Bangalore University 2007-2nd Sem Diploma Mechanical Engineering I - Strength of material Stdte - Question Paper
|
Register Number |
|
III Semester Diploma Examination, November 2007 CIVIL ENGINEERING BOARD STRENGTH OF MATERIALS
Time : 3 Hours ]
[ Max. Marks : 100
Note: (1) Section -1 is compulsory.
(2) Answer two questions each from Sections - II,m andTV.
|
SECTION -1 | ||
|
Fill in the blanks with appropriate word/words : |
5x1 = | |
|
(i) |
The unit of section modulus is | |
|
(ii) |
The ultimate tensile stress developed in called |
a body resisting the fracture is |
|
(iii) |
Shape of bending moment diagram when a beam is subjected to a u.d.l. is | |
|
(iv) |
Property of a material which breaks into pieces when subjected to a sudden load is | |
|
(v) |
A strut is a member subiected to |
stress. |
|
Define the following : j... |
5x1 = | |
|
Poissons ratio | ||
|
(K) |
Proof resilience | |
|
'(-(iii) |
Radius of gyration | |
|
iiv) |
Point of contraflexure | |
|
(V) |
Torsional rigidity | |
SECTION - II
1.
2. (a) A steel bar of 50 mm x 50 mm in section is subjected to an axial pull of 200 kN. Taking E = 2 x 105 N/mm2 and Poissons ratio as 0.3, calculate alterations in length, side and volume of the bar. Calculate also the amount of energy stored in the bar during extension. 8
(b) A circular hollow column of external diameter 300 mm and internal diameter of 250 mm is 4.50 m long. It is subjected to an axial compressive load W. If the allowable stress in the material is 120 N/mm2, calculate the safe axial load W and shortening in its length. Assume E = 2 x 101 N/mm2. 7
3. (a) A bar 300 mm long is 50 mm square in Section for 100 mm of its length,
50 mm dia. for 120 mm length and 30 mm dia. for the remaining length, If a tensile load of 100 kN is applied to the bar, calculate the max and min. stresses induced in it and total elongation of the bar. E = 0.2 x 102 N/mm2. Assume uniform distribution of load over the cross-section. 8
(b)y-K steel rod of 20 mm dia., 6 m long is connected to two ends rigidly at 20 C.
'r Find the pull exerted when the temperature falls to 40 C 7
(i) if the ends do not yield and
(ii) if the ends yield by 1.1 mm Take E = 2 x 105 N/mm2 and
a = 1.2 x 10~5/C . \
5. (a) The moment of inertia of an area about the axes parallel to GG and at distances of 20 mm and 10 mm from it are 24 x 106 mm4 and 21 x 106 mm4 respectively. Find the area and 1GG. 5
State the Parallel Axis Theorem. 2
Find the moment of inertia about the. centroidal axes xt and yy of the angle
section 100 mm x 80 mm x 20 mm. '
6. (a) A cantilever beam 5 m long carries point loads of 30 kN, 20 kN and 10 kN at
distances of 1.0 m, 3 m and 5 m from the fixed end. In addition to this the beam also carries a u.d.l. of 10 kN/m over 3 m length from the free end. Construct SF and BM diagrams.
(b) A simply supported beam having a span of 6 m carries a u.d.l. of 12 kN/m over a length of 4 m commencing from left hand support. It also carries a point load of 10 kN at a distance of 1 m from the right support. Draw SF and BM diagrams giving all salient values.
V ' \
7. (a) A beam ABCD 12 m long is supported at B and C so that AB = 2 m, BC = 6 m
and CD = 4 m. It carries a u.d.l. of 50 kN/m from A to C and a point load of 40 kN at D. Construct SF and BM diagrams.
(b) A timber beam of rectangular section, simply supported over a span of 4 m is carrying a u.d.l. of 20 kN/m over the entire span. Calculate the width and depth of the beam, if the stress is not to exceed 8 N/mm2. Take the ratio of depth to width as 1.5.
SECTION - IV
(a) A solid shaft has to transmit a maximum torque of 2.3 kN - m. If the shear stress is not to exceed 75 N/mm2 and angle of twist should be limited to 0.34 degree in a length of 2 m, find a suitable diameter for the shaft.
Take C = 0.84 x 105 N/mm2.
(b) A boiler is subjected to an internal pressure of 2 N/mm . The thickness of the boiler plate is 20 mm and the permissible tensile stress is 120 N/mm2. Find the maximum permissible diameter when the efficiency of longitudinal joint is 90% and that of circumferential joint is 40%.
a) Determine the strength of a single rivetted lap joint, consisting of 15 mm thick plates with 20 mm dia. rivets. Also find the efficiency of the joint.
Take f = 150 N/mm2, f, = 300 N/mm2 and f 110 N/mm2.
t b s
TTiirn
(b) Find the strength of fillet welded joint shown in Fig. (i) Thickness of plates - 8 mm Size of weld - 6 mm
Take ft=150N/mm2
f = 100 N/mm2
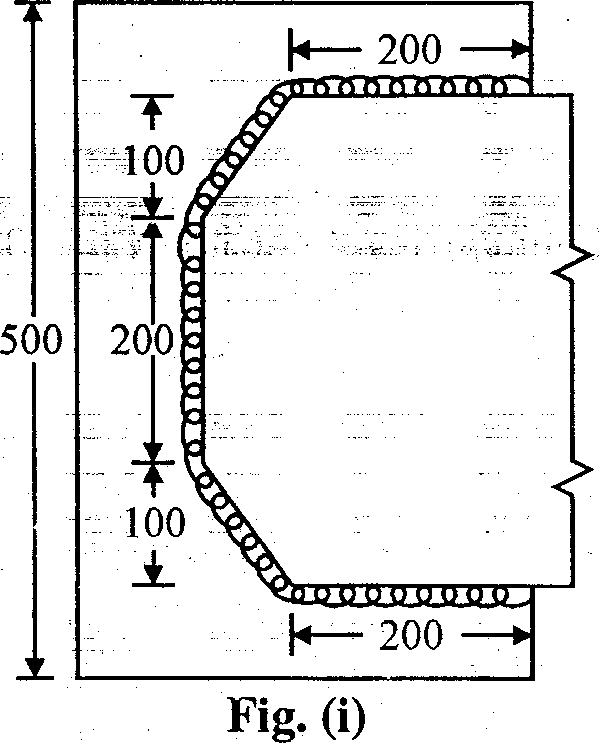 |
|
All measurements are in mm.. |
~p--
10. (a) The beam shown in Fig. (ii) is simply supported at the left end and hinged at the right end. If the magnitudes of P and Q are 20 kN each, find the magnitude and directions of reactions graphically.
P Q

hinge
2000
2000
2000
-+H-
Fig. (ii)
(b) A system of forces are acting at the comers of a rectangular block as shown in Fig (iii). Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant. 7 5 ON
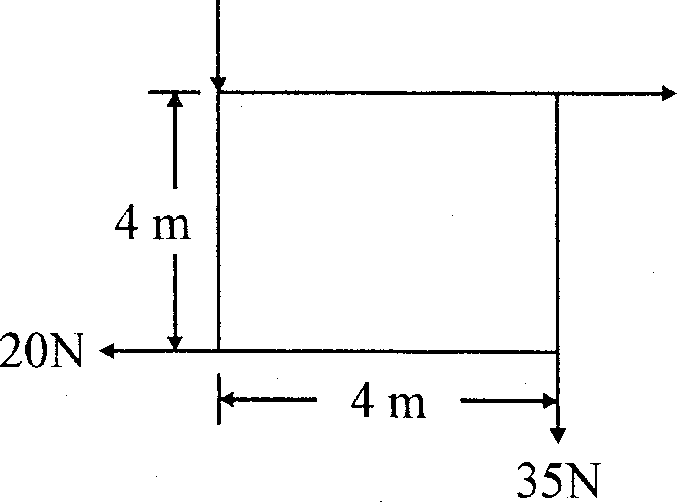
25N
Fig. (iii)
Final length = 78 mm
Final diameter = 7 mm
Yield load = 34 kN
Ultimate load = 61 kN
Calculate :
(i) Yield stress
(ii) Ultimate stress
(iii) Percentage elongation
(iv) Percentage reduction in area
(b) At a point in a strained material, the principal stresses acting are 100 N/mm2 and 60 N/mm2 both tensile : 7
Find
(i) Normal stress
(ii) Tangential stress
(iii) Resultant stress, if the plane is inclined at 30 to the minor axis.
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
