Thapar University 2006 B.Tech Chemical Engineering Material & Energy Balances - Question Paper
Thapar Institute of Engineering & Technology
Chemical Engineering (2nd Year)
Final Term exam
CH002 (Material & Energy Balances)
THAPAR INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY, PATIALA End-Semester Examination, First Semester (2006-2007)
Second year (Chem. Engg. & Biotech.) Material and Energy Balances (CH-002)
Time: 3 hr M.M.: 45
Attempt all questions.
Assume any missing data, suitably.
Q.1 (a) The heat capacity of ammonia, over a limited temperature range is given by the expression:
_ i Bm
= 0.487 + 2.29x]<r47 : Where Tis in f>F
lbF
J
and T is in C.
Determine the expression for Cp in
(2)
Uc
Q.l(b) Methanol is produced by the following reaction:
CO: - 3H2 CH3OH - H20
The fresh feed to the process contains hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and 0.4 mole% inerts. The reactor effluent passes to a condenser that removes essentially all the methanol and water formed during the reaction as product stream. The unconverted reactants and inerts are returned to the reactor as recycle stream. To avoid the buildup of the inerts in the system, a purge stream is withdrawn from the recycle stream.
The feed to the reactor (combined feed) contains 28 mole% CO2. 70 mole% H2. and 2 mole% inerts. The single-pass conversion of the hydrogen is 60%. Calculate the molar flow rates and molar compositions of the fresh feed, the molar flow rate of combined feed to the reactor, the molar flow rate and molar composition of recvcle stream and purge stream for a methanol production rate of 155 kmol/hr.
Q.2(a) One hundred moles of ethane (C2H6) are burned with 40 % excess air. Conversion of ethane is 100% complete. 25 % of ethane reacts to form CO and balance amount reacts to form CO2. Calculate the molar composition of the flue gas on wet basis. (3)
Q.2(b) A flowchart of a continuous steady-state process is shown below. Each stream contains two components. A and B. Calculate the flow rates and compositions of streams 1. 2. and 3. All percentages are by weight. (3)
a30 kg/h
|
lOOkg/h |-1 j | ||
|
50% A 50% B | 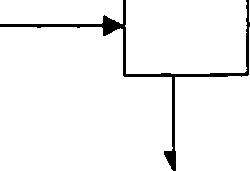 |
40 kg/h 90% A |
|
0% A |
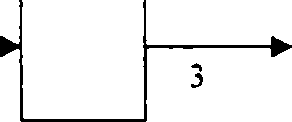 |
30 kg/h 70% B
Q.2(c) The gross calorific value of propane (CsHs) is 2219.71 kJ/mol at 25 C. Calculate its net calorific value. Latent heat of vaporization of water is 2442.5 kJ/kg.(3)
Q.3(a) A saturated solution of salicylic acid (HOC6H4COOH) in methanol contains 64 kg salicylic acid per 100 kg methanol (CH3OH). Calculate wt% and mol% compositions of the solution. (2)
Q.3(b) The average molecular weight of a flue gas sample is calculated by wo different engineers. One engineer uses the correct molecular weight of 28 for NS and determines the average molecular weight to be 30.08. the other engineer, using an incorrect value of 14. calculates the molecular weight to be 18.74.
(a) Calculate the volume % of N2 in the flue gas (b) if the remaining components of the flue gas are CO2 and O2. calculate the volume % of each of them. (2.2)
Q.3(c) A storage tank of DM water has a holding capacity of 1000 m\ The inflow DM water to the tank is 25 1/s having silica content of 0.005 mg/1. The supply of DM water from the tank to the boiler is 25 dm3/s. Suddenly the silica content in the feed water to the tank increases to 0.02 mg/1. Assuming that the inflow and the outflow from the tank remains constant at 25 1/s. calculate the time required for the silica content in the storage tank to rise to 0.01 mg/1. (4)
Q.4(a) The ethanol dehydrogenation reaction is carried out with the feed entering at 300 C. The feed contains 90 mol% ethanol (C2H5OH) and the balance acetaldehyde (CH3CHO). Feed enters the reactor at a rate of 150 mol/s. To maintain the temperature, heat is added to the reactor at a rate of 2440 kJ/s. The products are leaving at a temp, of 253 C. Calculate the fractional conversion of ethanol achieved in the reactor. (Reaction is : CjHjOHCHjCHO - H;) (7)
|
Data: | ||||||||||||
|
Q.4(b) The dry bulb temperature and dew point of ambient air were found to be 302 K and 291 K respectively. The barometer reads 100 kPa. The vapor pr. of water at 302 K. is 4.004 kPa. and vapor pr. of water at 291 K is 2.0624 kPa. Calculate %RH. (2)
Q.5 (i) What is Hess's law? (1)
(ii) What is Amagats law? (1)
(iii) What are yield, and selectivity w ith reference to a chemical reaction? (1)
(iv) What are the typical variables that are to be considered for degree of freedom analysis? (2)
(v) Define adiabatic flame temperature. (1)
(vi) How the gas composition on wet basis is different from the composition on dry basis? (1)
(vii) What is heat of reaction in terms of heat of combustion? (1)
(viii) What is partial saturation? (1)
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
