and Hj and H2 are steady-
state heads. The quantities qn, qi2, hp h2, qp q0 are considered small. Obtain the model of system. [9]

Q5) List Direct methods of process identification. Explain any two methods. [16]
OR
Q6) Explain Autotuning identification method. [16]
Q7) Explain Niederlinski index for analysis of stability of multivariable system. Consider the distillation system described as,
|
12.8.e_s -18.9.e_3s | ||||
|
xD |
1+16.7 5 1+215 |
R | ||
|
xB |
6.6.e_7 5 -19.4.e_3s |
V | ||
|
1+10.95 1+14.45 | ||||
Find N.I for this and comment on stability. Repeat the procedure for xh - V 8 xf - R pairing. [16]
OR
Q8) Explain Morari resiliency index. For the distillation process three choices of manipulated variables are : Reflux - Vapour boilup (R-V), Distillate 8 Vapour boilup (D-V), Reflux Ratio 8 Vapour boilup (RR-V)
The steady-state gain matrices are,
R - V D - V RR - V
|
kp |
|
Calculate MRI for each 8 comment on resiliency.
[16]
Q9) a) Explain Local 8 Global minimum 8 maximum.
b) Explain convex 8 concave objective functions. [18]
OR
QIO) Determine optimum values of xY and x2 for following functions. Also determine convexity or concavity. [18]
a) f (x) = 3 - 4 x1 x2 + 2 x2.
2 ~
x 2
b) f (x)=~T +-+ 4 x2.
4 xx
c) f (x)= 2 x1 + 2 xxx2 + 2.5 x2 + 7 xx
d) f (x)=(xj - x2 ) + x2 .
Minimize f (x) = x1 x2 subjected to g(x) = 25 - x12 - > 0 using Lagrange multiplier method. [8]
A poster is to contain 300 cm2 of printed matter with margin 6 cm at top 8 bottom and 4 cm at each side. Find the overall dimension that minimizes the total area of the poster. [8]
a)
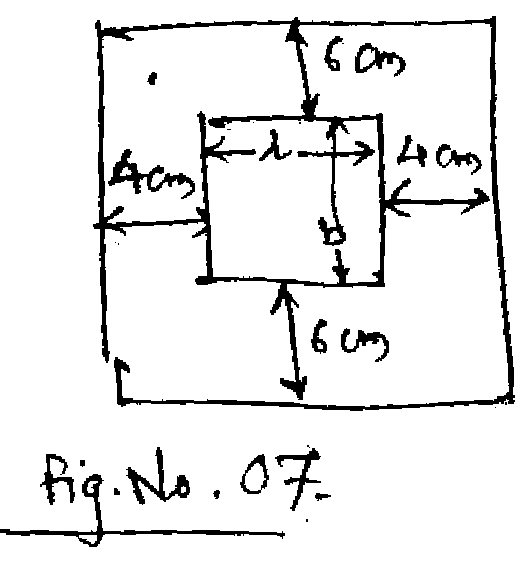 |
|
OR |
Explain steepest descent 8 steepest ascent methods of optimization. [8] ( Minimize f (x1, x2 )= x1 - x2 + 2 x12 + 2 x1 x2 + x22 starting from the
Q12) a)
using conjugate gradient method.
point xi
[8]
[3564] - 252 B.E. (Instrumentation & Control) INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION (1997 & 2003 Course)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. MarksxIOO
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer Three questions from Section I and Three questions from Section II.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QIA a) With the help of block diagram explain the different stages involved in the development of Automation Projects. [8]
b) With an example explain the role of SCADA in automation. [8]
OR
Q2) a) With example explain the term control system audit and its advantages. [8]
b) With the help of block diagram explain the different stages of preparing User Design Specifications. [8]
Q3) a) With an example explain different function blocks used in SFC. [8]
b) With reference to following points differentiate between Modbus (ASCII) and Modbus (RTU) transmission modes.
I) Characters 2) Error check 3) Frame Start 4) Frame end 5) Gaps in Message 6) Start bit 7) Stop Bit 8) Parity. [8]
OR
Q4) a) With an example explain query, response cycle in Modbus. [8]
b) With an example explain the role of MTU in a SCADA system. [8]
Q5) a) Explain similarities and differences between F ieldbus and conventional 4-20 mA system. [8]
b) With an example explain the Foundation Fieldbus model. [10]
OR
Q6) a) Write a short note on Device-net Protocol. [8]
b) List and explain at least five Universal commands used in HART. [10]
SECTION - II
Q7) a) With an example explain at least four major components of the DCS system. [8]
b) With the help of block diagram explain the Architecture of DCS from any make. [10]
OR
Q8) a) List and explain the I/O function blocks in the DCS system. [8]
b) With the help of block diagram explain the Architecture of DCS from any make. [10]
Q9) a) Explain any four Advanced Control blocks in a DCS system. [8]
b) Explain the how the alarms are classified and prioritized also explain why classification and prioritization is required. [8]
OR
QIO) a) Explain why and how database access management is done in any DCS system. [8]
b) Explain on what basis display hierarchy is created. [8]
QII) With the help of example explain the role of DCS system in a batch process automation. [IT]
OR
Q12) With the help of example explain the role of DCS system in a continuous process automation. [16]
P1165
[3564] - 251 B.E. (Instru.) COMPUTER TECHNIQUES & APPLICATIONS (2003 Course)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks: 100
Instructions to the candidates:-
1) Answer three questions from each section.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QI) a) List the various services offered by Operating Systems. [12]
b) With neat diagrams explain the following Disk scheduling algorithms. [6]
i) SCAN.
ii) C-SCAN.
iii) C-LOOK.
OR
Q2) a) Five processes (PI, P2, P3, P4, P5) arrive simultaneously with their CPU bursts of 8, 4, 9, 5 and 4 respectively. Their priorities are 3, I, 2, 0 and 4 with 0 being the highest priority and 4 being the lowest. For each of the following CPU scheduling algorithms, draw the Gantt chart and determine the average turn around time and average waiting time, showing all the calculations in detail. Ignore process switching overhead. Consider that the processes are non pre-emptive for the first three algorithms. [12]
i) First Come First Serve (FCFS).
ii) Shortest Job First (SJF).
iii) Priority scheduling.
iv) Round Robin (RR) with a time quantum of 3 CPU bursts.
b) Explain the four conditions necessary for occurrence of deadlocks. [6]
Q3) a) With the help of neat diagram, explain the concept of thrashing. [8] b) What is paging? Why is it needed in memory management? Explain the hardware required for paging. [8]
OR
Q4) a) With neat diagrams, explain any four types of Directory Structures. [8] b) Explain Swapping and Paging with respect to Memory Management. [8]
Q5) a) Write a note on Systolic Arrays on the basis of following points:
i) Functional block diagram. [4]
ii) Working. [4] b) Design a Huffman code for a source that puts out symbols al, a2, a3, a4
and a5 with their respective probabilities of occurrence as 0.2, 0.4, 0.2, O.l and 0.l. [8]
OR
Q6) a) Explain the different scheduling algorithms used in Real time systems. [8] b) What are Array processors? What are its applications? [8]
SECTION - II
Q7) Write short notes: [16]
a) IEEE 802.3.
b) TCP/IP.
OR
Q8) a) Explain the ISO-OSI seven layer model. [8]
b) Discuss the features and applications of Industrial Ethernet. [8]
Q9) a) List the 7 exceptions of ARM processors along with their vector addresses. [8]
b) Discuss the various levels of CMM. [8]
OR
QIO) a) Define Software reliability and discuss any six terms used to quantify the reliability of software products. [8]
b) Discuss the features of IEEE 488. [8]
Qll)a) Explain Integration testing and explain the following three Integration test approaches: [8]
i) Big-Bang Integration Testing.
ii) Bottom-Up Integration Testing.
iii) Top-Down Integration Testing.
b) Explain in brief any five steps in Software Development Life Cycle. [10]
OR
Ql2)Write short notes : [18]
a) White Box and Black box testing.
b) Validation testing.
c) CASE tools.
B.E. (Instrumentation & Control) INSTRUMENTATION FOR ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING (Elective) (2003 Course) (Sem. - I) (406264 (2))
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks: 100
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer 3 questions from Section I and 3 questions from Section II.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I Unit - I
QI) a) Enlist standard methods of pollution analysis. Explain one method in detail. [10]
b) Differentiate between online 8 offline measurements of pollutants. [8]
OR
Q2) a) Discuss on various sensors used for measurement pollution. [8]
b) Discuss on various biometric cycles. Explain Nitrogen cycle. [10]
Unit - 2
Q3) Explain following Environmental Testing. [16]
a) Dry heat.
b) Free fall.
c) Drop/Topple.
d) Bump.
OR
Q4) a) Write short note on water quality monitoring instrumentation. [8]
b) Write short note on ISO 14001. [8]
05) a) Explain instrumental setup for monitoring of aerosol 8 gaseous pollutants like S02& H2S. [10]
b) Explain scheme for monitoring of suspended particulate matters. [6]
OR
Q6) a) Explain HVAC Control. [8]
b) Explain environmental regulation 8 standards related to environmental toxicology 8 hazards. [8]
SECTION - II Unit - 4
Q7) a) Enlist Primary, Secondary 8 Tertiary treatments of domestic effluents.
Explain any one method of each treatment. [10]
b) Explain Investigations used for DO 8 BOD. [8]
0R
Q8) Explain different water quality monitoring instruments. Comment on recommended water quality instruments. [18]
Unit - 5
Q9) a) Explain effects of Radiation pollution. How it is controlled. [8]
b) What is Sonic boom? Explain any one noise measurement technique in detail. [8]
OR
Q1O) a) What is Noise mapping? Suggest control scheme for automobile noise.
[8]
b) Write a note on acid rain 8 its preventive measures. [8]
Unit - 6
QII) a) Suggest instrumentation setup for soil pollution reduction. [8]
b) Explain polarographic analysis of pesticides. [8]
OR
Q12) Write short notes on (any two) [16]
a) Analysis of micronutrients.
b) Trace elements analysis.
c) Environmental Impact assessment.
[3564]-245 B.E. (Instrumentation) DIGITAL CONTROL (1997 C 2003 Course)
[Max. Marks: 100
Time: 3 Hours]
Instructions to the candidates:
1) Answer 3 questions from Section I and 3 questions from Section II.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Use of logarithmic tables, slide rule, Mollier charts, electronic pocket calculator and steam tables is allowed.
6) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
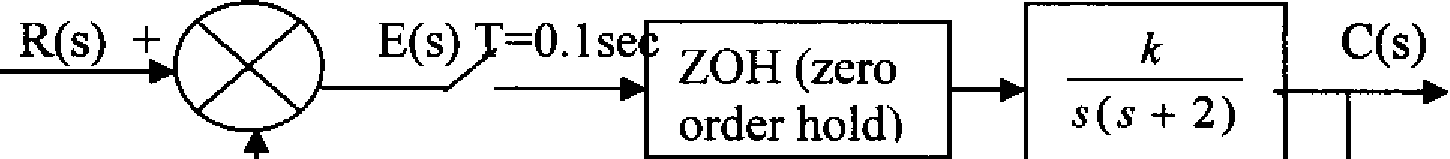
QV Find the range of K for the stability of the system shown in fig.l
[IT]
OR
Q2) a) The input output Relation of discrete time control system is described by the difference equationy (k- 2) + 3y (k- I) + 2y (k) = r (k) [8] Determine
i) Pulse Transfer Function
ii) Unit Impulse Response
iii) Unit Step Response
b) Examine the stability of the system represented by the characteristics equation using Jury stability. [8]
P (z) = z3 - 1.3z2 - 0.08z + 0.24 = 0
Q3) a) Derive the Position algorithm and velocity algorithm with reference to digital PID controller. [8]
b) Explain the Concept of Ringing of poles with suitable example. [8]
OR
Q4) Consider the plant with open loop transfer function. [16]
G p (s) _1
s(s +1)
Design a digital controller GD (z) such that closed loop system will exhibit a deadbeat response to a unit step input. The sampling period is I sec. Assume ZOH on input.
Q5) a) Derive the expression of solution of discrete State equation and find the State Transition Matrix of state model. [IP]
0
1
1
2
b) X(k +1)=
X(k)
[6]
- I -
Find the pulse Transfer Function of the system. X1(k +1)]_( 0 1 YX1(k) 1 (0
X2(k + 2) J _ [ - 6 - 5 J_X2(k)
Y1(k)
Y2(k)
OR
U(k)
+
1
v )
|
_ (1 0) _ (1 0) |
" X1(k) |
|
_ X 2(k)_ |
Q6) a) Obtain the State model of the following system using parallel programming.
[9]
TF _ ( z+1)( z + 3)
( z -1)( z - 2)( z - 3) b) Obtain the State model of the following system using Direct programming Method. [9]
3z - 11z
T.F:
(z -1)( z - 2)( z - 3)
Q7) a) Define Controllability and Observability of a system and Investigate the Controllability and observability of the system. [12]
|
' 0 |
1 |
0 " |
"0" | |
|
0 |
0 |
1 |
X(k)+ |
0 |
|
6 V |
11 |
6 j |
1 |
X(k +1) -
u (k)
Y (k) = [ 4 5 I] X (k) b) Explain the State Variable Feedback in shortly.
OR
Q8) Consider the system described by state space equation as
[IT]
|
' 0 1 " |
"0" | ||
|
X(k +1)= |
0.16 1 v J |
X(k) + |
_1_ |
U(k)
Y (k) = [ I 0] X (k). Determine the suitable state feedback gain matrix.
K that will place the system poles at zl = -0.5 + y'0.5 and z2 = -0.5 - y'0.5 using any two methods.
Q9) a) What are the reasons of dead time element incorporated in systems and explain the effect of dead time on system performance. [8]
b) Explain the Smith predictor and limitations of Smith predictor. [8]
OR
QI 0) Write short note on the following. [16]
a) Application of mathematical models in digital control.
b) Model based control.
QII) Consider a discrete time control system [18]
X (k + l) = 0.3679 X (K) + 0.6321 U (K), X (0) = l. Determine optimal control law to Minimize the following Performance Index.
1 2 1 9 J= - [X(10)] +-[X2(k)+u2 (k)]
Also Find J
OR
Q12) Explain the procedure of system Identification with suitable diagram. What are the different parametric methods of system identification? Explain any two with suitable mathematical model. [18]
P1285 [3564]-255 B.E. (Instrumentation)
FIBER OPTIC INSTRUMENTATION (406264(3)) (2003 Course)
Time: Q Hours] [Max. Marks : 100
Instructions:
1) Answer Q questions from Section-I and Q questions from Section-II.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
Q) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
4) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
QI) a) What are the advantages of Optical Fiber Communication? What are the difficulties in Optical Fiber Communication? [8]
b) Explain Total Internal Reflection and Acceptance Angle and derive the expression for Numerical Aperture. [9]
OR
Q2) a) Explain step index fiber and graded index optical fiber, giving an expression for the possible refractive index profiles? Using simple ray theory concepts, discuss the transmission of light through the fiber. Also explain evanescent field in optical fiber. [12]
b) Briefly indicate with the aid of suitable diagrams the difference between meridional and skew ray paths in step index fibers. [5]
Q3) a) Explain the reasons for pulse broadening in optical fiber. Explain how the pulse broadening limits the length of optical fiber in digital communication. [9]
b) Describe linear and nonlinear scattering losses in optical fibers. [8]
OR
Q4) a) Explain the drawing of optical fibers from prepared glasses with regard to: [8]
i) multicomponent glass fiber.
ii) silica-rich fibers.
b) Describe with the aid of suitable diagrams, three common techniques used for the mechanical splicing of optical fibers. [9]
Q5) a) Compare advantages and disadvantages of LED and laser diode as a source in optical fiber. [6]
b) Explain what is population inversion and also explain working of a laser diode. [10]
OR
Q6) a) Explain the experimental set up for the study of measurement of various fiber misalignments. [8]
b) State the two major categories of fiber-fiber joint, indicating the difference between them. Briefly discuss the problem of Fresnel reflection at all types of optical fiber joints and how it may be avoided. [8]
Q7) a) What are the advantages and disadvantages of Optical Fiber Sensors over traditional sensors? Also discuss the disadvantages of Optical Fiber Sensors. [IP]
b) Write a note on 'Optical Power Meter'. [5]
OR
Q8) a) What are various ways to classify Optical Fiber Sensors? Explain one extrinsic type of Optical Fiber Sensors, with the help of following points.
i) Principle of operation with diagram.
ii) Advantages and disadvantages.
iii) The parameters, measured by this sensor. [9]
b) Write a note on 'Interferometric Optical Fiber Sensor'. [8]
Q9) Explain with suitable diagram working of 'Optical Fiber Brag Grating'. Also explain measurement of temperature by using Fiber Brag Grating. What are the advantages and disadvantages of Fiber Brag Grating? [17]
OR
Q10)a) What do you understand by 'Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing? What are the advantages and disadvantages of Distributed Optical Fiber Sensing? [9]
b) Write a note on 'Optical Time Domain Reflectometer (OTDR)'. [8]
Q11)a) Give major reasons, which have led to the development of optical amplifiers, outlining the attributes and application areas for these devices.
b) Write a note on 'Integrated Opto-Electronic Device'. [8]
OR
Q12)a) Discuss the function and operation of polarization transformers and frequency translators with specific reference to coherent optics. [8]
b) Explain with the aid of suitable diagrams, following integrated optical devices: [8]
(i) Beam splitter (ii) Directional coupler.
nnn
[3564]-255 - 2 -
P1284 [3564]-253 B.E. (Instrumentation 8 Control)
ADVANCED BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION (406270) (2003 Course) (Elective - II) (Sem. - II)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 100
Instructions:
1) All questions are compulsory.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
Explin vrious modes of ESU? Explin different electrode configuration.
QI b
Q2) b
Q3)
[10]
Distinguish between [6]
Externl nd implnted pcemkers.
A.C. nd D.C. Defibrilltor.
Defibrilltor nd pcemker.
OR
Explin vrious equipment nd fcilities used in ICU. Explin instrument tht is used for continuous ECG mesurement in ICU. [10]
Wht is hert lung mchine? Why during hert surgery nturl lungs lso by pss? List five pumps hed in HLM. [6]
Explin the role of telemetry system in medicl field. Drw nd explin generl block schemtic of biotelemetry system. Enlist various pplictions of telemetry in medicl field. [8]
Explin the working Principle of Electrophoresis Instrument in pthologicl Lbortory. [8]
OR
Explin the conductivity type blood cell counter for RBC nd WBC mesurement. [10]
Q4) b
Wht is n utonlyser? Describes vrious sub systems of uto nlyzer.
[6]
Drw nd explin sttionry node X-ry tube. Specify the trget mteril used in genertion of X-ry? Give the technicl reson for it's used. [10] Hounsfield number nd window width control in CT scnning system. [8]
OR
Explin the principle of CT-scnning. How it overcomes the drw bck of X-Ry imging? [6]
QT ) b)
c)
QU ) b)
QV )
b)
QW )
b)
QIO))
b)
QIIA)
b)
c)
Q72
b)
Discuss X-ry properties nd X-ry film used for imging. [6]
Explin X-ry Fluoroscopy nd its pplictions. [6]
SECTION - II
Enlist properties of ultrsound. Discuss the vrious modes of ultr sound trnsmission. [10]
Specify the frequency rnges used in ultrsound imging for bdominl, Brin Exmintion nd for ophthlmic nd peditric study in M-scn Mode. [6]
OR
Why Nl (Ti) is most populr in rdionuclide imging? Explin the principle of PET imging. [10]
Why to use vrious method of imging? [6]
Explin in brief vrious types of dilysers used for hemodilysis. [10] Define hemodilysis, peritonel dilysis nd Priming volume. [6]
OR
Explin different pplictions of LASER in the field of ophthlmology with net digrm nd operting procedure. [10]
Explin how Lser differs thn norml light in connection with the followings:- [6]
(i) Colour (ii) Coherence (iii) Power (iv) Diversion.
Describe three importnt crdinl considertions of which designer should wre t the time of designing orthrosis nd prosthesis. [6]
Define orthrosis and Prosthesis concepts used in rehbilittion engineering. List out two exmple of ech. [6]
Discuss vrious mterils used for wheel chir design. [6]
OR
Wht is kidney stone? Explin lithotripsy bsed on coustic shock wve with plsm explosion s efficient method of destruction for kidney stone.
Define following four criticl performnce fctors in wheel design to optimize interction of wheel with ground :- [8]
(i) Cster flutter, (ii) Cster flot, (iii) Trcking, (iv) Alignment.
B.E. (Instrumentation & Control)
LASER APPLICATIONS IN INSTRUMENTATION (2003 Course) (Elective - I)
Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 100
Instructions to the candidates :
1) Answer three questions from section I and section II.
2) Answer to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Use of electronic pocket calculator is allowed.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
Q1) a) State the different processes due to which the small gain coefficients of laser get affected. [8]
b) Write short notes on: [8]
i) Laser modes.
ii) Q switching.
OR
Q2) a) Explain in detail the process of emission and absorption of radiation.[8]
b) Explain the importance of Einstein's equations in emissions of radiation.
[8]
Q3) a) What are different laser system features which are applicable to most commercial and industrial lasers? Explain each in short. [9]
b) Estimate the efficiency of a GaAs laser operating well above threshold. The refractive index of material is 3.6 and laser cavity length is 0.4 mm. The loss coefficient is 900 per metre length and the internal quantum efficiency is 0.75. [4]
c) What are the steps that should be followed in a safe laser laboratory operation? [5]
OR
Explain the construction and working of GaAs homojunction semiconductor diode laser. [8]
How the laser products are classified for safety standards? [4]
b)
c)
Q5) a) b)
Q6) a) b)
Q7) a) b)
Q8) a) b)
Q9) a) b)
Q10)a)
b)
Calculate the threshold pumping power of a Nd: Glass laser for critical population inversion of 8 x 1021 / m3 and sponteneous life time of 200 is. The upper level is at an energy of 1.5eV. [6]
Describe how Fabry-Perot interferometer is used with small coherent length source for displacement measurements. [8]
What is Speckle Pattern? Describe subjective and objective speckles. [8]
OR
Describe the dynamic tracking of speckle pattern for displacement measurements. [8]
What are the properties of speckle pattern? Describe each in short. [8]
SECTION - II
What is the principle of operation of Laser velocimeter? Explain. [8]
What are the two options for the electronic processing of the Doppler signal? Compare it. [8]
OR
Explain the frequency domain processing of Doppler signal in detail.[8]
What are the performance parameters of operation of laser velocimeter? Discuss. [8]
Show that the frequency of the sagnac signal in RLG is proportional to the angular velocity of rotation. [8]
Explain in detail the closed loop configuration of Fiber Optic Gyroscope.
[8]
OR
What is Sagnac effect? Show how is the phase shift is proportional to the angular velocity. [8]
What are the components required for all fiber FOG configuration? Explain each in short. [8]
Q11)a) A thin strip of the hologram undergoing stress parallel to the x-axis is illuminited by a He-Ne laser. The fringes are localized in a plane having slope of 1.5 per unit length in x-direction and the fringe spacing is found to be 1 mm. Hence find the strain. [8]
b) List out the applications of holographic interferometer that you know. Explain any one in detail. [10]
OR
Q12)a) Write a short note on Holographic Interferometer. [9]
b) What are different emulsions used to record the holograms? Mention the characteristics of it. [9]
B.E. (Instrumentation 8 Control) BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION ( 406264) (2003 Course) (Elective - I) (Sem.-I)
Time: 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 100
Instructions:
1) Answer any three questions from each Section.
2) Answers to the two sections should be written in separate books.
3) Neat diagrams must be drawn wherever necessary.
4) Figures to the right indicate full marks.
5) Assume suitable data, if necessary.
SECTION - I
QI) a) Define bio electrode. Explain various types of basic bio electrodes used for bioelectric potential measurements along with their materials. [8]
b) Give the typical values of amplitude and frequency of signal arising due to electrical activity of heart, brain, muscles and eyes. [8]
OR
Q2) a) Explain Electrode offset potential? How effect of electrode offset potential is overcome. Explain the various properties that bio-electrode should possesses. [10]
b) Define and discuss the term "Biosensors". [6]
Q3) a) Explain Einthoven triangle that connected with defining bipolar leads of ECG. [8]
b) Explain the block diagram of ECG machine. [8]
OR
Q4) a) Briefly discuss the various preamplifiers that are used in bio signal conditioning. [10]
b) Which information is missing in ECG related to heart defect? Suggest and elaborate on suitable instrument to diagnose the same. [6]
Q5) a) What is importance of Blood pressure measurement in cardiac performance? What are the advantages of direct and indirect B.P. measurement? What additional important information is possible to achieve by direct B.P. measurement that is not possible by indirect method.
[10]
b) List out various methods used for cardiac output measurement. Explain indicator dilution method with dilution curve. [8]
Explin electromgnetic blood flow mesurement with net digrm. [8] Discuss non invsive blood flow mesurement long with net digrm. [8] List out the microphones used in phonocrdiogrph. [2]
SECTION - II
QT ) b)
c)
QU ) b)
QV )
b)
QW )
b)
c)
QIO))
b)
QIIA)
b)
Q72
b)
Wht is EEG? Enlist vrious illness nd diseses for which EEG is effectively used. Explin the EEG montge system. [10]
Explin the EEG Amplifier with technicl detils. [6]
OR
Explin the functions of the followings. [10]
Cerebellum, cerebrum, thlmus nd hypothlmus, Medull oblongt, Pons.
Drw nd explin the structure of neuron. [6]
Enlist vrious ophthlmic instruments nd briefly explin them? Give their re of ppliction. [10]
Explin the role of Cones nd Rods in humn vision. [4]
Suggest suitble devices tht re used to recover the percentge losses in EAR or EYE, if some residul cpcity hs been remin with these orgns. [2]
OR
Define "Hering threshold". Explin the speech udiometer nd pure tone udiometer. [10]
Wht re three min sections of Humn uditory system? Explin the impednce mtching in humn hering phenomenon. [6]
Wht is Spiro gram? Drw nd explin Wedge Spiro meter for respirtory mesurement. [10]
Why inspired nd expired gs nlysis is of gret importnce. Drw nd explin Therml conductivity nlyzer. [8]
OR
Discuss the vrious precutions to minimize electric shock hzrds in medicl equipments. Define the terms 'Let go Current, Hold on current'.
Stte the condition of ptient t which support of ventiltor is essentil? Wht is role of nebulizers nd spirtors in ventiltor? [8]
[3564]-246
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
