Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IIT-M) 2012 GATE Mathematics with Answer Key - Question Paper
2012 MATHEMATICS - MA
Duration: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. Do not open the seal of the Question Booklet until you are asked to do so by the invigilator.
2. Take out the Optical Response Sheet (ORS) from this Question Booklet without breaking the seal and read the instructions printed on the ORS carefully.
3. On the right half of the ORS, using ONLY a black ink ball point pen, (i) darken the bubble corresponding to your test paper code and the appropriate bubble under each digit of your registration number and (ii) write your registration number, your name and name of the examination centre and put your signature at the specified location.
4. This Question Booklet contains 20 pages including blank pages for rough work. After you are permitted to open the seal, please check all pages and report discrepancies, if any, to the invigilator.
5. There are a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks. All these questions are of objective type. Each question has only one correct answer. Questions must be answered on the left hand side of the ORS by darkening the appropriate bubble (marked A, B, C, D) using ONLY a black ink ball point pen against the question number. For each question darken the bubble of the correct answer. More than one answer bubbled against a question will be treated as an incorrect response.
6. Since bubbles darkened by the black ink ball point pen cannot be erased, candidates should darken the bubbles in the ORS very carefully.
7. Questions Q.1 - Q.25 carry 1 mark each. Questions Q.26 - Q.55 carry 2 marks each. The 2 marks questions include two pairs of common data questions and two pairs of linked answer questions. The answer to the second question of the linked answer questions depends on the answer to the first question of the pair. If the first question in the linked pair is wrongly answered or is unattempted, then the answer to the second question in the pair will not be evaluated.
8. Questions Q.56 - Q.65 belong to General Aptitude (GA) section and carry a total of 15 marks. Questions Q.56 - Q.60 carry 1 mark each, and questions Q.61 - Q.65 carry 2 marks each.
9. Unattempted questions will result in zero mark and wrong answers will result in NEGATIVE marks. For all 1 mark questions, % mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. For all 2 marks questions, 2A mark will be deducted for each wrong answer. However, in the case of the linked answer question pair, there will be negative marks only for wrong answer to the first question and no negative marks for wrong answer to the second question.
10. Calculator is allowed whereas charts, graph sheets or tables are NOT allowed in the examination hall.
11. Rough work can be done on the question paper itself. Blank pages are provided at the end of the question paper for rough work.
12. Before the start of the examination, write your name and registration number in the space provided below using a black ink ball point pen.
|
Name | ||||||||
|
Registration Number |
MA | |||||||
Set of all real numbers
R
C
I
F
cn
Fn
R x R x ...x R
DJ (x y)
N (m,&2)
E ( X )
Cov( X ,Y )
Sn
Pn
Cn
Z(G)
i = J1
Set of all complex numbers Set of all integers A field
The set of all n-tuples of complex numbers The set of all n-tuples over F Cartesian product of rings R, R,..., R
Partial derivative with respect to x.
Normal distribution with mean fi and variance G1
Expectation of X
Covariance between X and Y
The group of all permutations on n symbols
The set of all polynomials of degree at most n
Cyclic Group of Order n Centre of the Group G
Q. 1 - Q. 25 carry one mark each.
Q1 The straight lines L ' x = 0, L : y = 0 and L : x + y = 1 are mapped by the transformation w = z2 into the curves Q, C2 and Q respectively. The angle of intersection between the curves at w = 0 is
(A) 0
(C) n /2
(D) n
(B) n / 4
Q.2 In a topological space, which of the following statements is NOT always true :
(A) Union of any finite family of compact sets is compact.
(B) Union of any family of closed sets is closed.
(C) Union of any family of connected sets having a non empty intersection is connected.
(D) Union of any family of dense subsets is dense.
|
Q.3 Consider the following statements: |
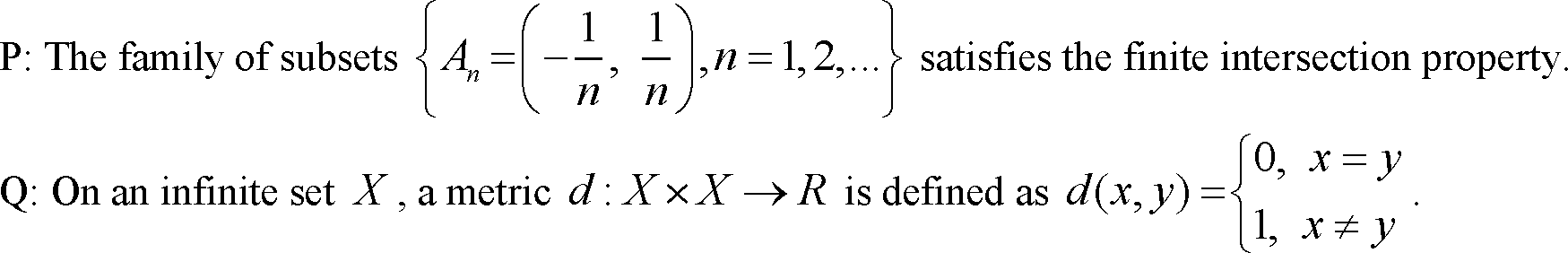 |
|
The metric space (X, d) is compact. R: In a Frechet (T) topological space, every finite set is closed. S: If f: R X is continuous, where R is given the usual topology and (X, r) is a Hausdorff ( T ) space, then f is a one-one function. Which of the above statements are correct? |
(B ) P and S
( C) R and S
(D) Q and S
(A) P and R
Q.4 Let H be a Hilbert space and S1 denote the orthogonal complement of a set S H . Which of the following is INCORRECT?
(A) For S, S2 H; S S2 S S2
(B) S c (S1)1
(D) S1 is always closed.
(C) {0}1= H
Q.5 Let H be a complex Hilbert space, T:H H be a bounded linear operator and let T * denote the adjoint of T . Which of the following statements are always TRUE?
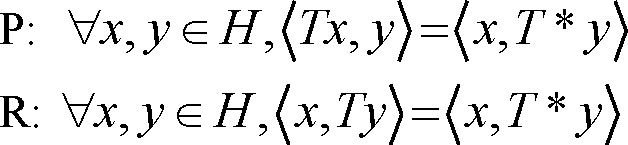 |
|
(A) P and Q |
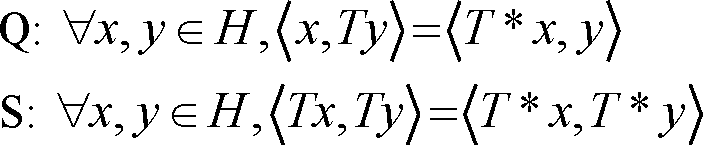 |
|
(C) Q and S |
(B) P and R
(D) P and S
Q.6 Let X = {a, b,c} and let '3=\$,{a},{b},{a,b}, X}be a topology defined onX . Then which of the following statements are TRUE?
P: (X, 3) is a Hausdorff space. Q: (X, 3) is a regular space.
R: (X, 3) is a normal space. S: (X, 3) is a connected space.
(A) P and Q (B) Q and R (C) R and S (D) P and S
Q.7 Consider the statements
P: If X is a normed linear space and M X is a subspace, then the closure M is also a subspace of X.
Q: If X is a Banach space and xn is an absolutely convergent series in X, then xn is convergent.
R: Let M1 and M2 be subspaces of an inner product space such that M1 M2 = {0} .Then
v m g -M, m G m2 ; ||m + m f =1 mt HI ml |2 .
S: Let f: X Y be a linear transformation from the Banach Space X into the Banach space Y . If f is continuous, then the graph off is always compact.
The correct statements amongst the above are:
(A) P and R only (B) Q and R only (C) P and Q only (D) R and S only Q.8 A continuous random variable X has the probability density function
3
3 - e 5
X
x > 0
<
f (x) =
0, x < 0. The probability density function of Y = 3X + 2 is
2 - 2(y-2)
5eS
0,
4 - 4(y-2)
5e , 0,
y > 2 y < 2 y > 2 y < 2
(A) f (y) =
(B) f (y) =
<
<
(C) f (y) =
(D) f (y) =
<
<
3 - t(y-2) -e 5 , y > 2 0, y < 2
1 - e
5
0,
y < 2
A simple random sample of size 10 from N(,a2) gives 98% confidence interval (20.49, 23.51). Then the null hypothesis H0 : ju = 20.5 against H : ju 20.5
Q.9
(A) can be rejected at 2% level of significance
(B) cannot be rejected at 5% level of significance
(C) can be rejected at 10% level of significance
(D) cannot be rejected at any level of significance
Q.10 For the linear programming problem
z = x + 2x2 + 3x3 - 4x4 2xj + 3x2 - x3 - x4 = 15 6xj + x2 + x3 - 3x4 = 21 8xj + 2x2 + 3x3 -4x4 = 30 X, x2, x3, x4 > 0,
Maximize Subject to
X = 4, x2 = 3, x3 = 0, x4 = 2 is
(A) an optimal solution
(B) a degenerate basic feasible solution
(C) a non-degenerate basic feasible solution
(D) a non-basic feasible solution
MA
Q.11 Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
(A) A convex set cannot have infinite many extreme points.
(B) A linear programming problem can have infinite many extreme points.
(C) A linear programming problem can have exactly two different optimal solutions.
(D) A linear programming problem can have a non-basic optimal solution.
2ni / 5
|
Q.12 Let a =e 1 and the matrix | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(A) - 5 (B) 0 (C) 3 (D) 5
Q13 Let V = C2 be the vector space over the field of complex numbers and B={(1, i),(i,1)}be a given ordered basis of V. Then for which of the following, B *={f, f }is a dual basis of B over C?
(A) f1(Z1, Z2) = 1(Z1 - iZ2), f2 (Z1 , Z2) = 1(Z1 + iZ2 )
(B) f1(z1, Z2) = 1(Z1 + iZ2), f2 (Z1 , Z2) = 1(iZ1 + Z2)
(C) f1(Z1, Z2) = 1( Z1 - iZ2), f2( Z1. Z2) = 1(-iZ1 + Z2)
(D) f1(Z1, Z2) = 1(Z1 + iZ2), f2 (Z1, Z2) = 1(-iZ1 - Z2)
Q.14 Let R = IxlxH and I = {0}. Then which of the following statement is correct?
(A) I is a maximal ideal but not a prime ideal of R .
(B) I is a prime ideal but not a maximal ideal of R .
(C) I is both maximal ideal as well as a prime ideal of R .
(D) I is neither a maximal ideal nor a prime ideal of R .
Q.15 The function u(r,6) satisfying the Laplace equation
d2u 1 du 1 d 2u
-= 0,
e < r < e
dr2 r dr r2 D62 subject to the conditions u(e,6) = 1, u(e2,6) = 0 is
(D) I
sin n6
(B) ln(e / r2)
v e - e j
(A) ln(e / r)
Q.16 The functional
1
j (/2 + (y + 2y')y" + kxyy + y2) dx, y(0) = 0, y(1) = 1, y(0) = 2, y(1) = 3
0
is path independent if k equals
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
(C) ln(e2/ r)
Q.17 If a transformation y = uv transforms the given differential equation
f (x)y" 4f '(x)y' + g(x)y = 0 into the equation of the form v" + h(x)v = 0, then u must be
(B) xf
(C) 1/2f
(A) 1/ f2
Q.18 The expression
(D) f2
1
, , sin(x y) is equal to D2 D
x y
x
(A) - cos( x y)
(B) sin( x y) + cos( x y)
3x . . .
(D) ysin( x y)
x
(C) cos( x y) + sin( x y)
Q.19 The function <fi(x) satisfying the integral equation
0
is
x
2
x
(D) 1 +
(A)
(B) x + 2
2
Q.20 Given the data:
| ||||||||||||
|
If the derivative of y(x)is approximated as: y'(xfc) (Ayfc + A2yk 1 A3yk) , then the value h |
of y'(2) is (A) 4
(B) 8
(C ) 12
(D) 16
1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
, then A50 is
Q.21 If A =
|
" 1 |
0 |
0 |
" 1 |
0 |
0 | ||
|
(A) |
50 |
1 |
0 |
(B) |
48 |
1 |
0 |
|
50 |
0 |
1 |
48 |
0 |
1 | ||
|
' 1 |
0 |
0" |
" 1 |
0 |
0 | ||
|
(C) |
25 |
1 |
0 |
(D) |
24 |
1 |
0 |
|
25 |
0 |
1 |
24 |
0 |
1 |
Q.22 If y = cmxr+m is assumed to be a solution of the differential equation
m=0
x2y" xy' 3(1 + x2) y = 0, then the values of r are
(A) 1 and 3
(B) -1 and 3
(C) 1 and -3
(D) -1 and -3
Q.23 Let the linear transformation T: F2 F3 be defined by T(x, x2) = (x, X + x2, x2) . Then the nullity of T is
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) 3
Q.24 The approximate eigenvalue of the matrix
-15 4 3"
A = 10 -12 6 20 -4 2
obtained after two iterations of Power method, with the initial vector [1 1 1]T , is (A) 7.768 (B) 9.468 (C) 10.548 (D) 19.468
Q.25 The root of the equation xex = 1 between 0 and 1, obtained by using two iterations of bisection method, is
(A) 0.25 (B) 0.50
Q. 26 to Q. 55 carry two marks each
1 (a - 2)2
(C) 0.75
(D) 0.65
Q26 Let j
dz = 4n, where the close curve C is the triangle having vertices at
- + 4
(* - 2)4
C
. f-1 -i' I V2,
a is
(A) 1 + i
and
, the integral being taken in anti-clockwise direction. Then one value of
(B) 2 + i
(C) 3 + i
(D) 4 + i
Q.27 The Lebesgue measure of the set A = j 0 < x < 1: x sin I I > 0 > is
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) ln2
(D) 1 - ln>/2
Q.28 Which of the following statements are TRUE?
P : The set {x e R :|cos x| < } is compact.
Q : The set {x e R :tanx is not differentiable} is complete.
to /_2 n+1
R : The set {x e R : V-is convergent} is bounded.
n=0 (2n +1)!
S : The set {x e R: f (x) = cosx has a local maxima} is closed.
(B) R and S
(C) Q and S
(D) P and S
(A) P and Q
Q.29 If a random variable X assumes only positive integral values, with the probability
vx-1
P( X = x) =
(B) 2/3
(C) 1
(D) 3/2
then E (X) is (A) 2/9
Q.30 The probability density function of the random variable X is
1
e A
-x/A
x > 0
f (x) =
where A > 0. For testing the hypothesis H0 : A = 3 against H : A = 5, a test is given as Reject H if X > 4.5 . The probability of type I error and power of this test are, respectively,
(A) 0.1353 and 0.4966 (C) 0.2021 and 0.4493
(B) 0.1827 and 0.379 (D) 0.2231 and 0.4066
Q.31 The order of the smallest possible non trivial group containing elements x and y such that
7 2 i 4,
x = y = e and yx = x y is (A) 1 (B) 2
(D) 14
(C) 7
Q.32 The number of 5-Sylow subgroup(s) in a group of order 45 is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3
(D) 4
Q.33 The solution of the initial value problem
y" + 2y' + 10y = 6 S(t), y(0) = 0, y'(0) = 0, where S(t) denotes the Dirac-delta function, is
|
(A) |
'Krt En (N |
(B) |
'Krt CO *00 |
(C) 2 e |
_t sin 3t |
|
Let |
2 O = cos 3 |
. 2 + i sin 3 |
( 0 , M = , Ii |
i (o , N= oJ 0 |
0 o2 j |
(D) 6 et sin3
and G = (M, N) be the group generated by the matrices M and N under matrix multiplication. Then (A) g/zg=C6 (B) G/Z(G)=S3 (C) g/zg)=C2 (D) g/z(G)=C4
Q.35 The flux of the vector field u =xi +yj + zk flowing out through the surface of the ellipsoid
2 2 2 x y z
t + 7 + r=1, a > b > c > 0, a2 b2 c2
(B) 2nabc
(C) 3nabc
(D) 4nabc
is
(A) nabc
dz 2 dz
Q.36 The integral surface satisfying the partial differential equation--+ z = 0 and passing through
the straight line x = 1, y = z is (A) (x 1) z + z 2 = y2
(B) x2 + y2 z2 = 1 (D) (x 1) z2 + z = y
(C) (y z) x + x2 = 1
Q.37 The diffusion equation
d 2u du
=, u = u(x, t), u(0, t) = 0 = u(n, t), u(x,0) = cos x sin5x
dx2 dt admits the solution
(A) sin 6x + e20t sin4x (B) sin4x + e20t sin6x J
e~20t r e36t r n
(C) sin3x + e15t sin5xj (D) sin5x + e20t sin xj
Q.38 Let f (x) and xf (x) be the particular solutions of a differential equation
y" + R( x) y' + S (x) y = 0.
Then the solution of the differential equation y" + R(x) y " + S (x) y = f (x) is
---+ ax + P f (x) (B) y =--+ ax + P f (x)
(A) y =
v2 y
(C) y = (-x +ax + P)f (x) (D) y = (x +ax + P)f (x)
Q.39 Let the Legendre equation (1 -x2)y"-2xy' + n(n + 1)y = 0 have nth degree polynomial solution
1 144
yn (x) such that yn (1) = 3. If j (yj (x) + y2 (x)) dx =
then n is
15
-1
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
Q.40 The maximum value of the function f (x, y, z) = xyz subject to the constraint xy + yz + zx - a = 0, a > 0 is
3
(A) a2 (B) (a/3)3/2 (C) (3/a)3/2 (D) (3a/2)3/2
1/ \ 4 4 e
Q.41 The functional 11 y2 + 4y2 + 8yex I dx, y(0) = , y(1) =--possesses :
3 3
0
1 x 4
(A) strong minima on y = - ex (B) strong minima on y = - ex
1 x 4
(C) weak maxima on y = - ex (D) strong maxima on y = - ex
Q.42 A particle of mass m is constrained to move on a circle with radius a which itself is rotating about its vertical diameter with a constant angular velocity m . Assume that the initial angular velocity is zero and g is the acceleration due to gravity. If 0 be the inclination of the radius vector of the
particle with the axis of rotation and 6 denotes the derivative of 6 with respect to t, then the Lagrangian of this system is
(A) ma2(02 +co2 sin2 &)+mga cos & (B) lfS2
(C) ma2{62 + 2o2 cosO)-mgasin0 (D) I*** +sin2)+mgas,
Q.43 For the matrix
" 2 3 + 2i -4"
M = 3 - 2i 5 6i -4 -6i 3 which of the following statements are correct?
P : M is skew-Hermitian and iM is Hermitian Q : M is Hermitian and iM is skew Hermitian R : eigenvalues of M are real S : eigenvalues of iM are real
(A) P and R only (B) Q and R only (C) P and S only (D) Q and S only
x
Q.44 Let T: be the map given by T(p(x)) = Jp'(t) dt. If the matrix of T relative to the
1
standard bases Bl = B2 = |1, x, x2, x31 is M and M denotes the transpose of the matrix M, then M + M' is
|
(A) (C) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Q.45 Using Eulers method taking step size = 0.1, the approximate value ofy obtained corresponding to
x = 0.2 for the initial value problem = x2 + y2 and y(0) = 1, is
dx
(A) 1.322
(B) 1.122
(C) 1.222
(D) 1.110
Q.46 The following table gives the unit transportation costs, the supply at each origin and the demand of e ach destination for a transportation problem.
Destination
|
D1 |
D2 |
D3 |
D4 |
Supply | |
|
O1 |
3 |
4 |
8 |
7 |
60 |
|
Origin O2 |
7 |
3 |
7 |
6 |
80 |
|
O3 |
3 |
9 |
3 |
4 |
100 |
|
Demand |
40 |
70 |
50 |
80 |
Let x denote the number of units to be transported from origin i to destination j. If the u-v method is applied to improve the basic feasible solution given by x12 = 60, x22 = 10, x23 = 50, x24 = 20, x = 40 and x = 60, then the variables entering and leaving the basis, respectively, are
(A) x and x
(C) x and x
(D) x and x
24
23
24
24
(B) x and x
Q.47 Consider the system of equations
|
5 |
1 |
1" |
x |
"10" | |
|
2 |
4 |
0 |
y |
= |
12 |
|
1 |
1 |
5 |
z |
-1 |
i i t 'j-'
Using Jacobis method with the initial guess x(0) y(0) z(0)J =[2.0 3.0 0.0] , the approximate solution [x(2) y(2) z(2) J after two iterations, is
(A) [2.64 1.70 1.12]T
(B) [2.64 1.70 1.12]T
(C) [2.64 1.70 1.12]T
(D) [2.64 1.70 1.12]T
Common Data for Questions 48 and 49:
The optimal table for the primal linear programming problem:
Maximize z = 6x +12x2 +12x3 6x4
Subject to x + x2 + x3 = 4
x + 4 x2 + x4 = 8
x, x2, x3, x4 > 0,
is
|
Basic variables (X) |
x1 |
x2 |
x3 |
x4 |
RHS Constants (b) |
|
x3 |
3/4 |
0 |
1 |
-1/4 |
2 |
|
x2 |
1/4 |
1 |
0 |
1/4 |
2 |
|
zj cj |
6 |
0 |
0 |
6 |
z = 48 |
Q 48 If y1 and y2 are the dual variables corresponding to the first and second primal constraints, then their values in the optimal solution of the dual problem are, respectively,
(A) 0 and 6 (B) 12 and 0 (C) 6 and 3 (D) 4 and 4
Q.49 If the right hand side of the second constraint is changed from 8 to 20, then in the optimal solution of the primal problem, the basic variables will be
(A) x and x (B) x and x (C) x and x (D) x and x
Common Data for Questions 50 and 51:
1
Consider the Fredholm integral equation u (x) = x + X Jxe1 u (t) dt.
0
Q.50 The resolvent kernel R( x, t; X) for this integral equation is
Xxet 1+ X
xe 1 -X
xe
xe
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
1+ X2
1 -X2
Q.51 The solution of this integral equation is
x +1
n
x
x
(A)
(C)
(D)
(B)
1+ X2
1 -X
1 -X2
Linked Answer Questions Statement for Linked Answer Questions 52 and 53:
The joint probability density function of two random variables X and Y is given as
6 9
-(x + y ), 0 < x < 1,0 < y < 1 0, elsewhere
f (x y)=1
Q.52 E(X) and E(Y) are, respectively,
2 3 (A) and 5 5
3 3 (B) - and -5 5
3 , 6 (C) - and 5 5
4 , 6 (D) and
5 5
Q.53 Cov( X, Y) is (A) - 0.01
(B) 0
(C) 0.01
(D) 0.02
Statement for Linked Answer Questions 54 and 55:
z2 + a z .
Consider the functions f (z) =- and g (z) = sinh( z--), a 0.
(z +1)2
2x
Q.54 The residue of f (z) at its pole is equal to 1. Then the value of a is
(A) -1 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) 3
Q.55 For the value of a obtained in Q.54, the function g(z) is not conformal at a point
TT (1 + 3i) 6
TT (3 + i) 6
2n
in
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
3
2
General Aptitude (GA) Questions (Compulsory) Q. 56 - Q. 60 carry one mark each.
Q.56 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence:
Given the seriousness of the situation that he had to face, his_was impressive.
(A) beggary (B) nomenclature (C) jealousy (D) nonchalance
Q.57 Choose the most appropriate alternative from the options given below to complete the following sentence:
If the tired soldier wanted to lie down, he ___ the mattress out on the balcony.
(A) should take
(B) shall take
(C) should have taken
(D) will have taken
Q.58 If (1.001)1259 = 3.52 and (1.001)2062 = 7.85, then (1.001)3321 =
(A) 2.23 (B) 4.33 (C) 11.37 (D) 27.64
Q.59 One of the parts (A, B, C, D) in the sentence given below contains an ERROR. Which one of the following is INCORRECT?
I requested that he should be given the driving test today instead of tomorrow.
(A) requested that
(B) should be given
(C) the driving test
(D) instead of tomorrow
Q.60 Which one of the following options is the closest in meaning to the word given below?
Latitude
(A) Eligibility (B) Freedom (C) Coercion (D) Meticulousness
Q. 61 - Q. 65 carry two marks each.
Q.61 There are eight bags of rice looking alike, seven of which have equal weight and one is slightly heavier. The weighing balance is of unlimited capacity. Using this balance, the minimum number of weighings required to identify the heavier bag is
(A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 8
Q.62 Raju has 14 currency notes in his pocket consisting of only Rs. 20 notes and Rs. 10 notes. The total money value of the notes is Rs. 230. The number of Rs. 10 notes that Raju has is
(A) 5 (B) 6 (C) 9 (D) 10
Q.63 One of the legacies of the Roman legions was discipline. In the legions, military law prevailed and discipline was brutal. Discipline on the battlefield kept units obedient, intact and fighting, even when the odds and conditions were against them.
Which one of the following statements best sums up the meaning of the above passage?
(A) Thorough regimentation was the main reason for the efficiency of the Roman legions even in adverse circumstances.
(B) The legions were treated inhumanly as if the men were animals.
(C) Discipline was the armies inheritance from their seniors.
(D) The harsh discipline to which the legions were subjected to led to the odds and conditions being against them.
Q.64 A and B are friends. They decide to meet between 1 PM and 2 PM on a given day. There is a condition that whoever arrives first will not wait for the other for more than 15 minutes. The probability that they will meet on that day is
(A) 1/4 (B) 1/16 (C) 7/16 (D) 9/16
Q.65 The data given in the following table summarizes the monthly budget of an average household.
|
Category |
Amount (Rs.) |
|
Food |
4000 |
|
Clothing |
1200 |
|
Rent |
2000 |
|
Savings |
1500 |
|
Other expenses |
1800 |
The approximate percentage of the monthly budget NOT spent on savings is
(A) 10% (B) 14% (C) 81% (D) 86%
MA 20/20
GATE 2012 - Answer Key - Paper : MA
|
|
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
