Bharathiar University 2008 B.Sc Computer Science - Question Paper
(FOR THE CANDIDATES ADMITTED (NO.OF PAGES: 10)
DURING THE ACADEMIC YEARS 2006 AND 2007 ONLY) AIDED
06 UCS 12 i . 06 UCE 12 j
s . _ . _ . _ . _ . _ . _ . _
SELF-FINANCING
NGM COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) :: POLLACHI END - OF - SEMESTER EXAMINAITONS : NOVEMBER - 2008 B.Sc. - COMPUTER SCIENCE MAXIMUM MARKS: 70
x III SEMESTER TIME: 3 HOURS
v____________________________________________________________________________________________
PART - III
RESOURCE MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES
SECTION - A
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS. (10 X 1 = 10 MARKS)
1. What is meant by infeasible solution?
2. --------- method is applicable to those linear programming problems that
start with infeasible but otherwise optimum solution.
3. Name any two methods for finding the initial basic feasible solution of a transportation problem.
4. State the mathematical form of an assignment problem.
5. Define Reorder level.
6. Define Economic order quantity.
7. State the meaning of the symbolic form ( a/bk): (d/e) of queering model.
8. What is meant by transient state?
9. Define dummy activity.
10. PERT is said to be--------oriented whereas CPM is said to be--------
oriented.
SECTION - B
ANSWER EITHER a OR b IN EACH OF THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS. (5 X 4 = 20 MARKS)
11. a) An animal feed company must produce 200 lbs of a mixture
containing the ingredients X1 and X2. X1 costs Rs.3 per Ib and X2 cost Rs.8 pa Ib. Not more than 80 Lbs of Xi can be used and minimum quantity to be used for X2 is 60 Lbs. Find how much of each ingredient should be used if the company wants to minimize the cost. Formulate the LPP.
(OR)
b) Solve the following LPP using graphical method. x1+2x2 < 2000 x1+x2 < 1,500 x2 < 600 x1,x2 > 0
12. a) Obtain initial basic feasible solution to the following transportation
problem by vogels approximation method.
Stores
|
I |
II |
III |
IV |
Availability | ||
|
A |
7 |
3 |
5 |
5 |
34 | |
|
Warehouse |
B |
5 |
5 |
7 |
6 |
15 |
|
C |
8 |
6 |
6 |
5 |
12 | |
|
D |
6 |
1 |
6 |
4 |
19 | |
|
Demand |
21 |
25 |
17 |
17 | ||
|
(3) ( 06 UCE 12/06UCS 12) b) A team of 5 horses has entered a jumping sh0ow contest. The number of Penalty points to be expected when each rider rides any horse is shown below. Riders | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
expected loss of the team?
13. a) Find EOQ for the following data:
= 1000 pieces = Rs.4/ order = Rs.250
Annual usage Expediting cost Ordering cost Inventory holding cost
= 20% of average inventory
(OR)
b) Neon lights in an industrial park are replaced at the rate of 100 units per day. The physical plant orders the neon lights periodically. It costs Rs.100 to initiate a purchase order. A neon light kept in a storage is estimated to cost about Rs.0.02 per day. Determine the optimum inventory policy for ordering the neon lights.
(4) ( 06 UCE 12/06UCS12)
14. a) A bank plans to open a single server drive-in banking facility at a
particular centre. It is estimated that 20 customers will arrive each hour on an average. If, an average, it requires 2 minutes to process a customers transaction determine.
i) The proportion of time that the system will be idle.
ii) On the average how long a customer will have to wait before reacting the server
?
iii) The fraction of customers who will have to wait.
(OR)
b) In a maintenance shop, the inter arrival times at tool crib are exponential with an average time of 10 minutes. The length of the service time is exponentially distributed with 6 minutes. Find
i) The probability that a person arriving at the booth will have to wait.
ii) Average length of the queue that forms and the average time that an operator spends in the system.
iii) Estimate the fraction of the day that tool crib operator will be idle.
15. a) A project has the following schedule. Construct the PERT
Network. And find its critical path.
Activity Time
1-2 4
1-3 1
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(OR) |
b) Draw the project network for the following precedence relationship
of activities of its time estimates and also find the critical path.
Proceeding Time estimates
Activity Activity Optimistic Most likely Pessimistic
|
A |
-- |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
|
B |
A |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
|
C |
--- |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
D |
C |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
|
E |
B, D |
0.5 |
1 |
1.5 |
|
F |
E |
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
G |
B, D |
3 |
3.5 |
7 |
|
H |
G |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
I |
F, H |
1.5 |
2 |
2.5 |
SECTION - C
ANSWER EITHER a OR b IN EACH OF THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS. (5 X 8= 40 MARKS)
16. a) Solve the following LPP using simplex method.
Maximize z = 4x 5x2+9x3+11x4 subject to
xi+x2+x3+x4 <15 7x1+5x2+3x3+2x4 < 120 3x1+5x2+10x3+15x4 < 100 x1,x2,x3,x4 > 0
(OR)
b) Use dual simplex method to solve the LPP.
Minimize Z= x1+2x2+3x3 subject to
x1-x2+x3 > 4 x1+x2+2x3 < 8 x2-x3 > 2 x1,x2,x3 > 0
17.a)Consider the following transportation table showing production and
|
transportation costs along with the supply and demand positions of factories. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
i) Obtain an initial basic feasible solution by using VAM.
ii) Find out an optimal solution.
(OR)
b) A department head has four subordinates, and few tasks to be performed. The subordinates differ in efficiency, and the tasks differ in their intrinsic difficulty. His estimate, of the time each man would take to per form each task, is given in the matrix below.
|
Tasks |
1 |
Men 2 |
3 |
4 |
|
A |
18 |
26 |
17 |
11 |
|
B |
13 |
28 |
14 |
26 |
|
C |
38 |
19 |
18 |
15 |
|
D |
19 |
26 |
24 |
10 |
How should the tasks be allocated one to a man, so as to minimize the total man - hours?
18.a) A contractor has to supply 10,000 bearings per day to an automobile manufacturer. He finds that, when he starts a production run he can produce 25,000 bearings per day. The cost of holding a bearing in stock for one year is Rs.2 and the set-up cost of a production run is Rs.1,800. How frequently should production be made?
(OR)
(8) ( 06 UCE 12/06UCS12)
b) A dealer supplies the following information with regard to a product dealt in by him:
Annual demand 10,000 units; ordering cost Rs.10 per order; price:
Rs.20/unit. Inventory carrying cost: 20% of the value of the inventory
per year.
The dealer is considering some back-order to occur. He has estimated that
the annual cost of back - ordering will be 25% of the value of inventory.
i) What should be the optimum no. of units of the product he should buy in a lot?
ii) What quantity of the product should be allowed to backordered, if any?
iii) What would be the maximum inventory?
iv) Would you recommend to allow back-order? If so, what would be the annual cost saving by adopting the policy of back- ordering?
19. a) In a railway marshalling yard, goods trains arrive at a rate of 30 trains/day. Assuming that inter-arrival time follows an exponential distribution and the service time is also exponential with an average of 36 minutes.
Calculate the following:
i) The mean queue size and
ii) the probability that the queue size exceeds 10
iii) IF the input of trains increases to an average of 33/day, what will be the change in (i) and (ii)
(OR)
b) On an average 96 patients per 25 hour day require the service of an emergency clinic. Also on an average, a patient requires 10 minutes of active attention. Assume that the facility can handle only one emergency at a time. Suppose that it costs the clinic Rs.100 per patient treated to obtain an average servicing time of 10 minutes, and the each minute of decrease in this average time would cost Rs.10 per patient treated. How much would have to be budgeted by the clinic to decrease the average size of the queue from 1 1/3 patient to V a patient?
20.a) A civil engineering firm has to bid for the construction of a dam.
The activities and time estimates are given below:
Activity
Most likely
1-2
2-3
2-4
2-8
17
18 15 19
Duration
Optimistic
14
14
13
16
Pessimistic
25
21
18
28
3-4 (dummy)
3-5
4-6
15
13
18
17
27
21
5-7 (dummy)
14
18
20
5-9
6-7 (dummy)
6-8 (dummy)
7-9
8-9
16
14
20
16
41
22
The policy of the firm with respect to submitting bids is to bid the minimum amount that will provide a 95% of probability of at best breaking even. The fixed costs for the project are eight lakhs and the variable costs are 9,000 every day spent working on the project. The duration is in days and the costs are in terms of rupees. What amount should the firm bid under this policy?
(OR)
b) Find the critical path and calculate the slack time for each event for the following PERT diagram. Find the duration of the project.
|
4 |
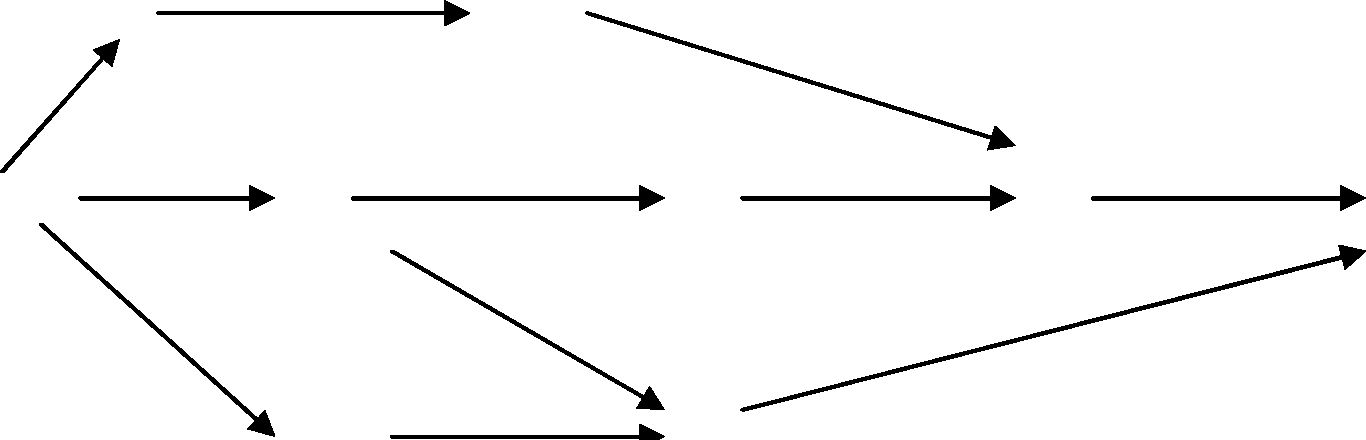 |
|
> |
A7.
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
