Bangalore University 2006-2nd Sem Diploma Mechanical Engineering I - Strength of material Annual Stdte - Question Paper
|
Register Number |
|
Tiird / Fourth Semester Diploma ( Annual ) Examination, 2006
CIVIL BOARD
( Course Cbdes : ME, AT, MY & MP )
Time : 3 Hours ] [ Max. Marks : 100
Instructions : i) Section V is compulsory.
ii) Answer any two full questions each from the remaining sections.
iii) Any missing data may suitably be assumed.
a) Define the following : 2
i) Bulk modulus
ii) 'Resilience.
b) A steel bar 300 mm long, 500 mm wide ard 12 mm thick is subjected to an axial pull of 84 kN. Determine the changes in
i) length
ii) width
iii) thicknesc and
iv) volume of the bar.
TakedS = 2 x 10 5 N/mm 2 and ji - 0-3. 8
a) Due to sudden onset of summer, the temperature has increased by 3nC. Calculate the temperature stress in a steel rail of length 15 m when the bolts and nuts are rigidly tightened. Take
Esteel = 2 x 10 5 N/mm 2
a steel = 12 x 10 ~6 /C. 2
b) A bar 300 mm long is 50 mm square in section for 120 mm of its length, 25 mm dia. for middle 80 mm of its length and 40 mm in dia. for the remaining length. If a tensile load of 100 kN is applied on the bar, calculate the maximum and minimum stresses induced in it and the total elongation.
Take E = 2 x 10 5 N/mm 2 . 8
a) Draw stress-strain diagram for a tensile test on a mild steel bar specimen and name the various stages. 4
b) A point in a sirained material is subjected to a tensile stress of 120 N/mm 2
and a compressive stress of 80 N/mm 2 acting at right angles to eacn other.
Find the normal, tangential and resultant stresses on a plane inclined at an angle of 30 to the ccmpressive stress axis. o
SECTION - II
4. a] Distinguish between shearing force and ben.jag moment. 2
b) A simply supported beam of span 6 m carries two point loads of 5 kN and 10 kN at 1 m and 2 m respectively from left support. The beam carries a udl of 10 kN/m over a length of 3 m from the right support. Draw $.F. and B.M. diagrams. 8
5. a) Define the following : 3
i) Neutral axis
ii) Moment of resistance.
b) The M.I. of a beam section 50 mm deep is 69-49 x 10 7 mm 4 . Find the longest span ovejr which a beam of this section, when simply supported could cany a udl of 50 kN/m run over the entire span. The bending stress in the material of the beam is not to exceed 110 N/mm 2 . 7
6. A beam of uniform section 7 m long carries a udl of 20 kN/m over the whole length and a concentrated load of 10 kN at the right end. If the beam is freely supported at the left end and 2 m from the right end, draw S.F. and B.M. diagrams indicating the salient values. Also locate the point of inflexion. 10
7. a) Define the following : 3
i) Moment of inertia
ii) Section modulus.
b) Calculate M.I. of an angle section 100 mm x 80 mm x 10 mm about an aids passing through the centroid and parallel to shorter leg. 7
8. a) The M.I. of an area about the axes parallel to GG and at distances 20 mm
and 10 mm from it are 24 x 10 6 mm 4 and 21 x 10 6 mm 4 respectively. Find the area and I qq . 4
. , -b) A hollow shaft of 20 mm outside diameter and 16 mm inside diameter is subjected to a torque of 40 N-m. Find the shear stresses at the outside and . inside of the shaft. 6
9. A solid shaft is required to transmit 750 kW @ 60 rpm. If the maximum value of shear stress is not to exceed 50 N/mm 2, calculate the diameter of the shaft.
If the above shaft is replaced by a hollow shaft, whose internal diameter is 0-6 times the external diameter, what will be the percentage of saving ?
The torque, max. shear stress, the material and the length of the shaft are in both cases. i ( i
| C.B.
lUUts
10. a) A boiler is subjected to an internal pressure of 2 N/mm 2. The thickness ef
the boiler plate is 20 mm and the permissible tensile stress is 120 N/mm 2. Find the maximum permissible diameter, when the efficiency of the longitudinal joint is 90% and that of circumferential joint is 40%. 4
b) Find the thickness of metal necessary for a steel cylindrical shell of internal diameter 150 mm to withstand an internal pressure of 50 N/mm 2. The max. hoop stress in the section is not to exceed 150 N/mm 2. ( Use Lame's equation) 6
11. a) State any four >?.dvantages of welded joints over riveted joints. 2
b) A 100 mm x 12 mm plate is connected to another plate by fillet welds around the end of the bar and also inside a machined slot as shown in fig. (i). Determine the size of the weld, if the joint is subjected to a pull of 140 kN. Take working stresses for transverse welds and longitudinal welds as 100 N/mm 2 and 80 N/mm.2 respectively. 8
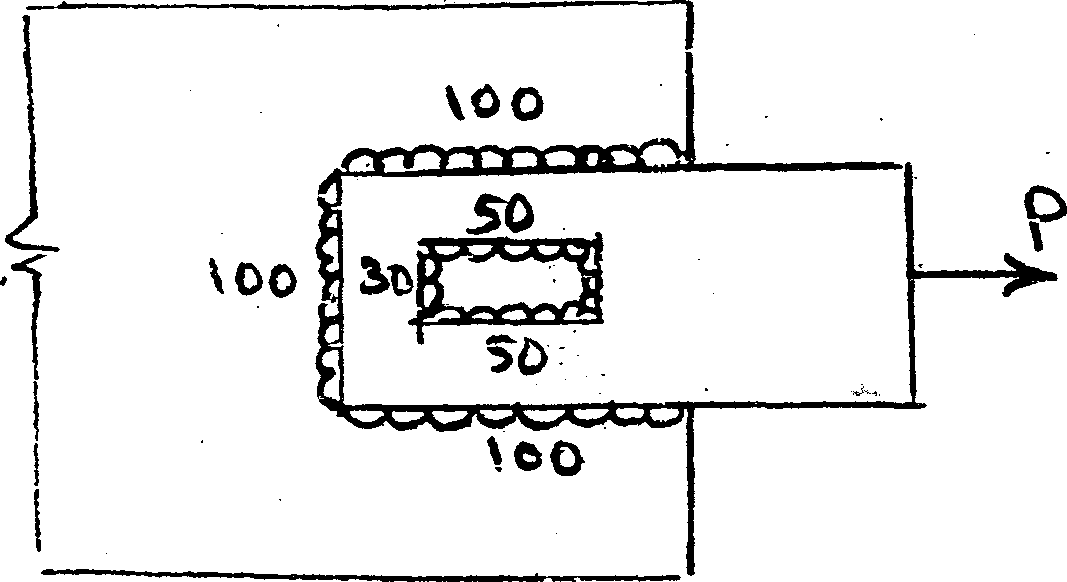
ALL DIMENSIONS ARE IN mm Fig (i)
12. A single riveted double cover butt joint in a structure is used for connecting two plates 12 mm thick. The dia. of the rivet is 24 mm. The permissible stresses are 120 N/mm 2 in tension, 100 N/mm 4v' single shear & 200 N/mm 2 in double
shear and in bearing.
Calculate the necessary pitch and efficiency of the joint.
10
SECTION-V
|
13. Determine graphically the resultant of a system of forces shown in Jig. (ii)- 10 |
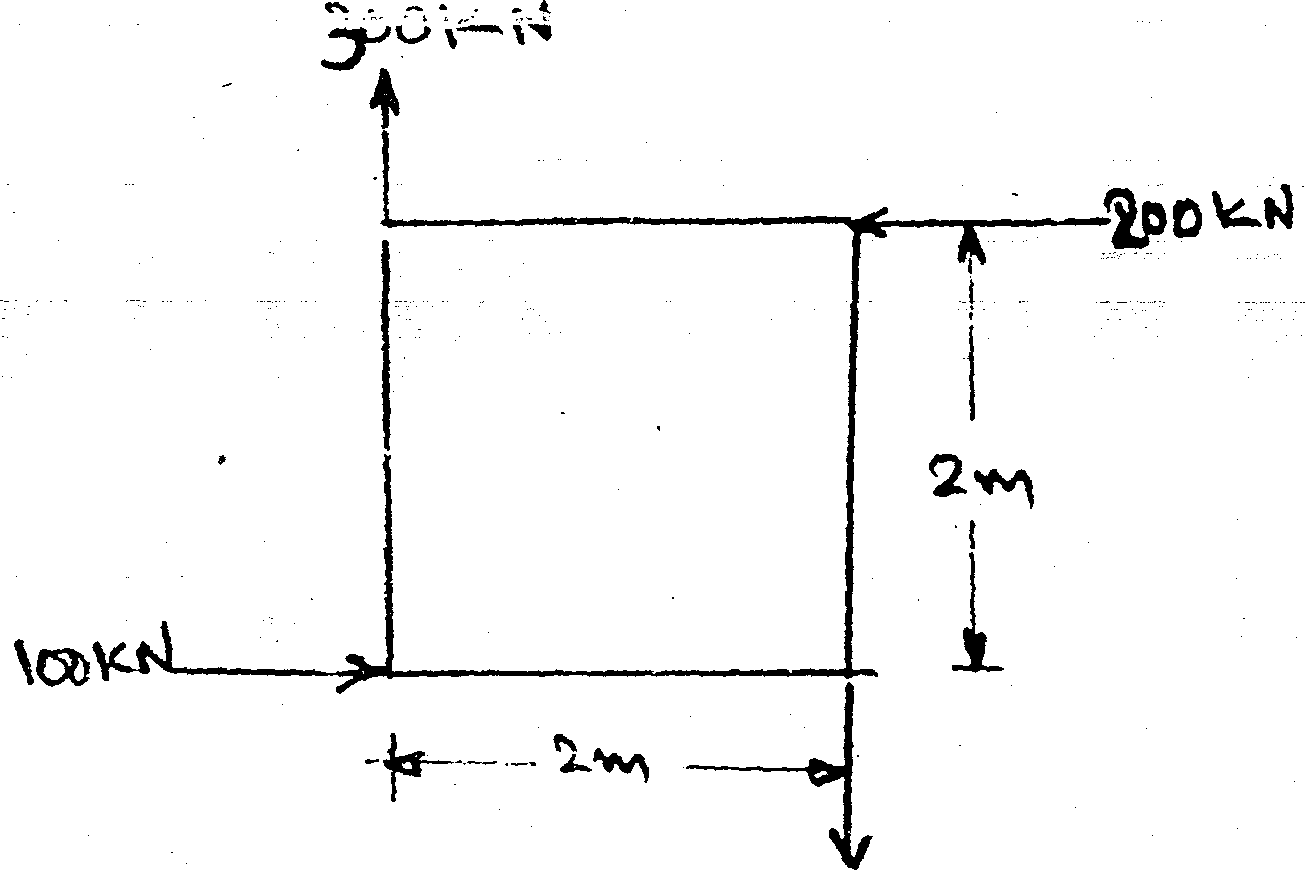 |
*60*4*4
14. The beam shown in Jig. (iii) is supported by hinge support at the left end and roller on the right end. If the magnitude of P and Q are 20 kN each, find the magnitude and direction of reactions. 10
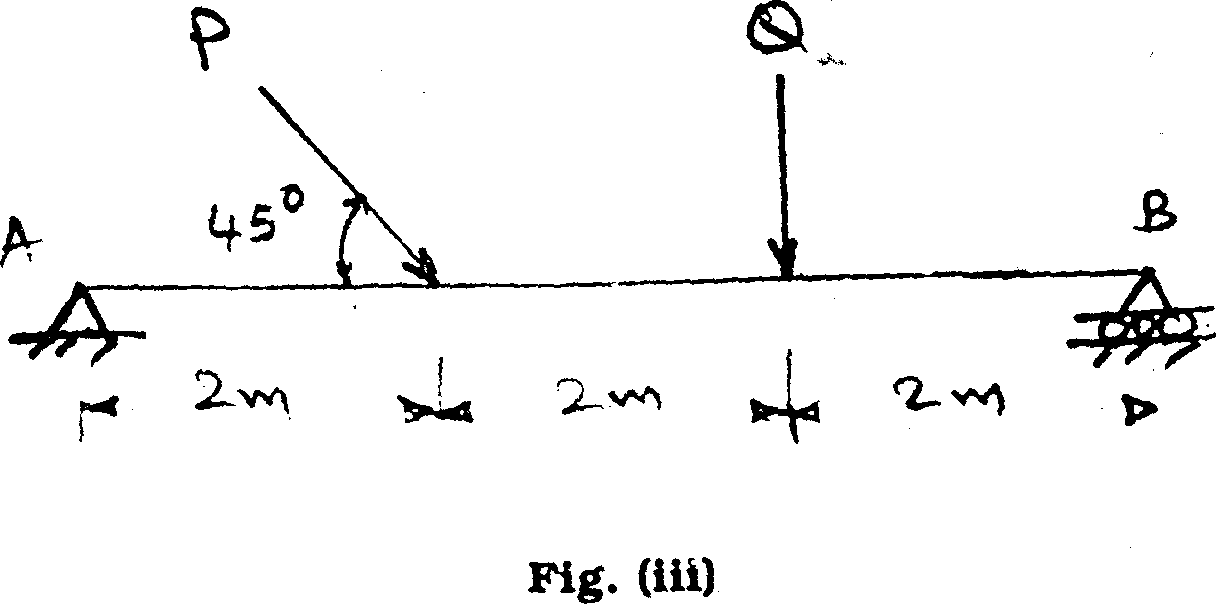
C.B.-1005
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
