Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati (IIT-G) 2006 M.Sc Mathematics Programmes of IIT - JAM Model - Question Paper
MATHEMATICS TEST PAPER
j
& : The set of all real numbers Z : The set of all integers
IMPORTANT NOTE FOR CANDIDATES
Objective Part:
Attempt ALL the objective questions (Questions 1-15). Each of these questions carries six marks. Each incorrect answer carries minus two. Write the answers to the objective questions in the Answer Table for Objective Questions provided on page 7 only.
Subjective Part:
Attempt ALL subjective questions (Questions 16-29). Each of these questions carries fifteen marks.
2n+1 + 3
n+1
equals
lim
n> 2n + 3n
(A) 3
(B) 2
(C) 1
(D) 0
Let f ( x) = ( x - 2)17( x + 5)24. Then
(A) f does not have a critical point at 2
(B) f has a minimum at 2
(C) f has a maximum at 2
(D) f has neither a minimum nor a maximum at 2
Let f (x, y) = x5y2 tan-1 |. Then x + y equals
x ) dx dy
(A) 2f
(B) 3f
(C) 5f
(D) 7f
Let G be the set of all irrational numbers. The interior and the closure of G denoted by G0and G, respectively. Then
are
|
(A) |
G0 |
= &, |
G = G |
|
(B) |
G0 |
G = t | |
|
(C) |
G0 |
= 0, |
G = t |
|
(D) |
G0 |
= G, |
G = t |
5 Let f (x) = | e l dt. Then f '(n/4) equals
sin X
(a) VTTe
(B) -42Te
(C) 42Te
(D) -Te
6. Let C be the circle x2 + y2 = 1 taken in the anti-clockwise sense. Then the value of the integral
12xy3 + y) dx + (3x2y2 + 2x) dy~\
C
|
equals | |
|
(A) |
1 |
|
(B) |
n/2 |
|
(C) |
n |
|
(D) |
0 |
7. Let r be the distance of a point P(x, y, z) from the origin O. Then V r is a vector
(A) orthogonal to OP
(B) normal to the level surface of r at P
(C) normal to the surface of revolution generated by OP about x-axis
(D) normal to the surface of revolution generated by OP about y-axis
8. Let T: t 3 t 3 be defined by
T(X2, x3) = (xi -X2, xi -X2, 0).
If N(T) and R(T) denote the null space and the range space of T respectively, then
(A) dim N (T) = 2
(B) dim R (T) = 2
(C) R(T) = N (T)
(D) N(T) c R(T)
9. Let S be a closed surface for which jj r. it da = 1. Then the volume enclosed by the
S
surface is
(A) 1
(B) 1/3
(C) 2/3
(D) 3
2 d2 y , dy x + kx--+ y = 0, x > 0,
2
dx2 dx
then k equals
(A) 3
(B) -3
(C) 2
(D) -1
11- If A and B are 3x3 real matrices such that rank (AB)=1, then rank (BA) cannot be
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 3
12. The differential equation representing the family of circles touching y-axis at the origin is
(A) linear and of first order
(B) linear and of second order
(C) nonlinear and of first order
(D) nonlinear and of second order
13- Let G be a group of order 7 and (f> (x) = x4, x e G. Then (f> is
(A) not one - one
(B) not onto
(C) not a homomorphism
(D) one - one, onto and a homomorphism
14. Let R be the ring of all 2x2 matrices with integer entries. Which of the following subsets of R is an integral domain?
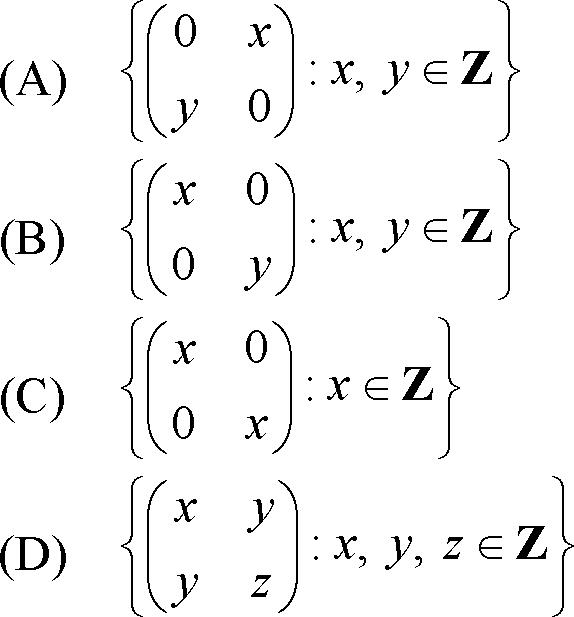
|
is | |
|
(A) |
1/2 |
|
(B) |
0 |
|
(C) |
-1/2 |
|
(D) |
W |
16. (a) Test the convergence of the series
W v
nn
n/2 n/2
lim i fn (x)dx - i (lim fn (X) )
nw J J \nw /
(6)
, n!3n
n=1
n=
(b) Show that
X2
ln (l + cos x) < ln2--
for 0 < x <n/2. (9)
17. Find the critical points of the function
f (x, y) = X3 + y2 -12X - 6y + 40.
Test each of these for maximum and minimum. (15)
18. (a) Evaluate jjxeydxdy, where R is the region bounded by the lines x = 0, y = 1 and the
R
parabola y = x 2. (6)
(b) Find the volume of the solid bounded above by the surface z = 1 - x2 - y2 and below by the plane z = 0. (9)
19. Evaluate the surface integral
jj x (12 y - y4 + z 2 )da,
S
where the surface S is represented in the form z = y2, 0 < x < 1,0 < y < 1. (15)
20. Using the change of variables, evaluate jjxydxdy, where the region R is bounded by the
R
curves xy = 1, xy = 3, y = 3x and y = 5x in the first quadrant. (15)
21. (a) Let u and v be the eigenvectors of A corresponding to the eigenvalues 1 and 3
respectively. Prove that u + v is not an eigenvector of A. (6)
(b) Let A and B be real matrices such that the sum of each row of A is 1 and the sum of each row of B is 2. Then show that 2 is an eigenvalue of AB. (9)
22. Suppose W and W2 are subspaces of t 4 spanned by {(1,2,3,4), (2,1,1,2)} and {(1,0,1,0), (3,0,1,0)} respectively. Find a basis of Wi I W2. Also find a basis of W + W2 containing {(1,0,1,0), (3,0,1,0)}. (15)
23. Determine y0 such that the solution of the differential equation
y'- y = 1 - e-x, y(0) = y0
has a finite limit as x ro. (15)
24. Let (p(x,y, z) = e1 siny. Evaluate the surface integral [[ da, where S is the surface
dn
S
rsl
of the cube 0 < x < 1, 0 < y < 1, 0 < z < 1 and is the directional derivative of f in the
dn
direction of the unit outward normal to S. Verify the divergence theorem. (15)
25. Let y = f (x) be a twice continuously differentiable function on (0, ro) satisfying
f(1) =1 and f'(x) = 2f , x > 0.
Form the second order differential equation satisfied by y = f (x), and obtain its solution satisfying the given conditions. (15)
: a, b, c, d e Z \ be the group under matrix addition and H be the
26. Let G =
subgroup of G consisting of matrices with even entries. Find the order of the quotient group G / H . (15)
27. Let
f x2 0 < x < 1
f (x) = 1 r
[V x x > 1.
Show that f is uniformly continuous on [0, ro). (15)
28. Find Mn = max \-x I, and hence prove that the series
x>0 [ n(1 + nx3)J
5
n=1n( + nx3 )
is uniformly convergent on [0, ). (15)
29. Let R be the ring of polynomials with real coefficients under polynomial addition and polynomial multiplication. Suppose
I={p g R : sum of the coefficients of p is zero}.
Prove that I is a maximal ideal of R. (15)
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
