Indian Institute of Information Technology 2010 Entrance Exams IIT Entrance Exams Iit-jee part-1 chemistry - Question Paper
It is the 2010 chemistry ques. paper part-1.
IIT - JEE (2010) PAPER I QUESTION & SOLUTIONS (CODE 0)
| ||||||||||
|
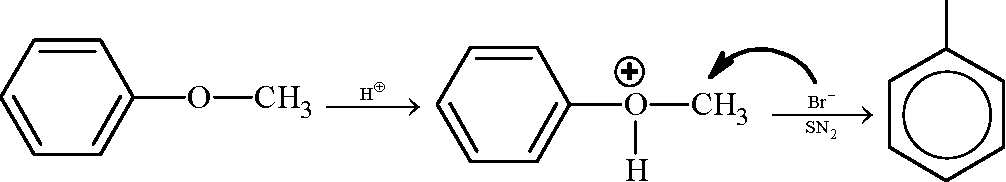
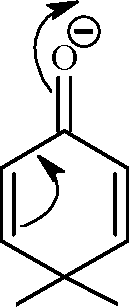
1. In the reaction / \-OCH3 r > the products are | ||||||||||
(A) Br A /) OCH3 and H2
(B) /)-Br and CBr
O
OH and CH3Br
(C)
(D)

\ /
<v\ f Br and CH3OH
Key: (D)
Sol.: HBr-> H + + Br -
|
OH | |
 |
f CH3Br |
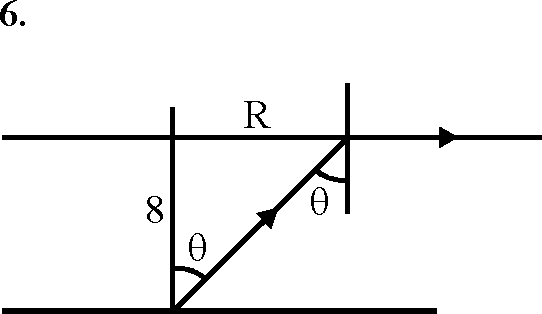
Plots showing the variation of the rate constant (k) with temperature (T) are given below. The plot that following Arrhenius equation is
|
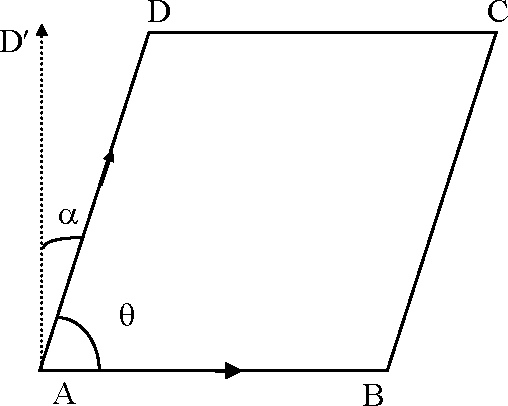
(A) | 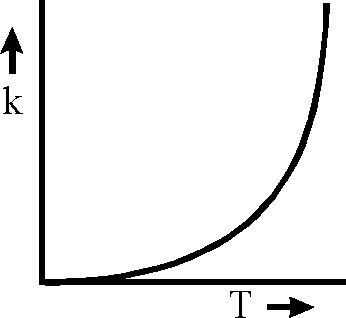 |
|
(C) | 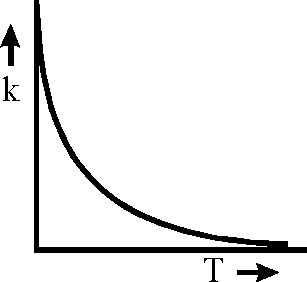 |
|
E | |
|
(B) | 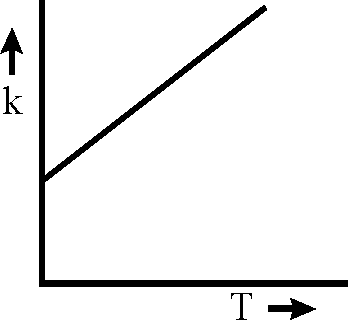 |
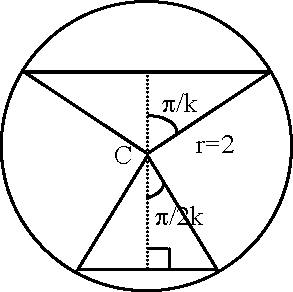
|
(D) | 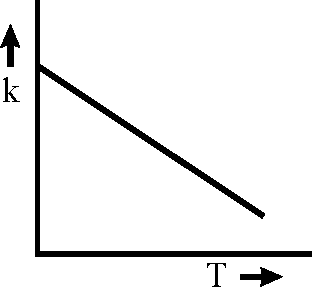 |
Key: (A) Sol.:
K = AeRT
Rate constant K increases exponentially with the rise in temperature. Since rate const. K also depends upon orientation factor A hence its maximum value is not at all infinity rather limited to an optimal value.
The species which by definition has ZERO standard molar enthalpy of formation at 298 K is
3.
(A) Br2 (g) (B) Cl2 (g)
(C) H2O (g) (D) CH4(g)
Bromine and water exist in liquid state at 298 K. Methane is not an elemental species. The ionization isomer of [Cr (H2O)4 Cl(NO2)] Cl is
Key:
Sol.:
4.
Key:
Sol.:
5.
(A) [Cr(H2O) (O2N)]Cl2 (B) [Cr(H2O)4 Cl2](NO2)
(C) [Cr(H2O)4Cl(ONO)]Cl (D) [Cr(H2O)4Cl2(NO2)] H2O
[Cr (H2O)4 Cl(NO2)] Cl, lo"lzallon s [Cr (H2O)4 Cl(NO2 )]+ + Cl-[Cr (H2O) Cl2] (NO2) , lomzaaon s [Cr (H2O)4 C]+ + NO2.
The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) is
COOHCH \
HOOC
CH2COOH
COOH
/
COOH
2
NCH=CH-N
/ \
COOH CH2 CH2 COOH
NCH2CH2N / 2 2 \
(A)
(B)
HOOC
2
COOH
COOHCH \
COOHCH2 H2C
\2 I
CH2COOH
2
H
/
(D)
(C)
N-CH-CH-N
/ I \
H CH2 CH2 COOH
/
COOH CH
CH2COOH
COOH
Key:
Sol.:
6.
Key:
Sol.:
7.
Key:
Sol.:
Based on facts
The bond energy (in kcal mol-1) of a CC single bond is approximately (A) 1 (B) 10
(C) 100 (D) 1000.
C - C single bond dissociation energy ranges between 88 to 150 K cal mol 1.
The synthesis of 3-octyne is achieved by adding a bromolkane into a mixture of sodium amide and an alkyne. The bromoalkane and alkyne respectively are
(A) BrCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2C = CH (B) BrCH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2C = CH
(C) BrCH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3C = CH (D) BrCH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2C = CH .
ch3 - CH2 - C = C - C - ch2 - ch2 - ch3
3 - octyne
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-Br
CH3 - CH2 - C = C-
CH3 - CH, - C = CH-
CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - C = C - CH2 - CH
3 octyne
|
The correct statement about the following disaccharide is |
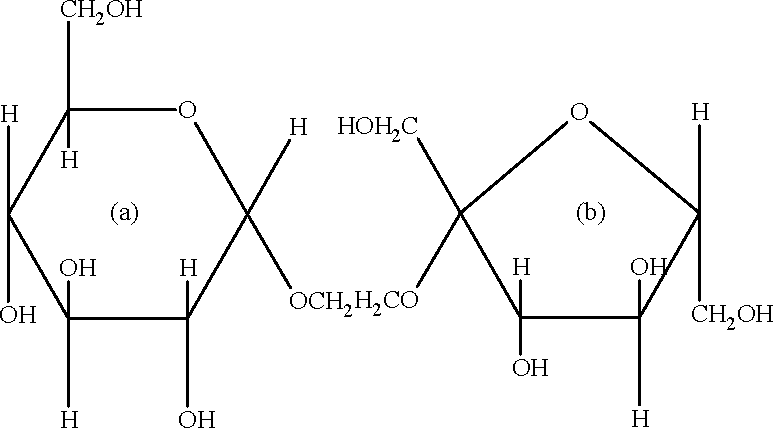 |
(A) Ring (a) is pyranose with a -glycosidic link (C) Ring (b) is furanose with a -glycosidic link Key: (A)
Sol.: Ring (a) is pyranose whereas ring(b) is furanose. a-anomeric form of ring (a) is attached through glycosidic bond.
(B) Ring (a) is furanose with a -glycosidic link (D) Ring (b) is pyranose with p -glycosidic link.
This section contains 5 multiple correct answer(s) type questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct.
9. In the Newman projection for 2, 2-dimethylbutane X
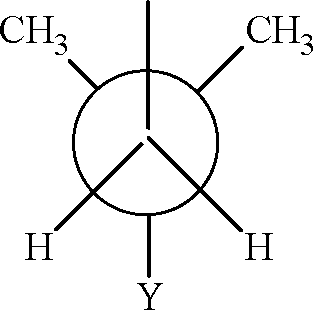
X and Y can respectively be (A) H and H (C) C2H5 and H Key: (B, D)
(B) H and C2H5 (D) CH3 and CH3.
Sol.:
H3CCch2-ch3 13 2 | 3 2 4 3
CH3
2, 2-dimethyl butane
Ci - C2 rotation CH. CH3
|
CH H | ||
|
H |  |
CH3 H |
|
C2H5 | ||
HCH
 |
|
HC2H5 |
180
rotation
X and Y become H and C2H5 CH3
U
H3CCCH2-CH3
CH3cH3
|
ch3 |
 |
|
ch3 | 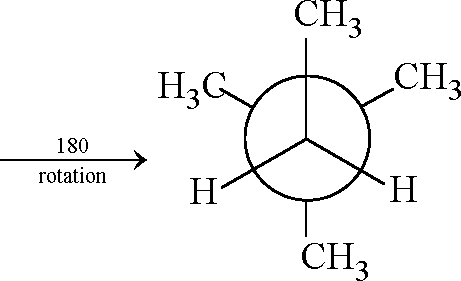 |
X and Y become CH3 and CH3
10. The regent(s) used for softening the temporary hardness of water is (are) (A) Ca3(PO4)2 (B) Ca (OH)2
(C) Na2CO3 (D) NaOCl.
Key: (B, C)
Sol.: Temporary hardness is due to the presence of bicarbonates of Ca and Mg. Temporary hardness can be removed by clarkes process which involves the addition of slaked lime Ca (HCO3 )2 + Ca (OH)2-> 2CaCO3 + 2H2O
Washing soda removes both the temporary and permanent hardness.
Ca (HCO3 )2 + Na2CO3-> CaCO3 + 2NaHCO3.
11. Among the following, the intensive property is (properties are)
(A) molar conductivity (B) electromotive force
(C) resistance (D) heat capacity.
Key: (A)
Sol.: EMF, resistance and heat capacity are extensive properties ofcourse, resistivity is an intensive property.
12. Aqueous solutions of HNO3, KOH, CH3COOH, and CH3COONa of identical concentrations are provided. The pair(s) of solutions which form a buffer upon mixing is(are)
(B) KOH and CH3COONa
(A) HNO3 and CH3COOH (C) HNO3 and CH3COONa
(D) CH3COOH and CH3COONa .
Key: (C, D)
Sol.: Mixture of weak acid and its salt are known as acidic buffer.
|
H+ NO- + CH3CO- Na CH3CO2H + Na+NO: strong acid weak acid |
 |
|
13. In the reaction |  |
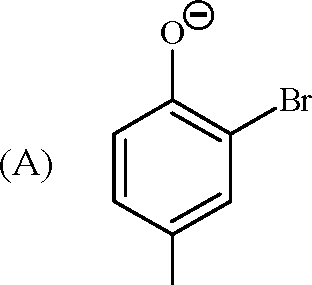 |
|
Br |
|
O |
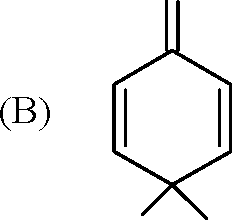 |
|
Br Br |
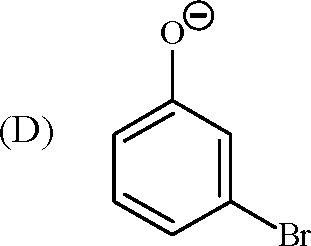 |
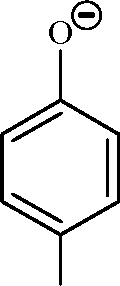 |
|
Br |
|
Key: (A, C) OH |
 |
is strongly activating towards EAS reaction and it is ortho-para directing
Br
H
Br
O
 |
|
Br I Br |
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon the first paragraph, 3 multiple choice questions and based upon the second paragraph 2 Multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions have four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Questions 14 to 16
Copper is the most noble of the first row transition metals and occurs in small deposits in several countries. Ores of copper include chalcanthite (CuSO4. 5H2O), atacamite (Cu2Cl(OH)3), cuprite (Cu2O), copper glance (Cu2S) and malachite (Cu2(OH)2CO3). However 80% of the world copper production comes from the ore chalcopyrite (CuFeS2). The extraction of copper from chalcopyrite involves partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
Partial roasting of chalcopyrite produces
(A) Cu2S and FeO (C) CuS and Fe2O3
(B)
CuFeS2 + O2 Cu2S + 2FeS + SO2
The sulphites of copper and iron are partially oxidized
2FeO + 2SO2
14.
(B) Cu2O and FeO (D) Cu2O and Fe2O3
Key:
Sol:
2FeS+3O2
2Cu2O + 2SO2.
2Cu2S-
3O2
Iron is removed from chalcopyrite as (A) FeO
(C) Fe2O3
(D)
Fe is removed in the form of FeSiO3.
FeO + SiO2
15.
(B) FeS (D) FeSiO3
Key:
Sol:
FeSiO,
16. In self-reduction, the reducing species is
(A) S (B) O2-
(C) S2- (D) SO2
Key: (C)
Sol: Cu2S + 2Cu2O-> 6Cu + SO2
S-2 oxidized into S+4 hence it is reducing species .
Paragraph for Questions 17 to 18
The concentration of potassium ions inside a biological cell is at least twenty times higher than the outside. The resulting potential difference across the cell is important in several processes such as transmission of nerve impulses and maintaining the ion balance. A simple model for such a concentration cell involving a metal M is :
M(s) | M+ (aq; 0.05 molar) || M+ (aq; lmolar) | M(s)
For the above electrolytic cell the magnitude of the cell potential |Ecell| = 70 mV.
17.
(B) Ecell > 0; AG < 0 (D) Ecell > 0; AG < 0
Key:
Sol:
18.
Key:
Sol:
0.0025
E -En " F = -2.303RT F
= 2 x 70 mV = 140 mV.
1
For the above cell
(A) Ecell < 0; AG > 0 (C) Ecell < 0; AG > 0
(B)
-2.303RT, 0.05
Eceii = -log-= a positive value
F 1
= 70 mV (given)
Hence AG < 0.
If the 0.05 molar solution of M+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar M+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be
(A) 35 mV (B) 70 mV
(C) 140 mV (D) 700 mV (C)
-2.303RT
log
log (0.05)2
SECTION - IV
Integer Answer Type
This Section contains TEN questions. The answer to each question is a Single Digit Integer ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question number in the ORS is to be bubbled.
The value of n in the molecular formula BenAl2Si6O18 is
19.
Key:
Sol.:
[Si6O18 ]12-
Be3Al2Bi6O18
[Si6O18 ]12-
20. The total number of basic groups in the following form of lysine is
"3NC"2C"2C"2C"2
C"C
O
Key: (2) Sol.:
C"
... v/
O
*
Based on VSEPR theory, the number of 90 degree F - Br - F angles in BrF5 is
|
21. Key: Sol.: | 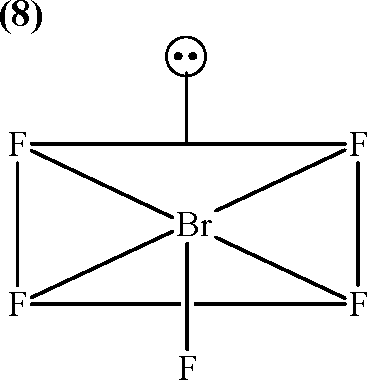 |
The structure of BrF5 is square pyramidal. The number of FBrF angles having the value of 90 is eight (8). Due to trivial distortion, however, the bond angles (FBrF) are slightly less than 90(85).
Amongst the following, the total number of compounds whose aqueous solution turns red litmus paper blue is
KCN K2SO4 (NH4)2C2O4 NaCl Zn(NO3)2
FeCl3 K2CO3 NH4NO3 LiCN
(3)
KCN, K2CO3, LiCN are basic salt can convert red litmus to blue.
Amongst the following, the total number of compounds soluble in aqueous NaOH is
H3 /CH3
3 N 3
22.
Key:
Sol.:
23.
|
COOH |
 |
|
.N. H3C 'CH 3 |
|
OH | |
 |
COOH |
Key:
Sol.:
(4)
|
OH |
 |
|
COOH |
 |
COOH OH
CH3
are soluble in aq. NaOH.
A student performs a titration with different burettes and finds titre values of 25.2 mL, 25.25 mL, and 25.0
24.
Key:
Sol.:
25.
Key
mL. The number of significant figures in the average titre value is
(3)
25.2 + 25.25 + 25.0 Average = =-
= 75.45 / 3 = 25.15 25.1.
No. of significant figure = 3.
The number of neutrons emitted when 935 U undergoes controlled nuclear fission to 54 Xe and 38 Sr is
(3)
235 tt v 142 , -5I
92 U 54 Xe + 38Sr + 30n .
Sol.:
26.
In the scheme given below, the total number of intramolecular aldol condensation products formed from
Y is
|
Key: Sol.: |  |
O . Z11/H2O |
l.NaOH(aq)
Y
2. Zn, H2O
|
OH |
 |
|
O |
O
NaOH(aq)
|
The concentration of R in the reaction R P was measured as a function of time and the following data is obtained : | ||||||||||
|
The order of the reaction is (0)
27.
Key:
Sol.:
R-> P
dc ~ nric 0.25 . -1
--after 0.05 min = -= 5 M min 1
dt 0.05
- after 0.12 min = 060 = 5 M min-1 dt 0.12
- after 0.18 min = 90 = 5 M min-1 dt 0.18
The average rate remains same throughout. This implies that rate is independent of concentration (zero order).
The total number of cyclic isomers possible for a hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C4H6 is
28.
Key
Sol.:
Cyclic isomers C4H6 CH3
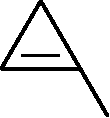
h2c
Total isomers = 5
ch3
PART II: MATHEMATICS
SECTION - I
Single Correct Choice Type
This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
has exactly
The number of 3 x 3 matrices A whose are either 0 or 1 and for which the system A
29.
two distinct solutions, is
(A) 0 (B) 29 - 1
(C)168 (D) 2
Key. (A)
Sol. Three planes cannot meet only at two distinct points. Hence A is correct.
1 x t ln (1 +1)
The value of lim f
x0 x3 J
(A) 0
dt is
30.
t4 + 4
(B)
(D)
12
64
1
(C)
Key. (B)
24
tln(1 +1) dt t4 + 4
lim
x 0
Sol.
x
xln(1 + x) ln(1 + x)
= lim--- = lim
(x4+4)3x2 x0 3x(x4+4)
1 ln(1 + x) 1 -lim --- = .
4x 3 x x 12
Let p and q be real numbers such that p # 0, p # -q. If a and p are nonzero complex numbers satisfying
a P
a + p = -p and a3 + p3 = q, then a quadratic equation having and as its roots is
31.
P a
(B) (p3 + q) x2 - (p3 - 2q) x + (p3 + q) = 0 (D) (p3 - q) x2 - (5p3 + 2q) x + (p3 - q) = 0
(A) (p3 + q) x2 - (p3 + 2q) x + (p3 + q) = 0 (C) (p3 - q) x2 - (5p3 - 2q) x + (p3 - q) = 0
Key. (B)
a p a2 +p2
Sol.
Pa ap
a3 + p3 = (a + p) {(a + p)2 - 3ap}
q = -p (p2 - 3ap)
q + p3 = 3a pp ap = (q + p )
3p
2 02_2 o (q + p3) _ 3p3 -2q- 2p3 p3 -2q
a2 + p2 = p2 - 2
3p
3p
3p
a2 +p2 p3 -2q
ap
q+p
x2 - (p , 2q) x + 1 = 0 (p3 + q)x2 - (p3 - 2q) x + (p3 + q) = 0
p + q
Equation of the plane containing the straight line -2-=3=4 and perpendicular to the plane containing the
32.
. , x y z , x y z .
straight lines == and == is 3 4 2 4 2 3
(A) x + 2y - 2z = 0
(B) 3x + 2y - 2z = 0 (D) 5x + 2y - 4z = 0
(C) x - 2y + z = 0
(C)
Key.
i j k
3 4 2
4 2 3
= 8i -j- 101c
Sol.
n = (3i + 4j + 21c) x (4i + 2j + 3k) =
The equation of plane containing the IInd and IIIrd given lines. r.(8i - j- 101c) = 0 8x - y - 10z = 0.
Now normal vector to the required plane is given by
j j k
= -26i + 52j - 261c
2 3 4
8 -1 -10
= -26(j - 2j + k)
The equation of the required plane is x - 2y + z = 0.
33. If the angle A, B and C of the triangle are in the an arithmetic progression and if a, b and c denote the
lengths of the sides opposite to A, B and C respectively, then the value of the expression
a c
sin2C + sin2A is
(B) f
(D) V3
Key.
Sol.
sinC
(A) 2
(C) 1
(D)
a c . A sinA . sinC .
sin2C + sin2A =-2sinC cosC+--2sinAcosA
= 2sin(A + C)
s
sinA
= 2 x
Let (o be a complex cube root of unity with ro # 1. A fair die is thrown three times. If r1 , r2 and r3 are the numbers obtained on the die, then the probability that 0 +ro'2 + 0 = 0 is
(A) 18
35.
(C) 9 9
(C)
Key.
Sol.
_ 2x 2x 2(3!)
Required prob. =
6 x 6 x 6
36. Let P, Q, R and S be the points on the plane with position vectors -2i - j, 4i,3i + 3j and respectively. The quadrilateral PQRS must be a
-3i + 2j
(A) parallelogram, which is neither a rhombus nor a rectangle
(B) square (C) rectangle, but not a square
(D) rhombus, but not a square
Key. (A)
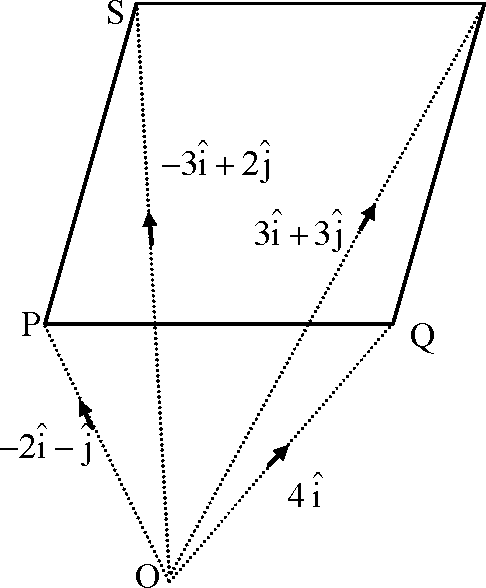 |
7R |
Sol. P: -2i -j, Q:4i,R:3j + 3j, S:-3i + 2j PQ = of P = 6i + j QR = 3i + 3j- 4i = -i + 3j PS = -3i + 2j + 2i + j= -i + 3j SR = 3j + 3j + 3i - 2j = 6i + j PQ. PS = (i + j)-i + 3j) = -3 # 0
Here PQ ||SR and PS ||QR but PQ is not perpendicular to PS
This section contains 5 multiple correct answer(s) type questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct.
Let z1 and z2 be two distinct complex numbers and let z = (1 - t) z1 + tz2 for some real number t with 0 < t < 1. If Arg(w) denotes the principal argument of a nonzero complex number w, then
37.
Key.
Sol.
(A) z - z 11 + |z - z2| = |z 1 - z2| (B) Arg (z - zO = Arg (z - z2)
(C) z-z1 t-!i = 0 (D) Arg (z - zO = Arg (z2 - z1)
z2 z1 z2 z1 (A, C, D)
As z = (1 - t) z1 + tz2 z
z1, z, z2 are collinear
z1
1-t z2
A, D are correct
z - z1 z - zj Also--=-L
z2 - z1 z2 - z1 (C) is correct.
38. Let A and B be two distinct points on the parabola y2 = 4x. If the axis of the parabola touches a circle of radius r having AB as its diameter, then the slope of the line joining A and B can be
(A)
r
(B) 1 r
(D) - 2
r
r
Key,
Sol.
(C, D)
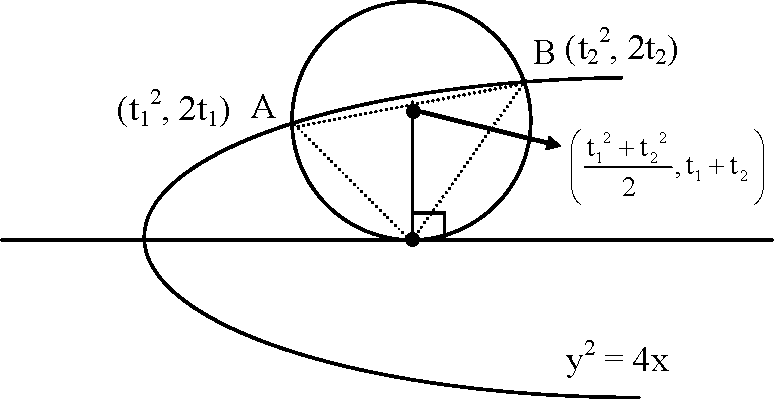
Slope of line AB
(t2 -t1)
M =
(t2 - t1)(t2 + t1) t1 + t2 As |t1 + t2| = r
Let f be a real-valued function defined on the interval (0, m) by f(x) = ln x + + sint dt. Then which of
39.
0
the following statement(s) is (are) true?
(A) f "(x) exists for all xe (0, m)
(B) f '(x) exists for all xe (0, m) and f ' is continuous on (0, m), but not differentiable on (0, m)
(C) there exists a > 1 such that |f '(x)| < |f(x)| for all xe(a, m)
(D) there exists p > 0 such that |f(x)| + |f(x)| < p for all xe (0, m)
(B, C)
Key.
Sol.
f(x) = lnx + + sint dt, x > 0
0
f '(x) = 1+>/1 + sinx , x > 0
x
Clearly f '(x) exists for all xe (0, m) and f '(x) is continuous on (0,m) but not differentiable on (0,m)
More over f '(x), f(x) > 0 Vxe (1, m)
x _ 1 _
and ln x + JV1 + sint dt> + V1 + sinx Vxe (n, m)
0 x
1 is not bounded.
x
(D) is incorrect .
Hence, option B, C are correct.
The value(s) of f x-(1dx is (are)
40.
0 1 + x2
22
(A) -n
(B) 105
(D) 171 -
15 2
(C) 0 (A)
1 x4 (1 - x)4
Key.
Sol.
dx
(1 + x2)
0
x2 +1
7
0
f(x6 -4x5 + 5x4)dxdx =i-4 f x , 1 +1 dx= 22-n 0 J1 + x2 21 0 -2
0 J
Let ABC be a triangle such that ZACB = and let a, b and c denote the lengths of the sides opposite to A,
6
41.
B and C respectively. The value(s) of x for which a = x2 + x + 1, b = x2 - 1 and c = 2x + 1 is (are)
(B) 1 V3
(D) 43
Key.
Sol.
|
A |
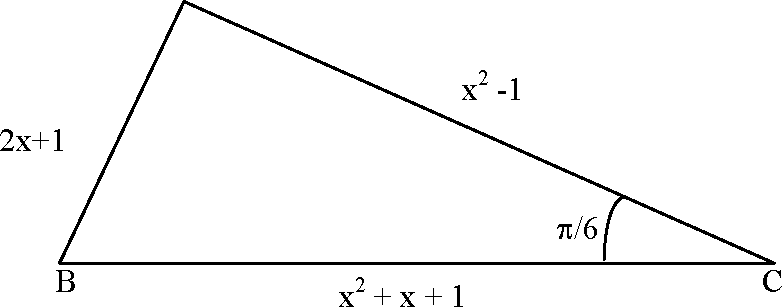 |
2.(x2 - 1)(x2 + x +1)
(x2 + 3x + 2)(x2 - x) + (x2 -1)2
V3=
(A) -(2 +V3)
(C) 2+V3
(B)
V3 = (x2 + x +1)2 + (x2 -1)2 - (2x +1)2 2 "
A.
2 " 2(x2 -1)(x2 + x +1)
y/3 (x + 2)x + x2 -1 2 = '
2(x + x +1) 2x2 + 2x -1 x2 + x +1
> x2 ( - 2)+x (3 - 2)++1=0
= -(>/, - 2) + (V3 - 2)2 - 4( - 2)V3 +1) = 3 +1 2(V3 - 2) '
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon the first paragraph, 3 multiple choice questions and based upon the second paragraph 2 Multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions have four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 42 to 44
Let p be an odd prime number and Tp be the following set of 2 x 2 matrices.
f [a b 1 Tp = \ A = :a,b,ce {0,1, 2, ...,p -1}}
I c a
Sol. 42 to 44
as A is symmetric b = c
det A = a2 - b2 = (a + b) (a - b)
a, b, c, e {0, 1, 2,.....p - 1}
no. of numbers of type np = 1 np + 1 = 1 np + 2 = 1 n e I
np + (p - 1) = 1
42. The number of A in Tp such that A is either symmetric or skew-symmetric or both, and det(A) divisible by p is
(A) (p - 1)2 (B) 2 (p - 1)
(C) (p - 1)2 + 1 (D) 2p - 1
Key. (D)
Sol. as det(A) is div. by p either a + b div. by p corresponding nu. Of ways = (p - 1) [excluding zero] or (a - b) is div. by p corresponding no. of ways = p Total number of ways = 2p - 1
The number of A in Tp such that the trace of A is not divisible by p but det (A) is divisible by p is [Note: The trace of a matrix is the sum of its diagonal entries.
(A) (p - q) (p2 p p + q)
43.
Key.
Sol.
44.
Key.
Sol.
45.
Key.
Sol.
(B) p3 - (p - 1)2 (D) (p - 1) (p2 - 2)
(C) (p - 1)2
(C)
as Tr(A) not div. by p a # 0 det(A) is div. by p a2 - bc div. by p no. of ways of selection of a, b, c
(p - 1)[(p - 1) x 1] = (p - 1)2 The number of A in Tp such that det (A) is not divisible by p is
(A) 2p2 (B) p3 - 5p
(C) p3 - 3p (D) p3 - p2
(D) 3 Total number of A = p x p x p = p3 No. of A such that det(A) div. by p = (p - 1)2 + no. of A in which a = 0 = (p - 1)2 + p + p - 1 = p2 3 2 required no. = p3 - p2.
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 45 to 46
2 2 x y
The circle x + y - 8x = 0 and hyperbola --- - 1 intersect at the points A and B.
Equation of a common tangent with positive slope to the circle as well as to the hyperbola is
|
(B) 2x - V5 y + 4 = 0 | ||
|
(D) 4x - 3y + 4 |
= 0 | |
|
\ |
A |
<V 23) |
|
J( 3,0) |
I (3,0)U4,0) | |
|
B |
S(6, - 23) | |
(A) 2x - -\/5 y - 20 = 0
(C) 3x - 4y + 8 = 0
(B)
Equation of tangent at point P(0) x sec 0 y tan 0
.(i)
1 - 0
3 2
since eq. (i) will be a tangent to the circle
4sec0 --1
3
sec2 0 tan2 0
9 4 by solving it we will get
|
Equation of the circle with AB as its diameter is (A) x2 + y2 - 12x + 24 = 0 46. Key. Sol. 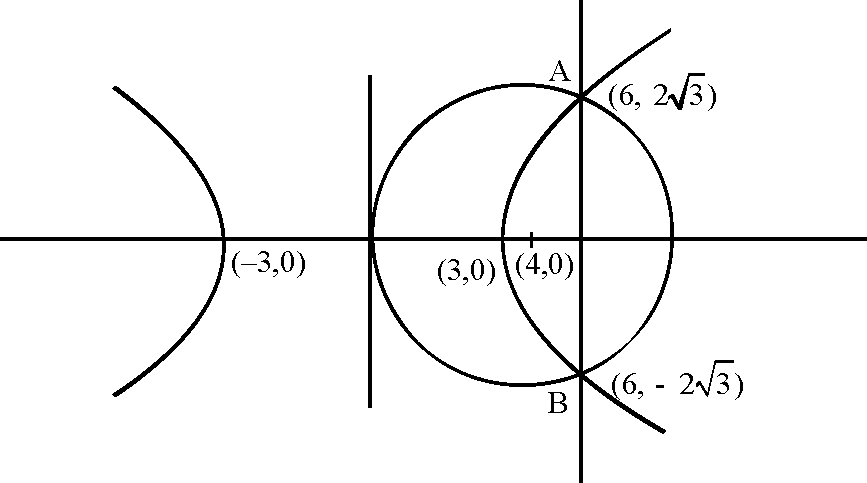 (C) x2 + y2 + 24x - 12 = 0 (A) x9 , (-x2 + 8x) - 1 + --- 9 4 4x2 = 36 + 9(-x2 + 8x) 13x2 - 72x - 36 = 0 x = 6, y -2>/3 Required equation of circle is (x - 6)2 + y2 - 12 = 0 x2 + y2 - 12x + 24 = 0 |
(B) x2 + y2 + 12x + 24 = 0 (D) x2 + y2 - 24x - 12 = 0 |
This Section contains TEN questions. The answer to each question is a Single Digit Integer ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question number in the ORS is to be bubbled.
2n 2n
47. Let ro be the complex number cos +isin . Then the number of distinct complex numbers z satisfying
Key. (1) Sol.
|
z +1 |
ro |
ro2 | |
|
ro |
z + ro |
l |
= 0 is equal to |
|
ro2 |
l |
z + ro |
2n . . 2n 1 . \/3
ro = cos--+ i sin =---+ i-
3 3 2 2
= 0
p.- l + ro + ro2 = 0]
- 0
ro z + ro
2
= 0
z 1
ro' 1 z + ro
Ci Ci - C2 & C2 C2 - C3 gives 0 0 z
ro-z-ro2 z+ro2-1 1 ro2 -1 1 -z-ro z + ro
z[(ro-z-ro2)(l-z- ro)-(ro2 -l)(z + ro2 -1)] = 0 z[z2] = 0 z3 = 0 = z = 0 Ans. is = l
ro is one of cube root of unity.
z +1 ro ro2 ro z + ro2 1 ro2 1 z + ro
Ri Ri + R2 + R3
z z
( n n | nn
48. The number of values of 0 in the interval I , I such that 0 # for n = 0, l, 2 and tan0 = cot50 as
I 2 2 J 5
well as sin20 = cos40 is Key. (3)
Sol. tan 0 = cot 50
tan 0 = tan I--50
, 2
0 = nn +0 - 50 2
n
60 = nn +
2
_ nn n
.(i)
0 = +n el 6 12
sin 20 = cos 40
sin 20 = 1 - 2 sin2 20 2sin220 + sin 20-1 = 0 2sin220 + 2sin20- sin 20-1 = 0 (2 sin 20 - 1)(sin 20 + 1) = 0
sin20 = -1,
2
20=n ,, 6 6
sin20 = -1
20 = -n 6
0 =
0 =
All three values of 0 which satisfy the eq. (i).
For any real number x, let [x] denote the largest integer less than or equal to x. Let f be a real valued function defined on the interval [-10, 10] by
49.
Key.
Sol.
|
f(x) = |
x - [x] [1 + [x] - x |
if [x]is if [x] is |
|
(4) | ||
|
[1 -{x} , |
0 < x < 1 | |
|
f(x) = |
{x} , |
1 < x < 2 |
|
1-{x} , |
2 < x < 3 |
Here f(x) is periodic with period 2 and cos nx is also periodic with period 2 f(x) cos nx is periodic with period 2.
" 2 40
f f(x)cosnx dx = 10f f(x)cosnx dx = -
0
Hence, f(x)cosnx dx = in J
_ i 10 n2
= 4.
50. If the distance between the plane Ax - 2y + z = d and the plane containing the lines
x -1 y - 2 z - 3 . x - 2 y - 3 z - 4 r- .
-=-=-and-=-=- is V6 , then |d| is
2 3 4 3 4 5
Key. (6)
Sol. The equation of the plane containing the given lines will be a(x - 1) + b(y - 2) + c(z - 3) = 0 where a, b, c are direction ratios of normal to the plane considering vectors parallel to the two lines 2i + 3j + 4k and 3i + 4j + 5k So 2a1 + 3b1 + 4c1 = 0 3a1 + 4b1 + 5c1 = 0
15 -16 10 -12 8 - 9 So the plane is x - 2y + z = 0 Hence distance between two planes
2 2 x y
51. The line 2x + y = 1 is tangent to the hyperbola ---- = 1 . If this line passes through the point of
a b
intersection of the nearest directrix and the x-axis, then the eccentricity of the hyperbola is Key. (2)
Sol. Since the line 2x + y - 1 = 0 is tangent so, C2 = a2m2 - b2
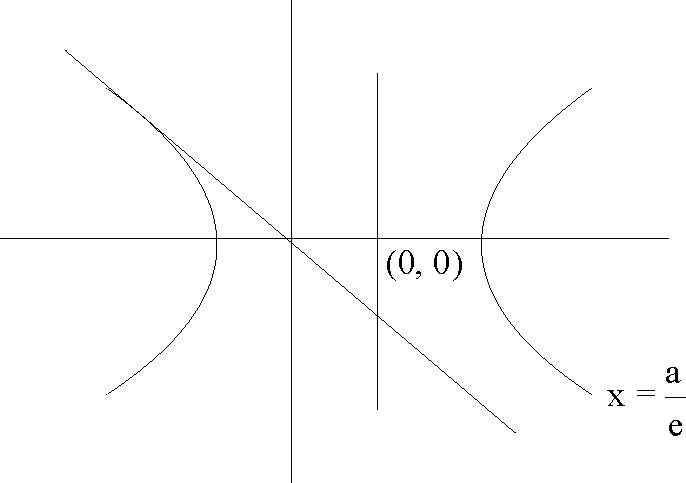
1 = 4a2 - b2 .....(i)
Also line passes through |--,0
e
21 - - | = 1
So,
4a2 = e2
(ii)
Using (i) and (ii) e = 2
Let Sk, k = 1, 2, ... , 100, denote the sum of the infinite geometric series whose whose first term is
k-1
52.
1 1002 100 .
and the common ratio is . Then the value of--h'V fk2 - 3k + 1|S,
100! > k
k
Key. (4)
Sol.
St =
We have Si = 1 S2 = 1
S3 =
1
100 - -Now, (k2 - 3k +1)
k=11 1
((k2 - 3k +1)
( - 3)! (k -1)! 1
1 +1 --L
2! 98! 99!
(k -1)!
1 1
= S1 + S2 + S3 +
100
99!
1 f2 100 1 .
-+ V (k2 -3k +1) = 4.
100! > kl
1 100
= 1 + 1 + 1+x
2 k=4
=1+1+-+ 2
4
So,
53. Let f be a real-valued differentiable function on R (the set of all real numbers) such that f(1) = 1. If the y-intercept of the tangent at any point P(x, y) on the curve y = f(x) is equal to the cube of the abscissa of P, then the value of f(-3) is equal to Key. (9)
Sol. eq. of tangent at P(x, y)
Y - y = (X - x) dx
dy 3
y-integer y - x = x dx
- y = - x dx x
-j -1dx 1
I.F. = e x = x
The solution
1 r 2 1 d
y x = j - x x dx x J x
-=-+c
x 2
f(1) = 1 C = 3
2
3x - x
f(x) = y = f (-3) = 9
2
T. _ , . . , _ i-2j , 2j +j + 31c , , ,
54. If a and b are vectors in space given by a ==- and b =-==, then the value of
V5 V14
(a + b)(xbjx(-2b) is
Key. (5) _ _
Let I = (a x b) x (a - 2b) = (a x b) x a - 2(a x b) x b
=| a |2 b - (a.b)a - 2(a.b)b + 21 b | a.
= b + 2a
(2a + b)l =| 2a + b |2 = 5
55. The number of all possible values of 0, where 0 < 0 < n, for which the system of equations
(y + z) cos30 = (xyz) sin 30
. 2cos30 2sin30 xsin30 =--1--
y z
(xyz) sin30 = (y + 2z) cos30 + ysin 30 have a solution (x0, y0, z0) with y0 z0 # 0, is Key. (3)
Sol. (y + z)cos30 = (xyz) sin 30 (A)
. 2cos30 2sin30 _
x sin 30 =-+--(B)
y z
(xyz) sin 30 = (y + 2z) cos 30 + y sin 30 (C)
When cos 30 # 0.
2z
y + 2z
y + z
tan30:
xyz y(xz - 2) xyz - y
as y # 0
(y + z) (xz - 2) = 2z(xz)
xyz + xz2 - 2z - 2y = 2xz2
xyz = 2y + 2z + xz2
Again, 2z(xz - 1) = (y + 2z) (xz - 2)
2xz2 - 2z = xyz + (2xz2 - 4z - 2y)
xyz = 2y + 2z
from (i) and (ii) xz2 = 0
x = 0 as z # 0 from (A) (y + z) cos 30 = 0 y + z = 0 But when cos 30 = 0 from (B) sin 30 = 0 not possible
.(i)
.(ii)
y = -z putting in (B) and (C) x = 0
sin 3 0 = cos 3 0
n 5n 3n
So
12 12 4
56. The maximum value of the expression Key. (2)
1
1
Sol. Let y =
sin2 0 + 3sin0cos0 + 5cos2 0 , , ~ ~n , 3 .
3 + 2 cos 20 +sin 20
2
5 3 5
< 2cos20 + sin20 < 2 2 2
1
max. value of y =
3-
2
This section contains 8 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
An AC voltage source of variable angular frequency ro and fixed amplitude V0 is connected in series with a
57.
capacitance C and an electric bulb of resistance R (inductance zero). When ro is increased
(A) the bulb glows dimmer (B) the bulb glows brighter
(C) total impedance of the circuit is unchanged (D) total impedance of the circuit increases.
(B)
Key.
Sol.
P = Vrms Irms cos
V 2 R
_ rms
_ Z Z
V 2r
rms
2
Z
Z-iR +roC2
As ro increase Z, decreases, so P increases.
Hence correct option is (B).
A thin flexible wire of length L is connected to two adjacent fixed points and carries a current I in the clockwise direction, as shown in the figure. When the system is put in a uniform magnetic field of strength B going into the plane of the paper, the wire takes the shape of a circle. The tension in the wire is
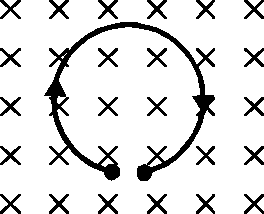
58.

(B)-IBL.
n
(D)
4n
(A) IBL
IBL
2n
(C)
(C)
Key.
Sol.
2T - iB(2R)
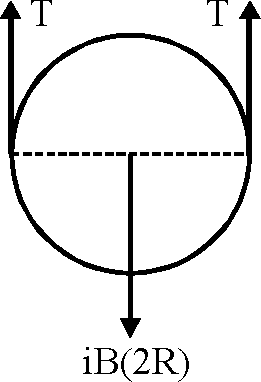
iBL
T -
2n
"ence correct option is (C).
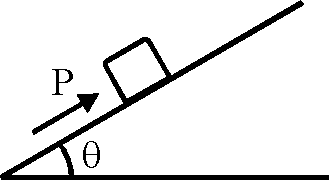
59. A block of mass m is on an inclined plane of angle 0. The coefficient of friction between the block and the plane is |i and tan 0 > |i. The block is held stationary by applying a force P parallel to the plane. The direction of force pointing up the plane is taken to be positive. As P is varied from P1 = mg (sin
0 - |i cos 0) to P2 mg (sin 0 + |i cos 0), the frictional force f versus P graph
will look like (A)
f
(B)
f
P
-P
-P
P P
1 l 1 2
P.
|
(C) | |
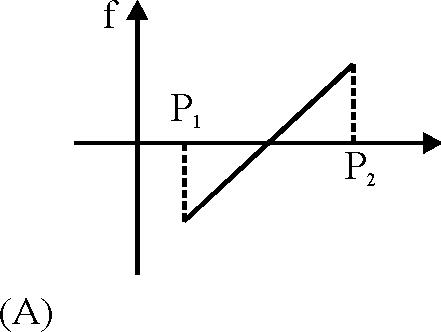 |
-P |
(D)
f
P. P2
1 2 P
Key.
Sol.
60.
Key.
Sol.
61.
P. = mg(sin 0 - |i cos 0) frictioninitial = |imgcos0 up along the plane frictionfinal = |imgcos0 down along the plane Hence correct option is (A).
A real gas behaves like an ideal gas if its (A) pressure and temperature are both high
(C) pressure is high and temperature is low
(D)
(B) pressure and temperature are both low (D) pressure is low and temperature is high.
For ideal gas behaviour pressure should be low and temperature should be high. Hence correct option is (D).
Consider a thin square sheet of side L and thickness t, made of a material of resistivity p. The resistance between two opposite faces, shown by the shaded areas in the figure is
(A) directly proportional to L
(B) directly proportional to t
(C) independent of L
(D) independent of t.
(C)
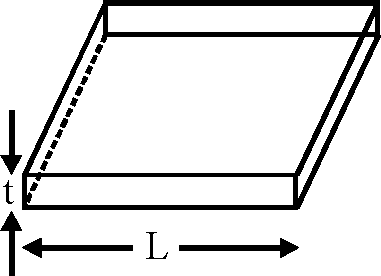
Key.
Sol.
62.
= p.Lt = p Lt t
R = p
A
Hence correct option is (C).
A thin uniform annular disc (see figure) of mass M has outer radius 4R and inner radius 3R. The work required to take a unit mass from point P on its axis to infinity is
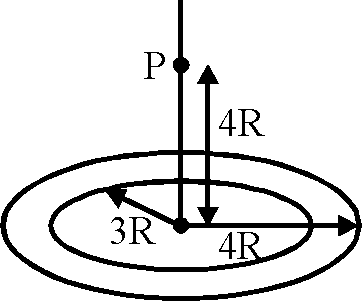
2GM
7R
GM
4R
2GM
(W2 - 5)
(-1).
(A)
(C)
(A)
(B)
7R
2GM
5R
(D)
Key.
Sol.
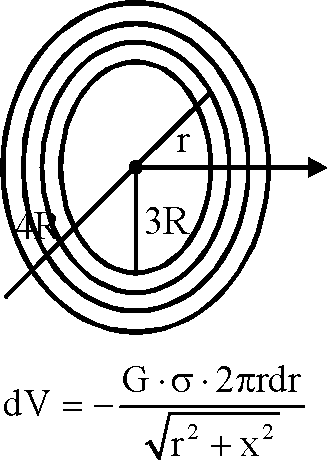 |
x |
|
V = -2tcGct J rdr | |
3R Vr2 + x2
2r dr = dz r rdr dz Vr2 + x2 2\/z
= "T7 = 2>2
V = -2tcGct! Vr2+ x
= -2nGr [4R>/2 - 5]
W = (1) [0 + 2tcGct(4rV2 - 5R)]
= 2nG--M-- (4R>/2 - 5R)
n(16 - 9)R 2nGM
-(W2 - 5).
7R
Hence correct option is (A).
Incandescent bulbs are designed by keeping in mind that the resistance of their filament increases with the increase in temperature. If at room temperature, 100 W, 60 W and 40 W bulbs have filament resistances R100, R60 and R40, respectively, the relation between these resistances is
63.
(A) = - + -
(B) R100 = R40 + R6'
R100 R40 R60
|
(C) R100 > R60 > R40 (D) Key. Sol. R = P |
(D) > > rL. R R R |
As temperature increase, resistance increases
So, R40 > R60 > R100 .
Hence correct option is (D).
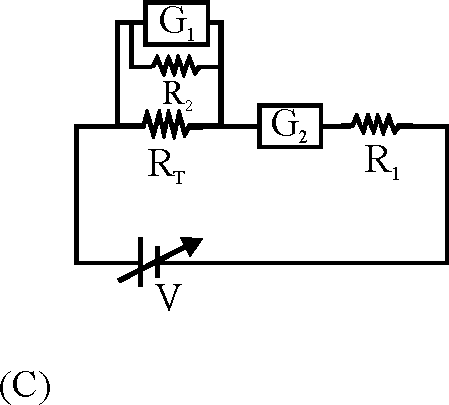
To verify Ohm's law, a student is provided with a test resistor RT, a high resistance R1, a small resistance R2, two identical galvanometers G1 and G2, and a variable voltage source V. The correct circuit to carry out the experiment is
64.
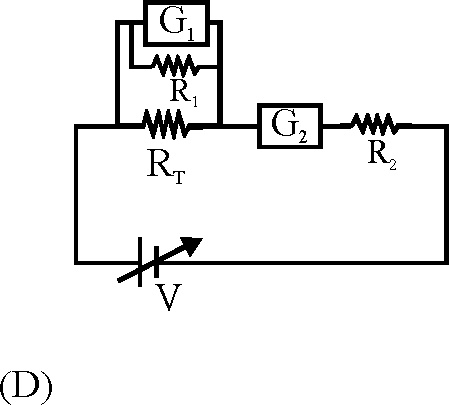
|
(A) |
 |
EYRn
WrL
rt
pn
v*L
rt
"dSfcbi
tS&i
R
R
-to*-
-to*-
V ' V
Key. (C)
Sol. An ideal voltmeter should have large resistance and an ideal ammeter should have low resistance.
Hence correct option is (C).
_Multiple Correct Choice Type_
This section contains 5 multiple correct answer(s) type questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONE OR MORE is/are correct.
65. A point mass of 1 kg collides elastically with a stationary point mass of 5 kg. After their collision, the 1 kg mass reverses its direction and moves with a speed of 2 ms-1. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct for the system of these two masses ?
(A) total momentum of the system is 3 kg ms-1
(B) momentum of 5 kg mass after collision is 4 kg ms-1
(C) kinetic energy of the center of mass is 0.75 J
(D) total kinetic energy of the system is 4 J.
Key. (A), (C)
Sol. (1) (V) + (5) (0) = (1) (-2) + 5 V'
V = 5V' - 2 (!)
V'+ 2 = 1
V - 0 =
V' = V - 2 (ii)
V = 5 (V - 2) - 2 From equation (i) and (ii)
V = 5V - 10 - 2 4V = 12
V = 3 m/s.
Pi = (1) (3) = 3 kg - m/s.
V = (1)(3) + (5)() = 1m/s
CM ~m/ *
6 2
1 1 3
kcm = 2(6)4 = 4 = 0.75J
Ktotal = 2(1)(3)2 = 4.5 J Hence correct options are (A), (C).
66. A few electric field lines for a system of two charges Q1 and Q2 fixed at two different points on the x-axis are shown in the figure. These lines suggest that
(A) |Q1 > |Q2|
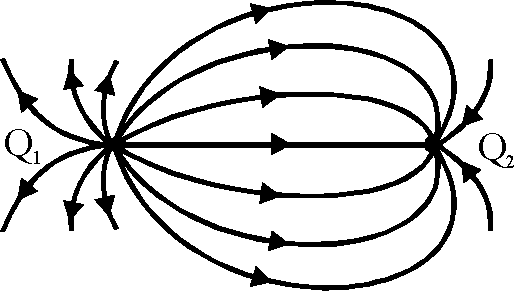
(B) |Q1| < |Q2|
(C) at a finite distance to the left of Q1 the electric field is zero
(D) at a finite distance to the right of Q2 the electric field is zero.
Key. (A), (D)
Sol. Density of field lines is more are Q1
|Q1 > |Q2|
Q1 and Q2 are of opposite signs
So, null point will be closer to charge of smaller magnitude i.e., Q2 Hence correct options are (A), (D).
67. A ray OP of monochromatic light is incident on the face AB of prism ABCD near vertex B at an incident angle of 60 (see figure). If the refractive index of the material of the prism is y/3 , which of the following is (are) correct ?
|
O | 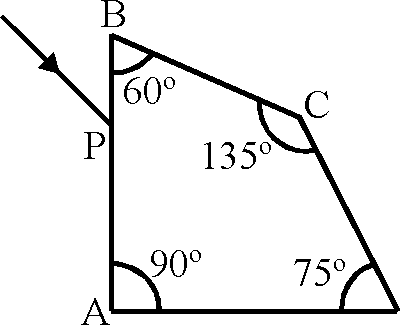 |
D |
(A) the ray gets totally internally reflected at face CD
(B) the ray comes out through face AD
(C) the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is 90
(D) the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is 120.
Key. (A), (B), (C)
Sol. 1 sin 60 = V3 sinr
r = 30
sin 0C =
C V3
0C = 35
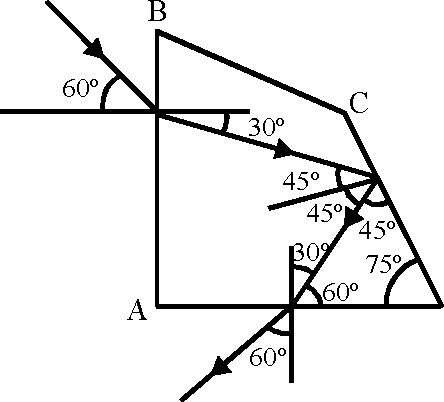 |
D |
At CD angle of incidence is greater than 0C .
At AD angle of incidence is less than critical angle So ray will come out of AD.
Angle of deviation
- 30 + 90 + 30 = 90
Hence correct options are (A), (B), (C)
V' 4 V,-
B
A
C
>T
T
68. One mole of an ideal gas in initial state A undergoes a cyclic process ABCA, as shown in figure. Its pressure at A is P0. Choose the correct option(s) from the following :
(A) internal energies at A and B are the same
(B) work done by the gas is process AB is P0V0f n4
P0
(C) pressure at C is 0
4
(D) temperature at C is
T
4
Key. (A), (B)
Sol. Internal energy of an ideal gas depends on temperature
WBC = nRT fnV
BC V1
P V 4V = (1)(R)-0VL in-R V0
= Wn4 Hence (A), (B) options are correct.
69. A student uses a simple pendulum of exactly 1 m length to determine g, the acceleration due to gravity. He uses a stop watch with the least count of 1 second fore this and records 40 seconds for 20 oscillations. For this observation, which of the following statement(s) is (are) true ?
(A) error AT in measuring T, the time period, is 0.05 seconds
(B) error AT in measuring T, the time period, is 1 second
(C) percentage error in the determination of g is 5%
(D) percentage error in the determination of g is 2.5%.
Key. (A), (C)
Sol. Error in measurement of T = s = 0.05 s
20
dg = 2dl g T
g- = 2 x-L
g 40
% error in calculation of g = 5%.
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon the first paragraph, 3 multiple choice questions and based upon the second paragraph 2 Multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these questions have four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Question Nos. 70 to 72
When a particle of mass m moves on the x-axis in a potential of the form V (x) = kx2, it performs simple
harmonic motion. The corresponding time period is proportional to , , as can be seen easily using
k
dimensional analysis. However, the motion of a particle can be periodic even when its potential energy increases on both sides of x = 0 in a way different from kx2 and its total energy is such that the particle does not escape to infinity. Consider a particle of mass m moving on the x-axis. Its potential energy is V(x) = ax4 (a > 0) for |x| near the origin and becomes a constant equal to V0 for |x| > X0 (see figure).
| ||||||||||||
|
X0 |
If the total energy of the particle is E, it will perform periodic motion only if (A) E < 0 (B) E > 0
70.
Key.
Sol.
(C) V0 > E > 0 (D) E > V0.
(C)
For periodic motion
Total energy should be less than V0 but greater than zero.
Hence (C) is correct.
For periodic motion of small amplitude A, the time period T of this particle is proportional to
1 lm
71.
(A) Aj-V a
(B)
(D)
Aa
1 ia
A\m
(C) A (B)
Key.
Sol.
72.
Dimensionally only B is correct.
The acceleration of this particle for |x| > X0 is (A) proportional to V0
V0
mX
(B) proportional to
V
(C) proportional to
(D) zero.
mX.
Key.
Sol.
(D)
For x > x0
potential energy is constant force on particle is zero. Hence (D) is correct.
Paragraph for Question Nos. 73 to 74
Electrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a nonzero value to zero as their temperature is lowered below a critical temperature TC(0). An interesting property of superconductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than TC(0) if they are placed in magnetic field, i.e., the critical temperature TC(B) is a function of the magnetic field strength B. The dependence of TC(B) on B is shown in the figure.
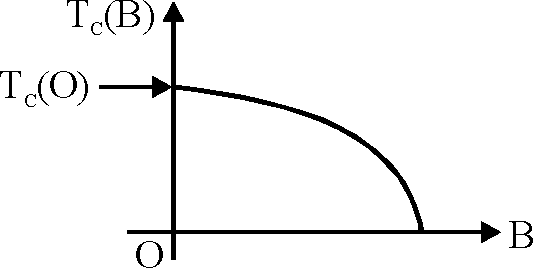
73. In the graphs below, the resistance R of a superconductor is shown as a function of its temperature T for two different magnetic field B1 (solid line) and B2 (dashed line). If B2 is larger than B1, which of the following graphs shows the correct variation of R with T in these fields ?
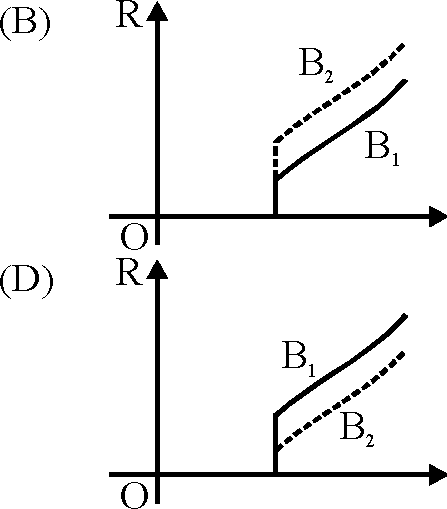 |
T T |
(A)
 |
T |
Key. (A)
Sol. As B increases, critical temperature decreases.
74. A superconductors has TC(0) = 100 K. When a magnetic field of 7.5 Tesla is applied, its TC decreases to 75 K. For this material one can definitely say that when
(A) B = 5 Tesla, TC(B) = 80 K (B) B = 5 Tesla, 75 K < TC(B) < 100 K
(C) B = 10 Tesla, 75 K < TC(B) < 100 K (D) B = 10 Tesla, TC(B) = 70 K.
Key. (B)
This Section contains TEN questions. The answer to each question is a Single Digit Integer ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question number in the ORS is to be bubbled.
A binary star consists of two starts A (mass 2.2. MS) and B (mass 1 MS), where MS is the mass of the sun. They are separated by distance d and are rotating about their center of mass, which is stationary. The ratio of the total angular momentum of the binary star to the angular momentum of star B about the center of mass is.
6.
r
2.2M,
11 r22 + 2.2r.2
11r22 11 r2 = 2.2 r.
2.2 r2 = 1 + \ 11 r22
2.2 ( 11
= 1 +-
2.2
front of it to 50 cm, the magnification of its image changes from m25 to m50. The ratio 25 is
m
The focal length of a thin biconvex lens is 20 cm. When an object is moved from a distance of 25 cm in
|f|
m
lf - u| 25 = 6.
50
A 0.1 kg mass is suspended form a wire of negligible mass. The length of the wire is 1 m and its crosssectional area is 4.9 x 10-7 m2. If the mass is pulled a little in the vertically downward direction and released, it performs simple harmonic motion of angular frequency 140 rad s-1. If the Young's modulus of
the material of the wire is n x 109 Nm 2, the value of n is 4.
2 K
m
YA Y(4.9 x10-7)
140 x140 =
75.
Key.
Sol.
r
11Ms
= 6 .
11
76.
Key.
Sol.
77.
Key.
Sol.
lm (1X0.1) 140 x140 = y(49) x10-7 y = 4 x 109 n = 4.
78. When two progressive waves y. 4 sin (2x - 6t) and y2 = 3 sin 2x - 6t - | are superimposed, the
amplitude of the resultant wave is Key. 5.
Amplitude - V42 + 32
Two spherical bodies A (radius 6 cm) and B (radius 18 cm) are at temperatures T1 and T2, respectively. The maximum intensity in the emission spectrum of A is at 500 nm and in that of B is at 1500 nm. Considering them to be black bodies, what will be the ratio of total energy radiated by A to that of B ?
Sol.
79.
Key.
Sol.
9.
(T1) (500 nm) = T2 (1500 nm)
T1 = 3T2
Ea -ct-4n(6cm)2(T1 )4 Eb - ct-4n(18cm)2 (T1)4
Ea
: (3)4 - 9.
V6
Gravitational acceleration on the surface of a planet is ng, where g is the gravitational acceleration on
80.
Key.
Sol.
2
the surface of the earth. The average mass density of the planet is 3 times that of the earth. If the escape
speed on the surface of the earth is taken to be 11 kms-1, the escape speed on the surface of the planet in kms-1 will be
3.
GMP
(i)
RP 11 11 R
-y/2geRe - 11 km / s
V22pRp - x (11)2
geRe
gPRP
GM
R
121
2
GMP R , 2 RP
RP
Me
R,
Mp
RP
121
2
(ii)
MP - 2 M,
(iii)
Rf - 3- r|
x = 3.
81. A stationary source is emitting sound at a fixed frequency f0, which is reflected by two cars approaching the source. The difference between the frequencies of sound reflected from the cars is 1.2% of f0. What is the difference in the speeds of the cars (in km per hour) to the nearest integer ? The cars are moving at constant speeds much smaller than the speed of sound which is 330 ms-1.
Key. 7.
V + VC V + VC
Sol. f1 -- f; f f
V - VC
C1
V + VC V + VC
f - l.f
0 100 0
Af -
= 2AVf = 1f
V 0 100 AVC = 7 km/hr.
82. When two identical batteries of internal resistance 1Q each are connected in series across a resistor R, the rate of heat produced in R is J1. When the same batteries are connected in parallel across R, the rate is J2. If J1 = 2.25 J2 then the value of R in Q is Key. 4.
So1' J1=( i!R IR
J2 = (R
2 l 0.5 + R )
2.25 = -4(a5 + R)2
(2 + R)2
9 = 4(R + 0.5)
4 = 2 + R
3 2R + 2
2 2 + R
6 + 3R = 4R + 2 R = 4Q.
83. A piece of ice (heat capacity = 2100 J kg-1 C-1 and latent heat = 3.36 x 105 J kg-1) of mass m grams is at -5C at atmospheric pressure. It is given 420 J of heat so that the ice starts melting. Finally when the ice-water mixture is in equilibrium, it is found that 1 gm of ice has melted. Assuming there is no other heat exchange in the process, the value of m is
Key. 8.
Sol. [ m(2100)(5) +1(3.36 x 105)] x 10-3 = 420
11m + 336 = 420 11m = 420 - 336 = 84 m = 8 gm .
84. An a-particle and a proton are accelerated from rest by a potential difference of 100 V. After this, their de
Xp
Broglie wavelengths are Xa and Xp respectively. The ratio -, to the nearest integer, is
Xa
Key. 3.
Sol. X h
V2mk
k = qV X h
Xp = |m7q X = |(4m)(2q) = 22 = 3
Xa v mpqp v (m)q
IIT - JEE (2010) PAPER II QUESTION & SOLUTIONS CODE 0
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
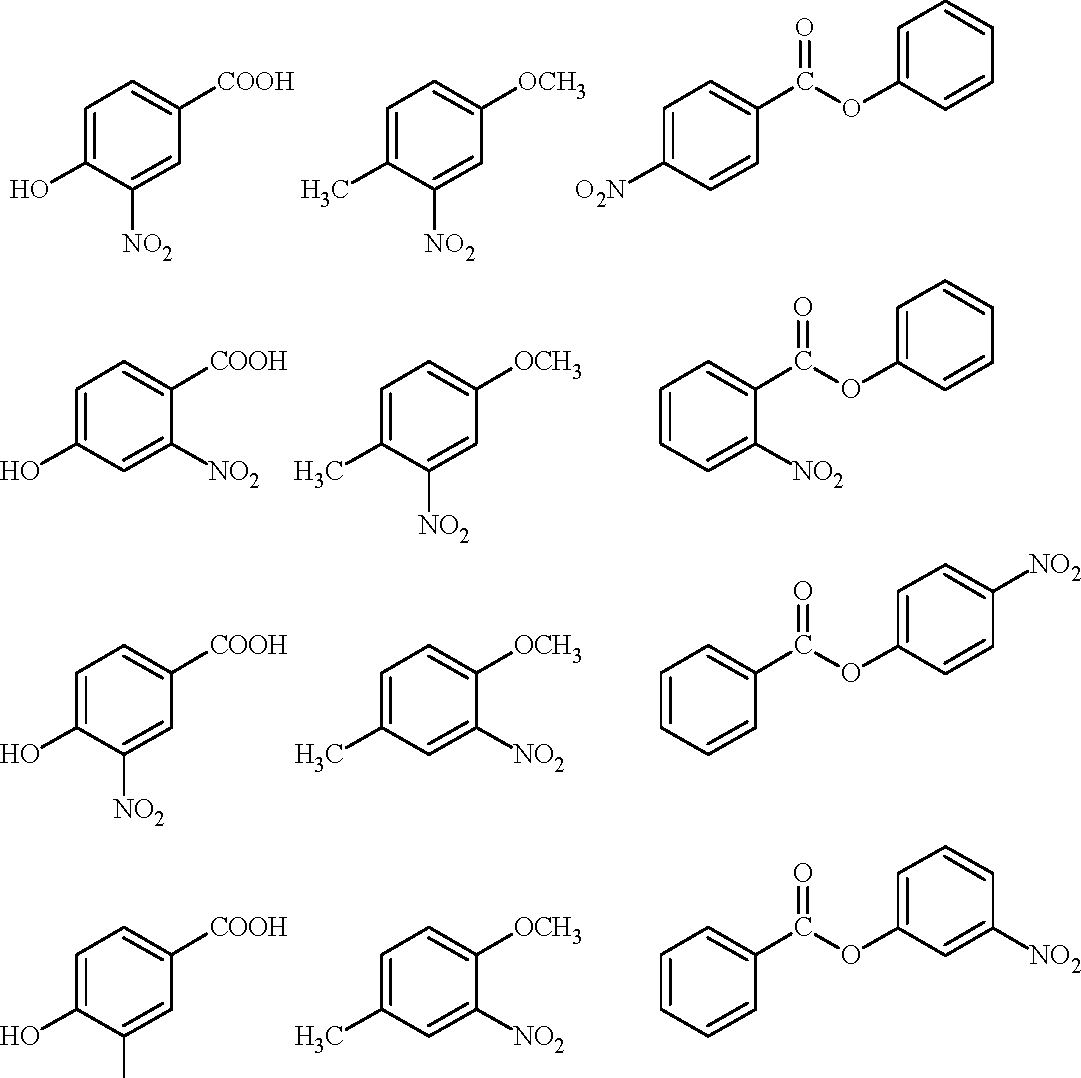
1. The compounds P, Q and S
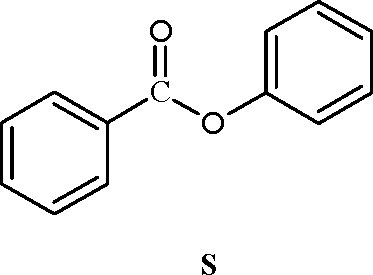
COOH
och3
HO'
P Q
where separately subjected to nitration using HNO3/H2SO4 mixture. The major product formed in each case respectively, is
H3C
(D)
(A)
(C)
(B)
 |
|
NO |
Key: (C)
|
COOH | |
 |
no2 |
|
OH | |
|
COOH | |
|
P |  |
|
OH | |
Sol.:
|
Q S | 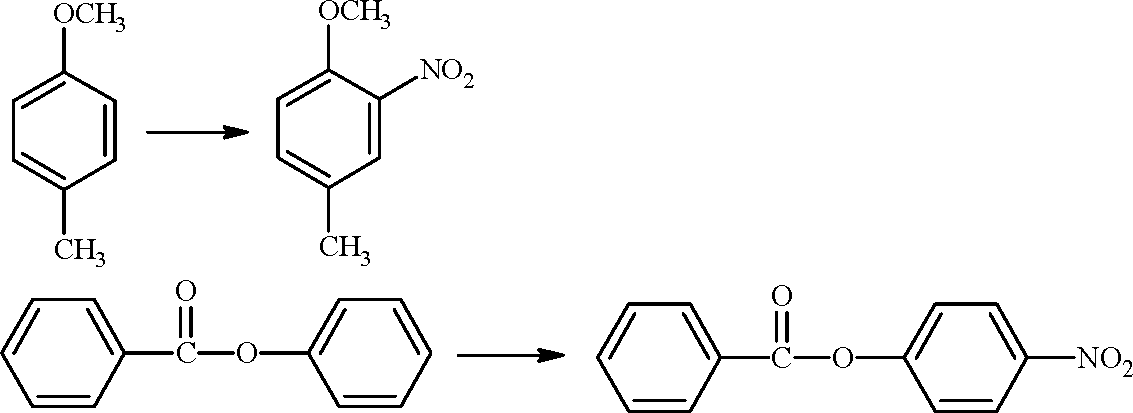 |
Assuming that Hunds rule is violated, the bond order and magnetic nature of the diatomic molecule B2 is (A) 1 and diamagnetic (B) 0 and diamagnetic
(C) 1 and paramagnetic (D) 0 and paramagnetic.
(A)
10 electron
CTfSCT *?s ct2sct *2s n2p rf2p (If Hunds rule is obeyed)
2 2 2 CT1SCT 1S CT2SCT 2-t2p-t2pJ
6 - 4
Bond order = -= 1
2
Paramagnetic if Hunds rule is obeyed Diamagnetic of Hunds rule is violated.
*2S n2p n0p (If Hunds rule is violated)
The packing efficiency of the two-dimensional square unit cell shown below is
(A) 39.27% (B) 68.02%
(C) 74.05% (D) 78.54%.
Let us consider the squerare plane (given) Area = L2
Area covered by 2 x nr2 (two circle)
4r = L
(D)
r =-L
4
2.
Key:
Sol.:
B0
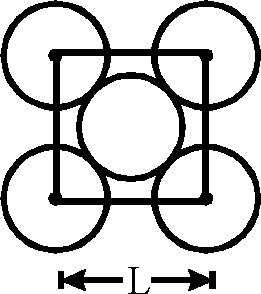
Key:
Sol.:
= nL2 = 16
nL2
<100
Area =2 n
nL2
4xL2
Packing efficiency =
3.14
<100 = 78.5%.
The complex showing a spin-only magnetic moment of 2.82 B.M. is (A) Ni (CO)4 (B) [NiCl4 ]
4.
(C) Ni (PPh3 )4 (D) [Ni (CN) ]2
Key: (B)
Ni28 4S23d8
Ni+24S03d8
Sol.:
4p
3d
4s
2 unpaired electron (n = 2) |i = yjn (n + 2) = V8 BM = 2.82 BM.
5.
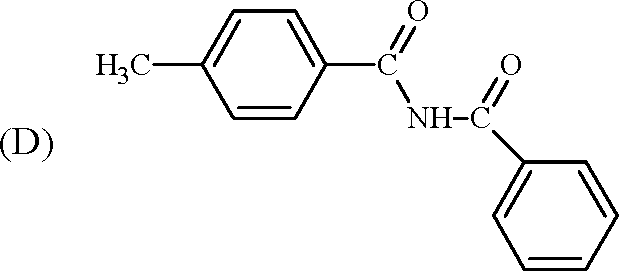
|
H,C- |  |
|
NH /?' O |  |
(C)
Key:
(C)
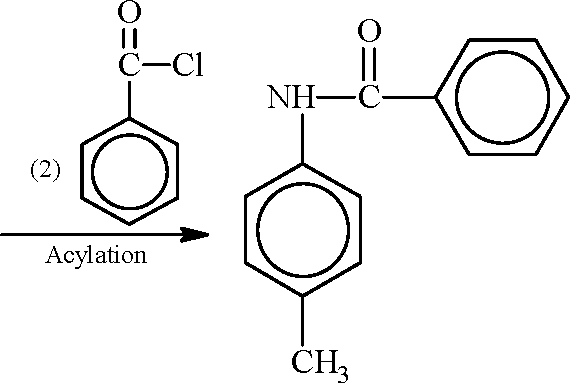
|
O |
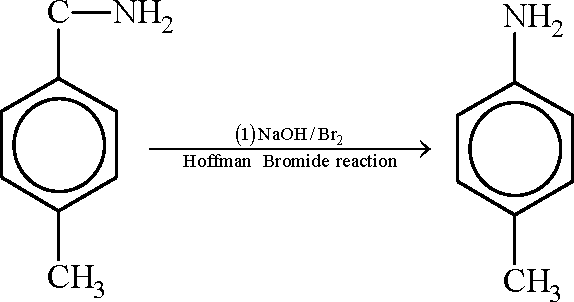 |
Sol.:
The species having pyramidal shape is
(A) SO3
(C) SiO32-
(D)
O I F F
Pyramidal
/
S.
6.
(B) BrF3 (D) OSF2
Key:
Sol.:
This section contains a group of 5 questions. The answer to each of the questions is a single-digit integer. ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question no. in the ORS is to be bubbled.
7. Silver (atomic weight = 108 g mol-1) has a density of 10.5 g cm-3. The number of silver atoms on a surface of area 10-12 m2 can be expressed in scientific notation as y x 10x . The value of x is
Key: (7)
Sol.: Consider a single layer square shaped arrangement of n x n silver atoms. Also assume the radius of each silver atom r.
Area of the layer = (2rn)2= 10-12m2 = 10-8cm2 Mass of the layer
Surface area x thickness x density = number of atoms x mass of single atom.
10-8 x 2r x10.5 = n2 x 108x 1.66 x10-24 [put 2rn = 10-4]
n3 = 5.855 x1010 n = 3.82 x103 .. number of silver atoms on the surface
= n2 =(3.82 x103 )2
= 1.4592 x 107 .. x = 7.
8. Among the following, the number of elements showing only one non-zero oxidation state is
O, Cl, F, N, P, Sn, Tl, Na, Ti
Key: (2)
Sol.: Fluorine and sodium shown only one non zero oxidation state, fluorine show - 1 and sodium shown + 1.
9. One mole of an ideal gas is taken from a to b along two paths denoted by the solid and the dashed lines as shown in the graph below. If the work done along the solid line path is ws and that along the dotted line path is wd, then the integer closest to the ratio wd/ws is
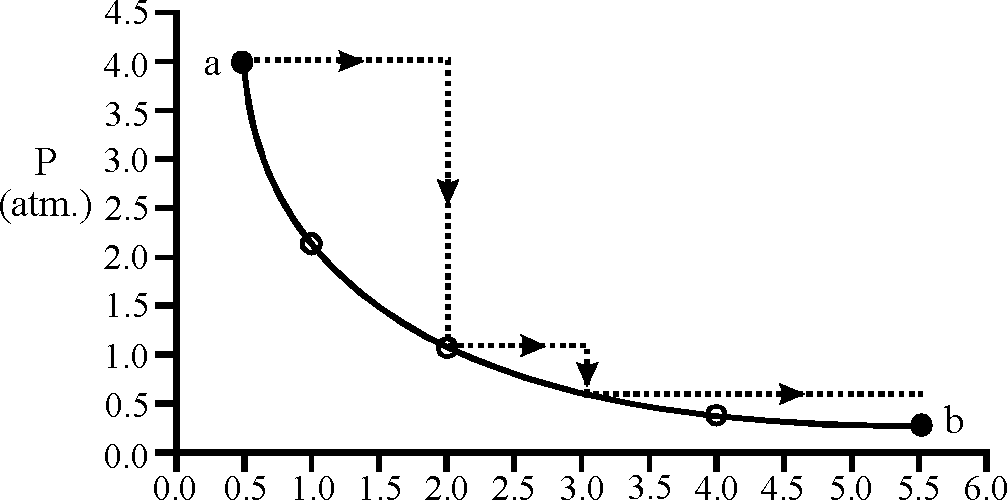
V(lit.)
Key: (2)
Sol.: wd = 4x 1.5 + 1 x 15 + 0.80 x 2.5 = 9.375
ws = 2.33 pV log
vi
= 2.33 x 4 x 0.5 log 5-5
0.5
4.606
w = 9.375 2. ws 4.606
10. The total number of diprotic acids among the following is H3PO4 H2SO4 H3PO3 H2CO3 H2S2O7 H3BO3 H3PO2 H2CrO4 H2SO3 Key: (6)
Sol.: The total number of diprotic acids are 6
O O O
/,S\
HO 11 OH O
/P\
HO H OH
,C
HO
OH
O
O
.Cr
O
,SOSOH
\
HO
HO
O
O O
11. Total number of geometrical isomers for the complex [RhCl(CO)(PPh3)(NH3)] is Key: (3)
Sol.: The total number of geometrical isomers for the complex [RhCl(O)(PPh3)(NH3)] is 3.
/S\
HO OH
OH
O
A B
\ /
M
D/ \
AB \ /
M
\
A C
\ /
M
D/ \
SECTION - III
Paragraph Type
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon each of the paragraphs 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Questions 12 to 14
Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous K2CO3 to give compound R, which upon treatment with HCN provides compound S. On acidification and heating, S gives the product shown below :
|
H3C OH | |
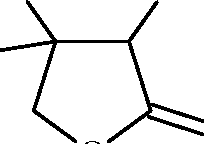 |
O |
|
O | |
h3c
12. The compounds P and O respectively are
CH3
CH3
,H H,C H
and 11
O
.CH
,CH
.H Hv
and
H
(A)
(B)
C
II
O
C
II
O
HC C
H3C
3
O
h3c
H3C CH
3 \ /CH2v CH
,ch2
H
H
H3C
H
H
H
CH
'C
II
O
C
II
O
(C)
Key: (B)
'30
C
II
O
(D)
C
and
and
CH
O
CH3
13. The compound R is
|
O | |
|
(A) | 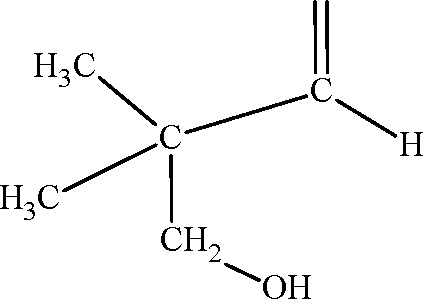 |
|
O | |
O
CH3 II
\ C C H
(B)
H3C
CH
OH
CH.
O
C
'CH H
ch3
I /C\H
,CH-CH H
,CH
h3c
(C)
(D)
H3C
CH
CH
C
OH
OH
Key: (A)
14. The compounds S is
O
O
CH3 II
\ C ,C H
CH.
3 c
CH
(A)
(B) H3C'
CH
h3c
ch2
H2C.
\
CN
CN
CN
CN
|H3 I
.CH
I / XOH
CH CH OH
ch3
\ Ch Noh
(D) H3C
(C)
h3c
ch2
ch2
OH
OH
14. (D) Sol.:(12-14)
H
H\ H
H
O
O
(Q)
(P)
|
K2CO3 |
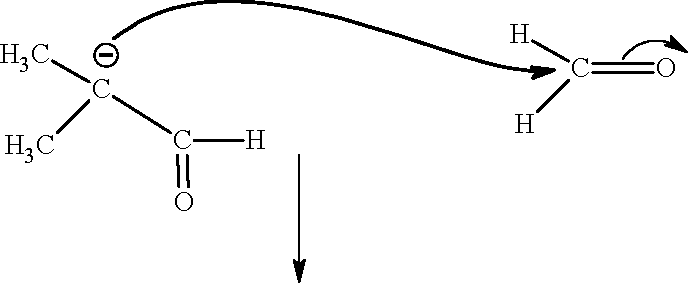 |
"O
O
C"3
C"3
Y
C"2
|
"3CC .oC C _C C"n 3 I I 2 CO2" C"3 |
 |
O"
-C"t
-O"
-C"v
O"
"3CC
C"3
(R)
"O
I
-LL "3Cc-
CN C"3
(S)
-C-
C"3
Paragraph for Questions 15 to 17
The hydrogen-like species Li2+ is in a spherically symmetric state S1 with one radial node. Upon absorbing light the ion undergoes transition to a state S2. The state S2 has one radial node and its energy is equal to the ground state energy of the hydrogen atom.
The state S1 is
15.
Key:
Sol.:
16.
Key:
Sol.:
(A) 1s (B) 2s
(C) 2p (D) 3 s
No. of radial node = n - I - 1
Since state S1 has 1 radial node it must be 2s orbital with n = 2 and I - 0 .
(B)
Energy of the state S1 in units of the hydrogen atom ground state energy is
(A) 0.75
(B) 1.50 (D) 4.50
(C) 2.25
(C)
Energy of state S1 =
13.6
3 eV/atom
= -13.6 x 2.25 eV / atom
= 2.25 times energy of ground state of hydrogen atom.
(C)
The orbital angular momentum quantum number of the state S2 is
(A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 2 (D) 3
(B)
Energy of S2 level = -13.6 eV/atom
13.6x 32
17.
Key:
Sol.:
13.6
This section contains 2 questions. Each question four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with one or more statement(s) given in Column II. For example, if for a given question, statement B matches with the statements given in q and r, then for that particular question, against statement B, darken the bubbles corresponding to q and r in the ORS._
Match the reactions in Column I with appropriate options in Column II. Column I Column II
18.
(p) Racemic mixture
(q) Addition reaction
(A) <Qn2c,- Qce-
(B)
O
OH OH
ch3
,/Cv/
-> h3c
cch3
I I
ch3 ch3
ch3
(r) Substitution reaction
(C)
|
__,O |
 |
 |
OH / -CH |
1 LiAlH4 2 H3O+
CH3
CH3
(s) Coupling reaction
(D)
Cl
HS
(t) Carbonation intermediate
Key: (A - r, s), (B -t), (C - p, q), (D - r) Sol.: (A)
<N2+ +
 |
|
CH3 |
OH
CH3 ch3
I 3 I 3
-C-C-
I
OH

ch3 ch3
H3CC-C-CH3
(B)
I I
OH OH
CH
3O
|
(C) | 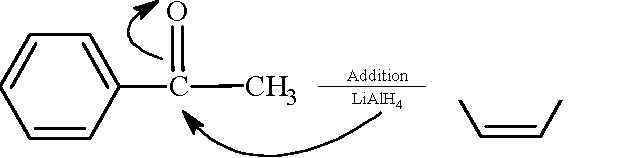 |
OAlH3 ,/ VC- |
 |
HO I C-1 Cch3 |
ch3
H
(D) lntramolecular substitution reaction
19. All the compounds listed in Column I react with water. Match the result of the respective reactions with the appropriate options listed in Column II.
|
Column I Column II | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sol.: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
If the distance of the point P(1, -2, 1) from the plane x + 2y - 2z = a, where a > 0, is 5, then the foot of the perpendicular from P to the plane is
20.
<A) If.4.-3
(C (.T7
(A)
|5 + a| = 15 a = 10
Key
Sol.
x.-1 = y. + 2 = z. -1 = -(-15)
If (x., y., z. ) is foot of perpendicular (x., y., z.) =(8/3, 4/3, -7/3)
9
4 1
A signal which can be green or red with probability 5 and 5 respectively, is received by station A and then
21.
3
transmitted to station B. The probability of each station receiving the signal correctly is . If the signal
4
received at station B is green, then the probability that the original signal was green is
(A)
(B)
(C) 21 23
(C)
E. original signal is green.
E2 original signal is red.
E signal received at station B is green.
P(E./E) = -p(E.)p(E)/Ei)-
7 p(E.)p(E/E.) + p(E2)p(E/E2)
|
4 5 |
[([ 4) |
+( |
4)] | |
|
// \2 / |
. X 2\ . | |||
|
( 3 ( |
1 ) |
1 |
3 |
1 1 3 ] |
|
I - I +I |
I |
+ |
x- |
- + x |
|
(( 4 J ( |
4 J J |
5 |
_ 4 |
4 4 4 _ |
(D) 20
Key
Sol.
20
23
22. Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram ABCD are given by AB = 2i + 10j+11k and AD = -i + 2j + 2k . The side AD is rotated by an acute angle a in the plane of the parallelogram so that AD becomes AD'. If AD' makes a right angle with the side AB, then the cosine of the angle a is given by
7
9
4/5
9
(A) -9
(B)
(D)
(C)
Key
Sol.
AB.AD > 0,
So 0 is acute.
AB.AD
8
cos0 =
AB||AD| 9 cos(a + 0) = 0 cosa.cos0 - sina. sin0 = 0 8cosa - -s/T7 .sina = 0
9
64cos2a = 17 sin2a cosa =
For r = 0, 1, ... , 10, let Ar, Br and Cr denote, respectively, the coefficient of xr in the expansions of (1+x)10, (1+x)20 and (1 + x)30 . Then
23.
Ar (B10Br - C10Ar) is equal to
(B) A10 (Bj20 - C10A10) (D) C10 - B10
(A) B10 - C10
(C) 0 Key (D)
Ar = 10Cr Br = 20Cr
Sol.
Cr = 30Cr 10
= B10 ArBr - Cw Ar2
=1 r=1
10 10 2 10cr.20cr - C10 (10cr)
= B
r=1 r=1
10 20 10 20 10 20 10 2 = B10 L C1 C1 + C2 C2 .... + C10 C10 J - C10 Cr J
= B10 .[30C10 - 1] - C10 [20C10 - 1J = C10 - B10
x
Let f be a real-valued function defined on the interval (-1, 1) such that e-x f(x) = 2 + jyl t4 +1 dt, for all xe
(-1, 1), and let f -1 be the inverse function of f. Then (f1)' (2) is equal to
(A) 1
(B)
(C)2
e
Key (B)
Sol. v f (f -1(x)) = x
(f1(x))' =-1-
f '(f-1(x))
We have to find (f 1(2))'
(f 1(2))' = -1-
f '(f(2))
When f-1 (x) = 2 f(x) = 2 x = 0
x
given e"x f(x) = 2 + JV t7 +1 dt
0
e"x (-f(x) + f '(x)) = x8 + 1 put x = 0 f '(0) = 3 (f1 (2))' = 1/3.
25. Let S = {1, 2, 3, 4). The total number of unordered pairs of disjoint subsets of S is equal to
(A) 25 (B) 34
(C) 42 (D) 41
Key (D)
Sol. S = {1, 2, 3,4}, then No. of unordered pairs of disjoint subsets of S is
= 41
2
This section contains a group of 5 questions. The answer to each of the questions is a single-digit integer. ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question no. in the ORS is to be bubbled.
+ 11 +
The local maximum of f(x) occurs at x = 2009
Hence, local maximum of g(x) also occurs at x = 2009. Hence the number of point of local maximum = 1.
|
. If |
Let k be a positive real number and let A =
28.
det (adj A) + det (adj B) = 10 , then [k] is equal to
{Note: adj M denotes the adjoint of a square matrix M and [k] denotes the largest integer less than or equal to k].
(4)
Key
Sol.
|A| = (2k - 1) (-1 + 4k9) + 2>/k (2 + 4Wk ) + 2>/k(4kVk + 2>/k)
(2k - 1) (4k2 - 1) + 4k + 8k2 + 8k2 + 4k = (2k - 1) (4k2 - 1) + 8k + 16k2
= 8k10 - 4k2 - 2k + 1 + 8k + 16k2 = 8k3 + 12k2 + 6k +1
|B| = 0 as B is skew symmetric matrix of odd order.
(8k3 + 12k2 + 6k + 1)2 = (103)2 (2k + 1)3 = 103 2k + 1 = 10 k = 4.5 [k] = 4.
29. Two parallel chords of a circle of radius 2 are at a distance V3 +1 apart. If the chords subtend at the center, n 2n
angles of and , where k > 0, then the value of [k] is k k
[Note : [k] denotes the largest integer less than or equal to k]
Key (3)
Sol. 2cos +2cos= -v/3 +1 k 2k
2cos-- cos-
2k 2k
-1 (2/3 + 1)2 = yf3 ->/3 - 1
2
2
4
-V3 -1 2
But cos
2k
n S n ,
cos = = cos k = 3. 2k 2 6
2k
30. Consider a triangle ABC and let a, b and c denote the lengths of the sides opposite to vertices A, B and C respectively. Suppose a = 6, b = 10 and the area of the triangle is 15>/3 . If ZACB is obtuse and if r denotes the radius of the incircle of the triangle, then r2 is equal to Key (3) B Sol. The area = 153
 |
|
C b = 10 |
102 + 62 - c2
2 x 10 x 6
-60 = 136 - c2 c2 = 196 c = 14.
cosC =
A 1573 15>/3 x 2 Since r = -- =-
s (10 + 6 +14)/ 2 30
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon each of the paragraphs 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 31 to 33
Consider the polynomial f(x) = 1 + 2x + 3x2 + 4x3
Let s be the sum of all distinct real roots of f(x) and let t = |s|.
-3
(B) I -11
,0
(A)
(C)
1
(D) I 0
31. The real number s lies in the interval
1
41
3 -1 . 4,- 2,
Key (C)
Sol. f(x) is constant function
- f(-4,f(-2,<0
f'(x) - 12x2 + 6x + 2 > 0 Vx e R
( 3 1
f(x) has only one real root in I--,--
( 4 2
The area bounded by the curve y = f(x) and the lines x = 0, y = 0 and x = t, lies in the interval
32.
(C) (9, 10)
<B> (61,11 (D) (
Key
Sol.
Required area t
A = g(t) = J f(x)dx
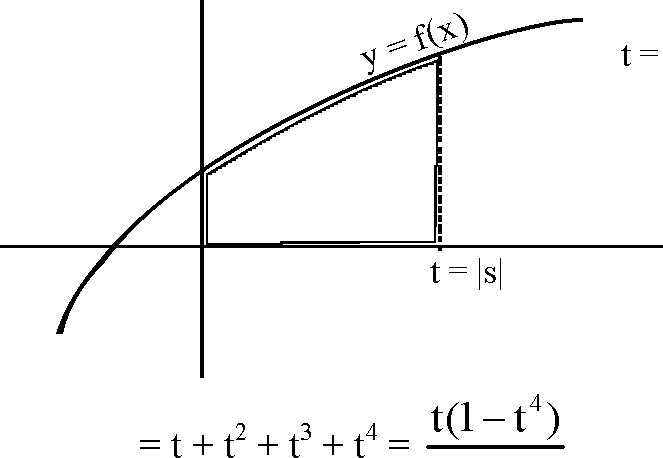 |
|
1 -1 ;'(t) -f(x) > 0 Vx > 0 |
t = |s| e
g(t) is increasing V t > 0
- g|2)<A<g(3
15 525 . (3 < A <-lies in | ,3
16 256 14
(B) decreasing in | -t, | and increasing in
I 4)
(C) increasing in (-t, t)
(B) 2
f'(x) = 12x2 + 6x + 2 is increasing
f ''(x) = 24x + 6 > 0 and 1
The function f'(x) is
(A) increasing in I -t, - 4- | and decreasing in
x >
Hence B is true.
33.
4,t 1
,t 4
(D) decreasing in (-t, t)
Key
Sol.
f''(x) < 0 1
x <
4
Paragraph for Questions Nos. 34 to 36
2 2 x y
Tangents are drawn from the point P(3, 4) to the ellipse + = 1 touching the ellipse at points A and B.
34.
2a/16I
(B)
15
(D) (3, 0) and | --5,5
(C)
(D)
Key
Sol.
= 0
|
.(i) |
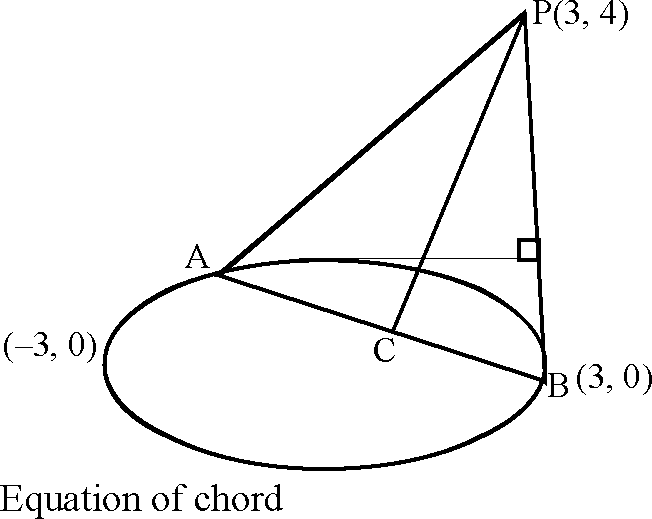 |
The coordinates of A and B are
(A) (3, 0) and (0, 2)
( 2
and (0, 2)
2 2 +y_
15
Contact AB
x + 3y - 3 = 0 .....(ii)
Solve (i) & (ii) we get
A = |- |,S) B(3, 0>
35. The orthocenter of the triangle PAB is (A) l 5,7
(C)
Key (C)
Sol. Equation of PE y - 4 = 3(x - 3) Equation of AD 8
y=5 .....
Solving (i) & (ii) we get x = -
11
7 25 5 , 8
<D> |J5,1
(B)
.(i)
y=
The equation of the locus of the point whose distances from the point P and the line AB are equal, is
36.
Key
Sol.
(A) 9x2 + y2 - 6xy - 54x - 62y + 241 = 0
(B) x2 + 9y2 + 6xy - 54x + 62y - 241 = 0 (D) x2 + y2 - 2xy + 27x + 31y - 120 = 0
(C) 9x2 + 9y2 - 6xy - 54x - 62y - 241 = 0 (A)
V(a-3)2 +(P-4)2 = (a+P_~3 10(a2 -6a + 9 + p2 -8p +16) = a2 + 9p2 + 9 + 6ap-6a- 18p
Required locus is 9x + y - 6xy - 54x - 62y + 241 = 0
This section contains 2 questions. Each question four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with one or more statement(s) given in Column II. For example, if for a given question, statement B matches with the statements given in q and r, then for that particular question, against statement B, darken the bubbles corresponding to q and r in the ORS._
|
37. Match the statements in Column-I with those in Column-II. |
Column I |
Column II | |
|
(A) |
The set of points z satisfying |z - i|z|| = |z +i|z|| is contained in or equal to |
(p) |
an ellipse with eccentricity 4/5 |
|
(B) |
The set of points z satisfying |z + 4| + |z - 4| = 10 is contained in or equal to |
(q) |
the set of points z satisfying Im z = 0 |
|
(C) |
If |w| = 2, then the set of points z = w - is w contained in or equal to |
(r) |
the set of points z satisfying |im z| < 1 |
|
(D) |
If |w| = 1, then the set of points z = w + is w contained in or equal to |
(s) |
the set of points z satisfying |Re z| < 2 |
|
(t) |
the set of points z satisfying |z| < 3 |
Key. (A-q, r), (B-p), (C-p, s, t), (D-q, r, s, t)
|z - i|z||=|z+i|z|| (A)
Putting z = x + iy
Sol.
We get y -x2 + y2 = 0
i.e., Im (z) = 0.
2ae = 8, 2a = 10
(B)
4
e =
5
|
(0, 3) |
 |
b2 = 25 (1 -15 ) = 9
2 2 x.+1-=1
25 9
z = 2(cos 0 + isin 0) -
= 2(cos0 + isin0) -2(cos0 - isin0)
3 5
z = cos 0 + isin 0 2 2
10e = 8
1
(C)
2(cos 0 + isin 0)
'(H
3 5
x = cos0, y = sin0
2 2
= 1
4 4
e2 = 1 -A = 16
25 25
4
5
(D) Let w = cos 0 + isin0
1
z = x + iy = w +--
w
x + iy = 2cos 0 x = 2cos0, y = 0
(q), (s)
38. Match the statements in Column - l with the values in Column-ll
|
Column I |
Column II | ||
|
(A) |
A line from the origin meets the lines 8 x - 2 y -1 z +1 ,x 3 y + 3 z -1 = = and 3 = = at 1 -2 1 2 -11 P and Q respectively. lf length PQ = d, then d2 is |
(p) |
-4 |
|
(B) |
The values of x satisfying tan-1(x + 3) - tan-1 (x - 3) = sin-1 |5 j are |
(q) |
0 |
|
(C) |
Non-zero vectors a,b and c satisfy a.b = 0, (b - a ).(b + c) = 0 and 2|b + c |=|b- a |. lf a =|ib + 4c, then the possible values of |i are |
(r) |
4 |
|
(D) |
Let f be the function on [-n, n] given by f(0) = 9 and f(x) = sin 9j / sin|yj for x # 0. The 2 n value of f f (x) dx is n - |
(s) |
5 |
|
(t) |
6 |
Key. (A - t), (B - p, r), (C - q), (D - r) Sol. (A) P(X + 2,1 -2X,X-1)
|PQ|=d2 =(X-21-3 J+(-2 + 4)I +(X-2)2
8 1 - 2X X-1
As OP and OQ are collinear 2|a + =-=-
3 -|a-3 |a + 1
(from last two)
X X + 2 = 0 . . .(i)
and X|a- 4|a + 3 X = (from 1st and lllrd) . . .(ii)
from (i) and (ii) 2X- 3|a = 5 . . . (iii)
from (i) and (iii) 3|i2 + 2|i - 1 = 0
1
3
so, X = 1, 3
"ence, d --or 6
9
(B) tan-1 (x + 3) - tan-1 (x - 3) - sin-1 (5jj
tan-1 (x + 3) - tan-1 (x - 3) - tan-1 (-4
Let tan-1(x + 3) = a, tan-1(x - 3) = p tan a - x + 3, tan p - x - 3
3
tan(a - P) - 4
_ tan a - tan p _ 3
1 + tan a tan p 4
- (x + 3) - (x - 3) - 3
- 1 + x2-9 - 4
x2 - 8 4
- x - 8 - <
- x2 -16
x = 4
(C) (b - a).(b + c) - 0 a -|ab
Put C -
- 0
(b - a).((4 - |a)b + a) - 0 (4-)|b|2 -1a|2-0 a.b - 0
(4-)|b|2-| a |2 (v a.b - 0)
Also 21 b + c |-1 b - a | again put C -
-|b - a|
a -|ab
-|(4-)b + a|-|b-a|
a -|ab
4
b +
IIT-JEE2010-Code-0-Questions and Solutions-Paper-I and II
(4 -p)21 b |2 +1 a |2 = 4| b |2 +41 a |2 since a.b = 0
((4-p)2-4)|b|2 = 31 a |2
((4-p)2-4)|b|2 = 3(4-p)|b|2
(4 - )2 - 4 = 12 - 3p 16 + p2 - 8p - 4 = 12 - 3p p2 - 5p = 0
p = 0 or 5. but p = 5 is not satisfying so p = 0.
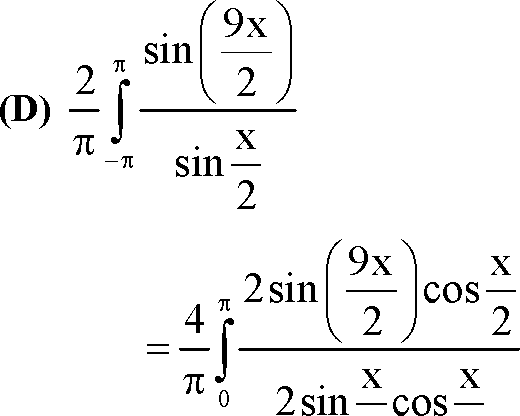
2 2 4 r sin5x 4 } sin4x
-+ _J i-
n' sin x n' sin x
Ii I2
I. = n, I2 = 0 4
So, xn = 4 . n
This section contains 6 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D), out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
A block of mass 2 kg is free to move along the x-axis. It is at rest and from t = 0 onwards it is subjected to a time-dependent force F(t) in the x direction. The force F(t) varies with t as shown in the figure. The kinetic energy of the block after 4.5 seconds is
(A) 4.50 J (B) 7.50 J
(C) 5.06 J (D) 14.06 J.
(C)
F(t)1 4N
39.
4.5s
-t
3s
O
Key.
Sol.
1
4x 3-1 x 2xi.5
2(V - 0) = 2V V =
2
= 6 -1.5 4.5 2
1
K
-(2)
= 81 = 5.06 J.
16
Hence correct option is (C).
A uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R carries uniform surface charge density of a per unit area. It is made of two hemispherical shells, held together by pressing them with force F (see figure). F is proportional to
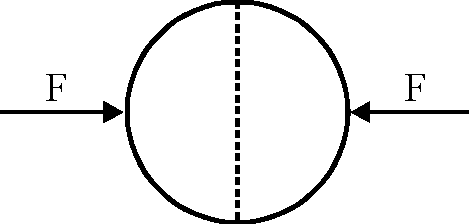
40.
1 2
(B) a2R
S0
(D) TF-
(A) a2R2
S0
(C) 080 R
(A)
Key.
Sol.
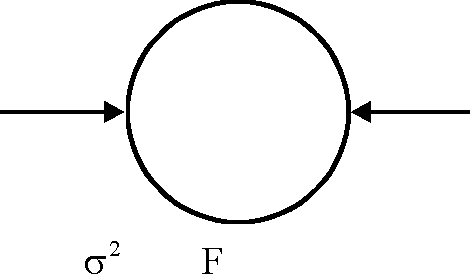 |
|
2e0 nR |
F
280
Hence correct option is (A).
41. A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still air with a vertical uniform electric field
8in
of strength x105 Vm-i. When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal
velocity 2 x 10-3 ms-1. Given g = 9.8 ms-2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 x 10-5 Ns m-2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m-3, the magnitude of q is
(A) 1.6 x10-19C
(C) 4.8 x10-19C
(B) 3.2x10-19C (D) 8.0 x10-19C .
Key.
Sol.
mg =fvise
4
3 nR3pg = 6nRvT
2 Pg
Eq = mg
q = q =
4 nR3pg 3 E 8x10-19C .
A Vernier calipers has 1 mm marks on the main scale. It has 20 equal divisions on the Vernier scale which match with 16 main scale divisions. For this Vernier calipers, the least count is (A) 0.02 mm (B) 0.05 mm
42.
Key.
Sol.
(C) 0.1 mm (D) 0.2 mm.
V.C. = 1 div of M.S. - 1 div V.S.
= 1 div of M.S. -16 div of M.S.
20
4
= div of M.S.
20
= 0.2 mm .
Hence correct option is (D).
A biconvex lens of focal length 15 cm is in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the lens and the mirror is 10 cm. A small object is kept at a distance of 30 cm from the lens. The final image is
43.
Key.
Sol.
(A) virtual and at a distance of 16 cm from the mirror
(B) real and at a distance of 16 cm from the mirror
(C) virtual and at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror
(D) real and at a distance of 20 cm from the mirror.
For lens
1___ = _!
V -30 = 15
V = 30 cm For mirror
u = + 20 cm v = - 20 cm For lens u = 10
V 10 = 15
_L = 3 + 2
V = 30
V = 6 cm from lens = 16 cm from mirror.
Hence correct option is (B).
A hollow pipe of length 0.8 m is closed at one end. At its open end a 0.5 m long uniform string is vibrating in its second harmonic and it resonates with the fundamental frequency of the pipe. If the tension in the wire is 50 N and the speed of sound is 320 ms-1, the mass of the string is (A) 5 grams (B) 10 grams
44.
(C) 20 grams (D) 40 grams.
Key. (B)
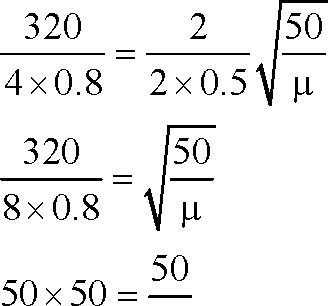
u = kg / m 50
m = x 0.5 x1000 gm 50
= 10 grams.
Hence correct option is (B).
This section contains a group of 5 questions. The answer to each of the questions is a single-digit integer. ranging from 0 to 9. The correct digit below the question no. in the ORS is to be bubbled.
A large glass slab (u = 5/3) of thickness 8 cm is placed over a point source of light on a plane surface. It is seen that light emerges out of the top surface of the slab from a circular area of radius R cm. What is the value of R ?
45.
Key.
 |
|
sin 0 = - tan 0: |
Sol.
R
R = 6 cm .
46.
Key.
Sol.
1 = 1 u = f
_! =
u1
2
20
+10 -12
Image of an object approaching a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 m along its optical axis is observed to move from m to m in 30 seconds. What is the speed of the object in km per hour ?
3.
1
v 3
25
_! =_
u1 = 100 u1 = -50 m
= _2_
50 u2 = 20
_! = 10 -14 _ u2 100
25
:18
: 3 km/hr .
v = -
30
u2 =-25 m 25 18=5 30 5 =
To determine the half life of a radioactive element, a student dN(t)
 |
|
Years |
47.
dN(t)
versus t. Here - is the rate oi
dt
plots a graph of in
dt
radioactive decay at time t. If the number of radioactive nuclei of this element decreases by a factor of p after 4.16 years, the value of p is
Key.
Sol.
8.
dN 1
In-= t
dt 2
dN -2t
-= e 2
dt
X = year
2
Tw = 069 = 1.38 years /2 ( 1
4.16 years = 3 half lives p = 8.
A diatomic ideal gas is compressed adiabatically to of its initial volume. In the initial temperature of
48.
Key.
Sol.
the gas is Ti (in Kelvin) and the final temperature is aTi, the value of a is
4.
Y-l
Y-l
aT 1 32 v
Tv
2
a = (32)5 = (32)5 = (25)5 = 4
2pF
HII -II-
2pF
49.
|
2MQ | ||||
| ||||
|
2MQ |
B
At time t = 0, a battery of 10 V is connected across points A and B in the given circuit. If the capacitors have no charge initially, at what time (in seconds) does the voltage across them become 4 V ? a*
[Take : ln5 = 1.6, fn3 = 1.1 ].
v = v0(1 -e-t/RC), R = -2x2- = 106Q , C = 4 x 10-6 F
Key.
Sol.
2.
2 + 2
4 = 10(1 - e-t/4)
-1/4 i r
e = 1.6 = fn5 - tn3 = 0.5 .
This section contains 2 paragraphs. Based upon each of the paragraphs 3 multiple choice questions have to be answered. Each of these question has four choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Paragraph for Question Nos. 50 to 52
When liquid medicine of density p is to be put in the eye, it is done with the help of a dropper. As the bulb on the top of the dropper is pressed, a drop forms at the opening of the dropper. We wish to estimate the size of the drop. We first assume that the drop formed at the opening is spherical because that requires a minimum increase in its surface energy. To determine the size, we calculate the net vertical force due to the surface tension T when the radius of the drop is R. When this force becomes smaller than the weight of the drop, the drop gets detached from the dropper.
50.
R
r
Key.
Sol.
2nrT - F. R
If the radius of the opening of the dropper is r, the vertical force due to the surface tension on the drop of radius R (assuming r << R) is
(A) 2nrT (B) 2nRT
2nr2T 2nR2T
(C)
(C)
51. If r = 5 x 10 4 m, p = 103 kgm 3, g = 10 ms2, T = 0.11 Nm 1, the radius of the drop when it detaches from the dropper is approximately
(A) 1.4 x 10-3 m (B) 3.3 x 10-3 m
(C) 2.0 x 10-3 m (D) 4.1 x 10-3 m.
Key. (A)
T
Sol. 2nr - mg
R
r2 -p4 nR3g R 3
T - g R4 3 B
4 (5x10-4)2 x0.11x 3
R4 -
< 25 x10 x 0.33 R --:-
R - 1.4 x 10 m .
52. After the drop detaches, its surface energy is
(A) 1.4 x 10-6 J (B) 2.7 x 10-6 J
(C) 5.4 x 10-6 J (D) 8.1 x 10-6 J.
Key. (B)
Sol. U - 4nR2s
- 4x 3.14x (1.4x 10-3)2 x0.11
- 2.7x10-6 J.
Paragraph for Question Nos. 53 to 55
The key feature of Bohr's theory of spectrum of hydrogen atom is the quantization of angular momentum when an electron is revolving around a proton. We will extend this to a general rotational motion to find quantized rotational energy of a diatomic molecule assuming it to be rigid. The rule to be applied is Bohr's quantization condition.
53.
(B)
f-
18n2l
A diatomic molecule has moment of inertia l. By Bohr's quantization condition its rotational energy in the nth level (n = 0 is not allowed) is
1 ( h2
n | 8n l h2
(D) n2
8n2l
(A)
Key.
Sol.
(D)
nh
2n
nh
2nl
lro
K = -l
2 4n2l2 n2h2
8n2l
Hence correct option is (D).
lt is found that the excitation frequency from ground to the first excited state of rotation for the CO
4
molecule is close to x 1011 Hz . Then the moment of inertia of CO molecule about its center of mass is n
close to (Take h = 2n x 10-34 J s)
(A) 2.76 x 1046 kg m2 (C) 4.67 x 1047 kg m2
(B)
54.
(B) 1.87 x 1046 kg m2 (D) 1.17 x 1047 kg m2.
Key.
Sol.
(4 - 1)h2 8n2l
= 1011 32nl
3 x 2nx 10-
= 101
32ol
l = 1.87 X10-46 kgm2.
ln a CO molecule, the distance between C (mass = 12 a.m.u.) and O (mass = 16 a.m.u.), where
55.
1a.m.u. = 3 x10 kg, is close to
(A) 2.4 x 10-10 m (C) 1.3 x 10-10 m (C)
1.87 x10-46
(B) 1.9 x 10-10 m (D) 4.4 x 10-11 m.
Key.
Sol.
r
12x16 28 '
1.87 x 10-
r2 = i 6 x10-20 -1-10
r = 1.3 x10-m. Hence correct option is (C).
This section contains 2 questions. Each question four statements (A, B, C and D) given in Column I and five statements (p, q, r, s and t) in Column II. Any given statement in Column I can have correct matching with one or more statement(s) given in Column II. For example, if for a given question, statement B matches with the statements given in q and r, then for that particular question, against statement B, darken the bubbles corresponding to q and r in the ORS._
56. Two transparent media of refractive indices 1 and |i3 have a solid lens shaped transparent material of refractive index |i2 between them as shown in figures in Column II. A ray traversing these media is also shown in the figures. In Column I different relationship between 1, |i2 and |i3 are given. Match them to the
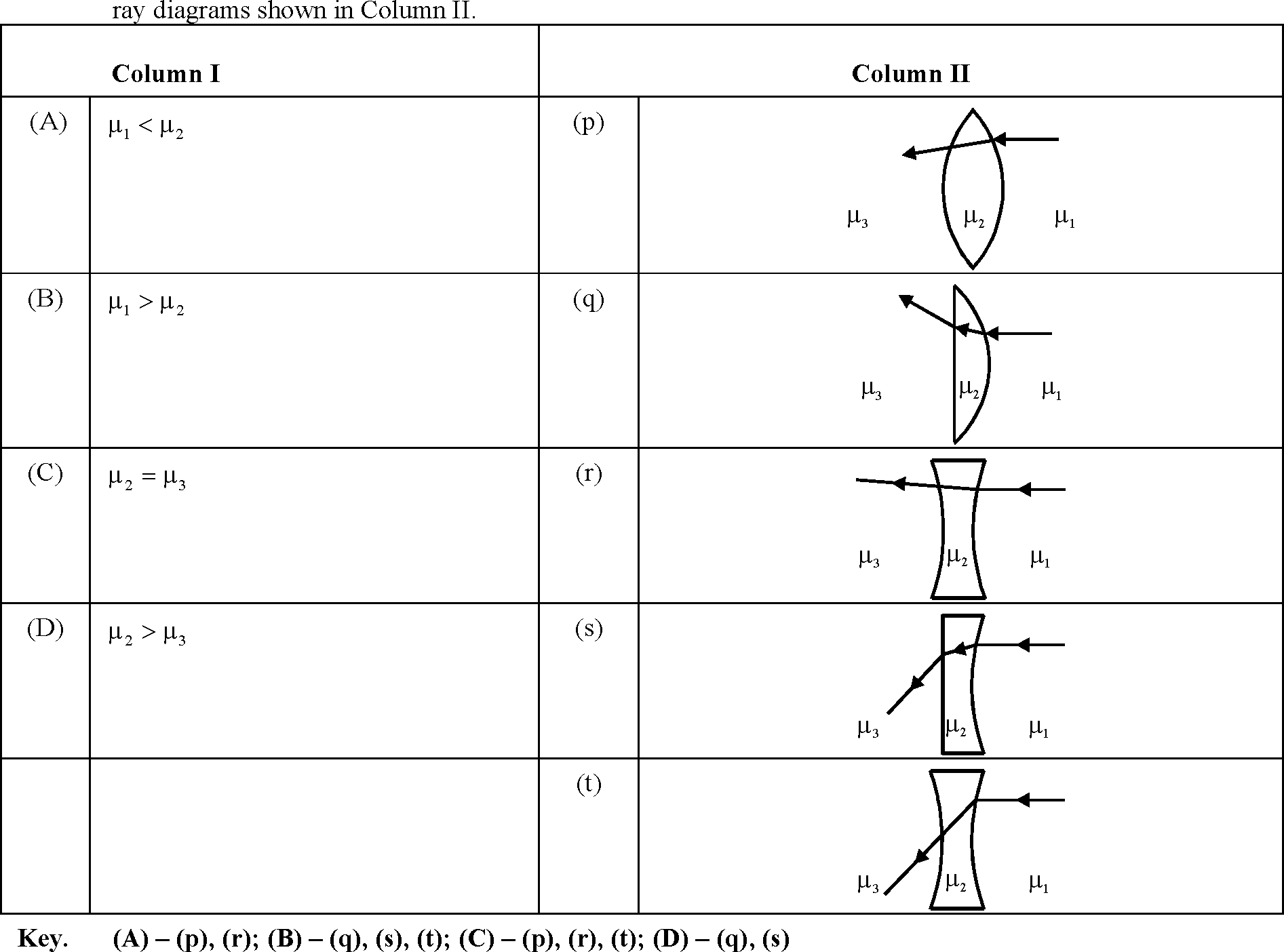
57. You are given many resistances, capacitors and inductors. These are connected to a variable DC voltage source (the first two circuits) or an AC voltage source of 50 Hz frequency (the next three circuits) in different ways as shown in Column II. When a current I (steady state for DC or rms for AC) flows through the circuit, the corresponding voltage V1 and V2. (indicated in circuits) are related as shown in Column I. Match the two :
Column II
Column I
(A) I * 0, V1 is proportional to I
(p)
H-
i
6mH
3|iF
V
(B)
(q)
I * 0, V2 > V1
6mH
2Q
V
Vi V,
(C)
V1 = 0, V2 > V1
(r)
i -wm-
6mH
2Q
V
o
(D)
(s)
I * 0, V2 is proportional to I
H-
6mH
3|iF
V
o
(t)
*-
-II
1kQ 3|iF
V
>
Key. (A) - (r), (s), (t); (B) - (q), (r), (s), (t); (C) - (p), (q); (D) - (q), (r), (s), (t),
Sol. XL = 2n(50)(6 x 10-3) = 6n x 10-1
Xc =-
Xc > Xl.
NARAYANA IIT ACADEMY 59
-1 (k-1)! k
- VC V - VC
26. Let a1, a2, a3, ... , an be real numbers satisfying a1 = 15, 27 - 2a2 > 0 and ak = 2a1 - a2 for k = 3, 4, ... , 11.
a, + a2 +... + a, 1 , , , ~ a1 + a2 +... + an . ,
11 11
Key (0)
C =120 C
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
