Bengal Engineering and Science University 2007 B.E Civil Engineering Pavement Engineering - Question Paper
the ques. paper is with the attachment. Ex/BESUS/ CE-803/4/07
B.E. (CE) Part-IV 8th Semester Examination, 2007
(Elective-I) (CE-803/4)
Time : 3 hours Full Marks : 100
Use separate answerscript for each half.
Assume data reasonably, if required.
FIRST HALF (Answer Q.No.l and TWO from the rest.)
1. Answer any four from the following: - |4X5]
(a) Discuss the investigations required for soil stabilized road
(b) Write short note on Mehras method of stabilization
(c) Discuss the proportion of soil-lime mixture for stabilizing soil
(d) Design approach of IRC:37-200l
(e) Drainage measures in pavement layers.
2. (a) Discuss the effect of increased compactive effort on compaction.
(b) Proctor compaction test was conducted on a soil sample and the following observations were made:
Water Content (%) 7.7 11.5 14.6 17.5 19.5 21.2
Mass of wet soil (kg) 1.7 1.89 2.03 1.99 1.96 1.92
If the volume of mould used was 992 c.c. and the specific gravity of soil grain was 2.71, make necessary calculations draw (i) compaction curve, (ii) 80% and 100% saturation lines and also determine the degree of saturation at MDD & OMC. [5+10]
3. (a) Why lime is ideally suitable for stabilizing clayey soil in our country? Discuss briefly. Explain the mechanism of soil lime stabilization.
(b) Find the proportions of the materials A, B, and C (by Rothfutch's method) so that the mixture may approximate to the desired grading, using the data given below: -
|
I.S. Sieve |
Percentage passing | |||
|
Desired Grading |
Material A |
Material B |
Material C | |
|
40 mm |
100 |
85 |
- |
l |
|
20 mm |
85-100 |
65 |
- |
- |
|
10 mm |
65-100 |
20 |
- |
- |
|
4.75 mm |
55-85 |
10 |
100 |
- |
|
2.36 mm |
40-70 |
7 |
87 |
- |
|
425 \i |
25-45 |
2 |
52 |
100 |
|
75.ii ........... |
10-25 |
Trace |
Nil |
53 |
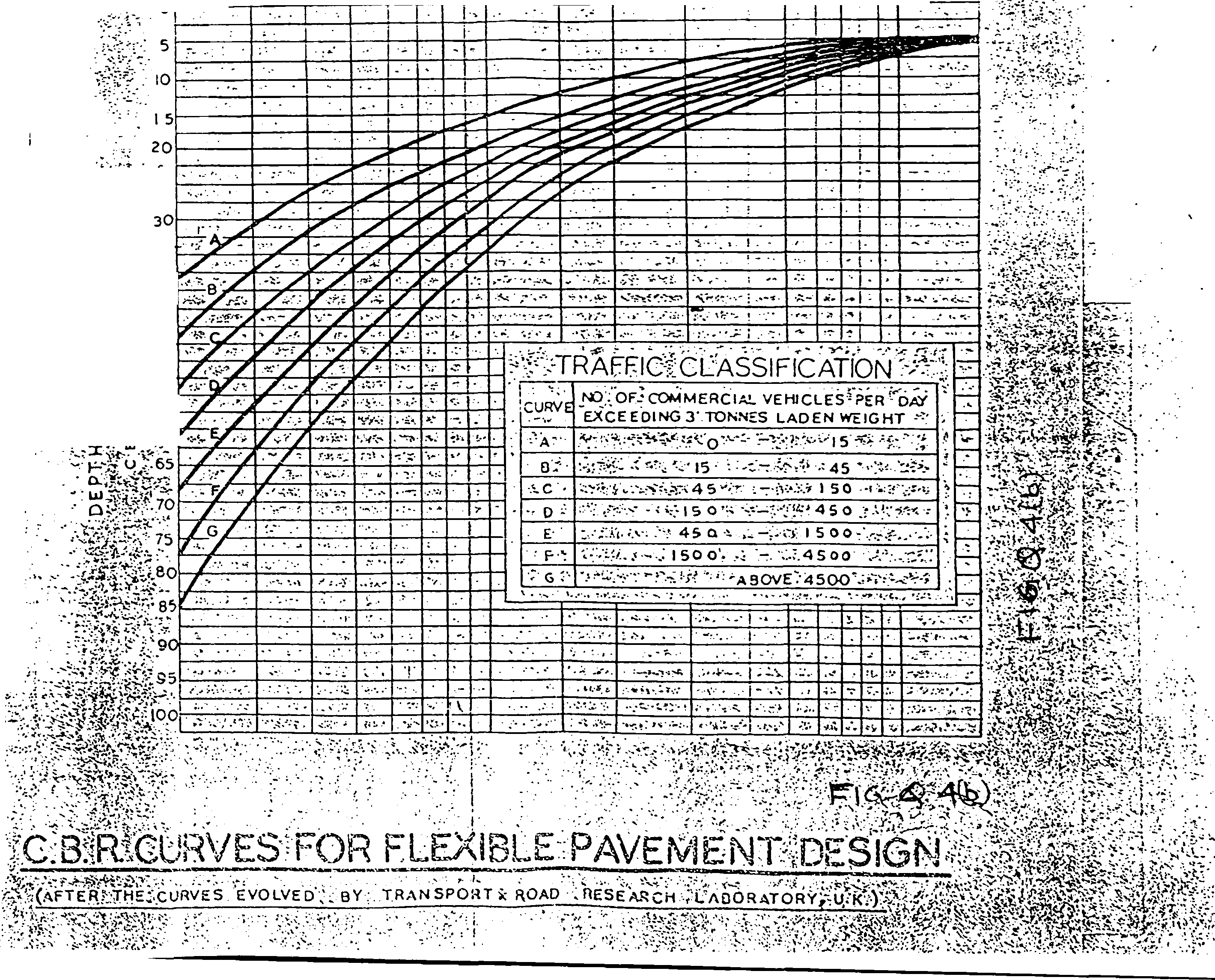
4. A flexible pavement is recently constructed on a subgrade of 4% CBR with single layers of 40 mm bituminous concrete, and 80mm dense bituminous macadam; two layers of each 75 mm water bound macadam; two layers of each 75 mm brick bats and one layers of 80 mm coarse sand. The road is of 4 lane single carriageway. It is designed for a life of 15 years and the estimated VDF is 2.5. If the road would have been designed by IRC: 37-1970 what would be the thickness of different layers? Assume CBR of WBM, brickbat consolidation and sand as 95%, 25% and 15% respectively. The relevant Charts of IRC:37-2001 and IRC:37-1970 are given in Fig.Q.4(a) & 4(b). (15)
SECOND HALF fAnswer Q.No.5 and TWO from the rest.)
5. Write brief on any three
a) Highway Transportation Costs and Benefits
b) Importance of Pavement Serviceability Index in evaluation of pavement performance
c) Road Safety Audit
d) Important safety aspects to be considered in design of horizontal alignment of a roadway
e) Implication of broken line, solid line, double broken line and combination of broken and solid line in road making.
6. a) Discuss on two layer theory of flexible pavement design and compare it with Single
layer theory.
b) A plate load test was undertaken on a subgrade as well as on a 25 cm thick WBM layer using 76 cm diameter rigid plate. The unit load to cause deflection of 0.6 cm in both the above surface was 0.75 kg/cm2 and 3.0 kg/cm2 respectively. Determine the thickness of base course to sustain a wheel load of 2 x 105 N at 0.7 MPa tyre pressure at a deflection of 5 mm. Relevant charts is given in Fig. 6.0
7. a) Discuss on the nature and causes of following defects of road pavement
i) Fatty surface; ii) Smooth surface; iii) Hungry surface; iv) Alligator crack; v) Edge crack and vi) Rutting b) Discuss on necessity of dowel bars in rigid pavement.
8. a) Why it is taken to a very conservative design in rigid pavement if more than 25% of
two lane two way commercial vehicles are considered in traffic estimation?
b) What is the significance if LSF in design of rigid pavement?
c) Design the tie bar system of a rigid pavement for the given consideration
i) Allowable working stress in steel - 1250 kg/cm2, ii) Maximum permissible bond stress - 17.5kg/cm2, iii) Slab thickness - 30 cm iv) Slab size - 3.5m X 5.0m.,
v) Density of concrete - 2400kg/m3.
|
.7- 'f < A.'' :-$ '\i *v - :* % 4. | 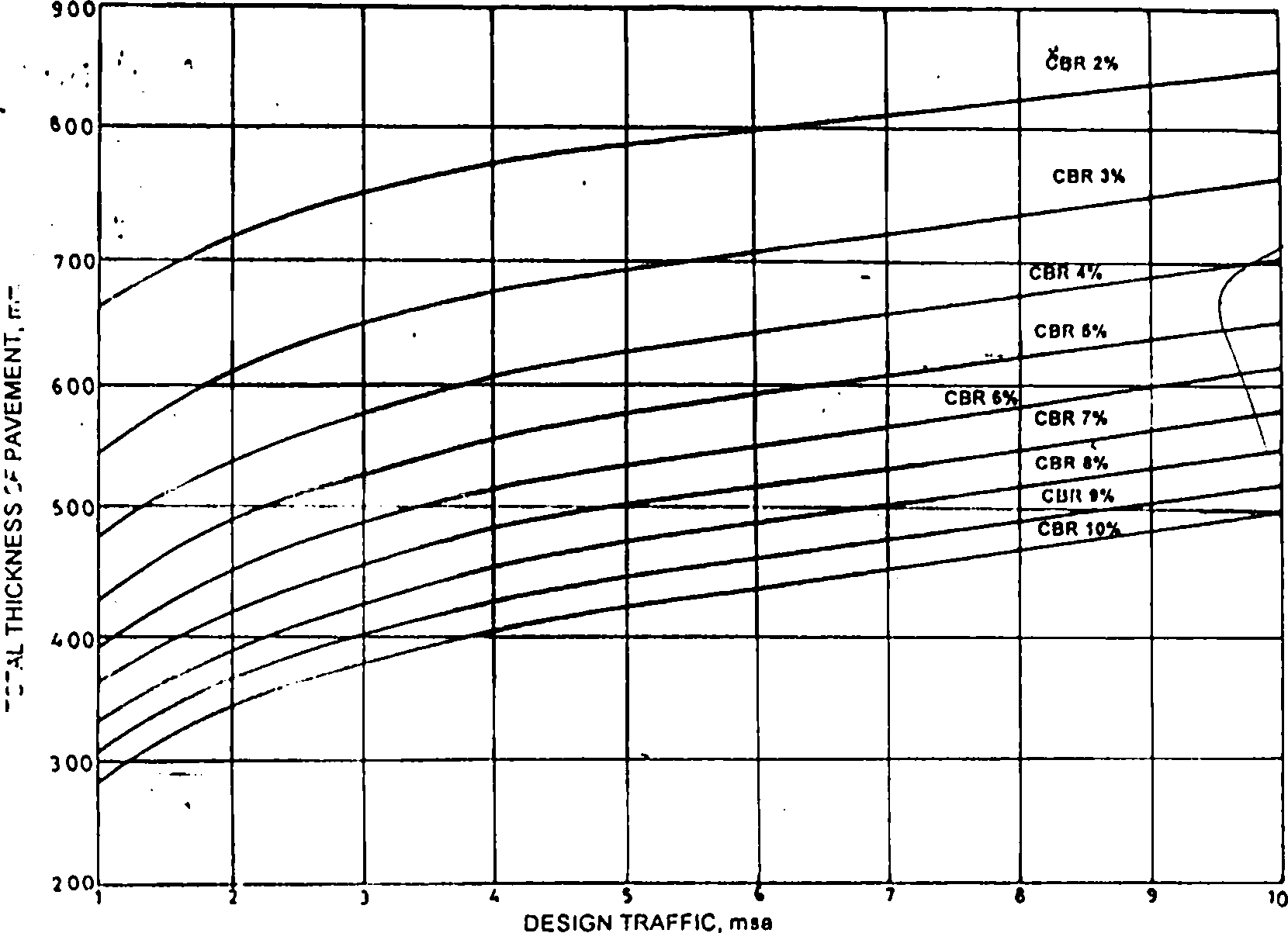 |
|
Fig. 4QPavcmcnt Thickncss Design Chart for Traffic 1-10 msa | |
x .


|
** f *: * | |
 |
..* 1 |
zKfe 25
oik-ir
<* v?
- S835
gs?
- =- O
H"<f50
<-Y.
- ;Fz .60
|
* v j w* V f v-w:& ... *v> r |
 |
: >:/-v. .***
S.'.'Swfett' .. V>V- ,',
-v. I'. r- -j- K- ' - CALIFORNIA- BEa=ING . .RATIO-?ER ce*-t
? - ' ' - > PlATEj-EiC 37 - , !IC
2:i- >3 ' 4 5 V 6 7-8 9 10 * 15 '-20 ; 30 40 50 60' 50 IOO ' ivv-.itvl-V...'.;;;..:
OH----------------' '
|
TMO-layer deflect'c" *ctor F.{ | 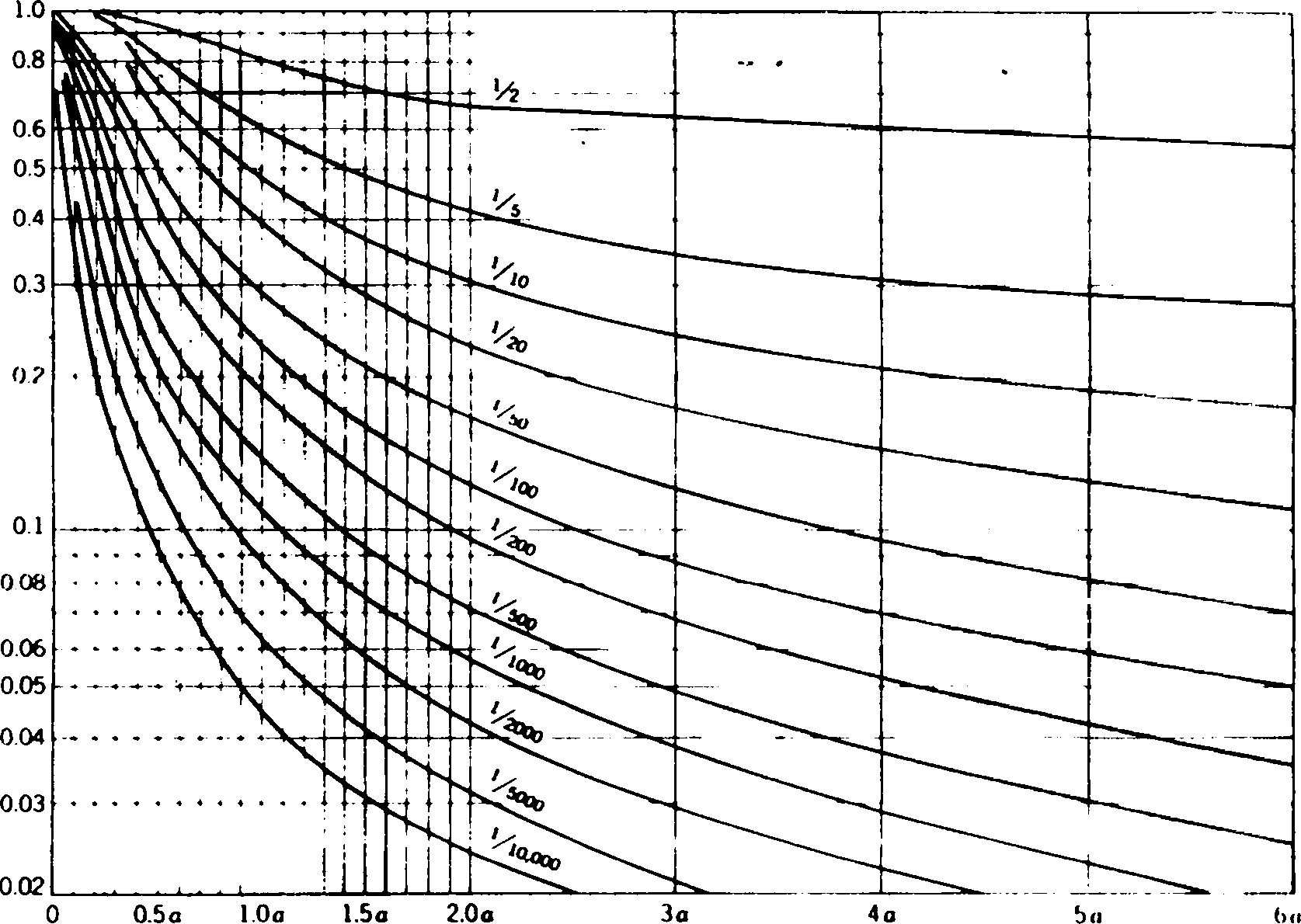 |
|
Thickness of reinforcing layer (multiples of radius of contact) JnlliicriM v >111 j < * % (v%o-l;i\rt l lirui \ . (! ioiii Itui im.Mn , t'ttn Ktm.imIi lit mm I I'JMj | |
|
Attachment: |
| Earning: Approval pending. |
