Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati (IIT-G) 2007 JAM Geology - Question Paper
JAM 2007 Geology
Full ques. Paper in attachment
Geology Paper 2007
IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CANDIDATES
Attempt ALL the 44 questions.
Questions 1-30 (objective questions) carry three marks each and questions 31-44 (subjective questions) carry fifteen marks each.
Write the answers to the objective questions in the Answer Table for Objective Questions provided on page 9 only.
1. The occurrence of ammonites in a sequence suggests
(A) Cenozoic age and freshwater environment
(B) Cenozoic age and marine environment
(C) Mesozoic age and freshwater environment
(D) Mesozoic age and marine environment
2. Which of the following sedimentary structures is erosional in nature?
(A) Cross-stratification
(B) Flute casts
(C) Graded bedding
(D) Ripple marks
3. Group I contains some minerals and Group II gives a list of crystal systems. Find the correct match.
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
P. |
Gypsum |
1. |
Hexagonal |
|
Q. |
Beryl |
2. |
Triclinic |
|
R. |
Galena |
3. |
Monoclinic |
|
S. |
Axinite |
4. |
Cubic |
(A) P-3, Q-2, R-4, S-l
(B) P-l, Q-3, R-4, S-2
(C) P-2, Q-l, R-4, S-3
(D) P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-2
4. A mineral with patchy blue colour and variable hardness is
(A) azurite
(B) kaolinite
(C) kyanite
(D) sillimanite
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
P. |
Maleri |
1. |
Oligocene |
|
Q. |
Karewa |
2. |
Plio-Pleistocene |
|
R. |
Ariyalur |
3. |
Cretaceous |
|
S. |
Barail |
4. |
Triassic |
|
(A) |
P-l, |
Q-2, |
R-3, |
S-4 |
|
(B) |
P-2, |
Q-l, |
R-4, |
S-3 |
|
(C) |
P-4, |
Q-3, |
R-2, |
S-l |
|
(D) |
P-4, |
Q-2, |
R-3, |
S-l |
6. Of the following alternatives, the most suitable condition for a road cut in a hilly terrain is where the foliations
(A) are vertical
(B) dip away from the slope
(C) dip towards the slope at high angle
(D) dip towards the slope at low angle
7. Which of the following series of stratigraphie units is arranged in the order from older to younger age?
(A) Cheyair Rewa - Sausar - Gondwana
(B) Sausar - Cheyair - Rewa - Gondwana
(C) Gondwana - Rewa - Cheyair - Sausar
(D) Rewa - Gondwana - Sausar - Cheyair
8. Which of the following rocks can form good aquifers?
(A) Sandstone and highly jointed granite
(B) Sandstone and massive granite
(C) Sandstone and shale
(D) Shale and massive granite
Group I
Granite
Group II
1. Dacite
|
Q. |
Granodiorite |
2. |
Trachyte | |
|
R. |
Diorite |
3. |
Rhyolite | |
|
S. |
Syenite |
4. |
Andesite | |
|
(A) |
P-l, Q-2, R-4, S-3 | |||
|
(B) |
P-2, Q-l, R-3, S-4 | |||
|
(C) |
P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-2 |
4 | ||
|
(D) |
P-3, Q-2, R-4, S-l |
10. Staurolite, andalusite and sillimanite form during progressive regional metamorphism of
(A) arenaceous rocks
(B) siliceous carbonate rocks
(C) basic igneous rocks
(D) argillaceous rocks
11. Which of the following is a strike-slip fault?
(A) Normal fault
(B) Reverse fault
(C) Thrust fault
(D) Transform fault
12. A fold in which the hinge line plunges in the direction of dip of the axial plane is '
(A) overturned fold
(B) reclined fold
(C) recumbent fold
(D) upright fold
13. Match the fossil taxa listed in Group I with their characteristic morphological features in Group II.
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
P. |
Paradoxides |
1. |
Two pendent stipes |
|
Q. |
Didymograptus |
2. |
Sinistrai coiling |
|
R. |
Physa |
3. |
Genal spines |
|
S. |
Ceratites |
4. |
Sutures with undivided ; |
(A) P-3, Q-2, R-4, S-l
(B) P-3, Q-l, R-2, S-4
(C) P-2, Q-l, R-4, S-3
(D) P-2, Q-l, R-3, S-4
14. Beach placers in India are an important source of
(A) copper
(B) lead
(C) thorium
(D) uranium
15. The reservoir rock for petroleum in Bombay High is
(A) feldspathic sandstone
(B) graywacke
(C) limestone
(D) orthoquartzite
16. Which of the following stratigraphie units contains dinosaur fossils?
(A) Lameta
(B) Muth Quartzite
(C) Siwalik
(D) Subathu
17. Isostasy involves
(A) eustatic change
(B) gravitational balance
(C) magnetic reversal
(D) thermal balance
18. A graded stream is characterized by
(A) increase in erosion relative to deposition
(B) increase in deposition relative to erosion
(C) equilibrium between erosion and deposition
(D) formation of graded bedding
19. Barchans are crescent-shaped dunes in which the ends of the crescent
(A) point in the upwind direction
(B) are at right angles to the wind direction
(C) have no relation to the wind direction
(D) point in the downwind direction
20. Continued crystallization of augite after the formation of plagioclase can result in
(A) hyalopilitic texture
(B) ophitic texture
(C) porphyritic texture
(D) trachytic texture
21. The basaltic lava flow having ropy and wavy surface is known as
(A) aa
(B) pahoehoe
(C) tuff
(D) volcanic breccia
22. Minerals in which of the following pairs do NOT form a natural association?
(A) Corundum - Sillimanite
(B) Nepheline - Quartz
(C) Olivine - Clinopyroxene
(D) Olivine - Orthopyroxene
23. Scratches produced on the fault plane are known as
(A) boudins
(B) mullions
(C) plumose structure
(D) slickensides
24. Which of the following processes of ore formation produces gold deposits in the form of reef?
(A) Hydrothermal
(B) Magmatic injection
(C) Magmatic segregation
(D) Supergene enrichment
25. Match the organisms listed in Group I with their respective symmetry elements in Group II.
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
P. |
Brachiopods |
1. |
Asymmetric |
|
Q. |
Pelecypods |
2. |
Plane of symmetry bisects the two valves |
|
R. |
Echinoids |
3. |
Plane of symmetry lies between the two valves |
|
S. |
Helically coiled gastropods |
4. |
Five-fold radial symmetry |
|
(A) |
P-l, Q-2, R-3, S-4 | ||
|
(B) |
P-4, Q-l, R-2, S-3 | ||
|
(C) |
P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l | ||
|
(D) |
P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-l | ||
26. The presence of reef corals in a sedimentary sequence indicates that deposition took place
(A) near the equator
(B) near the poles
(C) in fluvial environment
(D) in deep sea environment
|
Group I |
Group II | ||
|
P. |
Point Bar |
1. |
Sea |
|
Q. |
Cirque |
2. |
River |
|
R. |
Yardang |
3. |
Glacier |
|
S. |
Berm |
4. |
Wind |
(A) P-2, Q-3, R-4, S-l
(B) P-3, Q-l, R-4, S-2
(C) P-2, Q-l, R-3, S-4
(D) P-3, Q-2, R-l, S-4
28. Which of the following sedimentary rocks is/are formed by chemical precipitation? P : limestone Q : chert R : sandstone S : shale
(A) P only
(B) both P and Q
(C) both P and R
(D) both Q and S
29. A geomorphic feature produced at divergent plate boundary is
(A) folded mountain belt
(B) guyot
(C) island arc
(D) oceanic ridge
30. The pressure-temperature ranges of the metamorphic facies P: Granulite, Q: Zeolite, R: Amphibolite, S: Greenschist increase in the order
(A) Q < R < S < P
(B) Q < P < R < S
(C) Q < S < R < P
(D) Q < R < P < S
31. (a) Give the ratios of silicon to oxygen in forsterite and enstatite. (6)
(b) What are the sodic and calcic end members of the plagioclase group of minerals? List the remaining members of the sequence in the order of increasing calcium content. (9)
(b) What is an optic axis? Draw the optical indicatrix separately for uniaxial positive and negative minerals. (9)
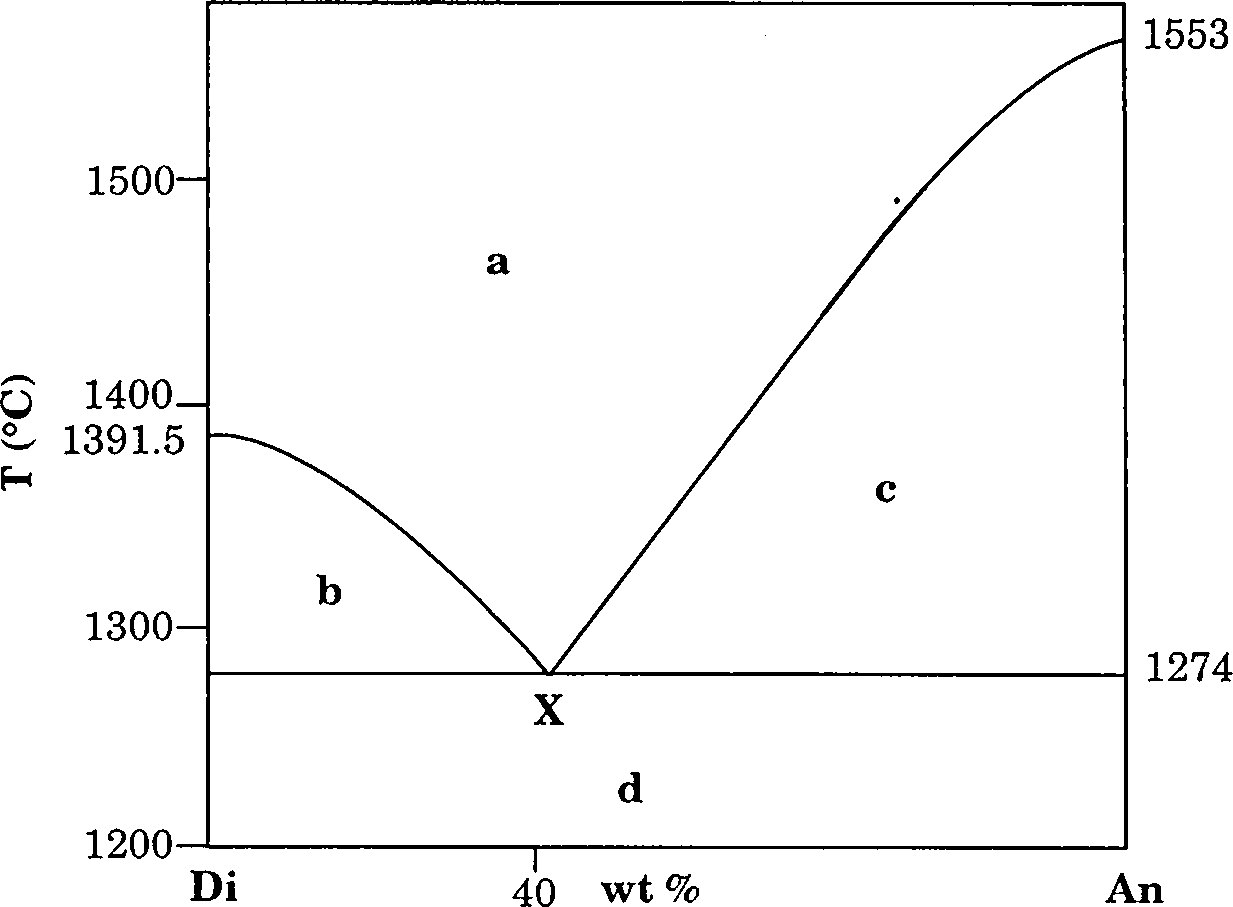
P : Eocene to Oligocene
Q : Palaeocene to Pliocene
R : Oligocene to Miocene
S : Eocene to Recent
What is the age of the rock? Give reason. (6)
(b) Name the stratigraphic succession which constitutes the younger greenstone belt of Southern India. Give its three main subdivisions at the group level in the stratigraphic order. (9)
(b) Name a characteristic upper Gondwana plant fossil, and a brachiopod shell with a long, straight hinge line. (6)
36. (a) What is the oldest stratigraphic unit of the Gondwana Supergroup? Give the age range of the Gondwana Supergroup, and also the name of one locality where there is evidence of marine influence within the Lower Gondwana. (9)
(b) Name the volcanic rocks of Permian age in the Himalaya, and of Proterozoic age in the Singhbhum-Orissa craton. (6)
37. (a) Draw schematic sections showing a normal fault, a thrust and a fold. Indicate, using
pairs of arrows, the nature of forces involved in the formation of these structures. (9)
(b) What are the outcrop patterns of horizontal and vertical beds with respect to contour lines? (6)
38. (a) What is a moraine? How does a moraine differ from an esker in regard to sorting of grains? (6)
(b) With the help of neat diagrams, show the difference between an atoll, a fringing reef and a barrier reef. (9)
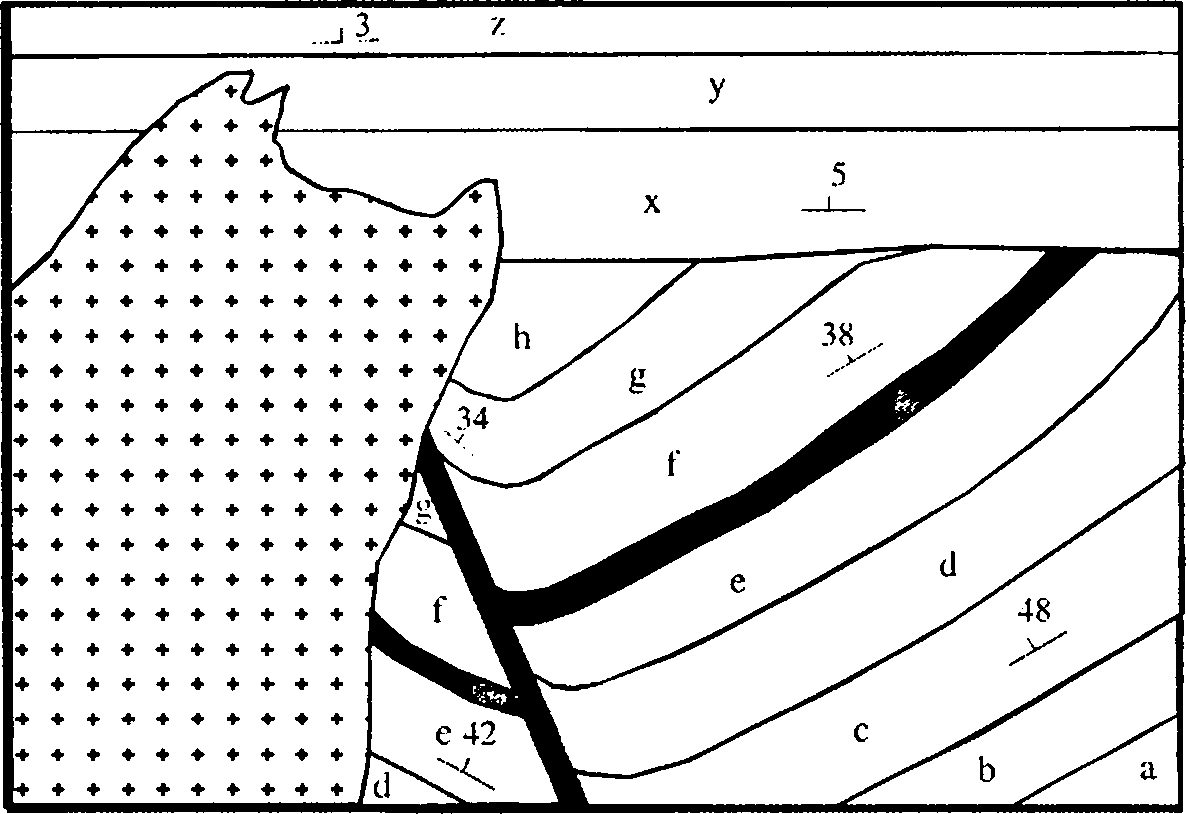
The map given below shows the outcrop pattern of rocks of normal sequence (a to z) in a flat terrain, with dark bands representing basic rocks and + symbol indicating granitoids. Find out the structures present, sequence of magmatic activities, sequence of deformational events, and the overall order of stratigraphic superposition. (15)
40. (a) What is the difference between syngenetic and epigenetic ore deposits? Give one example of a syngenetic ore deposit from India. (6)
(b) Draw a fold trap and label it to show the cap rock, reservoir rock and the site of petroleum accumulation. Give one example each for cap and reservoir rocks. (9)
41. (a) What is the difference in the nature of transmission of thrust of water in the reservoir of a Gravity Dam and that of an Arch Dam? Which of these dams is wider at the base?
(b) What is the difference between aquiclude and aquifuge? Give one example for each. (9)
42. (a) Draw neat diagrams showing trough cross-stratification, asymmetric ripples and graded bedding. (9)
(b) Give two characteristics indicating textural immaturity of sandstones. (6)
43. (a) Name one radiometric method used for dating of Precambrian rocks and of rocks upto about 50000 years old. (6)
(b) What is the difference between central - and fissure - type volcanic eruptions? Give one example of landforms for each. (9)
44. (a) Give schematic diagrams illustrating the Elastic Rebound Theory for the origin of Earthquakes. In which type of plate boundary do deep focus earthquakes occur? (9)
(b) A blue-coloured amphibole is characteristic of subduction zone metamorphism. Name this mineral and the associated metamorphic facies. (6)
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
