Birla Institute of Technology (BIT Mesra) 2007 B.E Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering - Question Paper
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, PILANI
I Semester 2007-2008
Comprehensive exam (4-12-2007) Duration: three hours
Course: CE C361 (Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering) Max. Marks: 120
-Attempt all ques. and in the identical sequence as provided in the ques. paper.
- Use both sides of ans book pages.
- every part of a particular ques. should be answered at 1 place.
- ans of every new ques. should begin on a fresh page.
1. A deep cut of height 12m having side slope of 1.5:1 (horizontal:vertical) intersects plane of contact of 2 strata at a height of 2m above base of cut. The plane of contact of the 2 strata makes an angle 120 with horizontal. The lower stratum is less pervious than the upper one. The soil of the upper stratum is having unit weight of 1.9 t/m3 with level ground surface. The values of c and ? ranging from the 2 strata are 0.25 kg/cm2 and 150 respectively. Check whether a slide is likely to occur along the plane of contact ranging from 2 strata. If a slide is not likely to occur, obtain out factor of safety against sliding. (14)
2. Briefly define about subsequent clay minerals: Kaolinite, Montmorillonite, Illite. (6)
3. A flow net for seepage under the sheet piling is shown in Fig. 1. Estimate approximately the volume of seepage in cu m/day/m length of the piling, if the permeability of the sand is 10 x 10-3 cm/s. If the saturated unit of sand is 22.8 kN/m3, what is the factor of safety against piping by heave in front of the piles? (?w = 9.8 kN/m3)
Fig. one (10)
4. 2 soils A (k = 0.5 cm/s) and B (k = 0.05 cm/s) are organizes in the manner shown in Fig. two in a tube. What is total head at elevations 0m & 3m. Determine the volume of flow. (10)
4.5m
water
3m
A B Fig. 2
1m 1m
datum 0m
5. Determine the ultimate bearing capacity of a rectangular footing, 2m x 3m in plan, founded at a depth of 1m beneath ground surface. The load on the footing acts at an angle of 200 to the vertical and is eccentric in the direction of width and length by 0.3m and 0.5m respectively. Shear strength parameters of soil are c’ = 40 kN/m2 and ?’ = 300. Unit weight of soil = 16 kN/m3. Water table is located at a depth of 1.5m beneath footing base. Use IS:6403-1981 recommendations. Angle of internal friction governs shear failure. Interpolate ranging from general (?’ ? 360) and local (?’ ? 290) shear failure to get governing bearing capacity factors. (Nc = 30.14, Nc’ = 16, N? = 22.4, N?’ = 6.39, Nq = 18.4, & Nq’ = 7.3 for ?’ = 300) (15)
6. A plate load test conducted in a sandy soil at a depth of 1m on a plate of 0.6m x 0.6m size yielded an ultimate load of 200 kN. The load settlement curve found was almost linear upto a load of 120 kN when settlement of the plate was obtained to be 24mm. calculate the allowable bearing pressure for a footing of size 1.2m x 1.2m proposed in the identical soil and at a depth of 1m. Bulk density of soil is 19.6 kN/m3 and maximum allowable settlement for footing is 25mm. Factor of safety against shear failure = 2.5. N? = 109.4 for ? = 400 & = 270 for ? = 450. Use IS recommendations. (10)
7. A group of nine piles, 12m long and 250mm in diameter is to be organizes in a square form in a clay soil with an avg. unconfined compressive strength of 60 kN/m2. Work out the centre to centre spacing of the piles for a group efficiency factor of 1. Neglect bearing at the tip of piles and presume adhesion factor = 0.9 (10)
8. A circular well of 4.5m external diameter and 0.75m steining thickness is embedded upto a depth of 12m in a uniform sand deposit. The angle of internal friction and submerged unit weight are 300 and one t/m3 respectively. The well is subjected to a resulting horizontal force of 50t and a total moment of 400 t-m at the scour level. Assuming well to be light well, calculate the allowable total equivalent resisting force due to earth pressure. Take factor of safety = 2. (5)
9. For the soil profile shown in Fig. 3.
(a) calculate the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer?
(b) What is the change in the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer, if water table rises to the ground surface?
(c) What is the change in the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer, if water table is lowered by four m with respect to condition (a)?
(d) What will be the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer, if water table rises up to an elevation of one m above the ground surface?(?w = 9.81 kN/m3) (2+3+3+2=10)
Ground surface
2m sand, ?dry = 14 kN/m3
Ground water table
4m sand, ?sat = 18 kN/m3
4m clay, ?sat = 19 kN/m3
void ratio, e = 0.8
LL = 40
sand
Fig. 3
10. If a 100 kN/m2 uniformly distributed load is applied at the ground surface of a soil profile as shown in Fig. three (LL is liquid limit in percent), what is the settlement of the clay layer caused by primary consolidation, if (a) the clay is normally consolidated, (b) the preconsolidation pressure is 200 kN/m2 and (c) preconsolidation pressure is 170 kN/m2. Use Cr = Cc/6. Cc = 0.009(LL – 10). (?w = 9.81 kN/m3) (10)
11. In an unconfined compression test, a clay sample of 10 cm long and four cm diameter fails under a load of 100 N at 20% strain. calculate the unconfined compressive strength and undrained shear strength of clay. Also show the stresses in Mohr’s circle (Not to Scale). (10)
12. The liquid limit, plastic limit and natural water content of soil A and B are provided in Table one beneath.
Table 1
Soil A Soil B
Liquid Limit (%)
Plastic Limit (%)
Water Content (%) 40
25
45 60
30
40
(a) Classify the soil A and soil B based on plasticity index? (b) define the consistency of soil A and soil B based on relative consistency and liquidity index? (c) Which soil is more compressible. (4+4+2=10)
BIRLA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & SCIENCE, PILANI
I Semester 2007-2008
Comprehensive Examination (4-12-2007) Duration: 3 hours
Course: CE C361 (Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering) Max. Marks: 120
-Attempt all questions and in the same sequence as given in the question paper.
- Use both sides of answer book pages.
- Each part of a particular question should be answered at one place.
- Answer of every new question should start on a fresh page.
1. A deep cut of height 12m having side slope of 1.5:1 (horizontal:vertical) intersects plane of contact of two strata at a height of 2m above base of cut. The plane of contact of the two strata makes an angle 120 with horizontal. The lower stratum is less pervious than the upper one. The soil of the upper stratum is having unit weight of 1.9 t/m3 with level ground surface. The values of c and f between the two strata are 0.25 kg/cm2 and 150 respectively. Check whether a slide is likely to occur along the plane of contact between two strata. If a slide is not likely to occur, find out factor of safety against sliding. (14)
2. Briefly describe about following clay minerals: Kaolinite, Montmorillonite, Illite. (6)
3. A flow net for seepage under the sheet piling is shown in Fig. 1. Estimate approximately the quantity of seepage in cu m/day/m length of the piling, if the permeability of the sand is 10 x 10-3 cm/s. If the saturated unit of sand is 22.8 kN/m3, what is the factor of safety against piping by heave in front of the piles? (gw = 9.8 kN/m3)
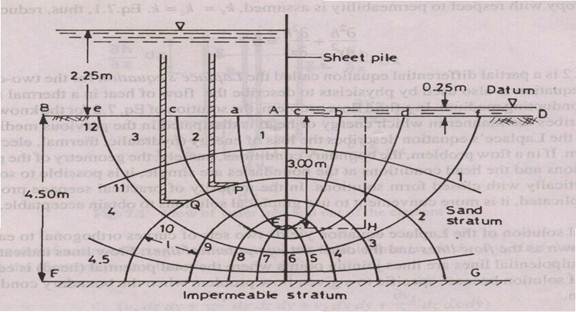
Fig. 1 (10)
4. Two soils A (k = 0.5 cm/s) and B (k = 0.05 cm/s) are arranged in the manner shown in Fig. 2 in a tube. What is total head at elevations 0m & 3m. Determine the quantity of flow. (10)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() 4.5m
4.5m
water
![]() 3m
3m
A B Fig. 2
![]()
![]() 1m 1m
1m 1m
datum 0m
5. Determine the ultimate bearing capacity of a rectangular footing, 2m x 3m in plan, founded at a depth of 1m below ground surface. The load on the footing acts at an angle of 200 to the vertical and is eccentric in the direction of width and length by 0.3m and 0.5m respectively. Shear strength parameters of soil are c = 40 kN/m2 and f = 300. Unit weight of soil = 16 kN/m3. Water table is located at a depth of 1.5m below footing base. Use IS:6403-1981 recommendations. Angle of internal friction governs shear failure. Interpolate between general (f 360) and local (f 290) shear failure to get governing bearing capacity factors. (Nc = 30.14, Nc = 16, Ng = 22.4, Ng = 6.39, Nq = 18.4, & Nq = 7.3 for f = 300) (15)
6. A plate load test conducted in a sandy soil at a depth of 1m on a plate of 0.6m x 0.6m size yielded an ultimate load of 200 kN. The load settlement curve obtained was almost linear upto a load of 120 kN when settlement of the plate was found to be 24mm. Compute the allowable bearing pressure for a footing of size 1.2m x 1.2m proposed in the same soil and at a depth of 1m. Bulk density of soil is 19.6 kN/m3 and maximum allowable settlement for footing is 25mm. Factor of safety against shear failure = 2.5. Ng = 109.4 for f = 400 & = 270 for f = 450. Use IS recommendations. (10)
7. A group of 9 piles, 12m long and 250mm in diameter is to be arranged in a square form in a clay soil with an average unconfined compressive strength of 60 kN/m2. Work out the centre to centre spacing of the piles for a group efficiency factor of 1. Neglect bearing at the tip of piles and assume adhesion factor = 0.9 (10)
8. A circular well of 4.5m external diameter and 0.75m steining thickness is embedded upto a depth of 12m in a uniform sand deposit. The angle of internal friction and submerged unit weight are 300 and 1 t/m3 respectively. The well is subjected to a resultant horizontal force of 50t and a total moment of 400 t-m at the scour level. Assuming well to be light well, compute the allowable total equivalent resisting force due to earth pressure. Take factor of safety = 2. (5)
9. For the soil profile shown in Fig. 3.
(a) Compute the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer?
(b) What is the change in the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer, if water table rises to the ground surface?
(c) What is the change in the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer, if water table is lowered by 4 m with respect to condition (a)?
(d) What will be the effective stress at the bottom of the clay layer, if water table rises up to an elevation of 1 m above the ground surface?(gw = 9.81 kN/m3) (2+3+3+2=10)
![]()
![]() Ground surface
Ground surface
2m sand, gdry = 14 kN/m3
![]()
![]() Ground water table
Ground water table
4m sand, gsat = 18 kN/m3

4m clay, gsat = 19 kN/m3
void ratio, e = 0.8
LL = 40
![]()
sand
Fig. 3
10. If a 100 kN/m2 uniformly distributed load is applied at the ground surface of a soil profile as shown in Fig. 3 (LL is liquid limit in percent), what is the settlement of the clay layer caused by primary consolidation, if (a) the clay is normally consolidated, (b) the preconsolidation pressure is 200 kN/m2 and (c) preconsolidation pressure is 170 kN/m2. Use Cr = Cc/6. Cc = 0.009(LL 10). (gw = 9.81 kN/m3) (10)
11. In an unconfined compression test, a clay sample of 10 cm long and 4 cm diameter fails under a load of 100 N at 20% strain. Compute the unconfined compressive strength and undrained shear strength of clay. Also show the stresses in Mohrs circle (Not to Scale). (10)
12. The liquid limit, plastic limit and natural water content of soil A and B are given in Table 1 below.
|
Table 1 |
||
|
|
Soil A |
Soil B |
|
Liquid Limit (%) Plastic Limit (%) Water Content (%) |
40 25 45 |
60 30 40 |
(a) Classify the soil A and soil B based on plasticity index? (b) Describe the consistency of soil A and soil B based on relative consistency and liquidity index? (c) Which soil is more compressible. (4+4+2=10)
| Earning: Approval pending. |
