Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT-M) 2011 B.Tech Aerospace Engineering gate- - Question Paper
2011 AEROSPACE ENGINEERING - AE
AE: AEROSPACE ENGINEERING
ONLINE Examination
Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. Questions must be answered using computers provided by the GATE at the examination centers. Each computer shall run specialized examination software that permits a maximum of one answer to be selected for questions of multiple choice type.
2. Your answers shall be updated and saved on the server periodically and at the end of the examination. The examination will automatically stop once the duration of the examination is over.
3. There are a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks. All questions are of objective type.
4. Questions Q.1 - Q.25 carry 1-mark each, and questions Q.26 - Q.55 carry 2-marks each.
5. Questions Q.26 - Q.30 are of numerical answer type. For each of these questions, the correct answer is a number. All other questions are of multiple choice type. Each of these questions carries four choices for the answer labeled A, B, C and D. Only one of the four choices is the correct answer.
6. Questions Q.48 - Q.51 (2 pairs) are common data questions and question pairs (Q.52, Q.53) and (Q.54, Q.55) are linked answer questions. The answer to the second question of the linked answer questions depends on the answer to the first question of the pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is unattempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated.
7. Questions Q.56 - Q.65 belong to General Aptitude (GA). Questions Q.56 - Q.60 carry 1-mark each, and questions Q.61 - Q.65 carry 2-marks each.
8. Unattempted questions will result in zero mark. There is no negative marking for questions of numerical answer type, i.e., for Q.26 - Q.30. For questions of multiple choice type, wrong answers will result in NEGATIVE marks. For Q.1 - Q.25 and Q.56 - Q.60, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. For Q.31 - Q.51 and Q.61 - Q.65, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. The question pairs (Q.52, Q.53), and (Q.54, Q.55) are questions with linked answers. There will be negative marks only for wrong answer to the first question of the linked answer question pair, i.e. for Q.52 and Q.54, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. There is no negative marking for Q.53 and Q.55.
9. Calculator is allowed whereas charts, graph sheets or tables are NOT allowed in the examination hall.
10. Rough work can be done in the specified area only.
11. Candidates may use the back side of this page to record their answers for their own convenience.
12. To login, type your Registration Number and password as per instructions provided in the envelope.
13. In order to answer a question, you may select the question using the left side selection panel on the screen and choose the correct answer by clicking on the radio button next to the answer. The answered questions shall be indicated by a solid black ball on the selection panel. In order to change the answer, you may just click on another option. If you wish to leave a previously answered question unanswered, you may click on DESELECT ANSWER button.
14. You may also select questions using NEXT and PREVIOUS buttons.
15. You may also mark questions for reviewing later using MARK button. All marked questions are indicated by a rectangle in the selection panel. Questions which are answered but are marked for the review are indicated by a solid black rectangle and questions which are not answered but are marked for the review are indicated by an outlined rectangle in the selection panel.
16. You must sign this sheet and leave it with the invigilators at the end of the examination.
DECLARATION I hereby declare that I have read and followed all the instructions given in this sheet.
Paper Code: AE Registration No:_Name:
Q. 1 - Q. 25 carry one mark each.
Q.1 Consider x,y,z to be right-handed Cartesian coordinates. A vector function is defined in this coordinate system as v = 3xi + 3xyj - yz2k , where i, j and k are the unit vectors along x, y and z axes, respectively. The curl of v is given by
(A) z 2i - 3 yk (B) z2 j + 3 yk (C) z 2i + 3 yj (D) - z 2i + 3yk
Q.2 Which of the following functions is periodic?
(A) f (x) = x2 (B) f (x) = log x (C) f (x) = ex (D) f (x) = const.
Q3 The function f (x1,x2,x3) = x2 + x + x -2x1 -4x2 -6x3 + 14has its minimum value at
(A) (1, 2, 3) (B) (0, 0, 0) (C) (3, 2, 1) (D) (1, 1, 3)
Q 4 Consider the function f (xj, x2) = x2 + 2x + e-x1 -x2. The vector pointing in the direction of maximum increase of the function at the point (1, -1) is
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
V- 5 j
V- 5 J
-6.73
-4
Vj
Q.5 Two simultaneous equations given by y = n + x and y = x -nhave
(A) a unique solution (B) infinitely many solutions
(C) no solution (D) a finite number of multiple solutions
Q.6 In three-dimensional linear elastic solids, the number of non-trivial stress-strain relations, strain-displacement equations and equations of equilibrium are, respectively,
(A) 3, 3 and 3 (B) 6, 3 and 3 (C) 6, 6 and 3 (D) 6, 3 and 6
Q.7 An Euler-Bernoulli beam in bending is assumed to satisfy
(A) both plane stress as well as plane strain conditions
(B) plane strain condition but not plane stress condition
(C) plane stress condition but not plane strain condition
(D) neither plane strain condition nor plane stress condition
Q.8 A statically indeterminate frame structure has
(A) same number of joint degrees of freedom as the number of equilibrium equations
(B) number of joint degrees of freedom greater than the number of equilibrium equations
(C) number of joint degrees of freedom less than the number of equilibrium equations
(D) unknown number of joint degrees of freedom, which cannot be solved using laws of mechanics
Q.9 Consider a single degree of freedom spring-mass-damper system with mass, damping and stiffness of m , c and k, respectively. The logarithmic decrement of this system can be calculated using
2nc nc 2nc 2nc
(A) , (B) , (C) (D)
a/4mk - c2 a/4mk - c2 sjmk - c2 -<Jmk - 4c2
Q10 Consider a single degree of freedom spring-mass system of spring stiffness k1 and mass m which
has a natural frequency of 10 rad/s. Consider another single degree of freedom spring-mass system of spring stiffness k2and mass m which has a natural frequency of 20 rad/s. The spring stiffness k2 is equal to
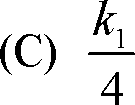
(D) 4k!
(B) 2kj
Q.11 Consider a simply supported two-dimensional beam

If the beam is converted into a fixed-fixed beam as
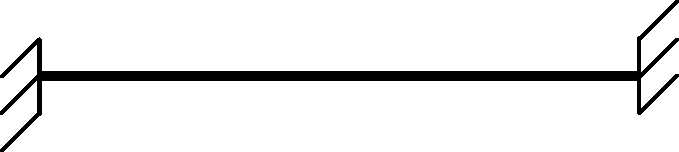
then the degree of static indeterminacy will
(A) increase by 3 (B) increase by 2 (C) decrease by 1 (D) decrease by 3
Q.12 An impulsive launch of a rocket minimizes the loss of burn-out velocity due to
(A) aerodynamic drag force only
(B) gravitational force only
(C) both aerodynamic drag and gravitational forces
(D) reaction jet control force
Q.13 Multi-staging in rockets improves the burn-out performance by increasing mainly stage-wise
(A) payload mass ratios (B) structural mass efficiencies
(C) propellant masses (D) control system masses
Q.14 In an un-powered glide of an aircraft having weight W, lift L and drag D, the equilibrium glide angle is defined as
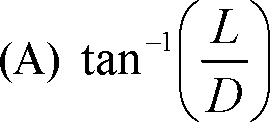
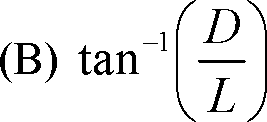
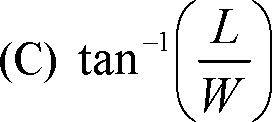
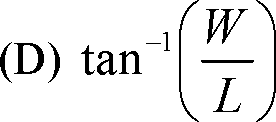
Q.15 Lift on an aircraft climbing vertically up is
(A) equal to its weight
(B) zero
(D) equal to the thrust
(C) equal to the drag
Q.16 If an aircraft is performing a positive yawing manoeuvre, the side slip angle
(A) is always zero (B) is never zero (C) is always negative (D) could be any value
Q.17 For an airplane to be statically stable, its centre of gravity must always be
|
(A) ahead of wing aerodynamic centre (C) ahead of neutral point |
(B) aft of the wing aerodynamic centre (D) aft of neutral point |
Q.18 It is seen that the drag polar of a certain aerofoil is symmetric about the Cd axis. This drag polar could refer to
(A) NACA 0012 (B) NACA 4415 (C) NACA 23012 (D) None of the above
Q.19 The aerodynamic centre of a supersonic aerofoil, with chord c, is located at
(A) the leading edge (B) 0.25c
(C) 0.5c
(D) 0.75c
Q.20 Winglets are used on wings to minimize
(A) skin friction drag (B) profile drag (C) wave drag
(D) induced drag
Q.21 Consider a potential flow with free stream velocity V,rj, over a spinning circular cylinder of radius R and circulation r. The stream function, y, where y = 0 on the cylinder surface, in cylindrical coordinates (r, 0) is given by
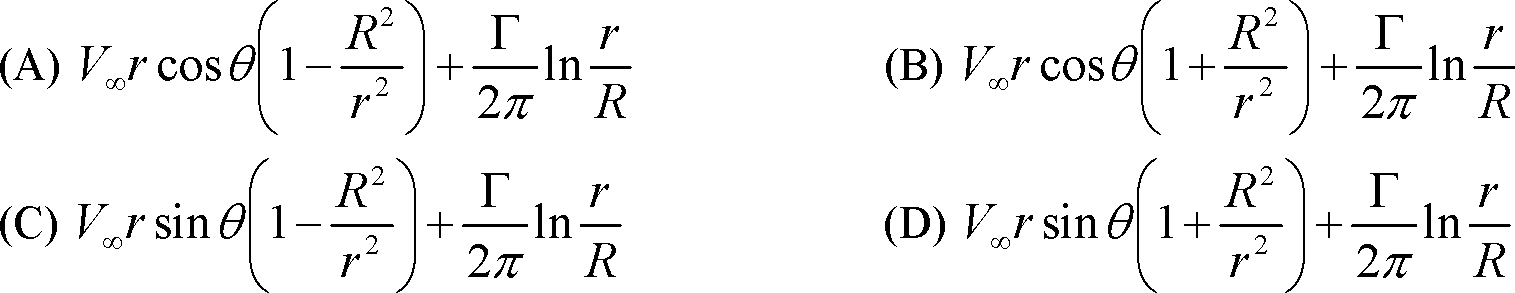
Q.22 A main objective of by-pass in a turbo-fan engine is to increase
(A) mass flow rate through engine inlet (B) turbine inlet temperature
(C) mass flow rate through exhaust nozzle (D) compressor pressure ratio
Q.23 The pressure ratio in any one stage of a jet engine compressor is limited by
(A) entry stagnation temperature in that stage
(B) entry Mach number in that stage
(C) pressure gradient induced separation in that stage
(D) mass flow rate in that stage
Q.24 Thermodynamic cycle on which the jet engine operates can be
(A) open Rankine cycle only (B) either open or closed Rankine cycle
(C) open Brayton cycle only (D) either open or closed Brayton cycle
Q.25 Propulsion efficiency of a jet engine is
(A) directly proportional to both the thrust power and the air mass flow rate
(B) inversely proportional to both the thrust power and the air mass flow rate
(C) directly proportional to the thrust power and inversely proportional to the air mass flow rate
(D) inversely proportional to the thrust power and directly proportional to the air mass flow rate
Q. 26 to Q. 55 carry two marks each.
Questions Q.26 to Q. 30 are numerical answer type. The answer to each of these questio ns is either a positive whole number, or a positive real number with maximum of 2 decimal places.
Q.26 Consider a cantilever beam having length L=1 m, square cross-section (width = depth = 0.01 m) and Youngs modulus 50 GPa. The beam is subjected to a transverse load P = 1 N at the mid-span (L/2) at the center of the cross-section. Under the small deformation theory, the transverse deflection of the beam (in mm) at its free-end is -
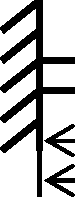
L
Q.27 Consider a beam in bending with a solid circular cross-section of 1 mm2, which is subjected to a transverse shear force of 1 N. The shear stress at the center of the cross-section (in N/mm2) is
Q.28 A simply supported slender column of square cross section (width=depth=d) has to be designed such that it buckles at the same instant as it yields. Length of the column is given to be 1.57 m and it is made of a material whose Youngs modulus is 200 GPa and yield stress is 240 MPa. The width, d, of the column (in cm) should be -
Q.29 A turbojet powered aircraft is flying at Mach number 0.8 at an altitude of 10 km. The inlet and exit areas of the engine are 0.7 m2 and 0.4 m2 respectively. The exhaust gases have velocity of 500 m/s and pressure of 60 kPa. The free stream pressure, density and speed of sound are 26.5 kPa, 0.413 kg/m3 and 299.5 m/s respectively. The thrust of the engine (in kN) is _
Q.30 A low speed wind tunnel has a contraction ratio of 14:1 and the cross-sectional area of the test section is 1 m2. The static pressure difference between the settling chamber and the test section is 40 cm of water column. Assume g = 9.81 m/s2,pair = 1.2 kg/m3and pwater = 1000 kg/m3. The speed of air in the test section (in m/s) is _
Questions Q.31 to Q.55 are multiple choice type.
Q.31 Consider the function f (x) = x - sin(x) . The Newton-Raphson iteration formula to find the root of the function starting from an initial guess x(0) at iteration k is
(A) x
(B) x1
(C) x
(D) x
(k)
(k)
1 - cos x(k) sin x(k) + x( k) cos xk
(k+1) = sin x(k) - x(k) cos xk
1 - cos x
(k+1) _
1 + cos x(k) sin x(k) + x( k) cos xk
(k+1) = sin x(k) - x(k) cos xk
1 + cos x
(k+1)
where a and b are real numbers. The two eigenvalues of this matrix A and A are real and distinct ( A ) when
Q.32
2 a b 2
(A) a < 0 and b > 0 (B) a > 0 and b < 0 (C) a < 0 and b < 0 (D) a = 0 and b = 0
Consider the matrix
Q 33 dy 3 t 2
The solution of = yet with initial condition y(0) = 1 is given by dt
(A)1 e (t+3)2
(B)
(D)
4e
(C)
(t + 2)2
5 + 2et (t2 - 2t + 2)
5 - 2et (t2 - 2t + 2)
9
1
Q.34 A jet engine is operating at a Mach number of 0.8 at an altitude of 10 km. The efficiency of the air intake is 0.8 and that of the compressor is 0.87. The total temperatures (in K) at the exits of the air intake and the compressor respectively are
(Ambient pressure = 26.5 kPa; Ambient temperature = 223.3 K; Gas constant, r= 14; Prc = 8)
(A) 251.9 and 458.2 (B) 234.9 and 486.8 (C) 251.9 and 486.8 (D) 234.9 and 458.2
Q.35 A rocket engine is tested on a test bed under the ideal condition of fully expanded jet. The exhaust velocity is 2 km/s through a nozzle of area 2.5 m1. The mass flow rate is 200 kg/s. The specific impulse of the propellant and the thrust developed respectively are (assume g = 9.81 m/s2)
(A) 175.87 s and 200 kN (C) 231.87 s and 200 kN
(B) 203.87 s and 400 kN (D) 280.87 s and 400 kN
Q.36 A body undergoes deformation under plane strain conditions when subjected to the following stresses (in MPa): ax = 450, ayy = 450, t = 75, txz = 0, ryz = 0. What are the remaining
components of stresses (in MPa) and strains? Assume the material to be isotropic and linear-elastic with Youngs modulus E = 200 GPa and Poissons ratio v= 1/3.
(A) azz = 0 = 0.00225, = 0.00225, Yxy = 0.002, Y*z = 0 = 0
(B) azz = 300, y*x = 0 001, yyy = 0 001, Yxy = 0001, Yxz = 0 Yyz = 0
(C) azz = 300, y = 0.00225, = 0.00225, = 0.001, Xz = 0, = 0
(D) azz = 0 y*x = 0 001, yyy = 0 001, Yxy = 0 002, Yxz = 0 Yyz = 0
Q.37 Which of the following Airys stress functions could satisfy the given boundary conditions, assuming constant values of axx = P, ayy = Q and Txy = R, along the boundary?
|
,x |
|
2 2 (A) 0 = Py + Q- - Rxy |
22 (B) 0 = p-+Qy+Rxy x 2 y 2 (D) 0 = P + Q- + Rxy |
Q.38 An aircraft is performing a coordinated turn manoeuvre at a bank angle of 30o and forward speed of 100 m/s. Assume g = 9.81 ms-2. The load factor and turn radius respectively are
(A) (2/V3) and 1.76 km (B) V3 and 17.6 km
(C) 2 and 0.18 km (D) (2/V3) and 17.6 km
Q.39 An aircraft in a steady level flight at forward speed of 50 m/s suddenly rolls by 180 and becomes inverted. If no other changes are made to the configuration or controls of the aircraft, the nature of the subsequent flight path taken by the aircraft and its characteristic parameter(s) (assume g = 9.81
ms-2) are
(A) straight line path with a speed of 50 m/s
(B) upward circular path with a speed of 50 m/s and radius of 127.4 m
(C) downward circular path with a speed of 50 m/s and radius of 127.4 m/s
(D) downward circular path with a speed of 25 m/s and radius of 254.8 m/s
Q.40 An aircraft with a mass of 5000 kg takes off from sea level with a forward speed of 50 m/s and starts to climb with a climb angle of 15o. The rate of climb and excess thrust available at the start of the climb respectively (assume g = 9.81 ms-2) are
(A) 13.40 m/s and 13146.0 N (C) 13.40 m/s and 12694.1 N
(B) 12.94 m/s and 12694.1 N (D) 12.94 m/s and 13146.0 N
Q.41 A glider having a mass of 500 kg is taken to an altitude of 1000 m with a jeep moving on ground at 54 kmph. Upon reaching the required altitude in 50 s, the glider is released and starts its descent. Under the assumption of equilibrium glide, the range and endurance of the glider for a constant lift-to-drag ratio of 15 are
(A) 15.0 km and 1002.2 s respectively (C) 1.0 km and 601.3 s respectively
(B) 15.0 km and 601.3 s respectively (D) 1.0 km and 50 s respectively
Q.42
An elliptic orbit has its perigee at 400 km above the Earths surface and apogee at 3400 km above the Earths surface. For this orbit, the eccentricity and semi-major axis respectively are (assume radius of Earth = 6400 km)
(A) 0.18 and 8300 km (C) 0.22 and 8300 km
(B) 0.18 and 1900 km (D) 0.22 and 1900 km
Q.43
An aircraft in level flight encounters a vertical gust, which excites the phugoid mode. The phugoid motion completes 10 cycles in 50 s and its amplitude reduces to half of its maximum value in 25 s. The eigenvalues of the phugoid mode are
(A) -0.05 0.02i
(B) -0.5 0.2i
(C) -0.028 1.26i (D) 0.028 1 26i
Q.44 Consider the inviscid, adiabatic flow of air at free stream conditions, Mi = 2, pi = 1 atm and Ti = 288 K around a sharp expansion corner (0 = 20) as shown below. The Prandtl-Meyer function, v,
tan(M2 -1) - tan-1Vm2 -1
is given as a function of Mach number, M, as v(M) =
Assume air to be calorically perfect with y = 1.4. The Mach number, M2, downstream of the expansion corner is approximately
M1, p1, T1 . .
/-r-r77-rrrrrr7TT7'
 |
0 M2 |
(A) 2.00
(B) 1.76
(C) 2.83
(D) 3.14
Consider a steady two dimensional zero-pressure gradient laminar flow of air over a flat plate as shown below. The free stream conditions are U = 100 ms-1, pOT = 1.2 kg m-3, pOT = 1 atm and = 1.8 x10-5kg m"1s"1. The ratio of displacement thickness to momentum thickness of the boundary layer at a distance of 2 m from the leading edge is
Q.45
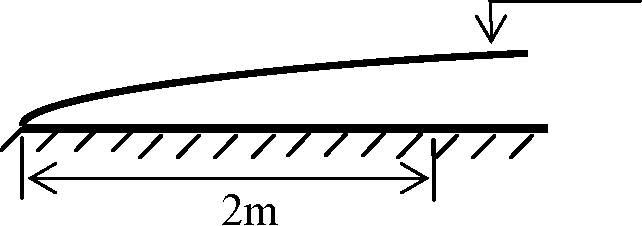 |
Boundary layer |
|
(C) 2.91 | |
(A) 7.53
(B) 2.59
(D) 0.39
Q.46 In the context of Prandtls lifting line theory for a finite wing, which of the following combinations of statements is TRUE?
P: The bound vortex is responsible for the lift force Q: The trailing vortices are responsible for the induced drag R: The bound vortex is responsible for the induced drag S: The trailing vortices are responsible for the lift force
(A) P,Q (B) Q,R (C) R,S (D) P,S
Q.47 Consider flow over a thin aerofoil at Mach number, M = 0.5 at an angle of attack, a. Using the Prandtl-Glauert rule for compressibility correction, the formula for lift coefficient, cl, can be written as
(A) 5.44a (B) 6.28a (C) 7.26a (D) 14.52a
Common Data Questions Common Data for Questions 48 and 49:
The partial differential equation (PDE) governing free vibrations of a uniform Euler-Bernoulli beam is
. d 4 w d2 w - + m2
given by El-4 + m = 0, where EI is the flexural stiffness, m is the mass per unit length,
dx4 dt2
w(x, t) is the bending displacement, x is the coordinate along the beam length, t is time and L is the beam length.
x = 0 x x = L
> I
L
Q.48 To solve the PDE, the number of boundary conditions (BC) and initial conditions (IC) needed are (A) 4 BC, 3 IC (B) 2 BC, 2 IC (C) 2 BC, 4 IC (D) 4 BC, 2 IC
Q.49 For the cantilever beam shown in the figure, which of the following CANNOT be a possible boundary condition?
d 2w d2 w d3w
(A) w(0, t) = 0 (B) t (L, t) = 0 (C) (0, t) = 0 (D) (L, t) = 0
Common Data for Questions 50 and 51:
Consider an inviscid, adiabatic flow of air at free stream Mach Number, M = 2, across a compression corner (0 = 20) as shown. The free stream total enthalpy is h0<X) = 810 kJ kg-1. Assume that air is calorically perfect with y = 1.4, R = 287 J kg-1 K-1.
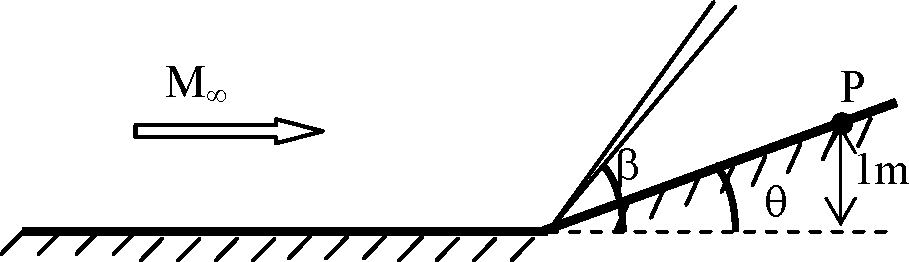
Q.50 The shock angle P is
(A) = 20 (B) > 20 and < 30 (C) = 30 (D) > 30
Q.51 The total temperature at point P is
(A) 806.37 K (B) 1128.92 K (C) 1612.74 K (D) 2257.84 K
Linked Answer Questions Statement for Linked Answer Questions 52 and 53:
A thin-walled (thickness << radius), hollow shaft of length 1m and mean radius, R = 5 cm has to be designed such that it can transmit a torque, T = 7 kN-m. A survey of different commercially available materials was made and following data was obtained from the suppliers (E: Youngs modulus, ry: yield stress in shear, p: density):___
|
Material |
E (GPa) |
tv (MPa) |
p (kg/m3) |
|
X |
200 |
550 |
7700 |
|
Y |
70 |
225 |
2700 |
|
Z |
110 |
375 |
4875 |
Q.52 Which of the above materials would you choose such that weight of the shaft is minimum?
(A) X only (B) Y only (C) Z only (D) X or Y
Q.53 If you assume a factor of safety of 2, what should be the approximate thickness of such a shaft?
(A) 0.5 mm (B) 1 mm (C) 2 mm (D) 4 mm
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 54 and 55:
Prandtls lifting line equation for a general wing is given by
a(y0 ) = 3?T + aL=0 (0 )+T f ( / dydy, where Ux is the free-stream velocity, a is the
2
angle of attack, y0 is the spanwise location, aL=0 (y0) gives the spanwise variation of zero-lift angle, c is the chord, b is the span, and r(y0) gives the spanwise variation of circulation.
Q.54 dr
The rate of change of circulation with angle of attack ra =-is
(A) inversely proportional to a (B) independent of a
(C) a linear function of a (D) a quadratic function of a
Q.55
Given that CL x f r(y~dy, the corresponding lift curve-slope L is
\ da
2
(A) independent of a (B) a linear function of a
(C) a quadratic function of a (D) a cubic function of a
General Aptitude (GA) Questions Q. 56 - Q. 60 carry one mark each.
Q.56 Choose the word from the options given below that is most nearly opposite in meaning to the given word:
Deference
(A) aversion
(B) resignation
(C) suspicion
(D) contempt
Q.57 Choose the most appropriate word(s) from the options given below to complete the following sentence.
We lost confidence in him because he never_the grandiose promises he had made.
(A) delivered
(B) delivered on
(C) forgot
(D) reneged on
Q.58 Choose the word or phrase that best completes the sentence below.
_in the frozen wastes of Arctic takes special equipment.
(A) To survive
(B) Surviving
(C) Survival
(D) That survival
Q.59 In how many ways 3 scholarships can be awarded to 4 applicants, when each applicant can receive any number of scholarships?
(A) 4 (B) 12 (C) 64 (D) 81
Q.60 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence.
The__of eviden ce was on the side of the plaintiff since all but one witness testified
that his story was correct.
(A) paucity
(B) propensity
(C) preponderance
(D) accuracy
Q. 61 to Q. 65 carry two marks each.
Q61 If (2y+1)/(y+2) < 1, then which of the following alternatives gives the CORRECT range of y?
(A) - 2 < y < 2 (B) - 2 < y < 1 (C) - 3 < y < 1 (D) - 4 < y < 1
Q.62 A student attempted to solve a quadratic equation in x twice. However, in the first attempt, he incorrectly wrote the constant term and ended up with the roots as (4, 3). In the second attempt, he incorrectly wrote down the coefficient of x and got the roots as (3, 2). Based on the above information, the roots of the correct quadratic equation are
(A) (-3, 4) (B) (3, -4) (C) (6, 1) (D) (4, 2)
Q.63 L, M and N are waiting in a queue meant for children to enter the zoo. There are 5 children between L and M, and 8 children between M and N. If there are 3 children ahead of N and 21 children behind L, then what is the minimum number of children in the queue?
(A) 28 (B) 27 (C) 41 (D) 40
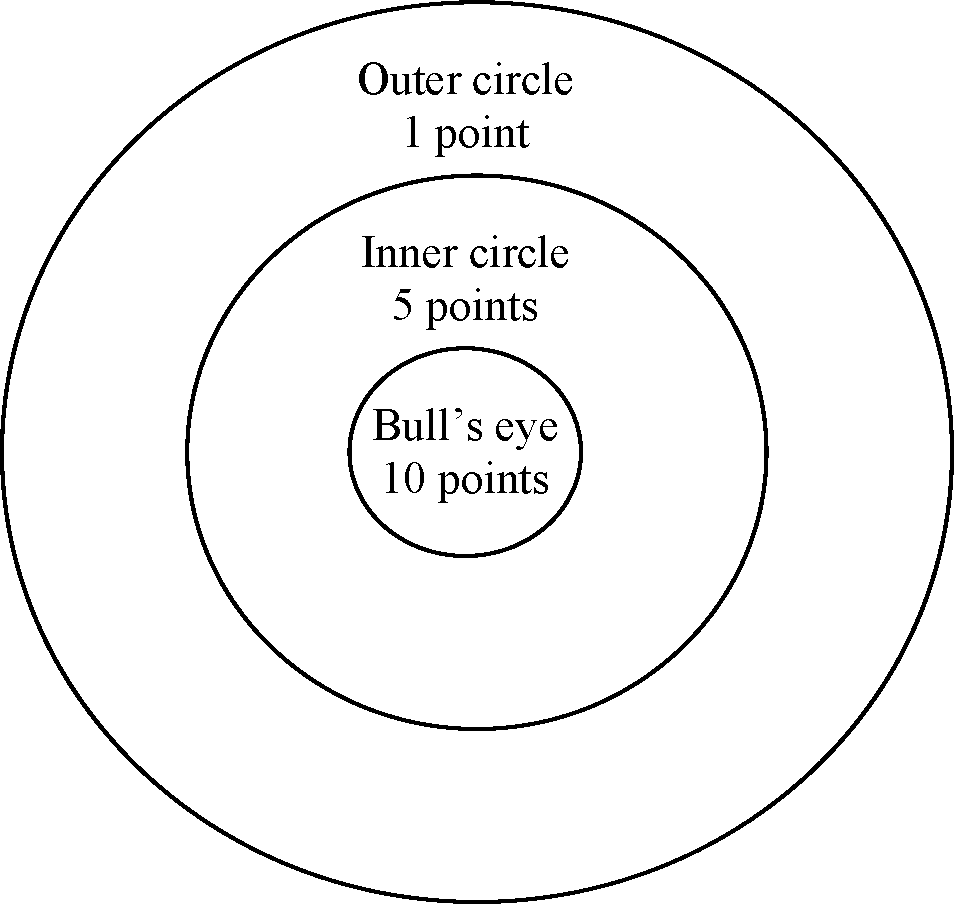
Q.64 Four archers P, Q, R and S try to hit a bulls eye during a tournament consisting of seven rounds. As illustrated in the figure below, a player receives 10 points for hitting the bulls eye, 5 points for hitting within the inner circle and 1 point for hitting within the outer circle.
The final scores received by the players during the tournament are listed in the table below.
|
Round |
P |
Q |
R |
S |
|
1 |
1 |
5 |
1 |
10 |
|
2 |
5 |
10 |
10 |
1 |
|
3 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
5 |
|
4 |
10 |
10 |
1 |
1 |
|
5 |
1 |
5 |
5 |
10 |
|
6 |
10 |
5 |
1 |
1 |
|
7 |
5 |
10 |
1 |
1 |
The most accurate and the most consistent players during the tournament are respectively (A) P and S (B) Q and R (C) Q and Q (D) R and Q
Q.65 Nimbus clouds are dark and ragged, stratus clouds appear dull in colour and cover the entire sky. Cirrus clouds are thin and delicate, whereas cumulus clouds look like cotton balls.
It can be inferred from the passage that
(A) A cumulus cloud on the ground is called fog
(B) It is easy to predict the weather by studying clouds
(C) Clouds are generally of very different shapes, sizes and mass
(D) There are four basic cloud types: stratus, nimbus, cumulus and cirrus
END OF THE QUESTION PAPER
AE
2
(C) 0 = P + Qy - Rxy
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
